The State of the American Middle Class
Who is in it and key trends from 1970 to 2023
The share of Americans who are in the middle class is smaller than it used to be. In 1971, 61% of Americans lived in middle-class households. By 2023, the share had fallen to 51%, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of government data.
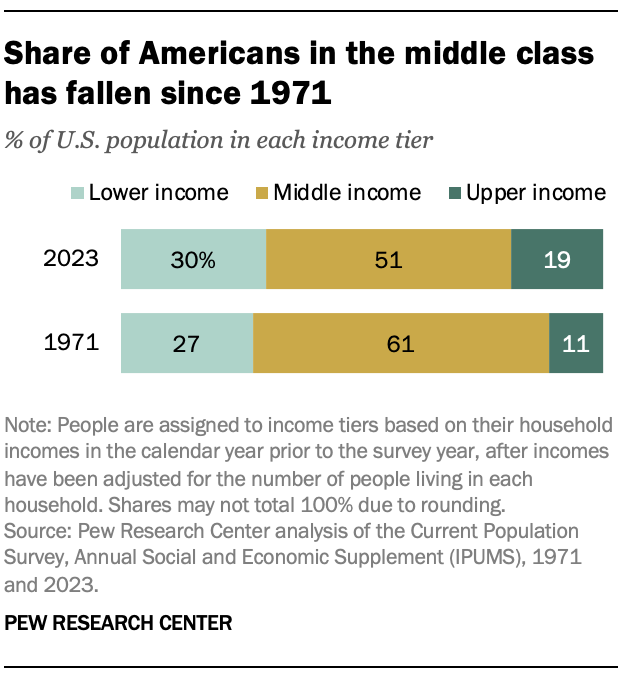
As a result, Americans are more apart than before financially. From 1971 to 2023, the share of Americans who live in lower-income households increased from 27% to 30%, and the share in upper-income households increased from 11% to 19%.
Notably, the increase in the share who are upper income was greater than the increase in the share who are lower income. In that sense, these changes are also a sign of economic progress overall.
But the middle class has fallen behind on two key counts. The growth in income for the middle class since 1970 has not kept pace with the growth in income for the upper-income tier. And the share of total U.S. household income held by the middle class has plunged.
Moreover, many groups still lag in their presence in the middle- and upper-income tiers. For instance, American Indians or Alaska Natives, Black and Hispanic Americans, and people who are not married are more likely than average to be in the lower-income tier. Several metro areas in the U.S. Southwest also have high shares of residents who are in the lower-income tier, after adjusting for differences in cost of living across areas.
Jump to:
Our report focuses on the current state of the American middle class. First, we examine changes in the financial well-being of the middle class and other income tiers since 1970. This is based on data from the Annual Social and Economic Supplements (ASEC) of the Current Population Survey (CPS), conducted from 1971 to 2023.
Then, we report on the attributes of people who were more or less likely to be middle class in 2022. Our focus is on their race and ethnicity, age, gender, marital and veteran status, place of birth, ancestry, education, occupation, industry, and metropolitan area of residence. These estimates are derived from American Community Survey (ACS) data and differ slightly from the CPS-based estimates. In part, that is because incomes can be adjusted for the local area cost of living only with the ACS data. (Refer to the methodology for details on these two data sources.)
This analysis and an accompanying report on the Asian American middle class are part of a series on the status of America’s racial and ethnic groups in the U.S. middle class and other income tiers. Forthcoming analyses will focus on White, Black, Hispanic, American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander and multiracial Americans, including subgroups within these populations. These reports are, in part, updates of previous work by the Center. But they offer much greater detail on the demographic attributes of the American middle class.
Following are some key facts about the state of the American middle class:
Households in all income tiers had much higher incomes in 2022 than in 1970, after adjusting for inflation. But the gains for middle- and lower-income households were less than the gains for upper-income households.
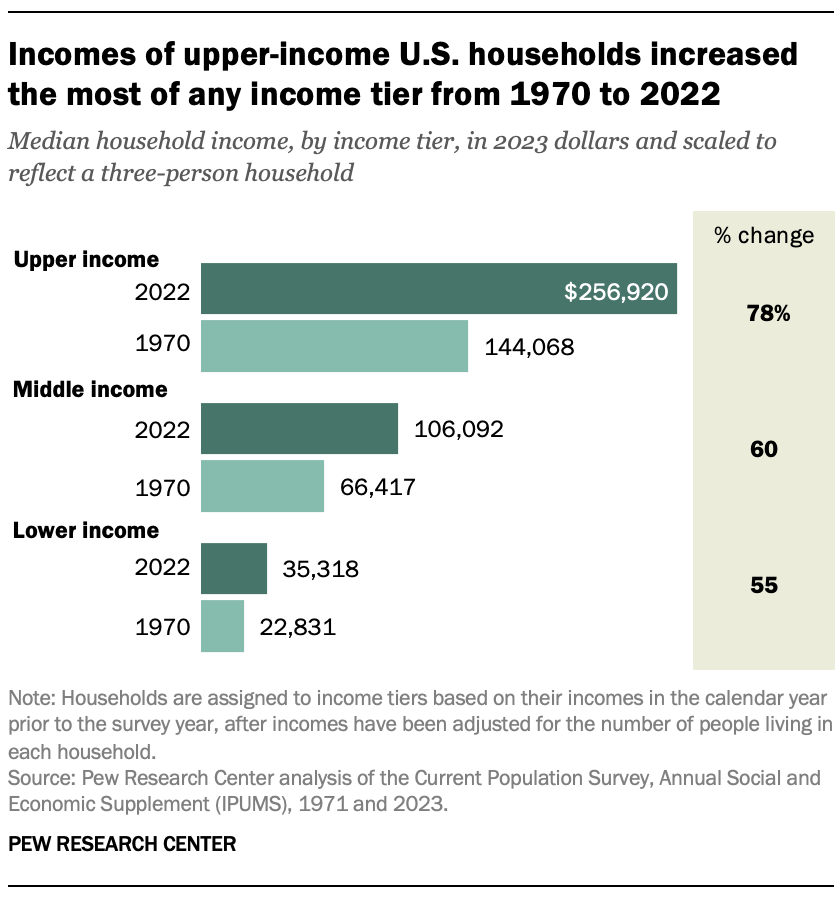
The median income of middle-class households increased from about $66,400 in 1970 to $106,100 in 2022, or 60%. Over this period, the median income of upper-income households increased 78%, from about $144,100 to $256,900. (Incomes are scaled to a three-person household and expressed in 2023 dollars.)
