Hurricane Lee’s historic intensification skyrockets storm to rare strength
Mary Gilbert and Allison Chinchar, CNN
Fri, September 8, 2023
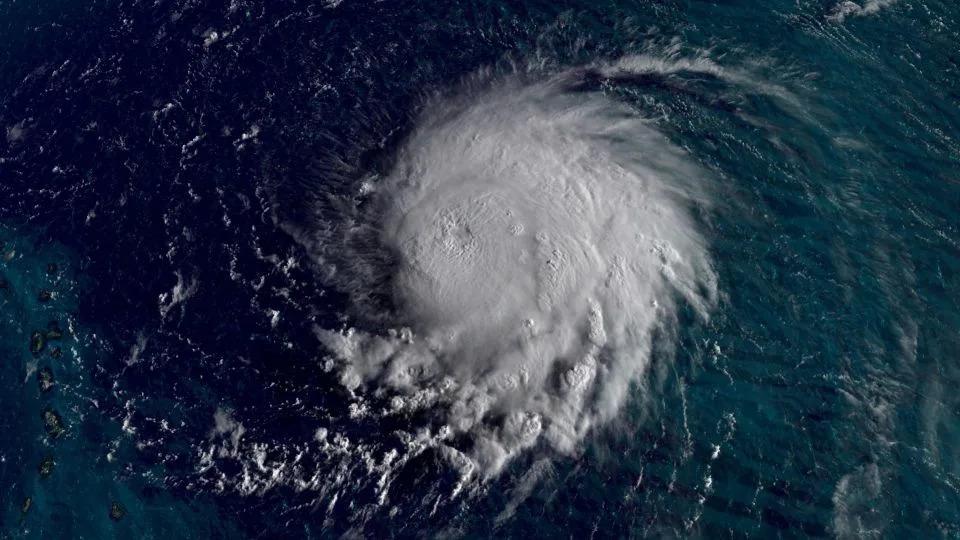

A satellite view of Lee at Category 5 strength. - CNN Weather
Hurricane Lee maintained its Category 4 strength Friday evening as the powerful storm’s indirect – yet dangerous – impacts were expected to reach the waters of the East Coast as early as this weekend.
The hurricane, which briefly strengthened to a rare Category 5 storm in the Atlantic Ocean, is packing destructive maximum sustained winds of 150 mph and is about 500 miles east of the northern Leeward Islands.
“Some fluctuations in intensity are likely over the next few days, however Lee is expected to remain a powerful major hurricane through early next week,” the National Hurricane Center said.
It’s too soon to know whether this system will directly impact the US mainland, but the storm will create dangerous coastal conditions like rip currents and large waves along the East Coast as soon as Sunday regardless of its final track.
Lee, which was a Category 1 storm Thursday, intensified with exceptional speed in warm ocean waters, more than doubling its wind speeds to 165 mph in just a day.
The storm’s winds increased by 85 mph in a 24-hour period, which tied it with Hurricane Matthew for the third-fastest rapid intensification in the Atlantic, according to NOAA research meteorologist John Kaplan. The monstrous hurricane struck Haiti in 2016, killing hundreds in the Caribbean nation while also wreaking havoc on parts of the US Southeast.
Dangerous surf and rip currents will spread across the northern Caribbean on Friday
The center of Lee will pass to the north of the Leeward Islands, the Virgin Islands and Puerto Rico this weekend and into early next week. Tropical storm conditions, life-threatening surf and rip currents could occur on some of these islands over the weekend.
Lee now in rare company
Lee hit a rare strength that few storms have ever achieved. Only 2% of storms in the Atlantic reach Category 5 strength, according to NOAA’s hurricane database. Including Lee, only 40 Category 5 hurricanes have roamed the Atlantic since 1924.
Category 5 is the highest level on the hurricane wind speed scale and has no maximum point. Hurricanes hit this level when their sustained winds reach 157 mph or higher. A 165-mph storm like Lee is the same category as Hurricane Allen, the Atlantic’s strongest hurricane on record, which topped out at 190 mph in 1980.
Hurricanes need the perfect mixture of warm water, moist air and light upper-level winds to intensify enough to reach Category 5 strength. Lee had all of these, especially warm water amid the warmest summer on record.
