By Rachael Rettner - Senior Writer
A new study provides more clues to the virus' origins.
(Image: © Shutterstock)
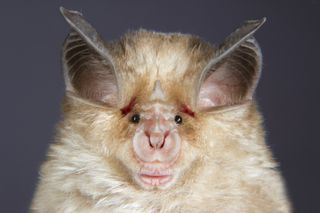
As a new coronavirus spreads in China and around the world, scientists are scrambling to find out exactly where it came from. Now, a new study provides more clues to the virus' origins, and points to bats as the most likely hosts.
In the study, published today (Jan. 29) in the journal The Lancet, the researchers analyzed 10 genome sequences of the novel coronavirus, dubbed 2019-nCoV, obtained from nine patients in China who were sick with the virus.
They found that all 10 of the genome sequences were extremely similar — they shared more than 99.98% of the same genetic sequence, the authors said. This suggests the virus made its "jump" to humans very recently, because if that jump had happened long ago, the virus sequences would have differed more, given the fast rate at which viruses tend to mutate and evolve.
"It is striking that the sequences of 2019-nCoV described here from different patients were almost identical," study co-lead author Weifeng Shi, a professor at the Key Laboratory of Etiology and Epidemiology of Emerging Infectious Diseases in Universities of Shandong Province, affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, said in a statement. "This finding suggests that 2019-nCoV originated from one source within a very short period and was detected relatively rapidly."
Related: 10 deadly diseases that hopped across species
Despite emerging in humans only recently, the virus has already infected about 6,000 people and caused 132 deaths in China, while spreading to 15 other countries, according to the World Health Organization. Most of the initial cases occurred in people who worked at or visited the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, China, where a variety of wild animals were sold.
To learn more about the virus' origins, the researchers compared the 2019-nCoV genetic sequence with those in a library of viral sequences, and found that the most closely related viruses were two coronaviruses that originated in bats; both of those coronaviruses shared 88% of their genetic sequence with that of 2019-nCoV. (When compared with two other coronaviruses known to infect people — SARS and MERS — 2019-nCoV shared about 79% of its genetic sequence with SARS and 50% with MERS.)
Based on these results, the authors said the 2019-nCoV likely originated in bats. However, no bats were sold at the Huanan seafood market, which suggests that another yet-to-be-identified animal acted as a steppingstone of sorts to transmit the virus to humans.
"It seems likely that another animal host is acting as an intermediate host between bats and humans," said study co-lead author Guizhen Wu, of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Overall, the outbreak of 2019-nCoV "again highlights the hidden virus reservoir in wild animals and their potential to occasionally spill over into human populations," the authors wrote.
A previous study suggested snakes, which were sold at the Huanan seafood market, as a possible source of 2019-nCoV. However, some experts have criticized the study, saying it's unclear if coronaviruses can infect snakes.

(Image: © Shutterstock)
As a new coronavirus spreads in China and around the world, scientists are scrambling to find out exactly where it came from. Now, a new study provides more clues to the virus' origins, and points to bats as the most likely hosts.
In the study, published today (Jan. 29) in the journal The Lancet, the researchers analyzed 10 genome sequences of the novel coronavirus, dubbed 2019-nCoV, obtained from nine patients in China who were sick with the virus.
They found that all 10 of the genome sequences were extremely similar — they shared more than 99.98% of the same genetic sequence, the authors said. This suggests the virus made its "jump" to humans very recently, because if that jump had happened long ago, the virus sequences would have differed more, given the fast rate at which viruses tend to mutate and evolve.
"It is striking that the sequences of 2019-nCoV described here from different patients were almost identical," study co-lead author Weifeng Shi, a professor at the Key Laboratory of Etiology and Epidemiology of Emerging Infectious Diseases in Universities of Shandong Province, affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, said in a statement. "This finding suggests that 2019-nCoV originated from one source within a very short period and was detected relatively rapidly."
Related: 10 deadly diseases that hopped across species
Despite emerging in humans only recently, the virus has already infected about 6,000 people and caused 132 deaths in China, while spreading to 15 other countries, according to the World Health Organization. Most of the initial cases occurred in people who worked at or visited the Huanan seafood market in Wuhan, China, where a variety of wild animals were sold.
To learn more about the virus' origins, the researchers compared the 2019-nCoV genetic sequence with those in a library of viral sequences, and found that the most closely related viruses were two coronaviruses that originated in bats; both of those coronaviruses shared 88% of their genetic sequence with that of 2019-nCoV. (When compared with two other coronaviruses known to infect people — SARS and MERS — 2019-nCoV shared about 79% of its genetic sequence with SARS and 50% with MERS.)
Based on these results, the authors said the 2019-nCoV likely originated in bats. However, no bats were sold at the Huanan seafood market, which suggests that another yet-to-be-identified animal acted as a steppingstone of sorts to transmit the virus to humans.
"It seems likely that another animal host is acting as an intermediate host between bats and humans," said study co-lead author Guizhen Wu, of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Overall, the outbreak of 2019-nCoV "again highlights the hidden virus reservoir in wild animals and their potential to occasionally spill over into human populations," the authors wrote.
A previous study suggested snakes, which were sold at the Huanan seafood market, as a possible source of 2019-nCoV. However, some experts have criticized the study, saying it's unclear if coronaviruses can infect snakes.
The 9 deadliest viruses on Earth
27 devastating infectious diseases
11 surprising facts about the respiratory system
Originally published on Live Science.
ALSO SEE
https://plawiuk.blogspot.com/2020/01/scientists-now-think-they-know-what.html
SEE https://plawiuk.blogspot.com/search?q=BATS
SEE https://plawiuk.blogspot.com/search?q=ZOONOSIS
SEE https://plawiuk.blogspot.com/search?q=CORONAVIRUS
SEE https://plawiuk.blogspot.com/search?q=WUHAN
No comments:
Post a Comment