Here’s How We Can Feed the World Without Wrecking the Planet – Comprehensive Solution
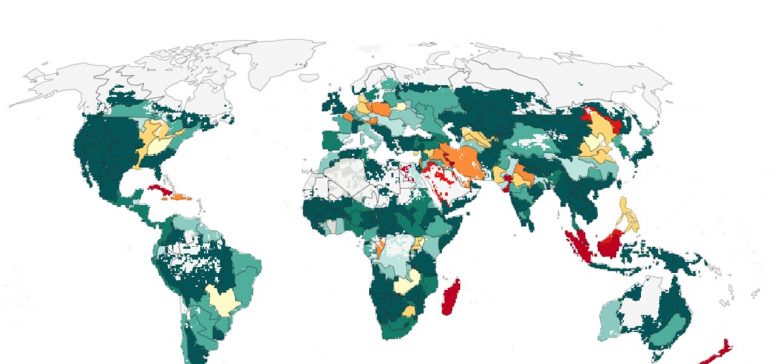
The potential for sustainable food system: Increases in calorie supply above current levels are possible in the green-colored areas; decreases due to overly detrimental food production are shown in red. Credit: Gerten et al. 2020
Almost half of current food production is harmful to our planet – causing biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation and water stress. But as world population continues to grow, can that last?
An international study now suggests a comprehensive solution package for feeding 10 billion people within our planet’s environmental boundaries.
Supplying a sufficient and healthy diet for every person whilst keeping our biosphere largely intact will require no less than a technological and socio-cultural U-turn. It includes adopting radically different ways of farming, reduction of food waste, and dietary changes.
“When looking at the status of planet Earth and the influence of current global agriculture practices upon it, there’s a lot of reason to worry, but also reason for hope – if we see decisive actions very soon,” Dieter Gerten says, lead author from PIK and professor at Humboldt University of Berlin.
“Currently, almost half of global food production relies on crossing Earth’s environmental boundaries. We appropriate too much land for crops and livestock, fertilize too heavily and irrigate too extensively. To solve this issue in the face of a still growing world population, we collectively need to rethink how to produce food. Excitingly, our research shows that such transformations will make it possible to provide enough food for up to 10 billion people.”
The researchers ask the question how many people could be fed while keeping a strict standard of environmental sustainability worldwide. These environmental capacities are defined in terms of a set of planetary boundaries – advisable limits to human interference with processes that regulate the state of the planet. The present study accounts for four of nine boundaries most relevant for agriculture: Biosphere integrity, land-system change, freshwater use, and nitrogen flows. Based on a sophisticated simulation model, these boundaries are scrutinized globally at a new level of spatial and process detail. This analysis demonstrates where and how many boundaries are being violated by current food production and in which ways this development could be reverted through adopting more sustainable forms of agriculture.
Globally differentiated picture: In some regions, less would be more
The encouraging result is that, in theory, 10.2 billion people can be fed without compromising the Earth system. This leads to very interesting conclusions, as Johan Rockström, director of PIK points out: “We find that currently, agriculture in many regions is using too much water, land, or fertilizer. Production in these regions thus needs to be brought into line with environmental sustainability. Yet, there are huge opportunities to sustainably increase agricultural production in these and other regions. This goes for large parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, for example, where more efficient water and nutrient management could strongly improve yields.”
As a side effect, such more sustainable agriculture can increase overall climate resilience and adaptability while also limiting global warming. In other places, however, farming is so far off local and Earth’s limits that even more sustainable systems could not completely balance the pressure on the environment, such as in parts of the Middle East, Indonesia, and to some extent in Central Europe. Even after recalibrating agricultural production, international trade will remain a key element of a sustainably fed world.
Hard to chew: Dietary changes needed
Importantly, there is the consumers’ end, too. Large-scale dietary changes seem to be inevitable for turning the tide to a sustainable food supply. For example, regarding China’s currently rising meat consumption, parts of animal proteins would need to be substituted by more legumes and other vegetables. “Changes like this might seem hard to chew at first. But in the long run, dietary changes towards a more sustainable mix on your plate will not only benefit the planet, but also people’s health”, adds Vera Heck from PIK. Another crucial factor is reducing food loss. In line with scenarios adopted in the present study, the most recent IPCC Special Report on land use found that currently, up to 30 percent of all food produced is lost to waste. “This situation clearly calls for resolute policy measures to set incentives right on both the producers’ and consumers’ ends”, Heck further lays out.
Perhaps the most sensitive and challenging implication of the study relates to land. “Anything involving land tends to be complex and contested in practice because people’s livelihoods and outlook depend on it. Transitioning to more sustainable land use and management is therefore a demanding challenge to policy-making. Key to success is that the regions affected need to see clear benefits for their development. Then there is a real chance that support for new directions will grow fast enough for stabilizing the Earth system”, says Wolfgang Lucht, co-chair for Earth System Analysis at PIK and co-author of the study.
Reference: “Feeding ten billion people is possible within four terrestrial planetary boundaries” by Dieter Gerten, Vera Heck, Jonas Jägermeyr, Benjamin Leon Bodirsky, Ingo Fetzer, Mika Jalava, Matti Kummu, Wolfgang Lucht, Johan Rockström, Sibyll Schaphoff and Hans Joachim Schellnhuber, 20 January 2020, Nature Sustainability.
DOI 10.1038/s41893-019-0465-1
DOI 10.1038/s41893-019-0465-1
The study was led by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). Aalto University researchers; Professor Matti Kummu and Mika Jalava, Postdoctoral Researcher, are from the Water and Environmental Engineering research group
No comments:
Post a Comment