Kristina Killgrove
Fri, March 3, 2023

A Yamnaya grave of a male horse rider found in Malomirovo, Bulgaria. He died between the ages of 65 and 75.
Archaeologists accidentally discovered the world's earliest horseback riders while studying skeletons found beneath 5,000-year-old burial mounds in Europe and Asia, a new study finds.
The ancient riders were part of the so-called Yamnaya culture, groups of semi-nomadic people who swept across Europe and western Asia, bringing the precursor to the Indo-European language family with them. The findings strengthen the hypothesis that the horse played an integral part in the expansion of this group, and therefore, in the spread of the Indo-European language.
The new analysis came from 217 human skeletons from the Pontic-Caspian steppe, a geographical area that runs roughly from Bulgaria to Kazakhstan. For decades, researchers have debated when horses were domesticated. In Kazakhstan, 5,000-year-old horse skeletons show wear on their teeth that could have been from bridles, while others have found possible fenced enclosures. In the same time period, horse milk peptides have been detected in the dental plaque of people from Russia. Importantly, the geographical explosion of the Yamnaya culture — which expanded across 3,000 miles (4,500 kilometers) over a mere century or two — suggests horses may have assisted as transportation animals.
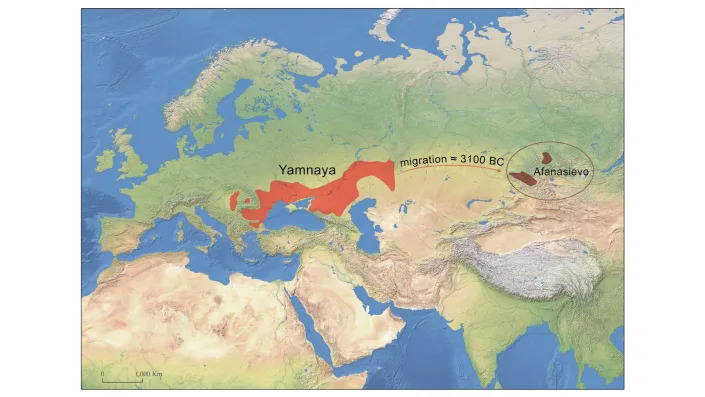
A map of the Yamnaya and Afanasievo distribution in Eurasia about 5,000 years ago.
But there was no direct evidence that the Yamnaya culture regularly domesticated horses.
So archaeologist Martin Trautmann of the University of Helsinki in Finland and his colleagues collected data on six diagnostic skeletal traits that have been collectively called "horsemanship syndrome." Since bone is a living tissue, it responds to stresses placed on it. Consistent horseback riding can cause trauma and spine degeneration, but it can also result in more subtle changes to the leg and hip bones as the human body adapts to regular riding.
Related: 1,400-year-old remains of headless horse and rider discovered in Germany

An Egyptian drawing of the goddess Astarte on horseback that dates to the 19th dynasty, about 1,500 years after the first known Yamnaya riders. This horse has a stock build and is smaller and shorter than modern horses are.

This limestone Egyptian relief shows a messenger on horseback from the Horemheb tomb, Saqqara, late 18th dynasty. Bronze Age riders are usually show a rider position known as
In the skeletons from 39 sites across Eastern Europe, Trautmann and colleagues found that two dozen had at least half of the traits of horsemanship syndrome.
They are most confident, however, about the identification of five Yamnaya culture individuals hailing from what is now Romania, Bulgaria and Hungary as likely equestrians.
"Our findings provide a strong argument that horseback riding was already a common activity for some Yamnaya individuals as early as 3000 [B.C.]," they wrote in their paper.

The Yamnaya people didn't ride Przewalski's horses, but these hoofed animals are likely close to what ancient horses looked like in terms of appearance, color and size.
Birgit Bühler, an archaeologist at the University of Vienna, told Live Science in an email that she is "excited about their research." However, Bühler, who has studied horsemanship syndrome but was not involved in this work, was concerned about the researchers' ability to measure changes to the hip sockets given the poor state of conservation of many of the bones. "Because two major traits are missing, I feel that caution is required in interpreting the evidence," she said.