The median income of lower-income households grew more slowly than that of other households, increasing from about $22,800 in 1970 to $35,300 in 2022, or 55%.
Consequently, there is now a larger gap between the incomes of upper-income households and other households. In 2022, the median income of upper-income households was 7.3 times that of lower-income households, up from 6.3 in 1970. It was 2.4 times the median income of middle-income households in 2022, up from 2.2 in 1970.
The share of total U.S. household income held by the middle class has fallen almost without fail in each decade since 1970. In that year, middle-income households accounted for 62% of the aggregate income of all U.S. households, about the same as the share of people who lived in middle-class households.
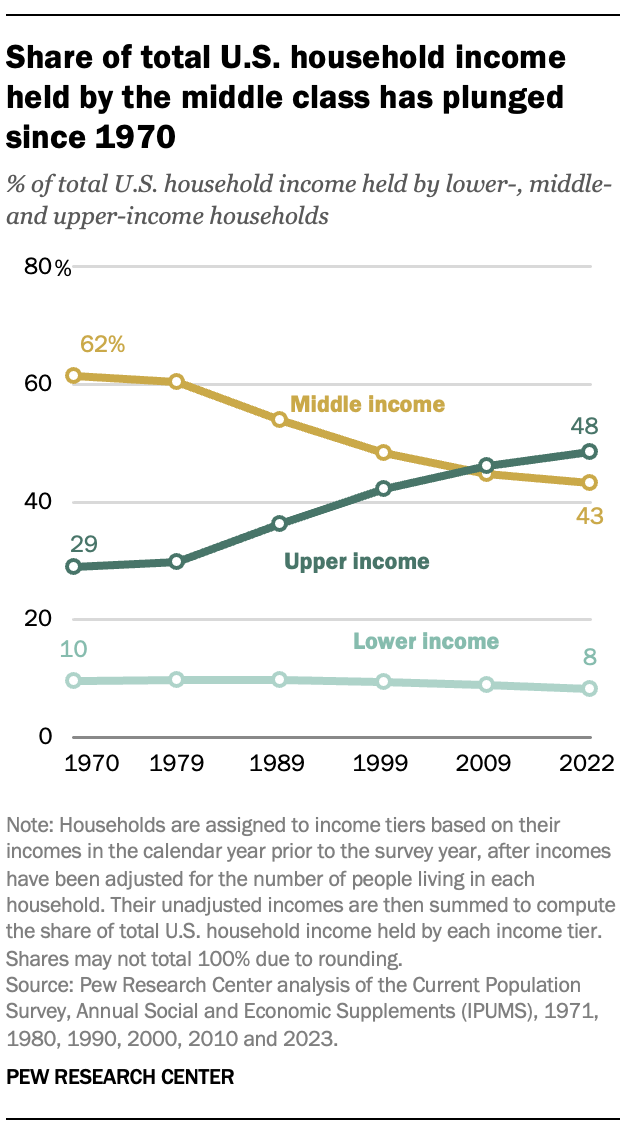
By 2022, the middle-class share in overall household income had fallen to 43%, less than the share of the population in middle-class households (51%). Not only do a smaller share of people live in the middle class today, the incomes of middle-class households have also not risen as quickly as the incomes of upper-income households.
Over the same period, the share of total U.S. household income held by upper-income households increased from 29% in 1970 to 48% in 2022. In part, this is because of the increase in the share of people who are in the upper-income tier.
The share of overall income held by lower-income households edged down from 10% in 1970 to 8% in 2022. This happened even though the share of people living in lower-income households increased over this period.
The share of people in the U.S. middle class varied from 46% to 55% across racial and ethnic groups in 2022. Black and Hispanic Americans, Native Hawaiians or Pacific Islanders, and American Indians or Alaska Natives were more likely than others to be in lower-income households.
