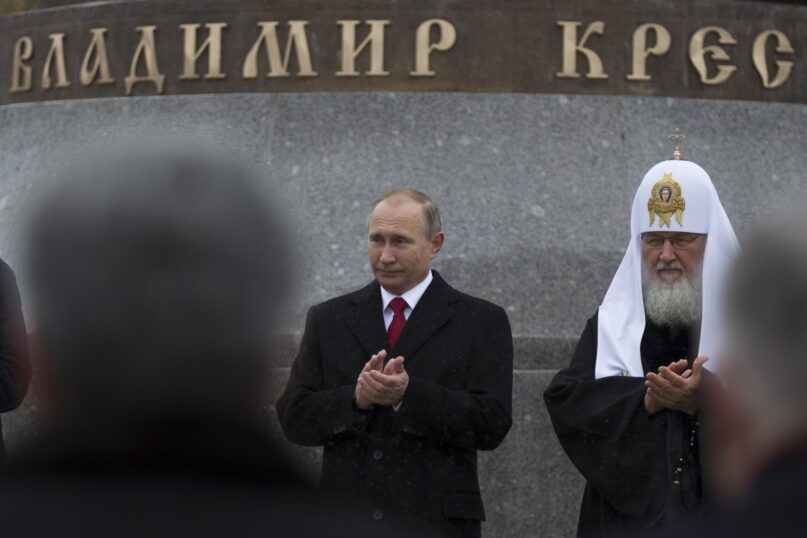
How Putin’s invasion became a holy war for Russia
THE CHURCH REPLACES THE PARTY AS THE STATE
Kirill's response to the war was the culmination of a decade-long effort to wrap Russia’s geopolitical ambitions in faith

This story is published in collaboration with Rolling Stone magazine.
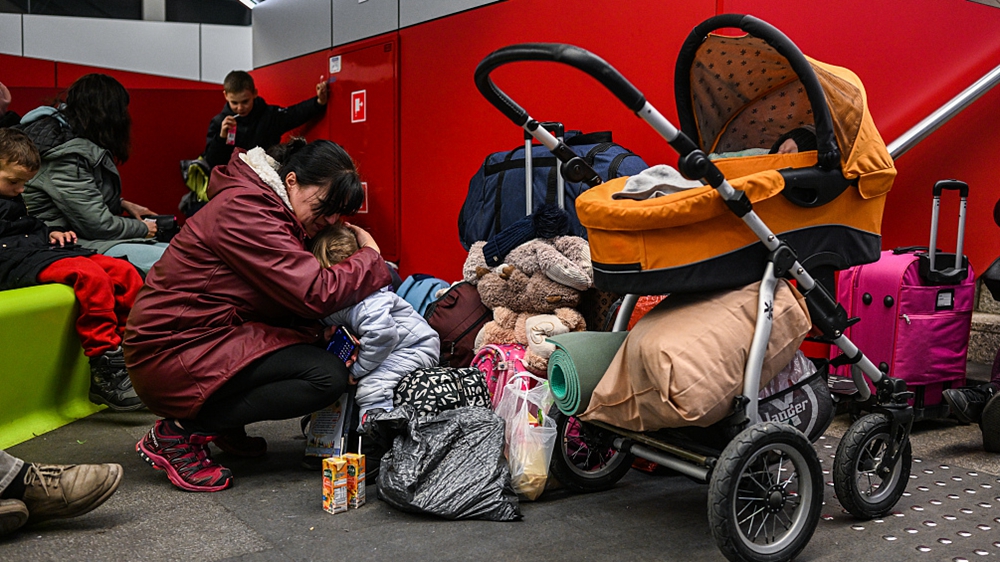
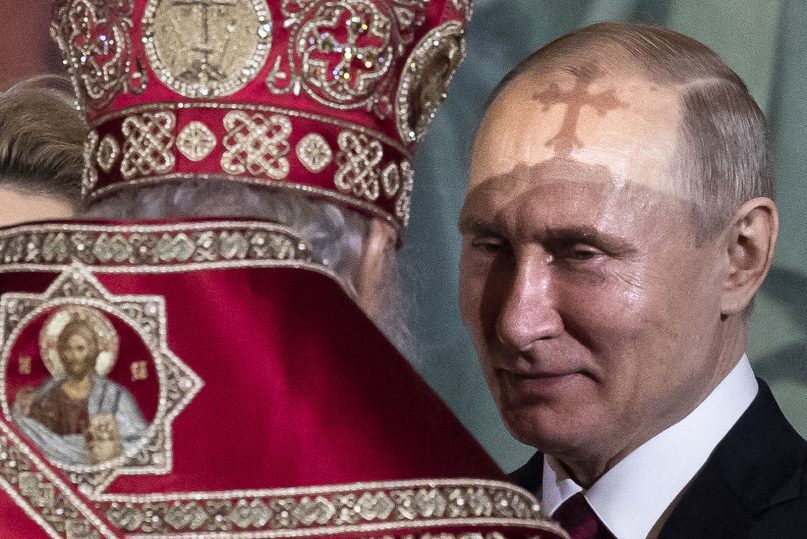
(RNS) — Two days before he launched a bloody invasion of Ukraine, Russian President Vladimir Putin sat alone in front of a camera and delivered a rambling, hour-long address. It outlined the ideological justification for what would ultimately become his “special military action” in Ukraine — an invasion that, as far as Putin was concerned, had more than a little to do with religion.
“Ukraine is an inalienable part of our own history, culture and spiritual space,” he said.
Two days later, Patriarch Kirill of Moscow, head of the Russian Orthodox Church, spoke to military leaders and published a statement in honor of Defender of the Fatherland Day. The cleric congratulated Putin for his “high and responsible service to the people of Russia,” declared the Russian Orthodox Church has “always striven to make a significant contribution to the patriotic education of compatriots,” and lauded military service as “an active manifestation of evangelical love for neighbors.”
Within hours, bombs began to rain down on Ukraine.
This religious ramp-up to war was the culmination of a decade-long effort to wrap Russia’s geopolitical ambitions in faith — specifically, the flowing vestments of the Russian Orthodox Church. Fusing religion, nationalism, a defense of conservative values that likens same-sex marriage to Nazism and a version of history that seeks to define Ukraine and other nearby nations as mere subsets of a greater “Russkiy mir” (Russian world), the partnership of Putin and Kirill laid the ideological and theological groundwork for the current invasion.
RELATED: With war in Ukraine, Pope Francis’ yearslong outreach to Kirill appears to be in ruins
But as explosions continue to rock Ukraine, some in the church are beginning to resist the religious appeals of Putin and Kirill, pushing back on efforts to recast naked Russian aggression as something that sounds a whole lot like a holy war.
The partnership of Putin, 69, and Kirill, 75, began around 2012, when the politician was reelected for a third term. It was then that Putin began embracing the Russian Orthodox Church — not necessarily as a point of personal conversion so much as a mechanism for political gain, something foreign policy experts often call “soft power.”
