BIDENOMICS
U.S. Oil Production Shattered Records Again in 2024
The U.S. oil production reached a new record high in 2024, surpassing the previous record set in 2023.
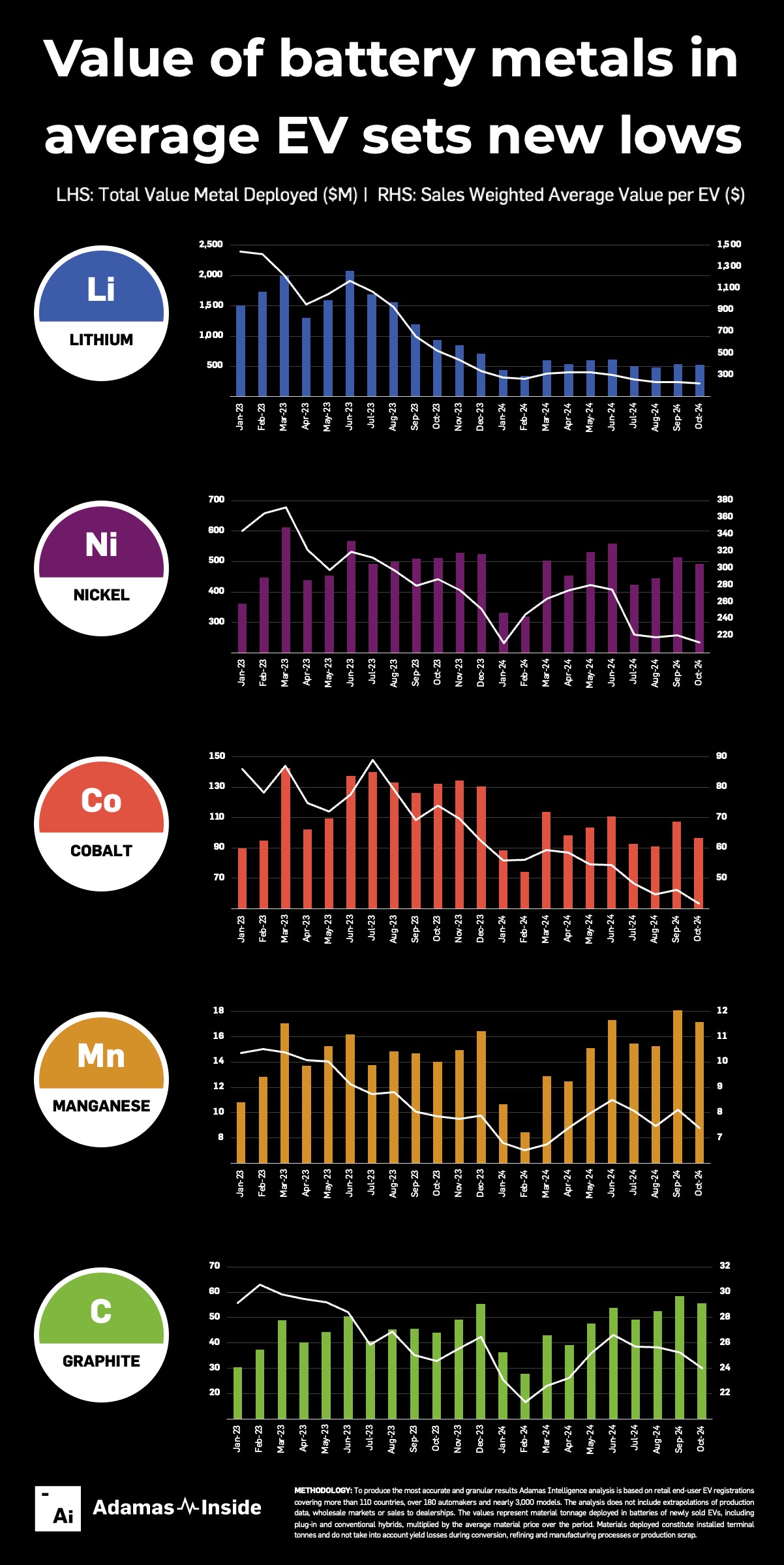
Technological advancements, including precision fracking and enhanced recovery techniques, have played a significant role in increasing productivity.
The record-breaking production has contributed to job creation, economic growth, and strengthened national energy security, but environmental concerns remain.
![]()
Despite ongoing concerns about global economic volatility, energy transition policies, and fluctuating demand, the U.S. energy sector has demonstrated its unmatched resilience and innovation.
Building on the record-breaking momentum of 2023, 2024 has proven to be another landmark year for oil production, driven by technological advancements, strategic investments, and favorable market conditions.
A Second Consecutive Oil Production Record
In 2023, U.S. oil production reached a record high, surpassing 12.9 million barrels per day, solidifying the country’s position as the world’s top oil producer. One of my 2024 energy sector predictions was that the U.S. would set a second consecutive record this year.
According to preliminary data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), production had averaged 13.249 million BPD year-to-date through December 13, 2024. Cumulative production for the year is estimated at 4.611 billion barrels by that date—just 110 million barrels shy of the previous annual record.
Given that producers have consistently exceeded 13 million BPD since January, the record likely fell by December 22, 2024. Even a conservative scenario of 12 million BPD would delay the milestone by under a day.
This achievement is a testament to the industry’s ability to adapt to shifting demand and market challenges while maintaining high levels of productivity.
The Driving Forces Behind the Production Record
The new record highlights the role of enhanced recovery techniques like precision fracking and improved drilling technologies, which have unlocked greater productivity from key oil fields. The Permian Basin continues to be the powerhouse of U.S. production, contributing a significant share of the growth through its cost-efficient operations.
