Ultrasound Blasts 'Jumpstarted' The Brains of 2 People in Coma-Like State
DAVID NIELD
31 JANUARY 2021
Scientists have reported finding some success in using low intensity, focused ultrasound to 'jumpstart' parts of the brains of people in coma-like conditions, reawakening certain functions in patients who had previously been in a "minimally conscious state" (MCS).
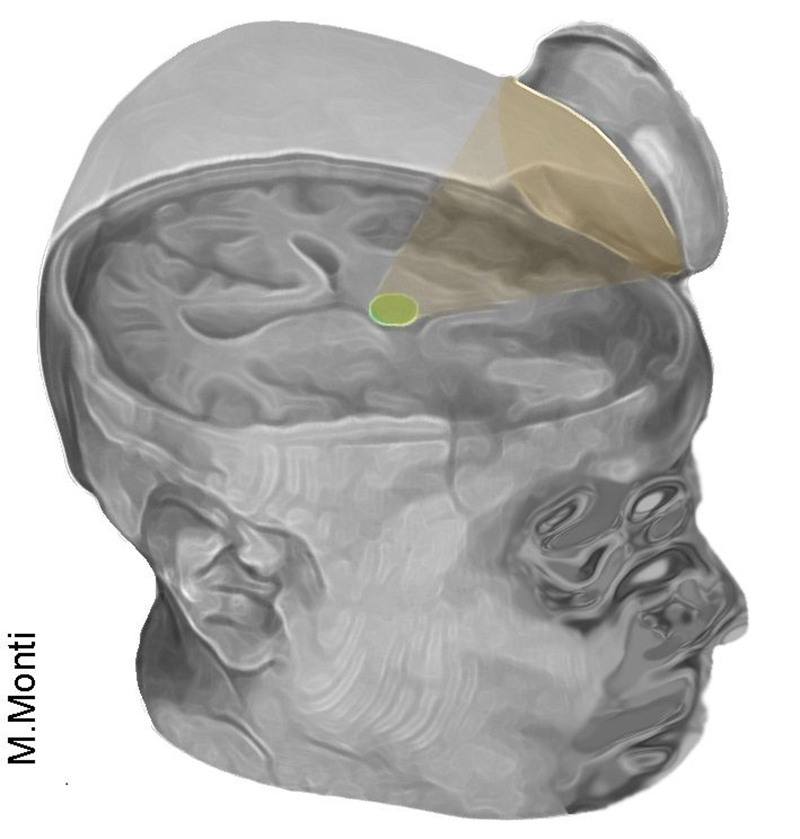
The method uses ultrasound stimulation to excite the neurons in the thalamus, a processing hub for the whole brain, and a region that's known to be weaker after a coma. Two 10-minute treatment sessions were given to three MCS patients, with a week between each session.
While one patient showed no response, researchers observed significant improvements in the other two patients. The research builds on similar findings from 2016, involving one patient who was recovering from surgery and a medically induced coma. In the new study, the coma-like states had lasted much longer.
A person in a minimally conscious state may show clear but subtle or inconsistent signs of consciousnesses. These signs, like blinking on command or wakefulness, are generally sustained enough that they aren't seen as reflexive behaviours, and they help to differentiate MCS from comas or vegetative states.
"I consider this new result much more significant because these chronic patients were much less likely to recover spontaneously than the acute patient we treated in 2016 – and any recovery typically occurs slowly over several months and more typically years, not over days and weeks, as we show," says neuroscientist Martin Monti, from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
"It's very unlikely that our findings are simply due to spontaneous recovery."
One of the patients to respond to the treatment was a 56-year-old man, who had been in a minimally conscious state for more than 14 months, unable to communicate at all. After treatment, he could not only look towards the photographs of relatives when their names were mentioned, he could also drop or grasp a ball on demand. When asked simple questions about his identity, he was able to shake his head 'yes' or 'no'.
The other patient to show signs of progress, a 50-year-old woman, had been in an even deeper MCS for more than two-and-a-half years. After the ultrasound sessions, she was able to understand speech and recognise basic objects, including a pencil and a comb.
Researchers say the technique is safe as it only uses a small amount of energy, and there were no changes to the blood pressure, heart rates, or blood oxygen levels of the patients.
"This is what we hoped for, but it is stunning to see it with your own eyes," says Monti. "Seeing two of our three patients who had been in a chronic condition improve very significantly within days of the treatment is an extremely promising result."
It's important to emphasise that the research is still in an early and experimental phase. While the 50-year-old woman showed increased signs of awareness months afterwards, the differences from the MCS starting point weren't that significant. And after a few months without treatment, the 56-year-old man had returned to something close to his original coma-like state.
Add in the one patient that didn't respond at all to the treatment, and the researchers remain cautious about how successful ultrasound can be, and how quickly it can be rolled out. Nevertheless, these results are very encouraging – there are definite signs that this kind of treatment could help some patients some of the time.
The treatment can be applied in a device about the size of a saucer, and the researchers are hoping that it can eventually be used in the home on patients who are in long-term minimally conscious or vegetative states.
"Importantly, these behaviours are diagnostic markers of emergence from a disorder of consciousness," says Monti. "For these patients, the smallest step can be very meaningful – for them and their families. To them it means the world."
The research has been published in Brain Stimulation.