THE CONVERSATION
Published: March 28, 2022
You might think all important dinosaur “discoveries” are made as soon as fossils are collected in the field – that palaeontologists instantly know the significance of what they’ve found.
This is often true. But sometimes, and maybe more often than you’d think, fossils will be stored in museum collections for years before the right researchers come along to “rediscover” them. This was the case for one Australian ankylosaur skull, which we’ve published about today in the journal Frontiers in Earth Sciences.
Originally discovered in 2005 near the regional Queensland town of Boulia, the specimen remained at the South Australian Museum until we enquired about the museum’s dinosaur collection.
Ankylosaurs, the so-called “armoured” dinosaurs, are a group of dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous – roughly 196 to 66 million years ago.
We can help you make informed decisions with our independent journalism.Get newsletter
Compared to other dinosaurs, such as the long-necked sauropods and smaller herbivorous ornithopods, ankylosaur remains are rarely found in Australia and the broader southern hemisphere. So you can imagine our excitement when we “rediscovered” Australia’s second ankylosaur skull.
An analysis of the skull bones and teeth suggests it belongs to the genus Kunbarrasaurus, which also contains the first Australian ankylosaur skull.
Read more: Introducing Australotitan: Australia's largest dinosaur yet spanned the length of 2 buses
A dinosaur from Boulia
The bones of the ankylosaur from Boulia were found encased in a large, hard rock called a concretion. Concretions often form around organic matter, and likely helped the initial preservation of the fossil. When it was discovered, all that was visible was a series of rock chunks that could have easily been overlooked.

Placing southern ankylosaurs in the family tree
Identifying this new ankylosaur as Kunbarrasaurus suggests this particular dinosaur was potentially more widespread in Queensland than previously thought, and may have existed for more than five million years. But what do ankylosaurs from Australia, and Gondwana more generally, tell us about the group’s evolution as a whole?
As it stands, the vast majority of ankylosaurs are from either North America, Europe, or Asia. And most are from the late Cretaceous (100 to 66 million years ago). However our study suggests a separate and possibly earlier diversity of ankylosaurs in the south, a theory which is supported by recent discoveries from South America and Africa.
The southern radiation of ankylosaurs includes the species from Australia, Chile and Antarctica, all of which together form the group called Parankylosauria.
Published: March 28, 2022
You might think all important dinosaur “discoveries” are made as soon as fossils are collected in the field – that palaeontologists instantly know the significance of what they’ve found.
This is often true. But sometimes, and maybe more often than you’d think, fossils will be stored in museum collections for years before the right researchers come along to “rediscover” them. This was the case for one Australian ankylosaur skull, which we’ve published about today in the journal Frontiers in Earth Sciences.
Originally discovered in 2005 near the regional Queensland town of Boulia, the specimen remained at the South Australian Museum until we enquired about the museum’s dinosaur collection.
Ankylosaurs, the so-called “armoured” dinosaurs, are a group of dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous – roughly 196 to 66 million years ago.
We can help you make informed decisions with our independent journalism.Get newsletter
Compared to other dinosaurs, such as the long-necked sauropods and smaller herbivorous ornithopods, ankylosaur remains are rarely found in Australia and the broader southern hemisphere. So you can imagine our excitement when we “rediscovered” Australia’s second ankylosaur skull.
An analysis of the skull bones and teeth suggests it belongs to the genus Kunbarrasaurus, which also contains the first Australian ankylosaur skull.
Read more: Introducing Australotitan: Australia's largest dinosaur yet spanned the length of 2 buses
What were ankylosaurs like?
Ankylosaurs were medium-to-giant herbivorous dinosaurs (anywhere between 200-5,000kg) that walked on four legs and were covered in armoured plates or spikes. Some are recognisable by tail clubs, such as the five-tonne Ankylosaurus magniventris from North America.
Of the 75 recognised ankylosaur species, only five are from the southern hemisphere. Several small and incomplete fossils are spattered across the ancient Gondwana supercontinent – which is now dispersed and broken up into Australia, India (which back then was in the southern hemisphere), Africa, Antarctica and South America.
These fossils offer tantalising hints of what was once a widespread ankylosaur presence in these regions. The five Gondwanan ankylosaur species are Kunbarrasaurus ieversi and Minmi paravertebra from Australia, Antarctopelta oliveroi from Antarctica, Spicomellus afer from Africa, and Stegorous elengassen from Chile.
Ankylosaurs were medium-to-giant herbivorous dinosaurs (anywhere between 200-5,000kg) that walked on four legs and were covered in armoured plates or spikes. Some are recognisable by tail clubs, such as the five-tonne Ankylosaurus magniventris from North America.
Of the 75 recognised ankylosaur species, only five are from the southern hemisphere. Several small and incomplete fossils are spattered across the ancient Gondwana supercontinent – which is now dispersed and broken up into Australia, India (which back then was in the southern hemisphere), Africa, Antarctica and South America.
These fossils offer tantalising hints of what was once a widespread ankylosaur presence in these regions. The five Gondwanan ankylosaur species are Kunbarrasaurus ieversi and Minmi paravertebra from Australia, Antarctopelta oliveroi from Antarctica, Spicomellus afer from Africa, and Stegorous elengassen from Chile.
A dinosaur from Boulia
The bones of the ankylosaur from Boulia were found encased in a large, hard rock called a concretion. Concretions often form around organic matter, and likely helped the initial preservation of the fossil. When it was discovered, all that was visible was a series of rock chunks that could have easily been overlooked.

