Old mines and gold waste power surge in Pan African’s shares
Bloomberg News | December 31, 2024 |

Credit: Pan African Resources
The best-performing South African miner this year is defying the country’s contemporary reputation for ever-more costly and lower-grade gold production.

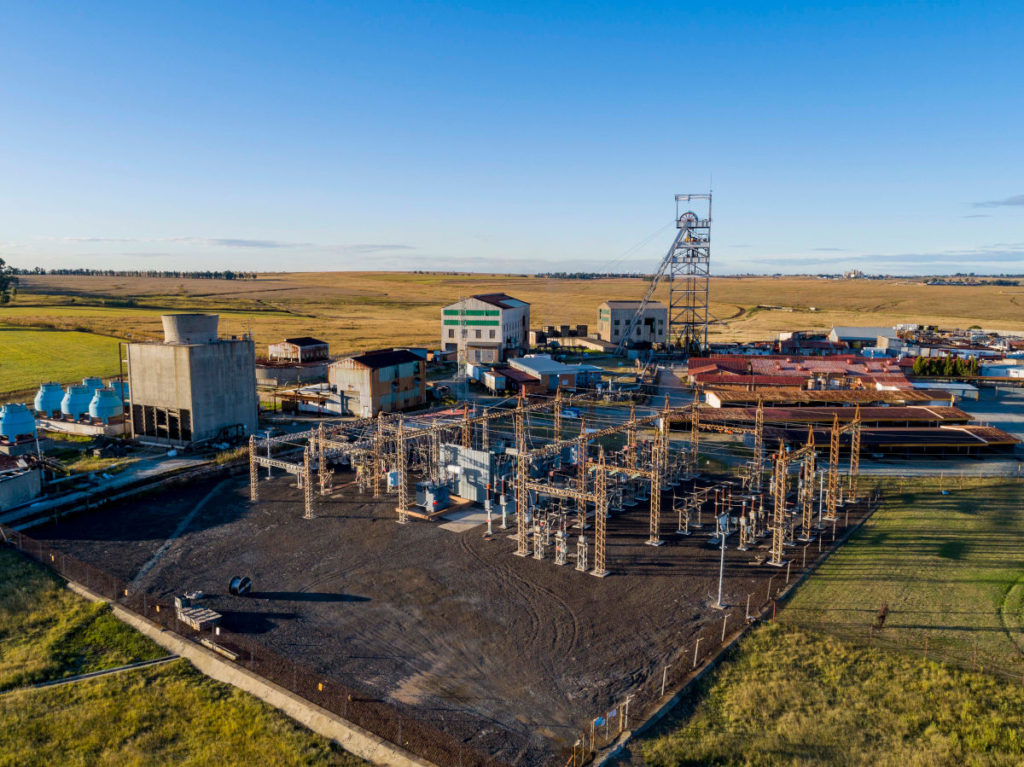
Pan African Resources Plc extracts the precious metal from waste dumps, known as tailings, left behind by decades of mining when South Africa was the world’s biggest gold producer. It’s also operating century-old underground shafts around Barberton, the site of the country’s first gold rush in the 1880s.
The stock has gained 94% in Johannesburg this year, more than triple the return of the next-best miner, Harmony Gold Mining Co. Ltd. It’s up by a similar amount in London, where it is listed on the Alternative Investment Market. The shares rose 0.3% in Johannesburg on Tuesday, hovering near the record high set earlier this month.
A gold price that’s been smashing through record after record – surging 27% since the start of the year and hitting an all-time high of $2,790.10 an ounce on Oct. 31 – has helped. Larger players haven’t scaled the same heights, partly because rising operational costs and weaker output across extensive global assets have offset the windfall of higher prices.
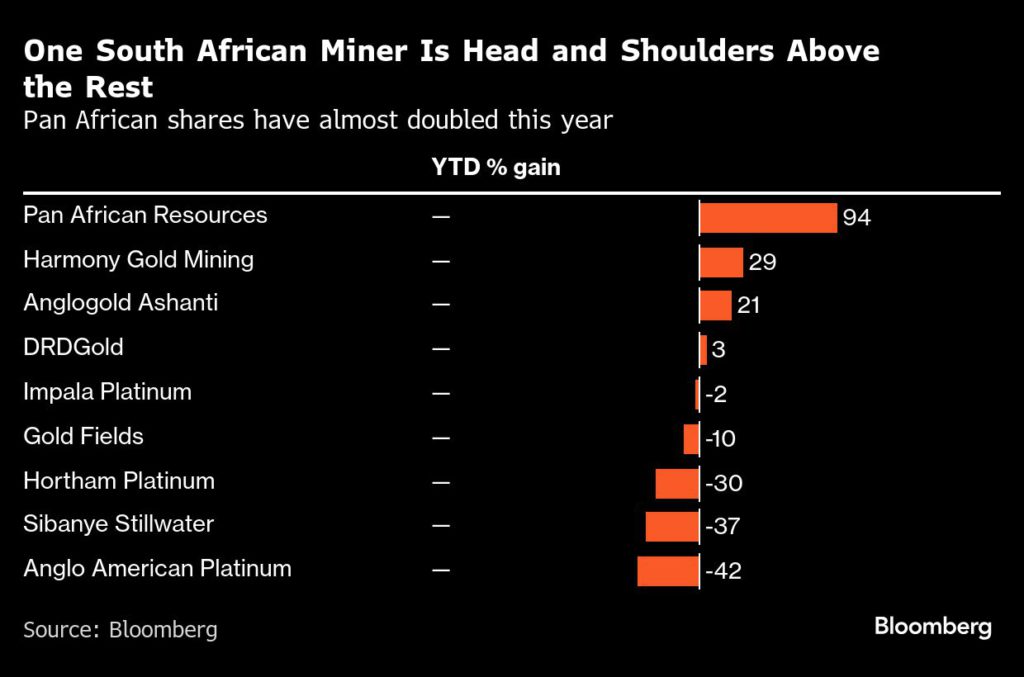
Pan African, which produced a relatively modest 186,000 ounces of the metal in 2023, has bolstered its portfolio of traditional deep mines with less expensive surface operations that process old tailings sites and will account for almost half of output in a few years.
“We can do what the major guys will find difficult to do, which is grow production – and low cost production – quite materially,” Pan African chief executive officer Cobus Loots said in an interview. The company’s third tailings project, Mintails, which is being ramped up, will provide an extra 50,000 to 60,000 ounces annually, he said. “I think the market’s quite excited about that.”