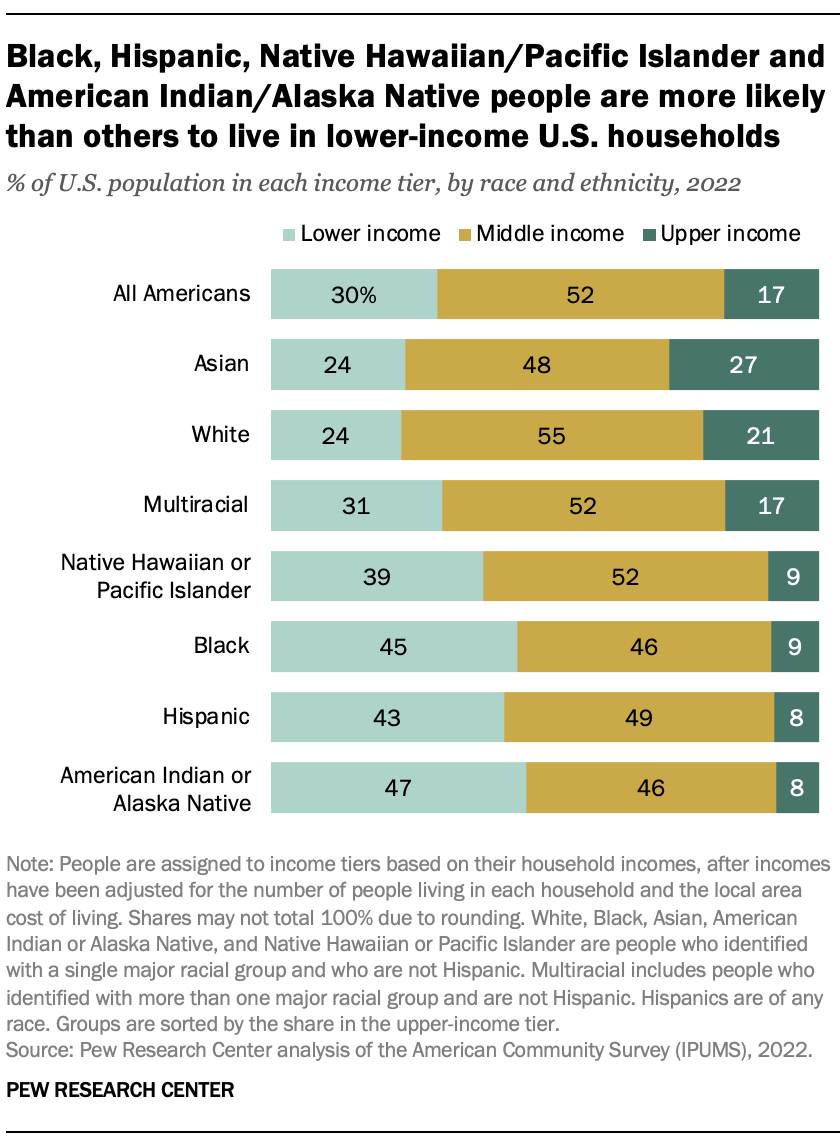
In 2022, 39% to 47% of Americans in these four groups lived in lower-income households. In contrast, only 24% of White and Asian Americans and 31% of multiracial Americans were in the lower-income tier.
At the other end of the economic spectrum, 27% of Asian and 21% of White Americans lived in upper-income households in 2022, compared with about 10% or less of Black and Hispanic Americans, Native Hawaiians or Pacific Islanders, and American Indians or Alaska Natives.
Not surprisingly, lower-income status is correlated with the likelihood of living in poverty. According to the Census Bureau, the poverty rate among Black (17.1%) and Hispanic (16.9%) Americans and American Indians or Alaska Natives (25%) was greater than the rate among White and Asian Americans (8.6% for each). (The Census Bureau did not report the poverty rate for Native Hawaiians or Pacific Islanders.)
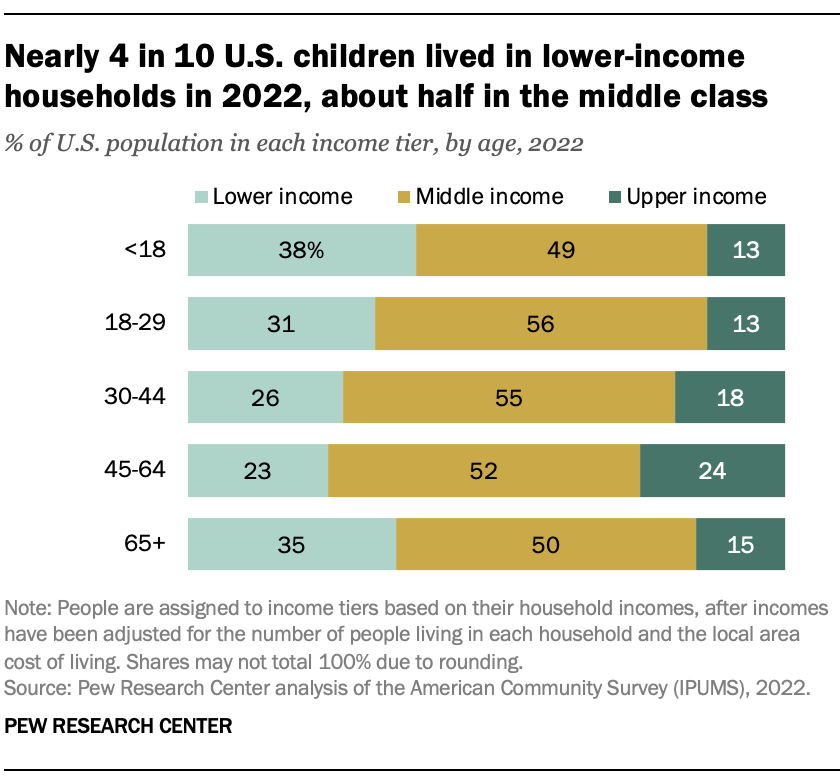
Children and adults 65 and older were more likely to live in lower-income households in 2022. Adults in the peak of their working years – ages 30 to 64 – were more likely to be upper income. In 2022, 38% of children (including teens) and 35% of adults 65 and older were lower income, compared with 26% of adults ages 30 to 44 and 23% of adults 45 to 64.
The share of people living in upper-income households ranged from 13% among children and young adults (up to age 29) to 24% among those 45 to 64. In each age group, about half or a little more were middle class in 2022.