The relationship between the president and the prelate escalated rapidly. Kirill, allegedly a former KGB staffer like Putin, hailed the Russian Federation president’s leadership as a “miracle of God.” Meanwhile, Putin worked to frame Russia as a defender of conservative Christian values, which usually meant opposing abortion, feminism and LGBTQ rights. The pitch proved popular among a broad swath of conservative Christian leaders, including prominent voices within the American religious right: In February 2014, evangelist Franklin Graham offered cautious praise for Putin in an editorial for Decision Magazine, celebrating the Russian president’s decision to back a law barring dissemination of “propaganda of nontraditional sexual relations” — a statute which, activists argued, effectively banned children from accessing media that presents LGBTQ identities and relationships in a positive or normalizing light. Graham would travel to Russia the following year, where he met with both Kirill and Putin, and told local media that “millions of Americans would like (Putin) to come and run for president of the United States.”
By 2017, Politico was already describing Russia as “the leader of the global Christian Right.”
The impact of this religious diplomacy was even greater in eastern European nations that once belonged to the Soviet Union, where the Russian Orthodox Church and its allies still enjoy outsized influence. When Moldova sought stronger ties with Europe, Orthodox clerics operating underneath the Moscow patriarchate campaigned against it, with one bishop telling the New York Times in 2016, “For me, Russia is the guardian of Christian values.” Things were similar in Montenegro, where the Serbian Orthodox Church has a close relationship with the Russian Patriarchate; priests there advocated against the nation’s plans to join NATO, and last year Russian Orthodox leaders lambasted Montenegro’s leaders for supporting “eurointegration.”
Kirill has long perpetuated a version of history that insists many countries that made up the former Soviet Union are one people with a common religious origin: namely, the 10th century baptism of Prince Vladimir I of Kiev, known as St. Vladimir. It’s often paired with a geo-political (and geo-religious) vision hundreds of Orthodox theologians and scholars recently decried as a heresy: a “transnational Russian sphere or civilization, called Holy Russia or Holy Rus’, which includes Russia, Ukraine and Belarus (and sometimes Moldova and Kazakhstan), as well as ethnic Russians and Russian-speaking people throughout the world.”
It’s a Russian world with Moscow as its political center, Kyiv as the spiritual heart, and Kirill as its religious leader.
“May God grant that the Moscow Patriarchate, which unites us not on the political level, not on the economic, but the spiritual level, might be preserved to take pastoral care of all the ethnoses united in the great historical Rus,’” Kirill said in 2018.
But Russia’s religious and political arguments hit a wall in Ukraine, where protests — aided, in some instances, by Orthodox clerics — thrust off a pro-Russian government in 2013 and 2014, triggering Putin’s annexation of the Crimean Peninsula. Frustration with Russia boiled over into the religious realm, exacerbating an existing divide between the Russian Orthodox Church and the Orthodox Church based Constantinople: In 2018, many of Ukraine’s Orthodox Christians declared independence from the Moscow Patriarchate. Kirill refused to acknowledge the new body, but the Orthodox Church in Constantinople, led by Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew, recognized it. So dangerous was this schism to Russia’s interests that Kremlin-linked hackers responded by reportedly infiltrating the email accounts of Bartholomew’s aides.
And then came 2022, where soft power morphed into support for outright war in Ukraine. Shortly after the invasion began, Kirill issued a statement making a vague call for peace and asking all parties to limit civilian casualties. But Archbishop Daniel, head of Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the USA, which is loyal to Kyiv, decried the statement as the words of a “religious politician” and rejected Kirill’s appeal to a “common centuries-old history” rooted in St. Vladimir’s baptism.
“To say that we share the same ethnic background and what have you — I think it’s a mistake,” Daniel said. “It’s an incorrect statement. And I wish the religious leaders would correct that terminology (when Kirill is) utilizing it.”
Kirill’s rhetoric has only escalated in the days since. He referred to Russia’s opponents in Ukraine as “evil forces,” and delivered a sermon on March 6 in which he suggested the invasion was part of a larger “metaphysical” struggle against immoral western (read: liberal) values.
“Today there is a test for the loyalty to this new world order, a kind of pass to that ‘happy’ world, the world of excess consumption, the world of false ‘freedom,’” Kirill said. “Do you know what this test is? The test is very simple and at the same time terrible — it is the Gay Pride parade.”
It’s a distillation of an argument Kirill has pushed for years, contrasting western values with those of the purported Russian world. For Kirill, this is often rooted in anti-LGBTQ sentiment: he has suggested acceptance of same-sex marraige is a “dangerous sign of the apocalypse,” and once blamed the rise of ISIS on efforts to escape “godless” western societies that embrace gay pride parades.
As for his take on the ongoing conflict, earlier this week Kirill reportedly presented an image of the Virgin Mary to Russian National Guard leader Viktor Zolotov.
“Let this image inspire young soldiers who take the oath, who embark on the path of defending the Fatherland,” Kirill said.
But after years of wielding faith as a tool for accruing power, Kirill’s support for the war — tacit or otherwise — may end up costing him influence this go round. To be sure, some of the pushback has come from expected corners: Kirill’s rhetoric triggered an immediate response from Orthodox Christians whose leadership is based in Kyiv, with one cleric dismissing Kirill as “discredited” and likening Putin to the antichrist.
Yet calls for change are also coming from inside the manse. Metropolitan Onuphry of Kiev, who oversees the Russian Orthodox faithful in Ukraine, immediately decried the invasion as “a disaster” and a “repetition of the sin of Cain, who killed his own brother out of envy.” Many of his priests in the country have since stopped commemorating Kirill during worship, and some even asked Onuphry to entertain breaking away from the Russian Orthodox Church — much to the chagrin of the patriarchate.
Outside of Ukraine, more than 280 Russian Orthodox priests — most of whom operate within Russia — recently signed a petition condemning the “fratricidal” invasion and emphasizing Ukraine’s right to self-determination. One of the signers was later arrested in Russia after he preached a sermon criticizing the war. Authorities reportedly charged him with “discrediting the use of the Armed Forces.”
Meanwhile, the Archbishop of Russian Orthodox churches in Western Europe has publicly implored Kirill to raise his voice with Russian authorities against the “monstrous and senseless war.” He also rejected the characterization of the conflict as a “metaphysical” battle.
“With all the respect that is due to you, and from which I do not depart, but also with infinite pain, I must bring to your attention that I cannot subscribe to such a reading of the Gospel,” read the archbishop’s letter.
And at least one Russian Orthodox Church in Amsterdam has made moves to leave the church because of Kirill’s stance on Ukraine, hoping to affiliate with Ecumenical Patriarchate Bartholomew. This despite an intimidating visit from a Russian archbishop: The cleric, who arrived in a car from the Russian embassy, told priests that the Moscow Patriarchate and the Russian Foreign Ministry were keeping an eye on their church.
“We cannot go back on our decision to distance ourselves from Patriarch Kirill,” read a statement from the church’s priests. “Our consciences will not allow that.”
