Justin Bachman, Bloomberg News

Workers near the top of the 526 ft. Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center spruce up the NASA logo standing on scaffolds in Cape Canaveral, Fla., Wednesday, May 20, 2020. , The Associated Press
Boeing Co.’s Space Launch System, the largest rocket in NASA’s history, will carry a price tag of at least US$9.1 billion -- or 30 per cent more than the previous estimate for a key element in the agency’s plan to return to the moon.
Additionally, the costs for new ground infrastructure at Florida’s Kennedy Space Center to support the deep-space exploration program has jumped to US$2.4 billion, Kathy Lueders, NASA’s associate administrator for human spaceflight, said in a blog post Wednesday. That’s also a 30 per cent increase, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration said in an email Thursday.
“NASA has notified Congress of these new commitments, and we are working at the best possible pace toward launch, including streamlining operational flow at Kennedy and assessing opportunities to further improve the efficiency of our integration activities,” Lueders wrote.
The new cost estimates are based on NASA’s pledge to fly the first SLS-powered Artemis mission around the moon, without crew, in November 2021. Addressing the escalating costs, NASA referred to its previous statements on “challenges associated with design development, manufacturing development, first-time production, and initial operations for SLS.”
Coronavirus Uncertainty
While the space agency is confident of meeting the November 2021 flight date, it’s too early to predict the full impact of work delays caused by the coronavirus pandemic, Lueders said. NASA will follow the first SLS flight with a crewed mission in 2023. A third Artemis flight to put astronauts on the moon is planned for 2024 to meet a challenge set by the Trump administration.
“Boeing is responsible for the rocket core and upper stages and we are making great progress,” the Chicago-based company said in a statement.
Jacobs Engineering Group Inc., the prime contractor for the ground support work at Kennedy Space Center, didn’t immediately reply to a request for comment.
In March, a NASA Inspector General report on the SLS program found that the agency has struggled with rising costs and delays, citing “program management, technical issues, and contractor performance.” By the end of the current U.S. fiscal year, which ends Sept. 30, NASA will have spent more than US$17 billion on the overall SLS program, according to the report. That’s 60 per cent more than NASA’s 2014 cost estimate.
The next big test for the SLS, which will stand taller than the Statue of Liberty, will be in October when engineers plan to fire all four main RS-25 engines simultaneously and drain the fuel tanks within eight minutes, simulating flight conditions.
NASA approved the rocket’s development in August 2014, setting the cost at US$7.02 billion with a first flight “no later than November 2018.” Throughout its history, the SLS program has enjoyed immense support in the Senate, and Congress has continued to fund the program despite setbacks in cost and schedule.
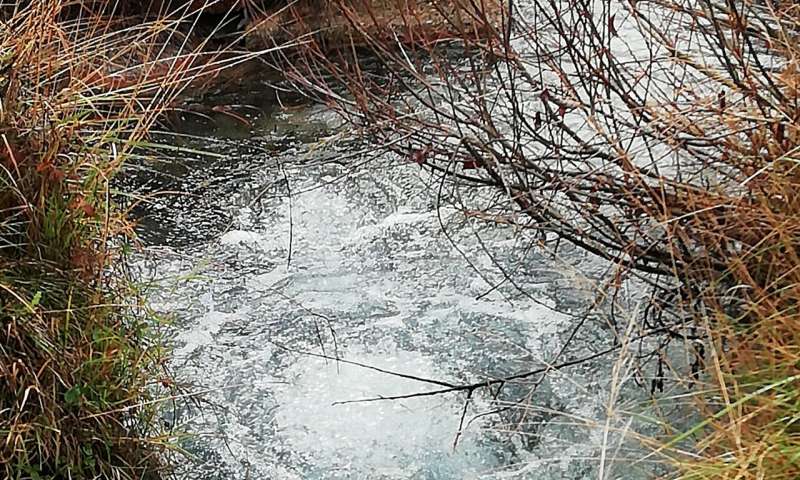




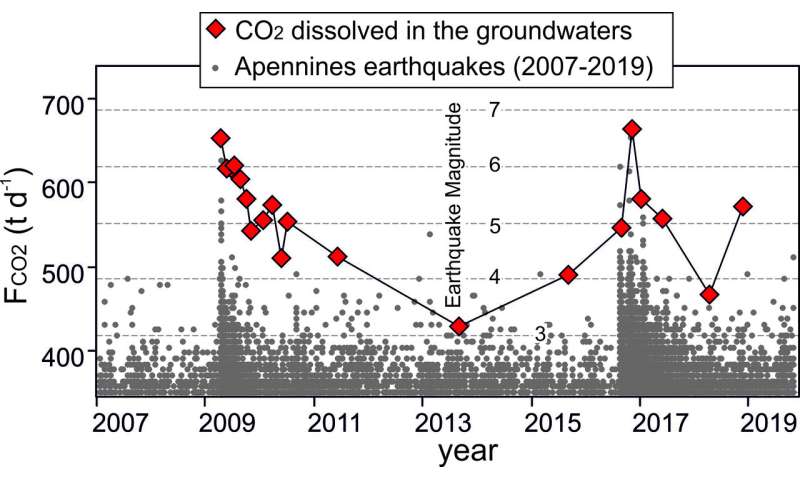
 The amount of CO2 dissolved in groundwater is so large that, in some cases, strong free CO2 emissions are associated with the water discharges. The emission in the picture is located at San Vittorino plain (Rieti) about 30 km far from the epicenter of the April 2009 L’Aquila earthquake. Credit: Giovanni Chiodini - INGV (first author)
The amount of CO2 dissolved in groundwater is so large that, in some cases, strong free CO2 emissions are associated with the water discharges. The emission in the picture is located at San Vittorino plain (Rieti) about 30 km far from the epicenter of the April 2009 L’Aquila earthquake. Credit: Giovanni Chiodini - INGV (first author)