Most of the skeletons were in such poor condition that horsemanship couldn't be analyzed. Taking that into account, however, "we guess that more than 30% of male adult Yamnaya individuals were riding frequently," Trautmann told Live Science in an email.
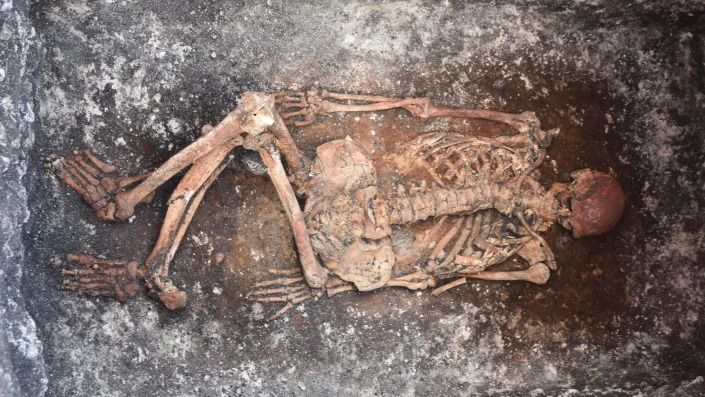
The remains of a horse rider found in Malomirovo, Bulgaria.
He had a Yamnaya-style burial, and radiocarbon dating puts him in the 30th century B.C.
Shevan Wilkin, a biomolecular archaeologist at the Institute of Evolutionary Medicine at the University of Zurich, who was not involved in this study, told Live Science in an email that the researchers' findings about the Yamnaya are interesting but "not surprising considering their vast Early Bronze Age expansions." Expanding so quickly and spreading their genes over such a vast area would have been difficult without horses.
Although skeletons with horsemanship syndrome are rarely found, their identification by archaeologists gives us new information about what it was like to live on the eastern steppe five millennia ago. "For now," Trautmann said, "it seems riding was mostly a male activity, probably connected to herding, and training probably started early."
The new discovery was described in an article published Friday (March 3) in Scientific Advances.
The world’s first horse riders
IMAGE: GRAVE OF A HORSE RIDER DISCOVERED IN MALOMIROVO, BULGARIA view more
CREDIT: MICHAŁ PODSIADŁO
The researchers discovered evidence of horse riding by studying the remains of human skeletons found in burial mounds called kurgans, which were between 4500-5000 years old. The earthen burial mounds belonged to the Yamnaya culture. The Yamnayans had migrated from the Pontic-Caspian steppes to find greener pastures in today´s countries of Romania and Bulgaria up to Hungary and Serbia.
Yamnayans were mobile cattle and sheep herders, now believed to be on horseback.
“Horseback-riding seems to have evolved not long after the presumed domestication of horses in the western Eurasian steppes during the fourth millennium BCE. It was already rather common in members of the Yamnaya culture between 3000 and 2500 BCE”, says Volker Heyd, Professor of Archaeology at the University of Helsinki and a member of the international team, which made the discovery.
These regions west of the Black Sea constitute a contact zone where mobile groups of herdsmen from the Yamnaya culture first encountered the long-established farmer communities of Late Neolithic and Chalcolithic traditions. For decades, the Early Bronze Age expansion of steppe people into southeastern Europe was explained as a violent invasion.
With the advent of ancient DNA research, the differences between these migrants from the east and members of local societies became even more pronounced.
“Our research is now beginning to provide a more nuanced picture of their interactions. For example, findings of physical violence as were expected are practically non-existent in the skeletal record so far. We also start understanding the complex exchange processes in material culture and burial customs between newcomers and locals in the 200 years after their first contact”, explains Bianca Preda-Bălănică, another team member from the University of Helsinki.
