Reuters | April 18, 2023 |
The largest end-use for tin is soldering in semiconductors.
Image courtesy of Pixabay.
A suspension of mining in Myanmar could lead to further tightening of global supplies of tin, China’s Yunnan Tin, the world’s top refined tin producer, said on Tuesday.

On Monday, Myanmar’s ethnic minority Wa militia said that from August the Wa region – a key tin producer – would suspend all mining activities to protect the remaining resources after more than a decade of “disruptive and wasteful mining”.
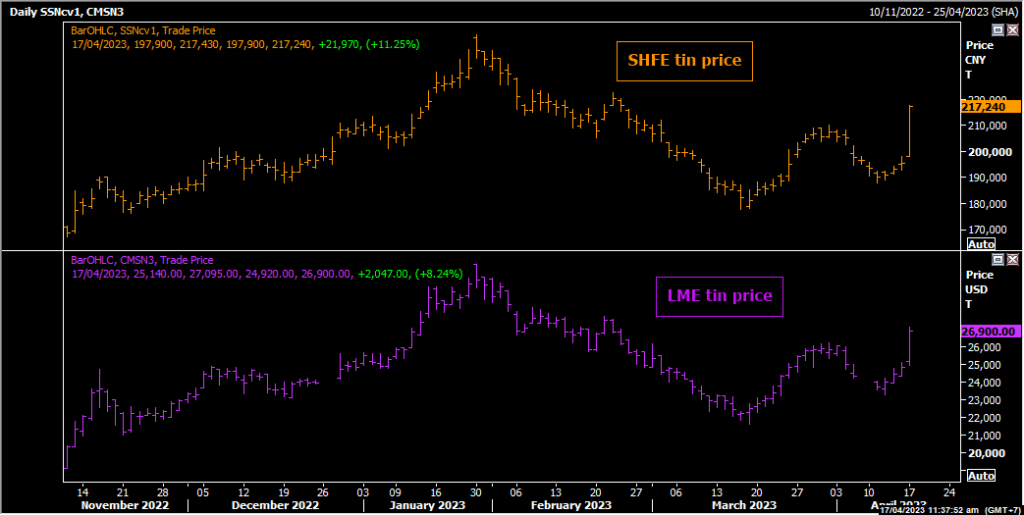
The news sent tin prices skyrocketing, with the most-traded May contract on the Shanghai Futures Exchange up as much as 17.5 per cent in two sessions and the benchmark three-month contract on the London Metal Exchange hitting a two-and-a-half month high.
“The company is closely monitoring the Chinese raw material supply,” Yunnan Tin told Reuters in a statement, adding that it would make “timely adjustment to its operations” as the impact on supply hinged on the implementation of the suspension.
The International Tin Association (ITA) said in a report on its website that “it is still unclear how and if these plans will be implemented.”
Myanmar accounted for 77 per cent of China’s tin ore imports last year, Chinese customs data showed. The Wa region is estimated to have accounted for over 70 per cent of Myanmar’s tin production in 2022, the ITA said.
The main tin mine in the self-declared Wa State, which borders China’s Yunnan province, is Man Maw, which produced around 32,000 tonnes of tin in 2020, the ITA said in a 2021 report.
“This tin is generally smelted in China and mining investment is thought to be sourced from China,” the report said.
Less significant tonnages of tin are also mined in Myanmar government-administered areas including the Mawchi mine in Kayah State and the Heinda mine in the Tanintharyi Region of southern Myanmar, the ITA added.
Myanmar is estimated to have the world’s third largest tin reserves at 700,000 tonnes – or 15 per cent of global reserves, behind Indonesia’s 800,000 tonnes and China’s 720,000 tonnes, US Geological Survey (USGS) data in 2023 showed.
Other major tin mining countries include Peru, Democratic Republic of Congo, Bolivia, Brazil and Australia.
Tin is used in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
Shares of Yunnan Tin hit their highest since June 2022 at 17.96 yuan ($2.61) on Tuesday. They jumped 10 per cent in the previous session on the Myanmar news.
Yunnan Tin last year produced 77,100 tonnes of refined tin, around a fifth of global output, ITA data showed.
China is the world’s biggest consumer of tin and is also the top producer of tin ore and refined tin. Four of the world’s top 10 refined tin producers are Chinese, data by the ITA showed.
($1 = 6.8719 yuan)
(By Siyi Liu and Mai Nguyen; Editing by Tom Hogue and Mark Potter)
A suspension of mining in Myanmar could lead to further tightening of global supplies of tin, China’s Yunnan Tin, the world’s top refined tin producer, said on Tuesday.