RELATED: Russian Orthodox parishes in Europe pressured from both sides as war rages in Ukraine
It remains to be seen whether these and other efforts will push Kirill to deviate from years of operating in lockstep with Putin. The Russian president’s drive to continue the war remains strong, as does his embrace of religious rhetoric: at a rally on Friday, Putin praised Russia’s troops in a way that echoed Kirill and paraphrased the Bible, saying, “There is no greater love than giving up one’s soul for one’s friends.”
But religious pressure on Kirill doesn’t appear to be letting up either. When Pope Francis held a meeting with Kirill this week to discuss the conflict, he made a point to warn against trying to justify armed invasion, expansion or empire with a Christian cross — something the Catholic Church knows something about.
“Once upon a time there was also talk in our churches of holy war or just war,” Francis told Kirill, according to the Vatican press office. “Today we cannot speak like this.”
Russia's Assault on Ukraine Has a Crusader Element
A religious historian breaks down the Orthodox Christian aspect to Putin's calculations.
By Charles P. Pierce
ESQUIRE

AFP CONTRIBUTORGETTY IMAGES
In her Substack shebeen, religious historian Diana Butler Bass takes a deep dive into how Christian ethno-nationalism has joined hands across the globe with reactionary Catholicism and, most importantly, with hyper-conservative Russian Orthodoxy to add a little old-time religious filigree to Vladimir Putin’s current depredations.
The dream gripping some quarters of the West is for a coalition to unify religious conservatives into a kind of supra-national neo-Christendom. The theory is to create a partnership between American evangelicals, traditionalist Catholics in western countries, and Orthodox peoples under the auspices of the Russian Orthodox Church in a common front against three enemies — decadent secularism, a rising China, and Islam — for a glorious rebirth of moral purity and Christian culture.
In the United States, Trumpist-religion is most often framed as “Christian nationalism.” It is, indeed, that. But it is also more — it is the American partner of this larger quest for Christian internationalism. No one has articulated this more clearly than Steve Bannon, who, despite his legal troubles, remains a significant force as a kind of philosophical apostle in right-wing Christian circles for a neo-Christendom.
The reaction in some quarters to Putin’s criminal war-making illustrates Butler Bass’s point. Rod Dreher, a “respected voice” among religious conservatives, who not long ago was luxuriating in the embrace of Hungarian strongman Victor Orban, would like you to know that this is a global conflict of…sexy time. From the American Conservative:
I know it is unpleasant for some of you to consider the decadence in the US and in the West in general in this context (e.g., “Bombs are falling in Ukraine, and you’re obsessing over trannies?!?”), but you should think twice about this. If we are now facing a renewal of the long struggle with Russia, and probably even a struggle against China too, allied with Putin’s Russia, then the leaders of Western countries had better think about how they are going to meet the demands of this struggle. They have no hope of doing so with a country in which they have abused and alienated a huge number of people for the crime of being white, heterosexual, culturally conservative, or clinging bitterly to their bigoted churches. We saw just the other day that Justin Trudeau actually seized the bank accounts of people supporting the trucker protests, under the guise of fighting domestic terrorism. I have absolutely no doubt that Washington will try the same. The woke left, having marched through the institutions, are weaponizing them against parents, children, families, church people, conservatives, and other deplorables.
(h/t to Roy Edroso for calling attention to this doozy of a take.)
Butler Bass goes on to an account of the historic role that Ukraine played in the formation both of the Russian state and the effect that the split between Ukrainian and Russian Orthodox churches have played in that history. And this is not ancient history, either.
When the Soviet Union collapsed, Ukraine had several different Orthodox churches, only one of which was in close relationship to Moscow. In 2018, two of those Ukrainian churches and some of the Moscow-leaning Orthodox parishes joined in a union and created a newly unified Orthodox Church of Ukraine, a fully independent national ecclesial body under no control from Moscow, with its head in the ancient seat of Orthodoxy in Kyiv.
Putin and the Moscow Russian Orthodox church authorities protested. They’ve been claiming the 1,000 years of Kyiv Christianity as its own — basically appropriating Ukraine’s church history — to the point of erecting a gigantic (and controversial) statue of St. Vladimir outside of the Kremlin.
Putin wants the weight of tradition on his side, and St. Vladimir validates both his religious and political aspirations. There should be no doubt that Putin sees himself as a kind of Vladimir the Great II, a candidate for sainthood who is restoring the soul of Holy Mother Russia. The Ukrainians, on the other hand, would like to remind the Russians that they were the birthplace of both Orthodoxy and political unity in Eastern Europe.
Now, Putin’s approximately as religious as a meat cleaver, but he can sense a center of power from centuries in the past. He has assiduously recruited the Russian Orthodox hierarchy into his dreams of a new Russian empire. (Remember it was performing in a Russian Orthodox cathedral that first got Pussy Riot in trouble with the folks in the Kremlin.) Butler Bass sees an old-school crusade hidden underneath all the tanks and cruise missiles.
The conflict in Ukraine is all about religion and what kind of Orthodoxy will shape Eastern Europe and other Orthodox communities around the world (especially in Africa). Religion. This is a crusade, recapturing the Holy Land of Russian Orthodoxy, and defeating the westernized (and decadent) heretics who do not bend the knee to Moscow’s spiritual authority.
If you don’t get that, you don’t get it. Who is going to control the geographical home, the “Jerusalem,” of the Russian church? Moscow? Or Constantinople? And, what does claiming that territory mean for Orthodoxy around the world? Will global Orthodoxy lean toward a more pluralistic and open future, or will it be part of the authoritarian neo-Christendom triumvirate?
Just what this nightmare needs: the influence of a 13th-century religious conflict.
Religious nationalism and the invasion of Ukraine
Under Putin, the Russian Orthodox Church has resumed its czarist role as an arm of state policy.

(RNS) — Is Russia’s invasion of Ukraine a religious crusade?
“I think the president of Russian Federation is making it a religious war,” Archbishop Daniel of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church in the U.S. told an interviewer for Religion News Service last week. That view is shared by John Schindler, a retired U.S. intelligence officer and historian with expertise in Eastern Europe, who argues that it was the establishment of the Orthodox Church in Ukraine separate from the Moscow patriarchate in 2019 that caused Russian President Vladimir Putin to invade.
The argument goes basically like this. Putin has wrapped his ambition to restore the Russian empire in a revived Russian Orthodox Church, long stifled by Communist hostility to religion. He considers Ukraine to be Russian heartland, spiritually as well as territorially.
After the 2014 Maidan revolution, in which the pro-Moscow president of Ukraine was ousted by protesters, deprived him of secular authority over the country, the establishment of an independent Orthodox Christian Church in the country, approved by Ecumenical Patriarch Bartholomew I in Istanbul, was the last straw. Ergo, the invasion.
RELATED: Putin is after more than land — he wants the religious soul of Ukraine
This seems to me to overstate the case. The Biden administration’s badly managed withdrawal from Afghanistan, the rise of a pro-Russian right in Europe and North America, and the dislocations of COVID-19 all gave Putin other reasons to imagine that the time was right to force Ukraine back into the Russian orbit.