Men were slightly more likely than women to live in middle-income households in 2022, 53% vs. 51%. Their share in upper-income households (18%) was also somewhat greater than the share of women (16%) in upper-income households.
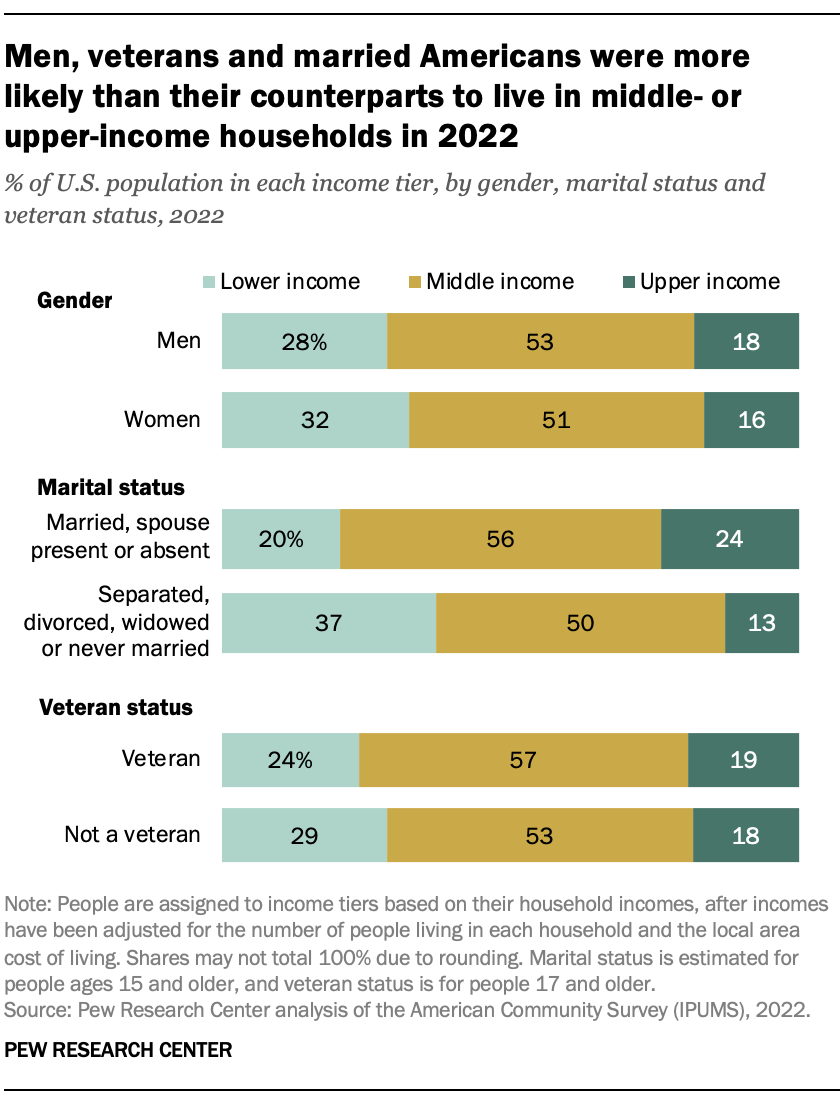
Marriage appears to boost the economic status of Americans. Among those who were married in 2022, eight-in-ten lived either in middle-income households (56%) or upper-income households (24%). In contrast, only about six-in-ten of those who were separated, divorced, widowed or never married were either middle class or upper income, while 37% lived in lower-income households.
Veterans were more likely than nonveterans to be middle income in 2022, 57% vs. 53%. Conversely, a higher share of nonveterans (29%) than veterans (24%) lived in lower-income households.
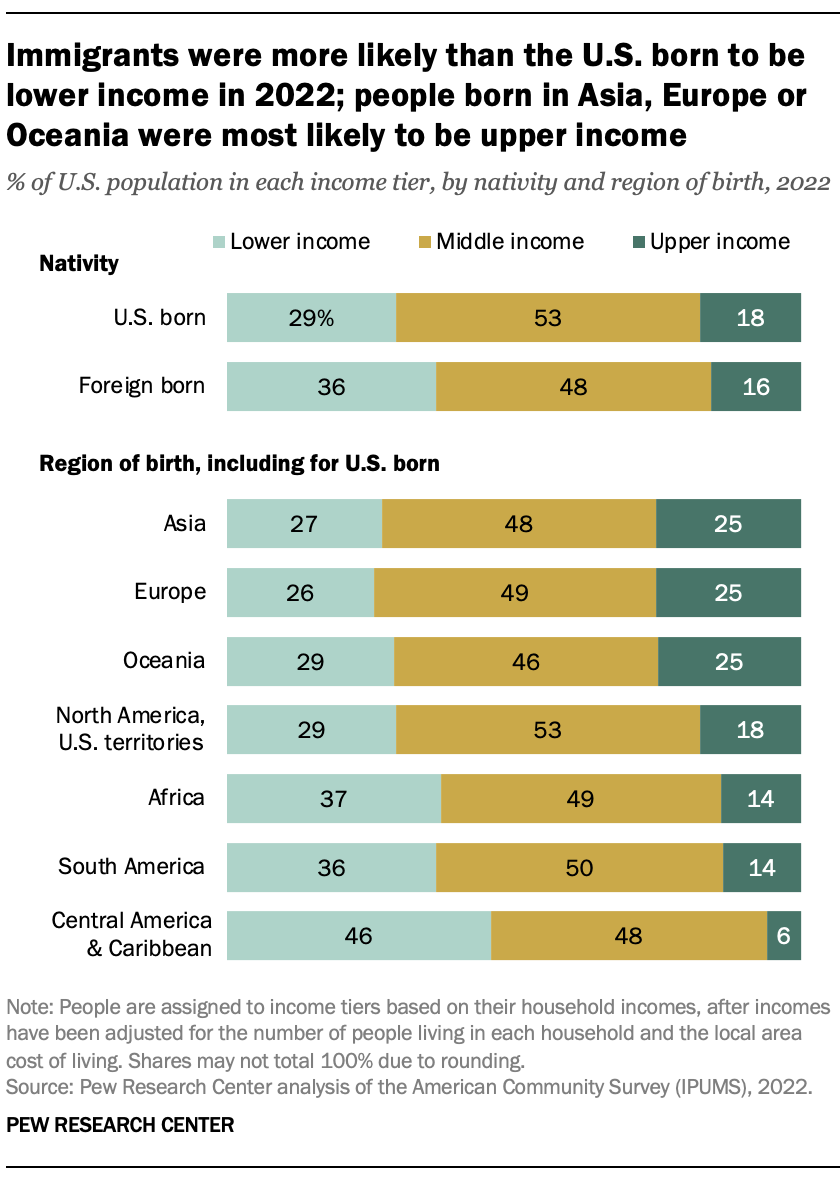
Immigrants – about 14% of the U.S. population in 2022 – were less likely than the U.S. born to be in the middle class and more likely to live in lower-income households. In 2022, more than a third of immigrants (36%) lived in lower-income households, compared with 29% of the U.S. born. Immigrants also trailed the U.S. born in the shares who were in the middle class, 48% vs. 53%.