Sea-surface temperatures across the portion of the Atlantic Ocean that Lee is tracking through are a staggering 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) above normal after rising to “far above record levels” this summer, according to David Zierden, Florida’s state climatologist.
Reaching Category 5 strength has become more common over the last decade. Lee is the 8th Category 5 since 2016, meaning 20% of these exceptionally powerful hurricanes on record in NOAA’s hurricane database have come in the last seven years.
The Atlantic is not the only ocean to have spawned a monster storm in 2023. All seven ocean basins where tropical cyclones can form have had a storm reach Category 5 strength so far this year, including Hurricane Jova, which reached Category 5 status in the eastern Pacific earlier this week.
HURRICANE LEE TO HIT NEWFOUNDLAND IN ALL THREE SCENARIOS
How close will Hurricane Lee get to the US?
Computer model trends for Lee have shown the hurricane taking a turn to the north early next week. But exactly when that turn occurs and how far west Lee will manage to track by then will play a huge role in how close it gets to the US.
Several steering factors at the surface and upper levels of the atmosphere will determine how close Lee will get to the East Coast.
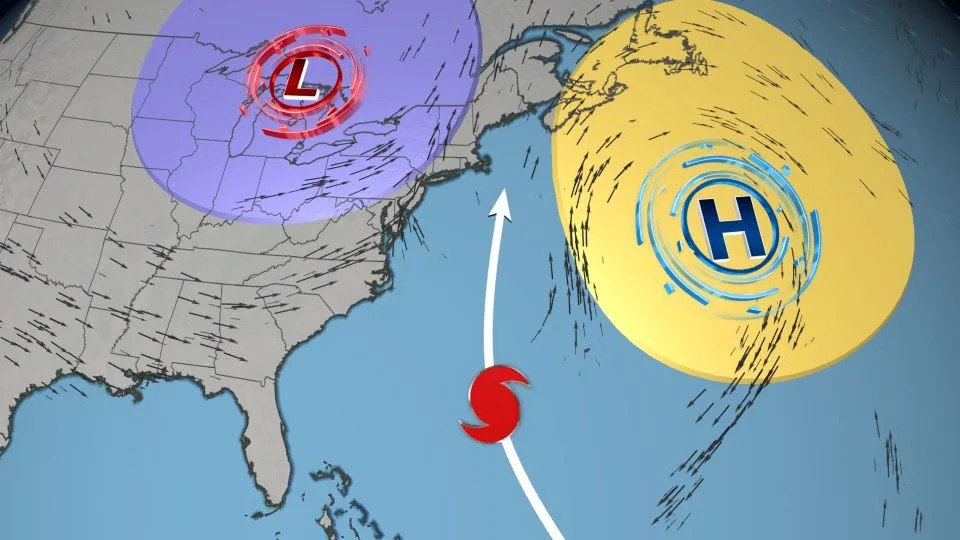
Lee's potential track next week will be determined by multiple atmospheric factors including a strong area of high pressure to its east (yellow circle) and the jet stream (silver arrows) to its west.
An area of high pressure over the Atlantic, known as the Bermuda High, will have a major influence in how quickly Lee turns. The Bermuda High is expected to remain very strong into the weekend, which will keep Lee on its current west-northwestward track and slow it down a bit.
As the high pressure weakens next week it will allow Lee to start moving northward.
Once that turn to the north occurs, the position of the jet stream – strong upper-level winds that can change the direction of a hurricane’s path – will influence how closely Lee is steered to the US.
Scenario: Out to Sea
Lee could make a quick turn to the north early next week if high pressure weakens significantly.
If the jet stream sets up along the East Coast, it will act as a barrier that prevents Lee from approaching the coast. This scenario would keep Lee farther away from the US coast but could bring the storm closer to Bermuda.