The miner’s “increasing production profile and decreasing cost profile” make it attractive relative to peers and insulate it from a lower gold price, according to Allan Gray Ltd., a Cape Town-based fund manager that increased its stake in Pan African to more than 17% in the quarter through September, making it the biggest holder of the shares, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
“I don’t think the market has fully internalized the cash flow that Pan African will be generating once Mintails is up and running,” said Sean Munsie, a portfolio manager at Allan Gray.
New ore bodies
Pan African has owned the Barberton complex – a trio of mines 300 kilometers east of Johannesburg that have produced more than 8 million ounces of gold over almost a century and a half – since 2007. The main operation, Fairview, still has two decades of mining left and the company hopes to prolong that by deploying modern technology to find new ore bodies, according to Loots. The company has also extended the life at Evander, the firm’s other underground asset which was acquired from Harmony Gold Mining Co. Ltd. 12 years ago.
“When the guys started mining these ore bodies, nobody thought they’d be mining them 140 years later,” said Loots. “With our exploration, we keep finding new high-grade ore bodies to mine.”
The world’s biggest gold producer for more than a century, South Africa was knocked off top spot almost 20 years ago and now ranks in 12th place – mining about a tenth as much as it did at its peak in 1970. Harmony – which operates the deepest mine on earth and is up nearly 30% this year – today produces the most gold from the country.
While the underground mines are profitable at the current gold price — with a cost of production of around $1,400 an ounce, according to Loots — the much lower-cost tailings operation gives the company a buffer against gold price volatility, said Brendon Hubbard, a portfolio manager at Johannesburg-based ClucasGray Investment Management, which holds Pan African shares.
“The timing was good in terms of this gold move that we’re seeing at the moment,” said Hubbard. “So the profitability metrics of Pan-African look really, really good.”
(By William Clowes and Khuleko Siwele)
Bloomberg News | December 31, 2024 |