On Monday, Myanmar’s ethnic minority Wa militia said that from August the Wa region – a key tin producer – would suspend all mining activities to protect the remaining resources after more than a decade of “disruptive and wasteful mining”.
The news sent tin prices skyrocketing, with the most-traded May contract on the Shanghai Futures Exchange up as much as 17.5 per cent in two sessions and the benchmark three-month contract on the London Metal Exchange hitting a two-and-a-half month high.

“The company is closely monitoring the Chinese raw material supply,” Yunnan Tin told Reuters in a statement, adding that it would make “timely adjustment to its operations” as the impact on supply hinged on the implementation of the suspension.
The International Tin Association (ITA) said in a report on its website that “it is still unclear how and if these plans will be implemented.”
Myanmar accounted for 77 per cent of China’s tin ore imports last year, Chinese customs data showed. The Wa region is estimated to have accounted for over 70 per cent of Myanmar’s tin production in 2022, the ITA said.
The main tin mine in the self-declared Wa State, which borders China’s Yunnan province, is Man Maw, which produced around 32,000 tonnes of tin in 2020, the ITA said in a 2021 report.
“This tin is generally smelted in China and mining investment is thought to be sourced from China,” the report said.
Less significant tonnages of tin are also mined in Myanmar government-administered areas including the Mawchi mine in Kayah State and the Heinda mine in the Tanintharyi Region of southern Myanmar, the ITA added.
Myanmar is estimated to have the world’s third largest tin reserves at 700,000 tonnes – or 15 per cent of global reserves, behind Indonesia’s 800,000 tonnes and China’s 720,000 tonnes, US Geological Survey (USGS) data in 2023 showed.
Other major tin mining countries include Peru, Democratic Republic of Congo, Bolivia, Brazil and Australia.
Tin is used in the electronics and semiconductor industries.
Shares of Yunnan Tin hit their highest since June 2022 at 17.96 yuan ($2.61) on Tuesday. They jumped 10 per cent in the previous session on the Myanmar news.
Yunnan Tin last year produced 77,100 tonnes of refined tin, around a fifth of global output, ITA data showed.
China is the world’s biggest consumer of tin and is also the top producer of tin ore and refined tin. Four of the world’s top 10 refined tin producers are Chinese, data by the ITA showed.
($1 = 6.8719 yuan)
(By Siyi Liu and Mai Nguyen; Editing by Tom Hogue and Mark Potter)
Column: Tin spooked by threat of supply disruption in Myanmar
Reuters | April 18, 2023 |

Tin prices leapt higher on Monday on news of a possible production halt in Myanmar, the world’s third-largest producer of the soldering metal.

London Metal Exchange three-month tin jumped by 11% to hit a two-month high of $27,705 per tonne and was last trading at $27,180. It took its lead from the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE), which was already seeing record levels of trading activity before the latest turmoil.
The unexpected threat to supply comes in the form of a statement from the Central Economic Planning Committee of the Wa State, Myanmar’s most powerful ethnic armed group that controls the tin-mining area on the border with China.
All mining and processing activities will be “suspended” from the start of August to preserve the remaining resource, according to a document seen by Reuters.
It seems a strange move, given tin is such an important source of revenue for the self-declared Wa State, and there may well be more to the announcement than meets the eye.
But it serves to highlight the importance of one of the most inaccessible parts of southeast Asia to the global tin supply chain.
China’s tin smelters are particularly exposed even though they have been trying to cut their dependence on Myanmar ore.


Reuters | April 18, 2023 |

Tin prices leapt higher on Monday on news of a possible production halt in Myanmar, the world’s third-largest producer of the soldering metal.