There are large gaps in the economic status of American residents by their region of birth. Among people born in Asia, Europe or Oceania, 25% lived in upper-income households in 2022. People from these regions represented 7% of the U.S. population.
By comparison, only 14% of people born in Africa or South America and 6% of those born in Central America and the Caribbean were in the upper-income tier in 2022. Together they accounted for 8% of the U.S. population.
The likelihood of being in the middle class or the upper-income tier varies considerably with the ancestry of Americans. In 2022, Americans reporting South Asian ancestry were about as likely to be upper income (38%) as they were to be middle income (42%). Only 20% of Americans of South Asian origin lived in lower-income households. South Asians accounted for about 2% of the U.S. population of known origin groups in 2022.
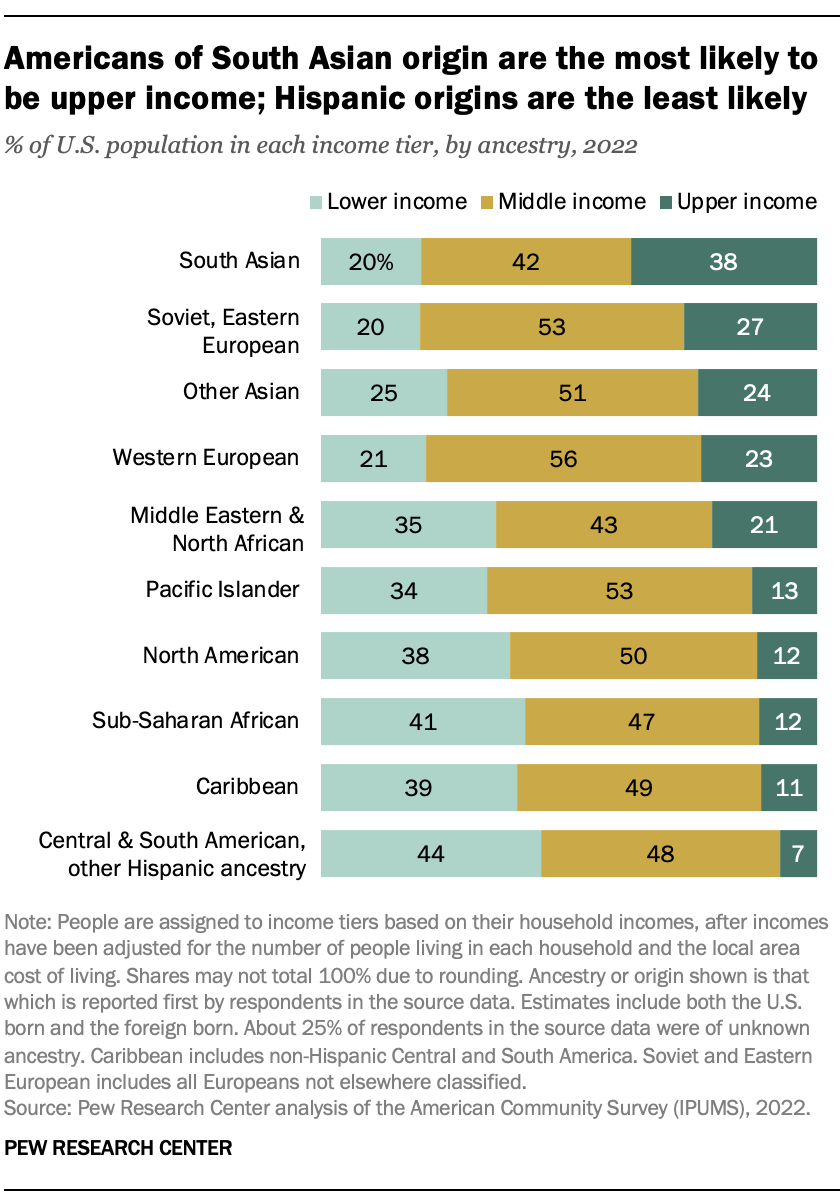
At least with respect to the share who were lower income, this was about matched by those with Soviet, Eastern European, other Asian or Western European origins. These groups represented the majority (54%) of the population of Americans whose ancestry was known in 2022.