But there can be no doubt that, under Putin, the Russian Orthodox Church has resumed its czarist role as an arm of state policy. This political religion — call it Russian Orthodox nationalism — has served not only to advance Putin’s goal of suppressing liberal democratic dissent at home but also to win the admiration of the pro-Christian right in Europe and America.
Writing nearly a century ago in the wake of the bloodletting of World War I, the eminent Columbia historian Carlton Hayes attacked what he called “a new religious syncretism, by virtue of which very many persons continue nominally to adhere to the faith of their ancestors and even to practice its cult, whilst they adapt it to the exigencies of nationalist worship and discipline.”
The flaunting of Christian imagery and language by those who stormed the Capitol on Jan. 6 is a prime example of such syncretism.
More than half a century ago, in the throes of the Vietnam War, the eminent Berkeley sociologist Robert Bellah praised what he called “the American civil religion” as “not the worship of the American nation but an understanding of the American experience in the light of ultimate and universal reality.”
RELATED: ‘A religious politician’: Head of US Ukrainian Orthodox Church slams Moscow Patriarch Kirill, Putin
Hayes, a devout convert to Catholicism, acknowledged that “to condemn nationalism because it depends on religious emotion would seem to me as futile as to condemn vegetation because it thrives on sunlight.” Bellah, a devout convert to Episcopalianism, understood that “(w)ithout an awareness that our nation stands under higher judgment, the tradition of the civil religion would be dangerous indeed.”
The engagement of religious emotions, ideas and ceremonies in national identity comes down to cases. At its best, as in Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address, it can give a nation a deeper understanding of itself and help make it whole. At its worst, as in the Jan. 6 assault, it can undermine a nation’s very foundations.
In the Russian invasion of Ukraine, we see it at its crusading worst.
Saint Vladimir: Is there a religious angle to the invasion of Ukraine?
One of the theories going around with Russia's invasion of Ukraine is that Putin wants to revive the grandeur of the Great Russian Empire or the Soviet Union the least. Another theory taking roots is Putin's quest to re-establish the Russian Orthodox Church.

VLADYMYR I AND VLADYMYRII
Russia's President Vladimir Putin has shocked the world with his anticipated yet daredevil decision to invade a sovereign nation with a powerful military alliance acting as its ally. And it's routine to have theories abound when such shocks are unleashed on intelligentsia. One of the theories doing round with Russia's invasion of Ukraine is that Putin wants to revive the grandeur of the Great Russian Empire or the Soviet Union the least. Another theory taking roots is Putin's quest to re-establish the Russian Orthodox Church.
Experts including Christian priests are writing columns unearthing the 'root cause' and 'real' motivation of Putin's attempt to capture Ukraine, a country with about 4.5 crore people, by the force of tanks, fighter planes and missiles. These experts find a link between Vladimir Putin and his namesake Vladimir I.
THE CHRISTIAN CONNECT
Vladimir I lived a thousand years ago and founded the first Russian Empire and also the Russian Orthodox Church. Vladimir I was declared a Saint for turning a pagan nation of the Rus (Russia and Ukraine) into Christian. He ruled from Kyiv (formerly spelt as Kiev and also Kyev), the capital of Ukraine.
There is a little back story to Vladimir I’s migration from paganism to Christianity. Those the ripe days of the Byzantine Empire but its Emperor Basil II was threatened by an uprising of military generals, writes London-based Christian priest and columnist Gilles Fraser here.
To save his chair, Basil II approached Vladimir I, the pagan ruler, with an offer. If Vladimir I helped Basil II save his rule, the Byzantine emperor would give him one of his daughters in marriage. This offer had a caveat. Vladimir I was to convert to Christianity.
The unprecedented and unthinkable offer of a pagan marrying a Byzantine princess was too tempting for Vladimir I to refuse. The powerful ruler that he was, Vladimir I crushed that revolt in the Byzantine Empire. He returned capital Kyiv in triumph and a Byzantine princess.
ALSO READ | First satellite pics after Ukraine invasion show civilians hit by Russian airstrikes
Back in Kyiv, Vladimir I summoned the citizenry to banks of River Dnieper for a mass baptism in 988. This was the birth of Russian Orthodox Christianity, which gave way to emotive religious concepts of “Holy Russia Motherland” and “Third Roman Empire” after the fall of the Byzantine Empire in mid-15th century.
Russian Orthodox Christianity continued to be a key ingredient of the Russian Empire soup until the communists led by another Vladimir, famously known as Lenin unleashed the Bolshevik Revolution and government in Russia in 1917.
To catch all the LIVE updates on the invasion of Ukraine by Russia, click here.
Lenin’s Russia outlived its founder vehemently attempting to crush every tenets of Russian Orthodox Christianity. When communist Russia, or the Soviet Union, collapsed under its own weight in 1991, it set of a series of events in the country’s politics that led to ascension through democratic channels of yet another Vladimir, Putin.
Now, the Christianity-revival theorists are suggesting that Vladimir Putin has a grander ambition than just capturing Ukraine. He wants to become Saint Vladimir II.
PUTIN AND CHRISTIANITY
Putin was born in a family that served former Russian dictator Joseph Stalin. His father was an atheist and mother is said to have been a devout Christian. Fraser said Putin’s mother baptised him in secret.
Putin wears a cross. Some of his shirtless photographs, particularly those from his fishing trip to Siberia, had gone viral some years ago.
ALSO READ | 'Putin is Hitler': Hundreds of Russians protest in Moscow against Putin's war in Ukraine
He is said to be deeply connected to his mother’s belief and also his hometown, which was known as Leningrad when Putin was in 1952 after Soviet Union’s founder Lenin. With the collapse of the Soviet structure, the city was rechristened back to Saint Petersburg in 1991.
The name change was described as “abandoning the legacy of the Russian revolutionary leader” that communists fiercely opposed but the Orthodox Church supported.
The same Russian Orthodox Church is said to be guiding Putin in re-establishing the Christian belief.
PUTIN, THE HOLY EMPEROR
Religious historian Diana Butler Bass has described Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in these words: “the world is witnessing a new version of an old tale — the quest to recreate an imperial Christian state, a neo-medieval “Holy Roman Empire” — uniting political, economic, and spiritual power into an entity to control the earthly and heavenly destiny of European peoples.”
She believes that whatever Putin is doing in Ukraine is a “dream gripping some quarters of the West for a coalition to unify religious conservatives into a kind of supra-national neo-Christendom”. The target secularism, communist China and Islam, she theorises.
“The theory is to create a partnership between American evangelicals, traditionalist Catholics in western countries, and Orthodox peoples under the auspices of the Russian Orthodox Church in a common front against three enemies — decadent secularism, a rising China, and Islam — for a glorious rebirth of moral purity and Christian culture,” Diana Butler Bass has argued.