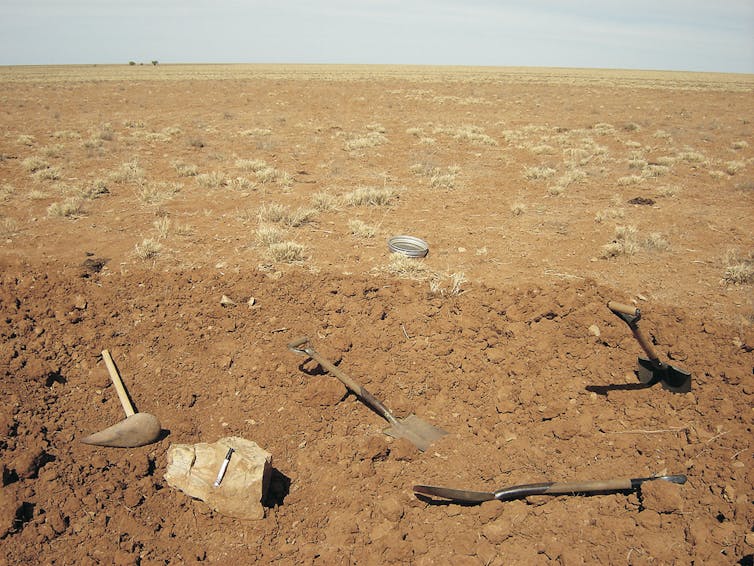
The Boulia ankylosaur was excavated from the Warra station in 2005.
(Block in the bottom left contains ankylosaur limb bones)
Benjamin Kear (Uppsala University)
The collected fossils include limbs, vertebrae, many armoured plates and, excitingly, a partial skull. Along with several skull bones, the skull also includes the impressions of many teeth from the upper jaw.
The entire skull block was scanned at the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne. The synchrotron shoots x-rays at the specimen, generating a series of images that can be processed to reveal the bones in 3D (as seen below).
This technique is often used for fossils that may otherwise get damaged or lose important information if physically removed from the rock.
We analysed the scans and discovered the bones are those of the roof of the mouth (or the palate). We also found several teeth “floating” within the block.
The collected fossils include limbs, vertebrae, many armoured plates and, excitingly, a partial skull. Along with several skull bones, the skull also includes the impressions of many teeth from the upper jaw.
The entire skull block was scanned at the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne. The synchrotron shoots x-rays at the specimen, generating a series of images that can be processed to reveal the bones in 3D (as seen below).
This technique is often used for fossils that may otherwise get damaged or lose important information if physically removed from the rock.
We analysed the scans and discovered the bones are those of the roof of the mouth (or the palate). We also found several teeth “floating” within the block.
Placing southern ankylosaurs in the family tree
Identifying this new ankylosaur as Kunbarrasaurus suggests this particular dinosaur was potentially more widespread in Queensland than previously thought, and may have existed for more than five million years. But what do ankylosaurs from Australia, and Gondwana more generally, tell us about the group’s evolution as a whole?
As it stands, the vast majority of ankylosaurs are from either North America, Europe, or Asia. And most are from the late Cretaceous (100 to 66 million years ago). However our study suggests a separate and possibly earlier diversity of ankylosaurs in the south, a theory which is supported by recent discoveries from South America and Africa.
The southern radiation of ankylosaurs includes the species from Australia, Chile and Antarctica, all of which together form the group called Parankylosauria.