On the other hand, only 7% of Americans with Central and South American or other Hispanic ancestry were in the upper-income tier, and 44% were lower income. The economic statuses of Americans with Caribbean, sub-Saharan African or North American ancestry were not very different from this.
Education matters for moving into the middle class and beyond, and so do jobs. Among Americans ages 25 and older in 2022, 52% of those with a bachelor’s degree or higher level of education lived in middle-class households and another 35% lived in upper-income households.
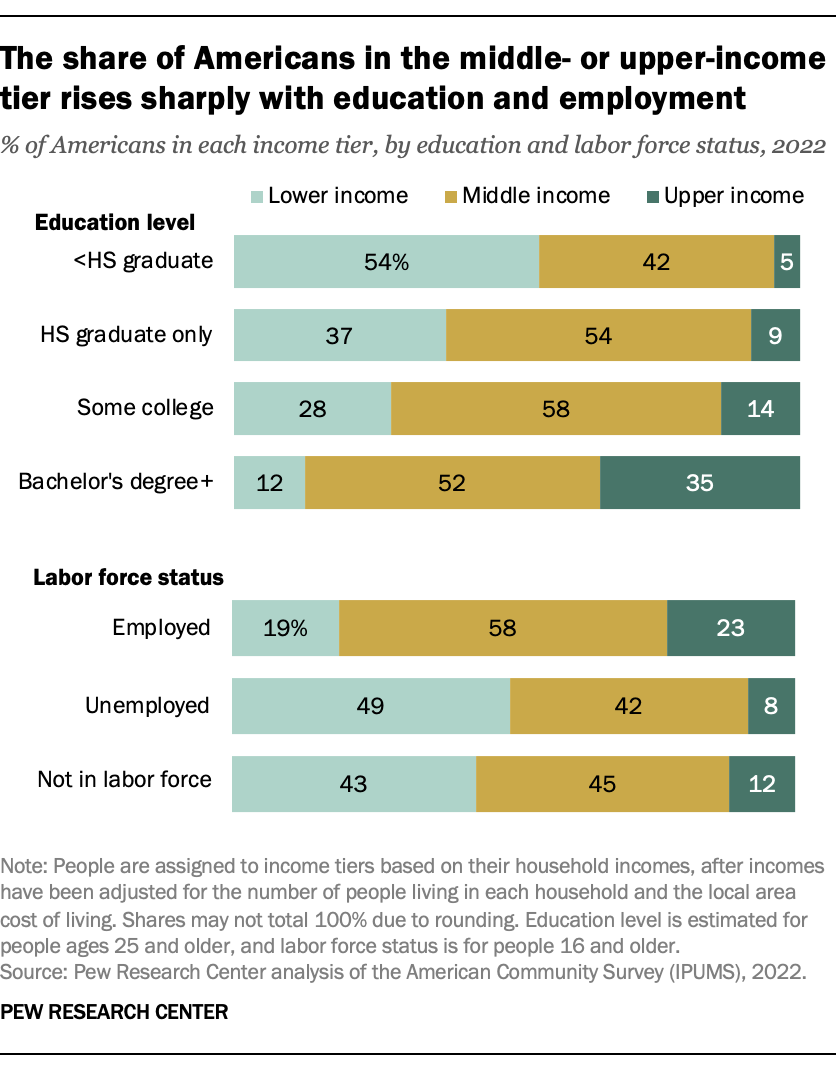
In sharp contrast, 42% of Americans who did not graduate from high school were in the middle class, and only 5% were in the upper-income tier. Further, only 12% of college graduates were lower income, compared with 54% of those who did not complete high school.
Not surprisingly, having a job is strongly linked to movement from the lower-income tier to the middle- and upper-income tiers. Among employed American workers ages 16 and older, 58% were in the middle-income tier in 2022 and 23% were in the upper-income tier. Only 19% of employed workers were lower income, compared with 49% of unemployed Americans.