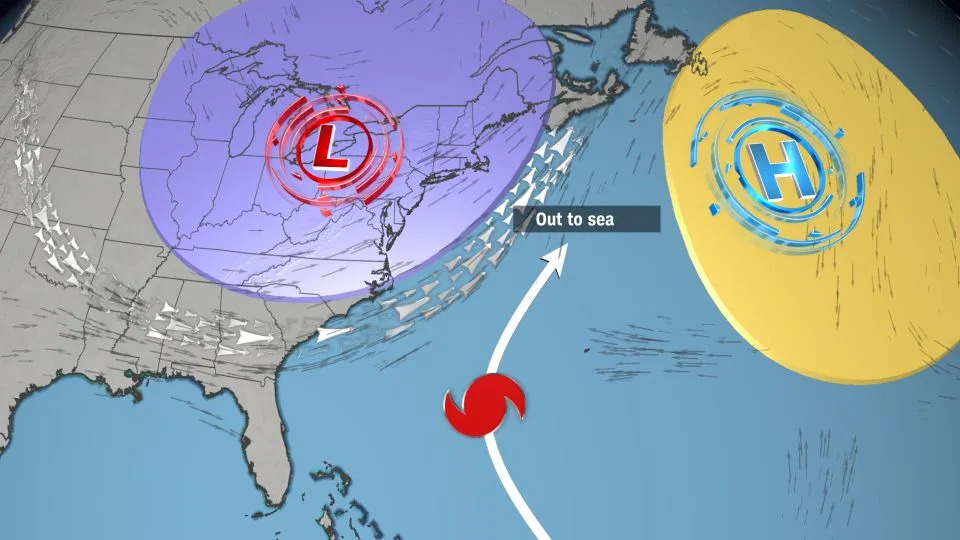
Track Scenario: An area of high pressure (yellow circle) to the east of Lee and the jet stream (silver arrows) to the west of Lee, can force the storm to track between the two, away from the US coast.
Scenario: Close to East Coast
Lee could make a slower turn to the north because the high pressure remains robust, and the jet stream sets up farther inland over the Eastern US. This scenario would leave portions of the East Coast, mainly north of the Carolinas, vulnerable to a much closer approach from Lee.
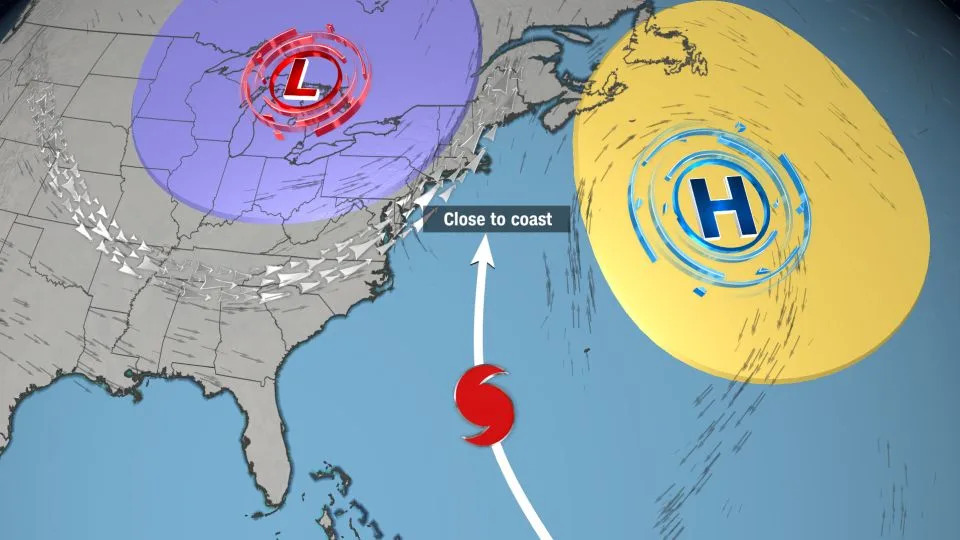
Track Scenario: An area of high pressure (yellow circle) to the east of Lee and the jet stream (silver arrows) to the west of Lee, can force the storm to track between the two, closer to the US coast.
All these factors have yet to come into focus, and the hurricane is still at least seven days from being a threat to the East Coast. Any potential US impact will become more clear as the Lee moves west in the coming days.
CNN Meteorologist Robert Shackelford and Aya Elamroussi contributed to this report.
No comments:
Post a Comment