ALSO READ | Russia invades Ukraine: The challenge before India
Former US President Donald Trump’s Christian nationalism appeal is being linked to Putin’s Russian Orthodox Church fervor. It could well be more than just coincidence that Trump found a “genius” in Putin’s “wonderful” move in Ukraine.
“I know Putin well,” Trump claimed commenting on Russia-Ukraine crisis.
There is a chatter of that Putin is establishing Third (and final) Roman Empire, predicted in Christian prophetic books. The first two were the ancient Roman Empire and medieval Byzantine Empire of Christianity.
BUT WHY NOW?
Neo-Christendom theorists point to the election of Pope Francis in 2013. After becoming the religious head of the Church, Pope Francis said he chose his name after a 12th-13th century St Francis of Assisi for a purpose. St Francis symbolised “poverty and peace”, Pope Francis said.
Subsequently, Pope Francis talked about opening up the church to the poor, outcastes and marginalised. The believers of Orthodox Church have reportedly not taken this lightly. Hence, the likes of Donald Trump and Putin gained support from white supremacists and Christian nationalists, the theorists say.
London’s St Mary Church priest Fraser has quoted a speech of Putin from 2013: “We see many of the Euro-Atlantic countries are actually rejecting their roots, including the Christian values that constitute the basis of Western civilisation.”
“They are denying moral principles and all traditional identities: national, cultural, religious and even sexual. They are implementing policies that equate large families with same-sex partnerships, belief in God with the belief in Satan,” Putin was quoted as saying.
ALSO READ | Ukraine's tragedy turns into spectator sport as thousands watch 'Russia special invasion'
This meant that Putin as a ruler believing in Russian Orthodox Church had to act. In 2014, Putin ordered Russian forces to annex Crimea to right a historical wrong. Secular political observers linked the 2014-Russian invasion of Ukraine to anti-Russia protests leading to removal of pro-Russia president from power.
Putin is apparently continuing to bring Russian Orthodox Church back to its glory through his adventures in Ukraine. His seat of power, Moscow is the Third Rome while Kyiv is “the Jerusalem” of the Third and the last Roman Empire. The theory finishes at that hoping Putin’s would it right.
Russian Orthodox parishes in Europe pressured from both sides as war rages in Ukraine
A Russian Orthodox parish in Amsterdam reportedly became the first Western Orthodox church to break ties with Moscow over the Russian invasion of Ukraine.

PARIS (RNS) — The war in Ukraine has split Russian Orthodox parishes across Europe, forcing believers outside Russia to either stay loyal to the church leadership in Moscow despite its support for the invasion, leave the church in protest or seek a messy middle ground.
While public opinion in Europe has almost unanimously denounced the war Russian President Vladimir Putin has unleashed, the small communities of Russian Orthodox faithful to the Moscow Patriarchate are in a bind because its head, Patriarch Kirill, has come out solidly in its favor.
Many of these believers are Western-born descendants of earlier emigres who have few links to today’s Russia but a faith anchored in the Russian tradition. Some belong to other Orthodox churches but happen to frequent a Russian church.
Archbishop John of Dubna in Paris, the head of a diocese of Russian Orthodox in Western Europe, struck a typical note by declaring solidarity with Ukraine and calling the war “monstrous and senseless” in an open letter to Patriarch Kirill March 9. While denouncing Kirill’s support of the war and asking for his intervention, Dubna stopped short of taking action that might signal a formal break.
Others stopped commemorating the patriarch in their liturgies, which ranks as a serious protest in Orthodox churches, but otherwise kept their dissent discreet. Only more attentive parishioners would notice on Sunday that the patriarch was not mentioned in normal commemorative prayers.
RELATED: Among Russian Orthodox, glimmers of dissent against the invasion of Ukraine

The Parish of St. Nicholas of Myra in Amsterdam. Photo by Jim Forest/Flickr/Creative Commons
The Parish of Saint Nicholas of Myra in Amsterdam, where several hundred worshippers from about 20 nations attend weekly services in Dutch, Russian or English, has learned how complicated this choice can be. Probably the first Western Orthodox church to break ties with Moscow over the Russian invasion of Ukraine, St. Nicholas went from loyal criticism of Moscow’s decision to switching its allegiance to the rival Ecumenical Patriarchate in Istanbul.
“There are many traditions within Russian Orthodoxy,” Archimandrite Meletios Webber, head of the parish, told the congregation on Monday (March 14).
The London-born archimandrite — a monsignor in Roman Catholic terminology — spoke in a clipped English accent at his church near central Amsterdam. Another Orthodox priest translated his remarks into Russian.
“This tradition cannot be attached to any organization or any thought which promotes violence and warfare,” said Meletios, born an Anglican but converted during his studies at Oxford by the influential British Orthodox theologian, Bishop Kallistos Ware.
Horrified by the ferocious fighting in Ukraine, the four priests of St. Nicholas first signed a petition in early March asking Patriarch Kirill to urge Russian authorities to end the war. But Kirill, doubling down like his ally Putin, came out in favor of the war, prompting a petition from Orthodox priests in Russia against the violence. Even the head of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church loyal to Moscow, Patriarch Onufry, appealed to Putin for “an immediate end to the fratricidal war.”

Archbishop Elisey. Photo by James Hyndman/Wikipedia/Creative Commons
The priests in Amsterdam decided they could no longer commemorate Kirill at their divine liturgies and informed their superior, Archbishop Elisey of the Moscow Patriarchate in The Hague.
On March 6, Archbishop Elisey turned up unannounced just before their Sunday service. He took over the celebration and made sure a deacon from outside the parish commemorated Kirill.
“His visit was like a spiritual tank sent to our parish,” one parishioner complained afterwards to the Dutch daily Nederlands Dagblad.
The archbishop, who came in a car from the Russian embassy, warned the priests that both the Moscow Patriarchate and the Russian Foreign Ministry were closely following developments in the parish.
The priests saw Archbishop Elisey’s warning as a threat but loyally mentioned his name during the service. “Then we started making contact with other hierarchs,” Meletios said.
“We have not left the Moscow Patriarchate,” the priests wrote on the parish website last week in an initial report about the archbishop’s unexpected visit. They listed examples from the past when dropping a patriarch’s name from a liturgy was not considered a schism.
But by Tuesday, March 8, a “Z” — the symbol widely used in support of Moscow’s intervention in Ukraine — was daubed on the church’s gates. During the week, the parish received enough other threats that it decided to close down until further notice.
RELATED: Putin is after more than land — he wants the religious soul of Ukraine
It was “no longer possible to function within the Moscow Patriarchate and provide a spiritually safe environment for their believers,” they concluded in another report on Saturday.
“We cannot go back on our decision to distance ourselves from Patriarch Kirill. Our consciences will not allow that,” they said. “So we see ourselves forced to link with the Ecumenical Patriarchate.”