Credit: Pan African Resources
The best-performing South African miner this year is defying the country’s contemporary reputation for ever-more costly and lower-grade gold production.

Pan African Resources Plc extracts the precious metal from waste dumps, known as tailings, left behind by decades of mining when South Africa was the world’s biggest gold producer. It’s also operating century-old underground shafts around Barberton, the site of the country’s first gold rush in the 1880s.
The stock has gained 94% in Johannesburg this year, more than triple the return of the next-best miner, Harmony Gold Mining Co. Ltd. It’s up by a similar amount in London, where it is listed on the Alternative Investment Market. The shares rose 0.3% in Johannesburg on Tuesday, hovering near the record high set earlier this month.
A gold price that’s been smashing through record after record – surging 27% since the start of the year and hitting an all-time high of $2,790.10 an ounce on Oct. 31 – has helped. Larger players haven’t scaled the same heights, partly because rising operational costs and weaker output across extensive global assets have offset the windfall of higher prices.

Pan African, which produced a relatively modest 186,000 ounces of the metal in 2023, has bolstered its portfolio of traditional deep mines with less expensive surface operations that process old tailings sites and will account for almost half of output in a few years.
“We can do what the major guys will find difficult to do, which is grow production – and low cost production – quite materially,” Pan African chief executive officer Cobus Loots said in an interview. The company’s third tailings project, Mintails, which is being ramped up, will provide an extra 50,000 to 60,000 ounces annually, he said. “I think the market’s quite excited about that.”
The miner’s “increasing production profile and decreasing cost profile” make it attractive relative to peers and insulate it from a lower gold price, according to Allan Gray Ltd., a Cape Town-based fund manager that increased its stake in Pan African to more than 17% in the quarter through September, making it the biggest holder of the shares, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
“I don’t think the market has fully internalized the cash flow that Pan African will be generating once Mintails is up and running,” said Sean Munsie, a portfolio manager at Allan Gray.
New ore bodies
Pan African has owned the Barberton complex – a trio of mines 300 kilometers east of Johannesburg that have produced more than 8 million ounces of gold over almost a century and a half – since 2007. The main operation, Fairview, still has two decades of mining left and the company hopes to prolong that by deploying modern technology to find new ore bodies, according to Loots. The company has also extended the life at Evander, the firm’s other underground asset which was acquired from Harmony Gold Mining Co. Ltd. 12 years ago.
“When the guys started mining these ore bodies, nobody thought they’d be mining them 140 years later,” said Loots. “With our exploration, we keep finding new high-grade ore bodies to mine.”
The world’s biggest gold producer for more than a century, South Africa was knocked off top spot almost 20 years ago and now ranks in 12th place – mining about a tenth as much as it did at its peak in 1970. Harmony – which operates the deepest mine on earth and is up nearly 30% this year – today produces the most gold from the country.
While the underground mines are profitable at the current gold price — with a cost of production of around $1,400 an ounce, according to Loots — the much lower-cost tailings operation gives the company a buffer against gold price volatility, said Brendon Hubbard, a portfolio manager at Johannesburg-based ClucasGray Investment Management, which holds Pan African shares.
“The timing was good in terms of this gold move that we’re seeing at the moment,” said Hubbard. “So the profitability metrics of Pan-African look really, really good.”
(By William Clowes and Khuleko Siwele)
Staff Writer | December 31, 2024
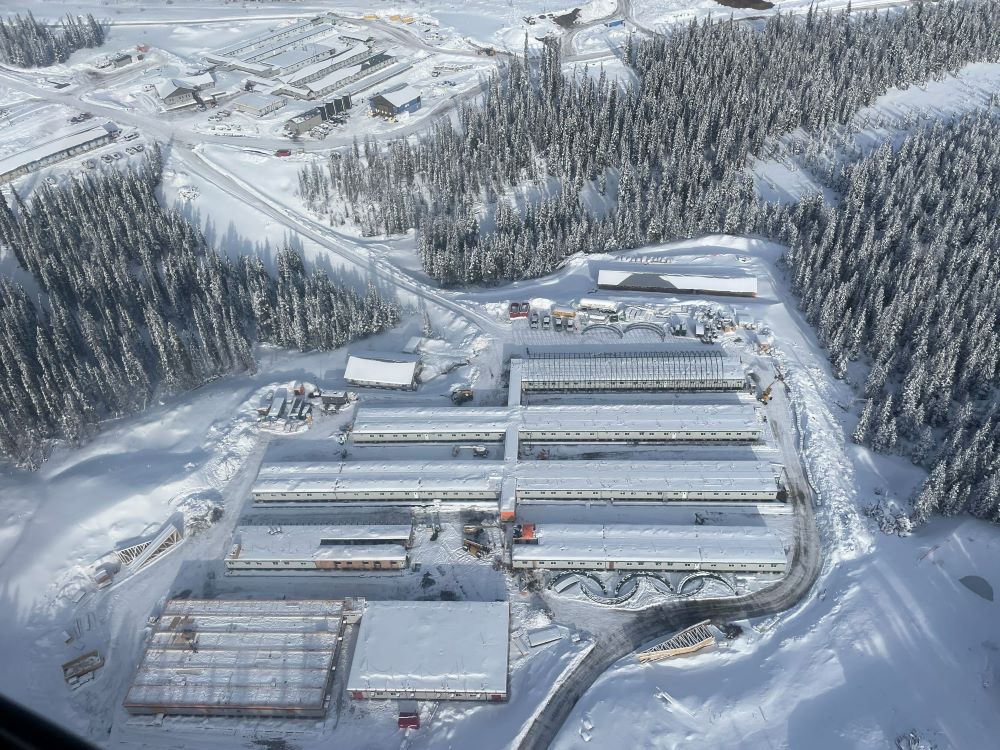

The Blackwater construction camp. Artemis Gold photo
Artemis Gold (TSXV: ARTG) has pushed back the completion date for its Blackwater mine in central British Columbia after experiencing delays with setting up the process control network during the holiday season.

The company now expects to commence processing of ore through the ball mill and first gold pour in January 2025 after it completes final commissioning of the wet plant.
Shares of Artemis Gold traded 0.7% higher on Tuesday morning on the announcement, sending the Vancouver-based miner’s market capitalization above C$3 billion ($2.1bn).
Artemis had previously maintained its first pour target of year-end 2024 despite multiple construction delays. The delays, mainly caused by the BC wildfires during the summer, have led to a 7% rise in the project’s initial capital costs — to C$780-C$800 million.
The Blackwater mine, located 160 km southwest of Prince George, is expected to become the province’s first new gold mine since the Brucejack in 2017.
Once in production, it is expected to produce 500,000 oz. of gold equivalent in each of its first 10 years, generating annual free cash flow of about C$500 million at an all-in sustaining cost of $712 per oz.
Expansion plans are also underway to extend the life of mine to 23 years.
No comments:
Post a Comment