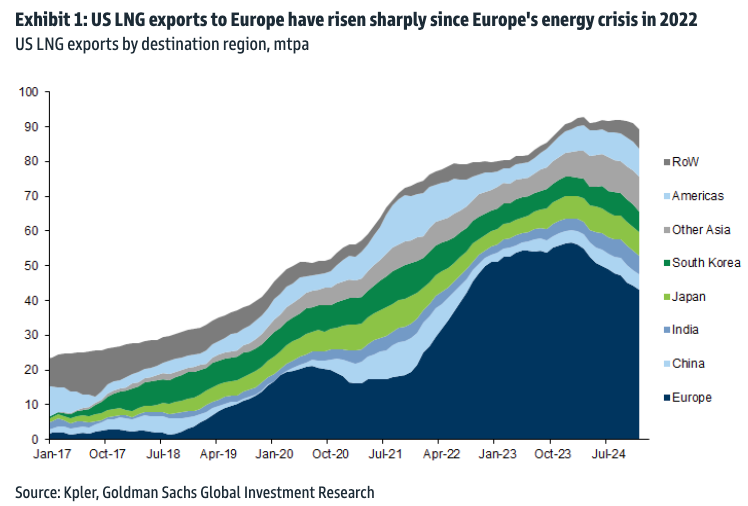
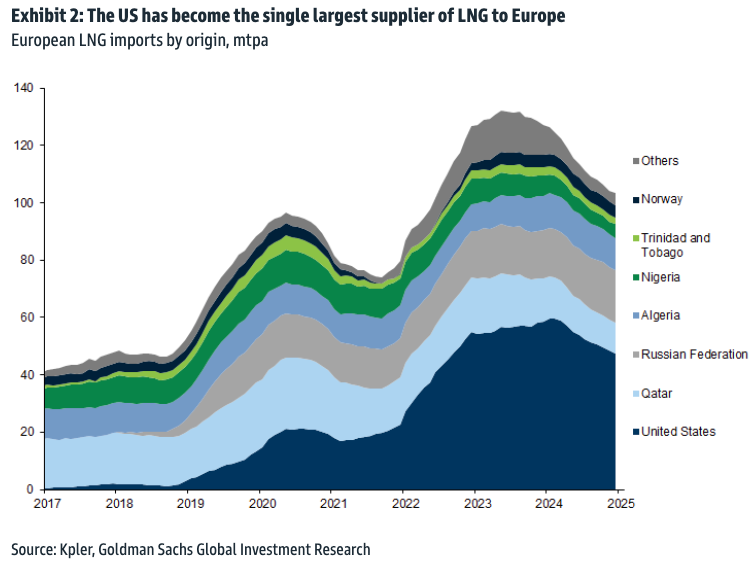
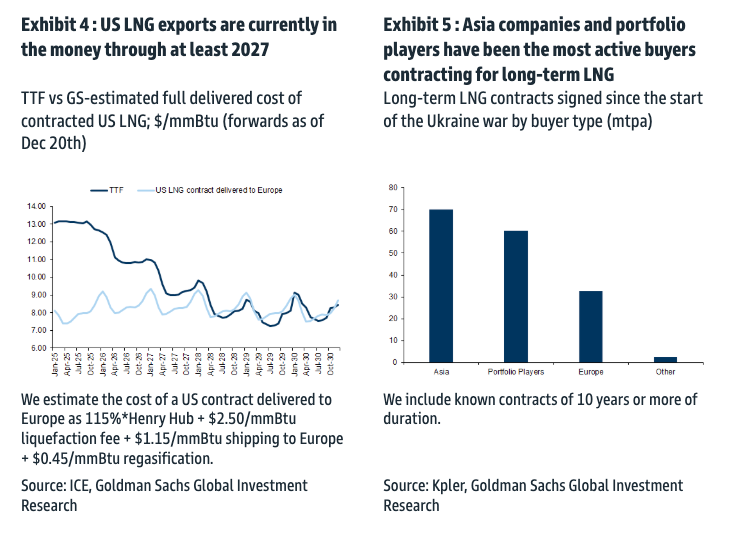
High demand for U.S. crude oil, particularly from Europe and Asia, has spurred production. Geopolitical tensions and shifting trade dynamics have positioned U.S. oil as a reliable alternative for global markets. Robust pipeline infrastructure and export terminals have further supported this expansion, enabling seamless transportation to international buyers.
At home, steady consumer demand for refined products, supported by healthy refining capacity, has ensured domestic market stability. This dual focus on international and domestic needs highlights the versatility and reliability of the U.S. energy sector.
Economic Benefits and Future Challenges
The shale industry’s growth has provided numerous jobs, strengthened local economies in production hubs, and bolstered national energy security. The economic ripple effects extend from upstream exploration to downstream refining, reinforcing the energy sector’s importance to the broader U.S. economy.
While these achievements are commendable, challenges remain. Addressing environmental concerns and aligning production with long-term sustainability goals will require ongoing investment in emissions-reduction initiatives and cleaner technologies. Balancing these priorities with the need for short-term growth will be key for the sector’s future.
A Testament to Resilience and Innovation
The U.S. oil production record of 2024 is a triumph of adaptability, innovation, and global competitiveness. It underscores the energy sector’s pivotal role in meeting global and domestic energy needs while contributing to economic growth.
With its unparalleled ability to overcome challenges and seize opportunities, the U.S. energy sector has cemented its place at the forefront of the global market—proving once again that resilience and innovation are the hallmarks of its success story.
U.S. crude oil production has demonstrated the sector’s ability to balance growing domestic demand, export markets, and geopolitical uncertainties. This new record reflects not only improved drilling and extraction methods, such as precision fracking and enhanced recovery techniques, but also the continued productivity of key oil-producing regions.
By Robert Rapier