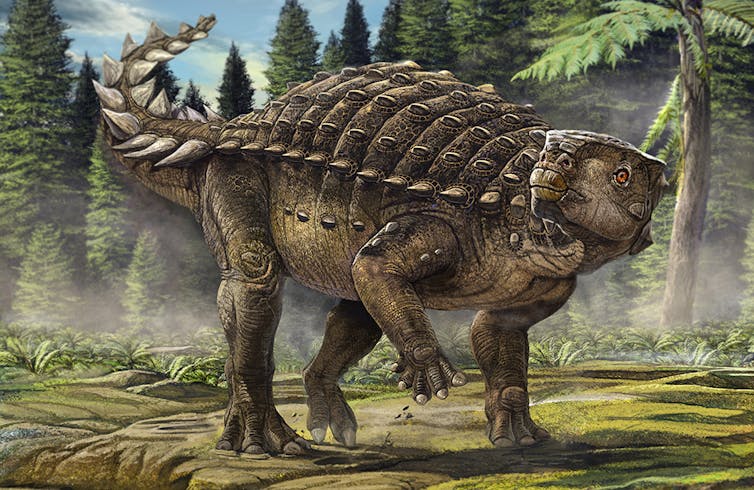
A reconstruction of Kunbarrrasaurus ieversi from Richmond, Queensland. Australian Geographic
The importance of the Boulia ankylosaur
Because the fossil block was scanned with x-rays and reconstructed in 3D, we were able to explore aspects of the ankylosaur’s airways, or “choanae”. These were not well preserved in the first and only other known Kunbarrasaurus skull.
Typically ankylosaur choanae are long, located close to the front of the snout and can have multiple openings within the palate. Coupled with complex nasal passages, these features point to the group generally having a keen sense of smell.
However, in the Boulia ankylosaur there is only one opening on each side, and they are located towards the back of the palate. This suggests Kunbarrasaurus did not have the complex nasal system seen in ankylosaurs such as Pawpawsaurus campbelli and Euplocephalus tutus. As such, it may have had a reduced sense of smell compared to most of its northern counterparts.
There is still a lot we don’t know about ankylosaur evolution, especially the Gondwanan species. Perhaps more of these discoveries await us in museum troves.
Read more: Dinosaurs were already in decline before the asteroid wiped them out – new research
Because the fossil block was scanned with x-rays and reconstructed in 3D, we were able to explore aspects of the ankylosaur’s airways, or “choanae”. These were not well preserved in the first and only other known Kunbarrasaurus skull.
Typically ankylosaur choanae are long, located close to the front of the snout and can have multiple openings within the palate. Coupled with complex nasal passages, these features point to the group generally having a keen sense of smell.
However, in the Boulia ankylosaur there is only one opening on each side, and they are located towards the back of the palate. This suggests Kunbarrasaurus did not have the complex nasal system seen in ankylosaurs such as Pawpawsaurus campbelli and Euplocephalus tutus. As such, it may have had a reduced sense of smell compared to most of its northern counterparts.
There is still a lot we don’t know about ankylosaur evolution, especially the Gondwanan species. Perhaps more of these discoveries await us in museum troves.
Read more: Dinosaurs were already in decline before the asteroid wiped them out – new research
Timothy Frauenfelder
PhD Candidate in Palaeontology, University of New England

PhD Candidate in Palaeontology, University of New England
Nicolas Campione
Senior lecturer, University of New England

Senior lecturer, University of New England
Phil Bell
Palaeontologist, Earth Science Faculty, University of New England
Palaeontologist, Earth Science Faculty, University of New England
Disclosure statement
Nicolas Campione receives funding from Australian Research Council.
Phil Bell received funding from the Australian Research Council.
Timothy Frauenfelder does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.

No comments:
Post a Comment