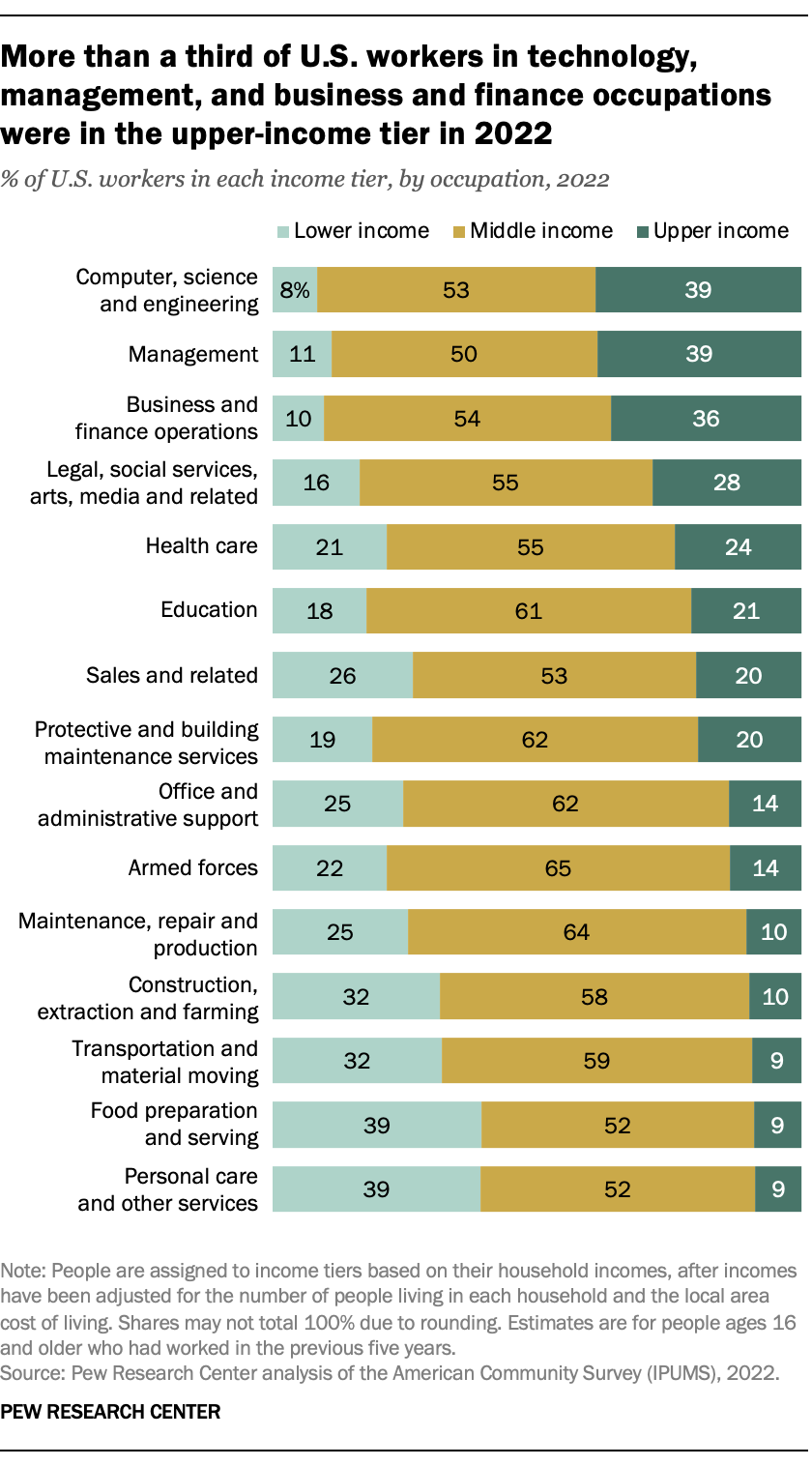
In some occupations, about nine-in-ten U.S. workers are either in the middle class or in the upper-income tier, but in some other occupations almost four-in-ten workers are lower income. More than a third (36% to 39%) of workers in computer, science and engineering, management, and business and finance occupations lived in upper-income households in 2022. About half or more were in the middle class.
But many workers – about one-third or more – in construction, transportation, food preparation and serving, and personal care and other services were in the lower-income tier in 2022.
About six-in-ten workers or more in education; protective and building maintenance services; office and administrative support; the armed forces; and maintenance, repair and production were in the middle class.
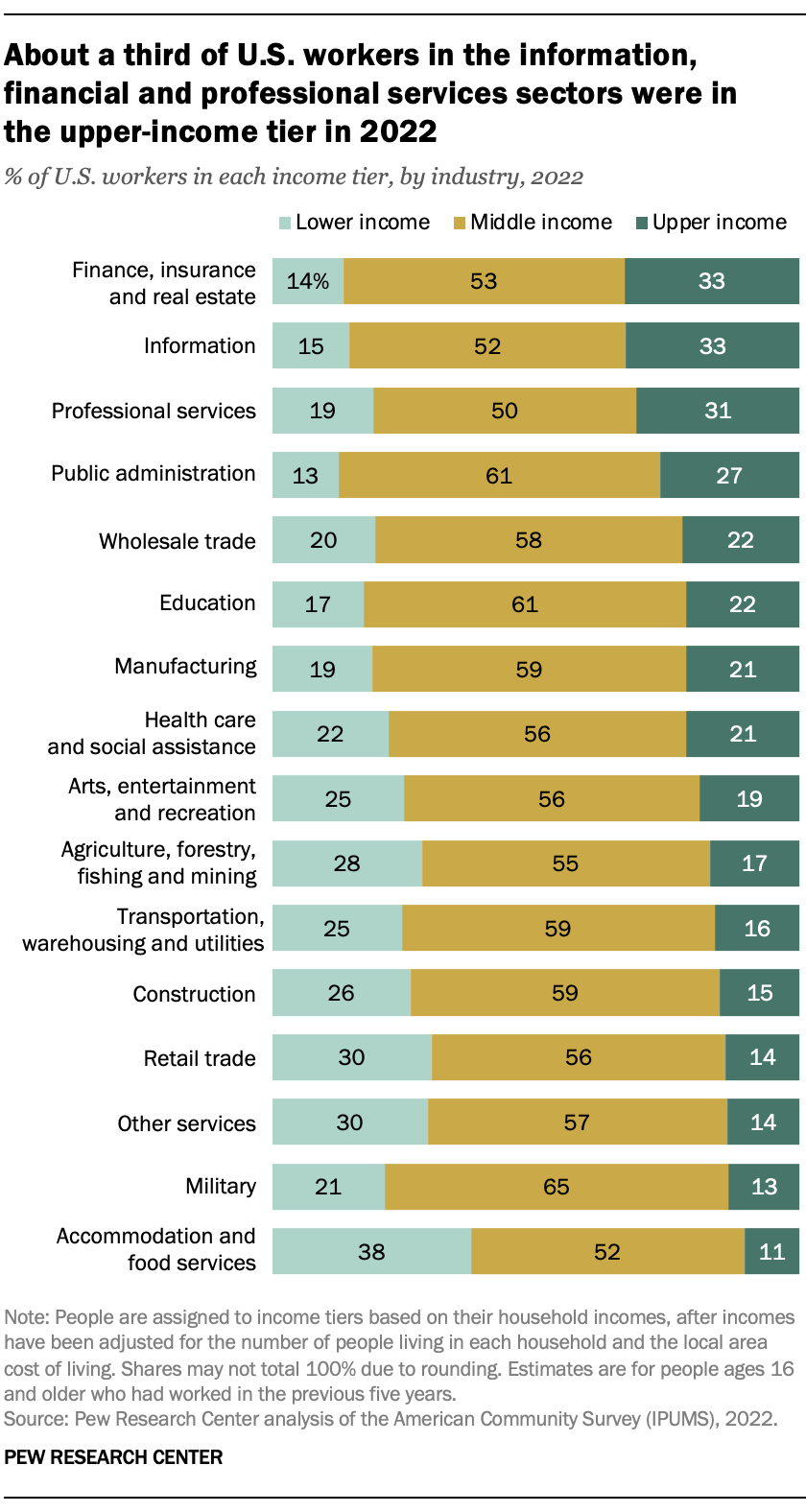
Depending on the industrial sector, anywhere from half to two-thirds of U.S. workers were in the middle class, and the share who are upper income or lower income varied greatly.