Russian Orthodox Patriarch Kirill in the Christ the Saviour Cathedral in Moscow, Russia, early Thursday, Jan. 7, 2021. (AP Photo/Alexander Zemlianichenko)
The priests have now asked Archbishop Elisey to officially dismiss them from his diocese and asked Metropolitan Athenagoras, the top cleric of the Ecumenical Patriarchate in the Benelux countries, to take them under his wing.
They took “this very difficult step with pain in our hearts,” they said. The parish council backed the decision, and a final parish vote on the issue will take place at the end of this month.
“We who live in the West and have lived in the West for the last 50 years have seen the Russian Church under very different circumstances from those under which it finds itself today,” Meletios said to explain the clergy’s decision. “Indeed, many of the best Russian parishes in Western Europe and the Americas have only been in the Russian Orthodox patriarchy for a very short period.”
“Our parish is and will continue to be open to all Orthodox Christians of good will. We are concerned with the kingdom of Heaven and not with any political movement of any kind of kingdom here on Earth,” he added.
“We see our own pain very clearly, but it is nothing compared with the pain of those who are being bombed out of existence in a country far away.”
Tom Heneghan is the former religion editor for Reuters. He lives in Paris.
Lara Marlowe: Ukraine war creates dramatic schism in Orthodox church
Tue, Mar 15, 2022,
Lara Marlowe in Lviv

A woman passes near a Moscow Orthodox church that was partially destroyed after being bombed by Russian aircraft, in Malyn, Ukraine. Photograph: Miguel A Lopes/EPA
This news story starts more than a thousand years ago, in AD 988, when Byzantine missionaries from Constantinople baptised the feudal pagan prince Volodymyr – Vladimir to Russians – his family and the inhabitants of Kyiv. For seven centuries, Kyiv remained the centre of their Orthodox church.
Tsar Peter the Great moved the seat of the church to Moscow in the 17th century. Until February 24th, when Vladimir Putin invaded Ukraine, the Orthodox patriarchate in Moscow was followed by millions of Orthodox Ukrainians, and commanded respect from most of the world’s 15 autocephalous or independent Orthodox churches.
The Russian church comprises 100 million of the world’s 260 million Orthodox Christians. It suffered a setback in January 2019, when Bartholomew I, the ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople who acts as the first among equals of Orthodox patriarchates, recognised the merger of two Ukrainian churches as the independent Orthodox Church of Ukraine.
In Moscow, Patriarch Kirill broke ties with Bartholomew and branded the Ukrainian church as heretics. Kirill supports the invasion of Ukraine and says that gay pride parades in the West are part of the reason for the war.
Approximately three-quarters of Ukraine’s 41 million population call themselves Orthodox. They belong to the rival churches, or have remained neutral.
The church, which was until now led by Moscow, calls itself the Ukrainian Orthodox Church, to which its adversaries tag on the suffix: Moscow Patriarchate. For the sake of clarity, I will call them Moscow Orthodox. The other church calls itself the Orthodox Church of Ukraine, which I will simplify as Kyiv Orthodox.
In a dramatic break with Moscow, Metropolitan Onufriy, the leader of the Moscow Orthodox Church in Ukraine, accused Russia of acting as Cain did when he murdered his brother Abel in the Bible.

Moscow patriarch Kirill’s letter to the World Council of Churches (WCC) on March 10th could have been written by Putin: “It is my firm belief that [the war’s] initiators are not the peoples of Russia and Ukraine, who came from one Kievan baptismal font,” he wrote. “The origins of the confrontation lie in the relationships between the West and Russia.
“By the 1990s Russia had been promised that its security and dignity would be respected. However, as time went by, the forces overtly considering Russia to be their enemy came close to its borders. . . The most terrible thing is not the weapons, but the attempt to ‘re-educate’, to mentally remake Ukrainians and Russians living in Ukraine into enemies of Russia.”
Putinism
Constantin Sigov is a Kyiv Orthodox Christian, professor of philosophy, organiser of ecumenical conferences and publisher of theological works. Sigov reproaches Kirill for conflating temporal and spiritual power and says Kirill’s letter to the WCC is tantamount to “a declaration of holy war on the West. He is a true ideologue of Putinism. . . The Kremlin is killing its mother. This is Sophocles, a Greek tragedy.”
Up to 40,000 Ukrainian refugees expected in Ireland by end of April
In Russia, 300 members of a group called Russian Priests for Peace signed a petition against Russia’s “murderous acts” in Ukraine. An Orthodox parish in Amsterdam this week became the first to formally sever ties with the Moscow patriarchate.
“This is a monumental move that will touch the entire planet. Orthodox churches in Ireland, the UK, US and China will do the same thing,” Sigov predicts.
Sigov says the Russian Orthodox Church prevented the independent Ukrainian church from being admitted to the WCC. “All that has changed now. The Russian church will be excluded from [WCC headquarters in] Geneva. Ties will be broken with Moscow at every level. This historic trend is irreversible. It is like the Dnieper river; it flows in only one direction.”

Patriarch Kirill’s support for the war is also likely to drive undecided Ukrainian Orthodox into the arms of the autocephalous, independent church, Sigov says.
The hypocrisy of Putin’s claim to protect Orthodox Christians in Ukraine is highlighted by the fact that Russian forces have killed Moscow Orthodox and destroyed sites that are holy to them, including the Svyatogorsk Lavra monastery, one of the three most sacred sites in Ukraine for Orthodox believers. The 16th century monastery in eastern Ukraine was bombed on March 12th, wounding refugees who sought safety there.
Russian world view
“I want us to leave the Moscow church. It is over. This is a natural response to events,” says Fr Iov Olchansky, the Moscow Orthodox priest who heads the Monastery of the Redemption in Lviv.
Fr Iov (33) is sheltering 40 refugees from eastern Ukraine. “I do not subscribe to the Russkiy Mir, the Russian world view,” he continues, showing me the Greek-style chapel he built on the grounds of the crumbling monastery. “I was educated at Mount Athos and in Rome. I have many friends among Greek Catholic priests.”

Fr Iov’s repeated references to Greek and Roman Catholics mark an aspiration to ecumenism, and a renunciation of Russian domination. He expresses himself in impeccable Ukrainian, another marker of allegiance to his beleaguered country. Asked if the war is splitting the Orthodox church, he replies, “On the contrary, it will unite the Orthodox church and Russia will be isolated.”
The Moscow Orthodox have been perceived as a Russian fifth column since the 2014-2015 Donbas war, when some of their clergy sided with Russian separatists. They were accused – with reason, according to Sigov – of refusing to bless or baptise Ukrainian soldiers loyal to Kyiv, and of storing weapons in church buildings.
Suspicion runs particularly high in western Ukraine, the birthplace of Ukrainian nationalism. Soldiers in Pochaiv, 140km from Lviv, said someone shone a laser pointer from the nearby Moscow Orthodox monastery on a landing strip, to mark it as a Russian target. A Ukrainian army chaplain said the army found stocks of food, packed for military use, and three legally registered firearms when it searched the monastery.
