Oklahoma rattled by shallow 5.1 magnitude earthquake

A 5.1 magnitude earthquake shook an area near Oklahoma City late Friday, followed by smaller quakes during the next several hours, the U.S. Geological Survey reported.
No injuries were reported and damage appeared to be minimal, mostly items overturned or shaken from shelves inside homes, according to Lincoln County Deputy Emergency Management Director Charlotte Brown.
"Nothing significant ... nothing other than lots of scared people," Brown said.
The earthquake struck at 11:24 p.m. and was centered 8 kilometers (5 miles) northwest of Prague, Oklahoma, about 57 miles (92 kilometers) east of Oklahoma City, the agency said.
Residents across the state from Lawton to Enid to Tulsa reported feeling the shaking to the U.S.G.S.
The initial earthquake was followed by at least eight smaller temblors through Saturday morning, ranging in strength from magnitude 2.5 to 3.4, according to the geological survey.
The earthquake was shallow—just 3 kilometers (1.8 miles) deep, according to the USGS—and temblors that hit close to the surface can make the shaking more intense.
At least six earthquakes, including two greater than magnitude 4, were recorded near another Oklahoma City suburb in January. In April, a magnitude 4 earthquake was among a series of six that struck the central Oklahoma town of Carney, about 40 miles (64 kilometers) northeast of Oklahoma City.
A 5.7 magnitude earthquake struck Prague in 2011, about 60 miles (97 kilometers) south of the state's strongest recorded earthquake site in Pawnee, which registered a magnitude 5.8 in 2016.
Thousands of earthquakes have been recorded in Oklahoma in recent years, many linked to the underground injection of wastewater from oil and natural gas extraction, particularly in what is known as the Arbuckle formation that includes the area around Prague.
The epicenter of the Saturday earthquake was nearly the exact spot of the epicenter of the 2011 quake, according to Matt Skinner, spokesperson for the Oklahoma Corporation Commission, which regulates the oil and gas industry in the state.
"That was one of the early areas where action was taken" to limit the injection of wastewater, said Skinner.
"Disposal wells within 10 miles of the quake" must stop operating temporarily, Skinner said.
The corporation commission has directed several producers to close some injection wells and reduce the volumes in others as a result of the quakes.
© 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
Ancient rocks improve understanding of tectonic activity between earthquakes
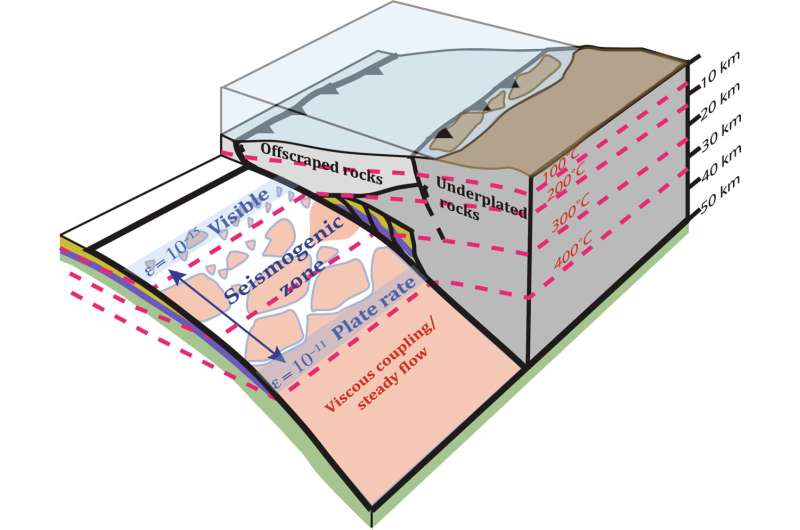
Rocks once buried deep in ancient subduction zones—where tectonic plates collide—could help scientists make better predictions of how these zones behave during the years between major earthquakes, according to a research team from Penn State and Brown University.
Clues from rock formations in Alaska and Japan allowed the scientists to develop a new model to predict the pressure solution activity in subduction zones, the researchers reported in the journal Science Advances.
Sedimentary rocks comprise grains surrounded by water-containing pores. When rocks are squeezed together under great pressure, the grains dissolve at their boundaries into the water present in pores, forming pressure solution. This allows the rocks to deform, or change shape, influencing how the tectonic plates slide past each other.
"It's like when you go ice skating—the blade on the surface ends up melting the ice, which allows you to glide along," said corresponding author Donald Fisher, professor of geosciences at Penn State. "In rocks, what happens is quartz grains dissolve at stressed contacts and the dissolved material moves to cracks where it precipitates."
The world's most powerful earthquakes happen in subduction zones, where one tectonic plate slides beneath the other. When these plates become stuck together, stress builds in the crust of the Earth—like a rubber band being stretched. When enough stress builds up to overcome the friction holding the plates together—like a rubber band snapping—an earthquake occurs.
"We've shown that pressure solution is a fundamental process during the interseismic period in subduction zones," Fisher said. "The occurrence of this pressure solution can really affect the amount of elastic strain that accumulates in different parts of the seismogenic zone."
Pressure solution is difficult to explore in the laboratory because it typically occurs very slowly over thousands to millions of years, Fisher said. Speeding up the process in the lab requires higher temperatures, which produces other changes in rocks that impact the experiments.
The scientists instead turned to rocks that once experienced these tectonic pressures and were later brought to the surface by geological processes. The rocks show microscopic shears—or breaks caused by strain—that contain textures that provide evidence for pressure solution, the scientists said.
"This work allows us to test a flow law, or model, that describes the rate of pressure solution in ancient rocks that were once down at the plate boundary and have been exhumed to the surface," Fisher said. "And we can apply this to active margins that are moving today."
A previous study by another team of scientists linked stress the rocks experienced and strain rate—or how much they deformed. In the new work, Fisher and his colleague, Greg Hirth, professor at Brown University, created a more detailed model that considers factors like the rocks' grain size and solubility, or how much of the rock material can dissolve into liquid.
"We were able to parameterize the solubility as a function of temperature and pressure, in a practical way that hadn't been done before," Fisher said. "So now we can plug in numbers—different grain sizes, different temperatures, different pressures and get the strain rate out of that."
The results can help reveal where in the seismogenic layer—the range of depths at which most earthquakes occur—that strain is occurring.
The researchers applied their model to the Cascadia Subduction Zone, an active fault that runs from northern California to Canada and by major cities such as Portland, Oregon, Seattle and Vancouver, British Columbia.
The temperature along the plate boundary and the amount of strain built up is well studied there, and the results of their model match crustal movements based on satellite observations, the scientists said.
"Cascadia is a great example because it's late in the interseismic period—it's been 300 years since the last major earthquake," Fisher said. "We may experience one in our lifetime, which would be the biggest natural disaster that North America can anticipate in terms of the potential for shaking and resulting tsunami."
More information: Donald M. Fisher et al, A pressure solution flow law for the seismogenic zone: Application to Cascadia, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi7279
Provided by Pennsylvania State University Long-dead marine organisms may influence next major earthquake
No comments:
Post a Comment