London Metal Exchange three-month tin jumped by 11% to hit a two-month high of $27,705 per tonne and was last trading at $27,180. It took its lead from the Shanghai Futures Exchange (ShFE), which was already seeing record levels of trading activity before the latest turmoil.
The unexpected threat to supply comes in the form of a statement from the Central Economic Planning Committee of the Wa State, Myanmar’s most powerful ethnic armed group that controls the tin-mining area on the border with China.
All mining and processing activities will be “suspended” from the start of August to preserve the remaining resource, according to a document seen by Reuters.
It seems a strange move, given tin is such an important source of revenue for the self-declared Wa State, and there may well be more to the announcement than meets the eye.
But it serves to highlight the importance of one of the most inaccessible parts of southeast Asia to the global tin supply chain.
China’s tin smelters are particularly exposed even though they have been trying to cut their dependence on Myanmar ore.
Myanmar’s tin rush
Myanmar was a significant producer of tin before World War Two but the industry had all but vanished by the end of the last century.
The first anyone knew of a significant new tin find was in 2013 when large quantities of ore and concentrates from Myanmar started turning up in China’s import figures.
Imports from Myanmar grew from 30,000 tonnes in 2012 to 89,000 tonnes in 2013 and mushroomed to almost 500,000 tonnes in 2016. The mid-decade peak coincided with a sharp drop in implied value, suggesting the movement of lower-grade stockpiled metal.
The raw materials import flow has since stabilized at around 150,000-200,000 tonnes a year.
What began as small-scale and artisanal mining quickly became mechanized and semi-formalized as the United Wa State Army (UWSA) took control of the core Man Maw mining area.
The International Tin Association visited the site in 2016 and estimated it was operating close to its 50,000-tonne-per-year contained metal capacity, albeit with significant potential for new finds.
The United States Geological Survey estimates production last year fell to 31,000 tonnes from 36,900 tonnes in 2021, still making the country the world’s third-largest supplier after China and Indonesia.
It’s a controversial one, too, given the UWSA was put on the United States sanctions list in 2003 for alleged narcotics trafficking.
Chinese dependence
The Myanmar tin boom occurred at the right time for China’s tin smelters, many of which were struggling to bring on new mining capacity as Beijing steadily tightened environmental controls on the mining sector.
But the risks of becoming overly dependent on its neighbor became apparent when Covid-19 restrictions massively disrupted both Myanmar’s mining output and the flow of raw materials over the border.
China’s smelters have been busy tracking down new potential sources of tin.
The ratio of Myanmar imports has fallen from nearly 100% of total ore and concentrates imports over the middle of the last decade to 77% in 2022.
Last year’s imports included 23,500 tonnes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, 11,500 tonnes from Australia and 3,000 tonnes from Nigeria as well smaller amounts from Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia and Russia.
However, it’s doubtful that supply from alternative sources could be ramped up fast enough or at a sufficient scale to offset the loss, even temporary, of material from Myanmar.
Myanmar was a significant producer of tin before World War Two but the industry had all but vanished by the end of the last century.
The first anyone knew of a significant new tin find was in 2013 when large quantities of ore and concentrates from Myanmar started turning up in China’s import figures.
Imports from Myanmar grew from 30,000 tonnes in 2012 to 89,000 tonnes in 2013 and mushroomed to almost 500,000 tonnes in 2016. The mid-decade peak coincided with a sharp drop in implied value, suggesting the movement of lower-grade stockpiled metal.
The raw materials import flow has since stabilized at around 150,000-200,000 tonnes a year.
What began as small-scale and artisanal mining quickly became mechanized and semi-formalized as the United Wa State Army (UWSA) took control of the core Man Maw mining area.
The International Tin Association visited the site in 2016 and estimated it was operating close to its 50,000-tonne-per-year contained metal capacity, albeit with significant potential for new finds.
The United States Geological Survey estimates production last year fell to 31,000 tonnes from 36,900 tonnes in 2021, still making the country the world’s third-largest supplier after China and Indonesia.
It’s a controversial one, too, given the UWSA was put on the United States sanctions list in 2003 for alleged narcotics trafficking.
Chinese dependence
The Myanmar tin boom occurred at the right time for China’s tin smelters, many of which were struggling to bring on new mining capacity as Beijing steadily tightened environmental controls on the mining sector.
But the risks of becoming overly dependent on its neighbor became apparent when Covid-19 restrictions massively disrupted both Myanmar’s mining output and the flow of raw materials over the border.
China’s smelters have been busy tracking down new potential sources of tin.
The ratio of Myanmar imports has fallen from nearly 100% of total ore and concentrates imports over the middle of the last decade to 77% in 2022.
Last year’s imports included 23,500 tonnes from the Democratic Republic of Congo, 11,500 tonnes from Australia and 3,000 tonnes from Nigeria as well smaller amounts from Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia and Russia.
However, it’s doubtful that supply from alternative sources could be ramped up fast enough or at a sufficient scale to offset the loss, even temporary, of material from Myanmar.