Horse riding is a pivotal moment in human history
The use of animals for transport, in particular the horse, marked a turning point in human history. The considerable gain in mobility and distance had profound effects on land use, trade, and warfare. Current research has mostly focused on the horses themselves. However, horse-riding is an interaction of two components – the mount and its rider – and human remains are available in larger numbers and more complete condition than early horse remains. Since horseback riding is possible without specialized equipment, the absence of archaeological finds with regard to earliest horsemanship does not come unexpected.
Traces of horsemanship can be found in the skeletons
“We studied over 217 skeletons from 39 sites of which about 150 found in the burial mounds belong to the Yamnayans. Diagnosing activity patterns in human skeletons is not unambiguously. There are no singular traits that indicate a certain occupation or behavior. Only in their combination, as a syndrome, symptoms provide reliable insights to understand habitual activities of the past.”, explains Martin Trautmann, Bioanthropologist in Helsinki and the lead author of the study.
The international team decided to use a set of six diagnostic criteria established as indicators of riding activity (the so-called “horsemanship syndrome”):
1. Muscle attachment sites on pelvis and thigh bone (femur);
2. Changes in the normally round shape of the hip sockets;
3. Imprint marks caused by pressure of the acetabular rim on the neck of the femur;
4. The diameter and form of the femur shaft;
5. Vertebral degeneration caused by repeated vertical impact;
6. Traumata that typically can be caused by falls, kicks or bites from horses.
To increase the diagnostic reliability, the team also used a stricter filtering method and developed a scoring system that takes into account the diagnostic value, distinctiveness and reliability of each symptom. Altogether, out of the 156 adult individuals of the total sample at least 24 (15.4%) can be classified as 'possible riders', while five Yamnaya and two later as well as two possibly earlier individuals qualify as 'highly probable riders'. “The rather high prevalence of these traits in the skeleton record, especially with respect to the overall limited completeness, show that these people were horse riding regularly”, Trautmann states.
If the primary use of horseback riding was as a convenience in a mobile pastoral lifestyle, in allowing a more effective herding of cattle, as means of swift and far-ranging raids or just as symbol of status needs further research.
Could it all have happened even earlier?
“We have one intriguing burial in the series” remarks David Anthony, emeritus Professor of Hartwick College USA and also senior co-author in the study.
“A grave dated about 4300 BCE at Csongrad-Kettöshalom in Hungary, long suspected from its pose and artifacts to have been an immigrant from the steppes, surprisingly showed four of the six riding pathologies, possibly indicating riding a millennium earlier than Yamnaya. An isolated case cannot support a firm conclusion, but in Neolithic cemeteries of this era in the steppes, horse remains were occasionally placed in human graves with those of cattle and sheep, and stone maces were carved into the shape of horse heads. Clearly, we need to apply this method to even older collections.”
CAPTION
Overview of the archaeological excavations in Malomirovo, Bulgaria
CREDIT
Michał Podsiadło
Short fact box: Who were the Yamnayans?
The Yamnayans were a population and culture that evolved in the Pontic-Caspian steppes at the end of the fourth millennium BCE.
By adopting the key innovation wheel and wagon, they were able to greatly enhance their mobility and exploit a huge energy resource otherwise out of reach, the sea of steppe grass away from the rivers, enabling them to keep large herds of cattle and sheep. Thus committing to a new way-of-life, these pastoralists if not first true nomads in the world expanded dramatically within the next two centuries to cover more than 5000 kilometers between Hungary in west and, in form of the so-called Afanasievo culture, Mongolia and western China in the east. Having buried their dead in grave pits under big mounds, called kurgans, the Yamnayans are said to be the first having spread proto-Indo-European languages.
More information on the research:
https://www.helsinki.fi/en/researchgroups/the-yamnaya-impact-on-prehistoric-europe
JOURNAL
Science Advances
SUBJECT OF RESEARCH
People
ARTICLE TITLE
First bioanthropological evidence for Yamnaya horsemanship
ARTICLE PUBLICATION DATE
3-Mar-2023
No comments:
Post a Comment