WAIT! WHAT? HAVE IS PRESENT TENSE THAT MEANS
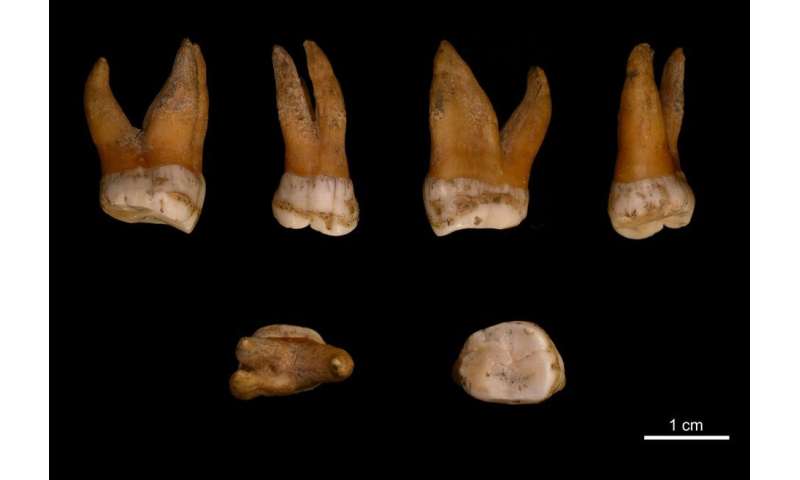
In 1997, the very first Neandertal DNA sequence—just a small part of the mitochondrial genome—was determined from an individual discovered in the Neander Valley, Germany, in 1856. Since then, improvements in molecular techniques have enabled scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology to determine high quality sequences of the autosomal genomes of several Neandertals, and led to the discovery of an entirely new group of extinct humans, the Denisovans, who were relatives of the Neandertals in Asia.
However, because all specimens well-preserved enough to yield sufficient amounts of DNA have been from female individuals, comprehensive studies of the Y chromosomes of Neandertals and Denisovans have not yet been possible. Unlike the rest of the autosomal genome, which represents a rich tapestry of thousands of genealogies of any individual's ancestors, Y chromosomes have a peculiar mode of inheritance—they are passed exclusively from father to son. Y chromosomes, and also the maternally-inherited mitochondrial DNA, have been extremely valuable for studying human history.
New method to identify Y chromosome molecules
In this study, the researchers identified three male Neandertals and two Denisovans that were potentially suitable for DNA analysis, and developed an approach to fish out human Y chromosome molecules from the large amounts of microbial DNA that typically contaminate ancient bones and teeth. This allowed them to reconstruct the Y chromosome sequences of these individuals, which would not have been possible using conventional approaches.
By comparing the archaic human Y chromosomes to each other and to the Y chromosomes of people living today, the team found that Neandertal and modern human Y chromosomes are more similar to one another than they are to Denisovan Y chromosomes. "This was quite a surprise to us. We know from studying their autosomal DNA that Neandertals and Denisovans were closely related and that humans living today are their more distant evolutionary cousins. Before we first looked at the data, we expected that their Y chromosomes would show a similar picture," says Martin Petr, the lead author of the study. The researchers also calculated that the most recent common ancestor of Neandertal and modern human Y chromosomes lived around 370,000 years ago, much more recently than previously thought.

It is by now well established that all people with non-African ancestry carry a small amount of Neandertal DNA as a result of interbreeding between Neandertals and modern humans approximately 50,000-70,000 years ago, quite shortly after modern humans migrated out of Africa and started spreading around the world. However, whether Neandertals might also carry some modern human DNA has been a matter of some debate.
These Y chromosome sequences now provide new evidence that Neandertals and early modern humans met and exchanged genes before the major out of Africa migration—potentially as early as 370,000 years ago and certainly more than 100,000 years ago. This implies that some population closely related to early modern humans must already have been in Eurasia at that time. Surprisingly, this interbreeding resulted in the replacement of the original Neandertal Y chromosomes with those of early modern humans, a pattern similar to what has been seen for Neandertal mitochondrial DNA in an earlier study.
Selection for Y chromosomes from early modern humans
At first, the complete replacement of both Y chromosomes and mtDNA of early Neandertals was puzzling, as such replacement events are quite unlikely to occur by chance alone. However, the researchers used computer simulations to show that the known small size of Neandertal populations may have led to an accumulation of deleterious mutations in their Y chromosomes which would reduce their evolutionary fitness. This is quite similar to situations where extremely small population sizes and inbreeding can sometimes increase the incidence of some diseases. "We speculate that given the important role of the Y chromosome in reproduction and fertility, the lower evolutionary fitness of Neandertal Y chromosomes might have caused natural selection to favor the Y chromosomes from early modern humans, eventually leading to their replacement," says Martin Petr.
Janet Kelso, the senior author of the study, is optimistic that this replacement hypothesis could be tested in the near future: "If we can retrieve Y chromosome sequences from Neandertals that lived prior to this hypothesized early introgression event, such as the 430,000 year old Neandertals from Sima de los Huesos in Spain, we predict that they would still have the original Neandertal Y chromosome and will therefore be more similar to Denisovans than to modern humans."
Explore further Neandertals had older mothers and younger fathers
More information: Martin Petr et al, The evolutionary history of Neanderthal and Denisovan Y chromosomes", Science; September 25th, 2020, science.sciencemag.org/cgi/doi … 1126/science.abb6460

















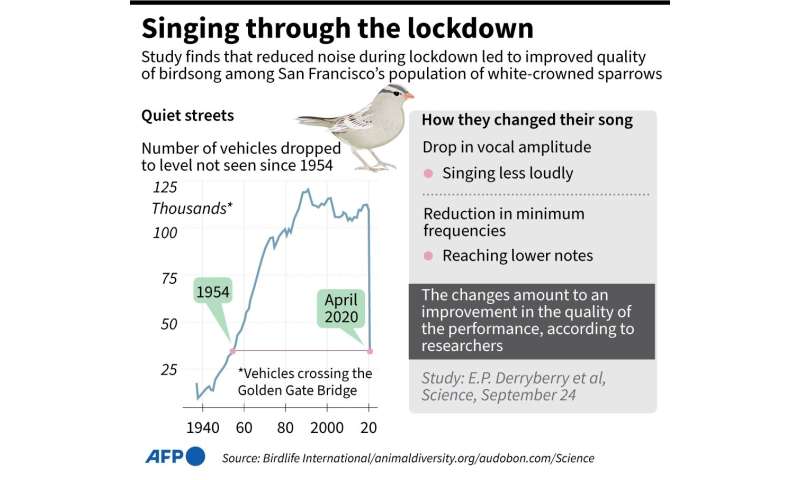
 Species factfile on the white-capped sparrows.
Species factfile on the white-capped sparrows.