Insecurity of supply
The speed of Monday’s price action says as much about market positioning as it does about the immediate supply impact.
The Shanghai tin market has recently seen extremely elevated levels of trading activity, with both turnover and open interest hitting fresh life-of-contract highs in March. Last month’s volumes of 5.34 million tonnes were 14 times greater than last year’s global production of 380,000 tonnes.
Shifts in ShFE market open interest suggest tin’s new speculative friends have been trading from the short side, or they were until Monday when open interest surged again into the price rally.
The bearish stance made sense given a significant easing in soldering demand from a slowing consumer electronics sector and the build in visible inventory in China.
ShFE-registered stocks have risen by 65% since the start of January to 9,056 tonnes, their highest level since 2017.
That will provide plenty of short-term cushion for Chinese buyers as they and everyone else wait to see if the Wa State is serious about suspending production.
However, the threat alone underscores the fragility of tin supply at a time when Indonesia, the largest exporter of the metal in refined form, is mulling an export ban to stimulate the build-out of downstream processing capacity.
The tin production sector has been chronically under-invested for many years and has ridden its luck on small-scale miners finding the big deposits, as was the case in Myanmar in the 2010s and Brazil in the 1990s.
A failure to diversify supply has left tin’s fortunes at least partly dependent on the shadowy UWSA and its opaque policy-making processes.
This is probably not going to be the last time tin gets spooked by unexpected news from Myanmar.
(The opinions expressed here are those of the author, Andy Home, a columnist for Reuters.)
(Editing by Paul Simao)
The speed of Monday’s price action says as much about market positioning as it does about the immediate supply impact.
The Shanghai tin market has recently seen extremely elevated levels of trading activity, with both turnover and open interest hitting fresh life-of-contract highs in March. Last month’s volumes of 5.34 million tonnes were 14 times greater than last year’s global production of 380,000 tonnes.
Shifts in ShFE market open interest suggest tin’s new speculative friends have been trading from the short side, or they were until Monday when open interest surged again into the price rally.
The bearish stance made sense given a significant easing in soldering demand from a slowing consumer electronics sector and the build in visible inventory in China.
ShFE-registered stocks have risen by 65% since the start of January to 9,056 tonnes, their highest level since 2017.
That will provide plenty of short-term cushion for Chinese buyers as they and everyone else wait to see if the Wa State is serious about suspending production.
However, the threat alone underscores the fragility of tin supply at a time when Indonesia, the largest exporter of the metal in refined form, is mulling an export ban to stimulate the build-out of downstream processing capacity.
The tin production sector has been chronically under-invested for many years and has ridden its luck on small-scale miners finding the big deposits, as was the case in Myanmar in the 2010s and Brazil in the 1990s.
A failure to diversify supply has left tin’s fortunes at least partly dependent on the shadowy UWSA and its opaque policy-making processes.
This is probably not going to be the last time tin gets spooked by unexpected news from Myanmar.
(The opinions expressed here are those of the author, Andy Home, a columnist for Reuters.)
(Editing by Paul Simao)
No comments:
Post a Comment