No more gatherings
Near Fr Iov’s monastery in Lviv, I meet a Moscow Orthodox volunteer who calls himself Aleksei, distributing hot meals from the back of a van. “People are hungry, but today we were told that this is our last food distribution, and that we can have no more gatherings. The Baptists and Catholics are still allowed to gather.”
Aleksei speaks Russian rather than Ukrainian. He shows me a photograph of a banner on his smartphone. It shows a golden onion dome, a symbol of the Orthodox church, with the words, “Russian Orthodox Church F**k Off”. The obscenity was famously used by Ukrainian soldiers defending Zmiinyi (Snake) Island in the Black Sea when Russian forces ordered them to surrender on the first day of the war.

“The territorial defence forces would not let us take the banner down for a whole day,” Aleksei continues. “They searched our food van and our basement for weapons. They did not find any.”
Aleksei admits that some Moscow Orthodox may have been disloyal to Ukraine. “You can accuse specific people, but not the whole church,” he says. “There are radical people in any church.”
When Ukraine was a republic of the Soviet Union, the Soviets banned the Greek Catholic church on the grounds that it had collaborated with the Nazis. The Greek Catholics grew much stronger after independence in 1991 and have maintained tense relations with the Moscow Orthodox in western Ukraine.
The number of Orthodox churches has diminished dramatically, and many believers have emigrated to Russia or the EU, Aleksei says. He claims five Moscow Orthodox priests in country parishes were forced to shut their churches and bring their families to Lviv when the war started.
“We try to keep it quiet, because we do not want to spark a religious war like in Northern Ireland,” Aleksei continues. “We are trying to calm things down and say that everything is all right. We are caught between two fires. We do not like Putin. We do not support him. But the locals don’t like us or recognise us as Ukrainians.”
Scott Kenworthy, Miami University
Patriarch Kirill’s support for the invasion of a country where millions of people belong to his own church has led critics to conclude that Orthodox leadership has become little more than an arm of the state – and that this is the role it usually plays.
The reality is much more complicated. The relationship between Russian church and state has undergone profound historical transformations, not least in the past century – a focus of my work as a scholar of Eastern Orthodoxy. The church’s current support for the Kremlin is not inevitable or predestined, but a deliberate decision that needs to be understood.
Soviet shifts
For centuries, leaders in Byzantium and Russia prized the idea of church and state working harmoniously together in “symphony” – unlike their more competitive relationships in some Western countries.
In the early 1700s, however, Czar Peter the Great instituted reforms for greater control of the church – part of his attempts to make Russia more like Protestant Europe.
Churchmen grew to resent the state’s interference. They did not defend the monarchy in its final hour during the February Revolution of 1917, hoping it would lead to a “free church in a free state.”
The Bolsheviks who seized power, however, embraced a militant atheism that sought to secularize society completely. They regarded the church as a threat because of its ties to the old regime. Attacks on the church proceeded from legal measures like confiscating property to executing clergy suspected of supporting the counterrevolution.
Patriarch Tikhon, head of the Church during the Revolution, criticized Bolshevik assaults on the Church, but his successor, Metropolitan Bishop Sergy, made a declaration of loyalty to the Soviet Union in 1927. Persecution of religion only intensified, however, with repression reaching a peak during the Great Terror of 1937-1938, when tens of thousands of clergy and ordinary believers were simply executed or sent to the Gulag. By the end of the 1930s, the Russian Orthodox Church had nearly been destroyed.
The Nazi invasion brought a dramatic reversal. Josef Stalin needed popular support to defeat Germany and allowed churches to reopen. But his successor, Nikita Khrushchev, reinvigorated the anti-religious campaign at the end of the 1950s, and for the rest of the Soviet period, the church was tightly controlled and marginalized.
Kirill’s campaigns
The dissolution of the Soviet Union brought yet another complete reversal. The church was suddenly free, yet facing enormous challenges after decades of suppression. With the collapse of Soviet ideology, Russian society seemed set adrift. Church leaders sought to reclaim it, but faced stiff competition from new forces, especially Western consumer culture and American evangelical missionaries.
The first post-Soviet head of the church, Patriarch Aleksy II, maintained his distance from politicians. Initially, they were not very responsive to the church’s goals – including Vladimir Putin in his first two terms between 2000 and 2008. Yet in more recent years, the president has embraced Russian Orthodoxy as a cornerstone of post-Soviet identity, and relations between church and state leadership have changed significantly since Kirill became patriarch in 2009. He quickly succeeded in securing the return of church property from the state, religious instruction in public schools and military chaplains in the armed forces.
Kirill has also promoted an influential critique of Western liberalism, consumerism and individualism, contrasted with Russian “traditional values.” This idea argues that human rights are not universal, but a product of Western culture, especially when extended to LGBTQ people. The patriarch also helped develop the idea of the “Russian world”: a soft power ideology that promotes Russian civilization, ties to Russian-speakers around the world, and greater Russian influence on Ukraine and Belarus.
Although 70%-75% of Russians consider themselves Orthodox, only a small percentage are active in church life. Kirill has sought to “re-church” society by asserting that Russian Orthodoxy is central to Russian identity, patriotism and cohesion – and a strong Russian state. He has also created a highly centralized church bureaucracy that mirrors Putin’s and stifles dissenting voices.
Growing closer
A key turning point came in 2011-2012, starting with massive protests against electoral fraud and Putin’s decision to run for a third term.
Kirill initially called for the government to dialogue with protesters, but later offered unqualified support for Putin and referred to stability and prosperity during his first two terms as a “miracle of God,” in contrast to the tumultuous 1990s.
In 2012, Pussy Riot, a feminist punk group, staged a protest in a Moscow cathedral to criticize Kirill’s support for Putin – yet the episode actually pushed church and state closer together. Putin portrayed Pussy Riot and the opposition as aligned with decadent Western values, and himself as the defender of Russian morality, including Orthodoxy. A 2013 law banning dissemination of gay “propaganda” to minors, which was supported by the church, was part of this campaign to marginalize dissent.
Putin successfully won reelection, and Kirill’s ideology has been linked to Putin’s ever since.
Russia’s annexation of Crimea and the eruption of conflict in the Donbas in 2014 also had an enormous impact on the Russian Orthodox Church.
Ukraine’s Orthodox churches remained under the Moscow Patriarchate’s authority after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Indeed, about 30% of the Russian Orthodox Church’s parishes were actually in Ukraine.
The conflict in Crimea and eastern Ukraine, however, intensified Ukrainians’ calls for an independent Orthodox church. Patriarch Bartholomew, the spiritual head of Orthodox Christianity, granted that independence in 2019. Moscow not only refused to recognize the new church, but also severed relations with Constantinople, threatening a broader schism.
Orthodox Christians in Ukraine were divided over which church to follow, deepening Russia’s cultural anxieties about “losing” Ukraine to the West.
High-stakes gamble
Kirill’s close alliance with the Putin regime has had some clear payoffs. Orthodoxy has become one of the central pillars of Putin’s image of national identity. Moreover, the “culture wars” discourse of “traditional values” has attracted international supporters, including conservative evangelicals in the United States.
But Kirill does not represent the entirety of the Russian Orthodox Church any more than Putin represents the entirety of Russia. The patriarch’s positions have alienated some of his own flock, and his support for the invasion of Ukraine will likely split some of his support abroad. Christian leaders around the world are calling upon Kirill to pressure the government to stop the war.
The patriarch has alienated the Ukrainian flock that remained loyal to the Moscow Patriarchate. Leaders of that church have condemned Russia’s attack and appealed to Kirill to intervene with Putin.
A broader rift is clearly brewing: A number of Ukrainian Orthodox bishops have already stopped commemorating Kirill during their services. If Kirill supported Russia’s actions as a way to preserve the unity of the church, the opposite outcome seems likely.
The Conversation is an independent and nonprofit source of news, analysis and commentary from academic experts. The Conversation is wholly responsible for the content.
Franklin Graham, Russia and the ‘Moralist International’
The war in Ukraine has made strange bedfellows of the international religious right.
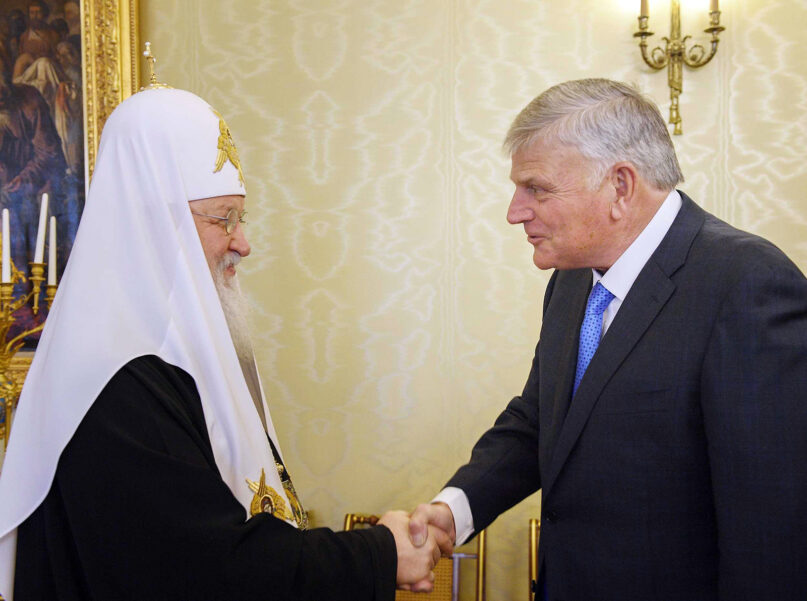

(RNS) — Four days before Russia invaded Ukraine, Franklin Graham tweeted, “Pray for President (Vladimir) Putin today. This may sound like a strange request, but we need to pray that God would work in his heart so that war could be avoided at all cost.”
I think we can mark that prayer down as unanswered. The Holy One’s response, assuming there was one, seems to have been more along the lines of what happened when Moses put the pinch on Pharoah to let the Hebrews go free. According to the Book of Exodus: “And the Lord hardened the heart of Pharaoh.”
Since Putin’s heart to date shows no sign of softening — last week he likened his opponents to a plague of gnats — Graham might assume the righteous prophet’s voice. As he did in 2015, for example, when he railed that then-President Barack Obama “has stood defiantly against God. And against his teaching. And the teachings of the Scriptures.
I’ll go out on a limb and say that to invade a country without provocation and promiscuously kill its civilians is to stand against Graham’s God and Scriptures.
RELATED: Samaritan’s Purse, Israelis will treat wounded Ukrainians in Lviv field hospitals
To his credit, Graham has committed Samaritan’s Purse, the relief organization he heads, to providing relief to the victims of Russian war-making. But as for his issuing a prophetic denunciation of Russia, I’m not holding my breath. It would mean disavowing an alliance he has been involved in for years.
That alliance is the subject of “The Moralist International: Russia in the Global Culture Wars,” a book by University of Innsbrück sociologist Kristina Stoeckl and Russian scholar Dmitry Uzlaner, forthcoming this fall from Fordham University Press. Stoeckl and Uzlaner show in fascinating detail how the Russian Orthodox Church turned itself into a leading promoter of “traditional family values” inside Russia and on the world stage as part of a “Moralist International” led by the American religious right.
Central to the story is Kirill, the current patriarch of Moscow, who, after the fall of the Soviet Union, seized on family values as a means by which his church could restore its traditional place in Russian society and realize an age-old ambition to supplant Constantinople as the “Third Rome” — the headquarters of Eastern Orthodoxy, if not of world Christendom.
In 2000, then-Metropolitan Kirill wrote a widely read article explaining how Russian Orthodoxy could become a public religion capable of “defining the future face of human civilization.” That meant not only standing against the morally corrupt values of secular liberalism but breaking out of a narrow Orthodox shell that eschewed alliances with conservatives in other faith communities.
Although culture warfare is alien to the Eastern Orthodox tradition, Kirill succeeded in having the Russian church embrace it after becoming Moscow patriarch in 2009. Thus, under his leadership Russians began to play an important part in the World Congress of Families, an American organization designed to spread a Christian-right agenda internationally.
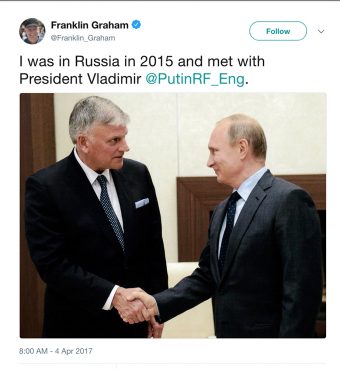
Franklin Graham tweets a photo of meeting with Russian President Vladimir Putin in April 2017.
It was after Putin was elected president of Russia for the third time in 2012 that he himself signed on to Kirill’s agenda, signing laws that established penalties for offending religious feelings and for displaying LGBT symbols. Putin’s goal of reestablishing the Russian empire dovetailed perfectly with Kirill’s messianic ambition for his church.
Along the way, Graham has been there to facilitate the cause, meeting with Putin in 2015 and with Kirill in 2019, tweeting after the latter encounter, “I’ve been in Moscow this week & had the privilege of meeting w/Patriarch Kirill of Moscow & All Russia. It was also a blessing to meet w/evangelical leaders & other officials while there. Pray for them & for more opportunities to share the truth, hope, & life found only in Jesus.”
RELATED: How Putin’s invasion became a holy war for Russia
It seems obvious that, however the war in Ukraine turns out, Putin will have turned himself into an international pariah. The same is likely true for Kirill, who has thus far served as the war’s foremost religious apologist.
At a conference hosted by Fordham’s Orthodox Christian Studies Center last week, Stoeckl said she expected that, because of the war, the Russians would be dropping out of the global family values movement — the Moralist International. “They were on the rise to become the leading moral voice,” she said.
As for Franklin Graham, who knows?