About a third of workers in the finance, insurance and real estate, information, and professional services sectors were in the upper-income tier in 2022. Nearly nine-in-ten workers (87%) in public administration – largely filling legislative functions and providing federal, state or local government services – were either in the middle class or the upper-income tier.
But nearly four-in-ten workers (38%) in accommodation and food services were lower income in 2022, along with three-in-ten workers in the retail trade and other services sectors.
The share of Americans who are in the middle class or in the upper- or lower-income tier differs across U.S. metropolitan areas. But a pattern emerges when it comes to which metro areas have the highest shares of people living in lower-, middle- or upper-income households. (We first adjust household incomes for differences in the cost of living across areas.)
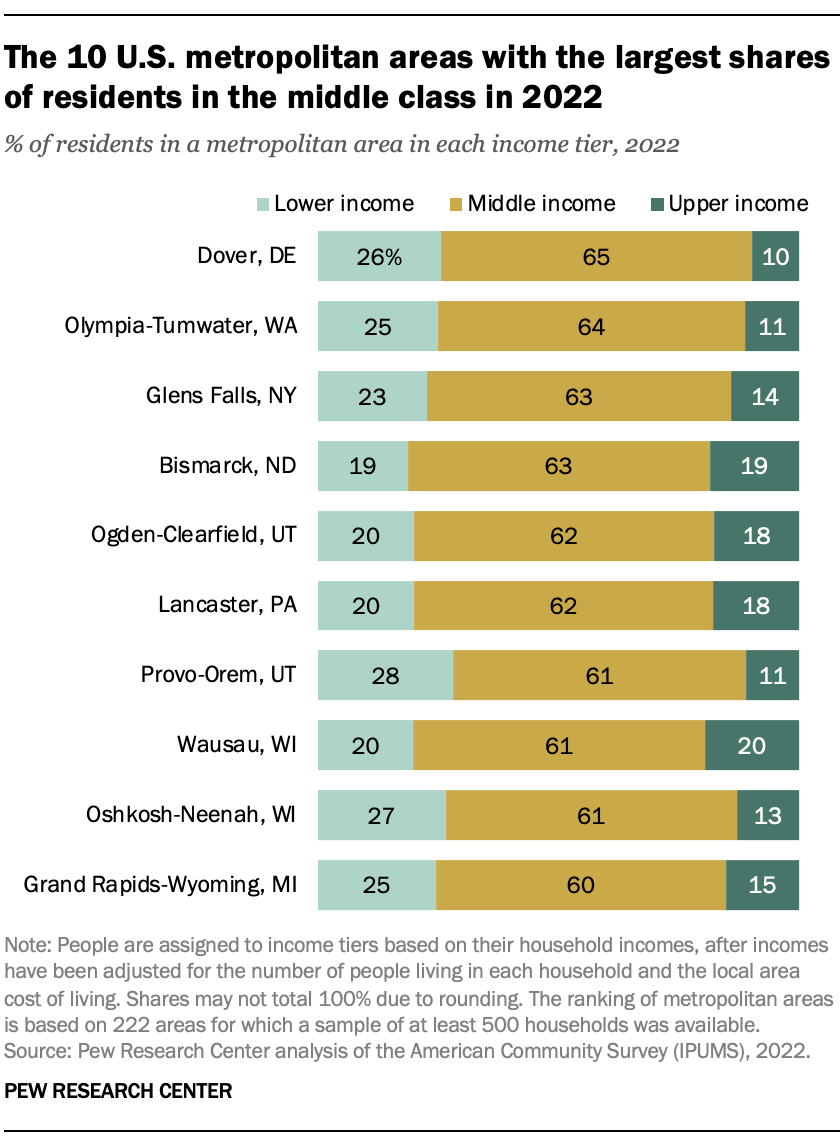
The 10 metropolitan areas with the greatest shares of middle-income residents are small to midsize in population and are located mostly in the northern half of the U.S. About six-in-ten residents in these metro areas were in the middle class.
Several of these areas are in the so-called Rust Belt, namely, Wausau and Oshkosh-Neenah, both in Wisconsin; Grand Rapids-Wyoming, Michigan; and Lancaster, Pennsylvania. Two others – Dover and Olympia-Tumwater – include state capitals (Delaware and Washington, respectively).
In four of these areas – Bismarck, North Dakota, Ogden-Clearfield, Utah, Lancaster and Wausau – the share of residents in the upper-income tier ranged from 18% to 20%, about on par with the share nationally.
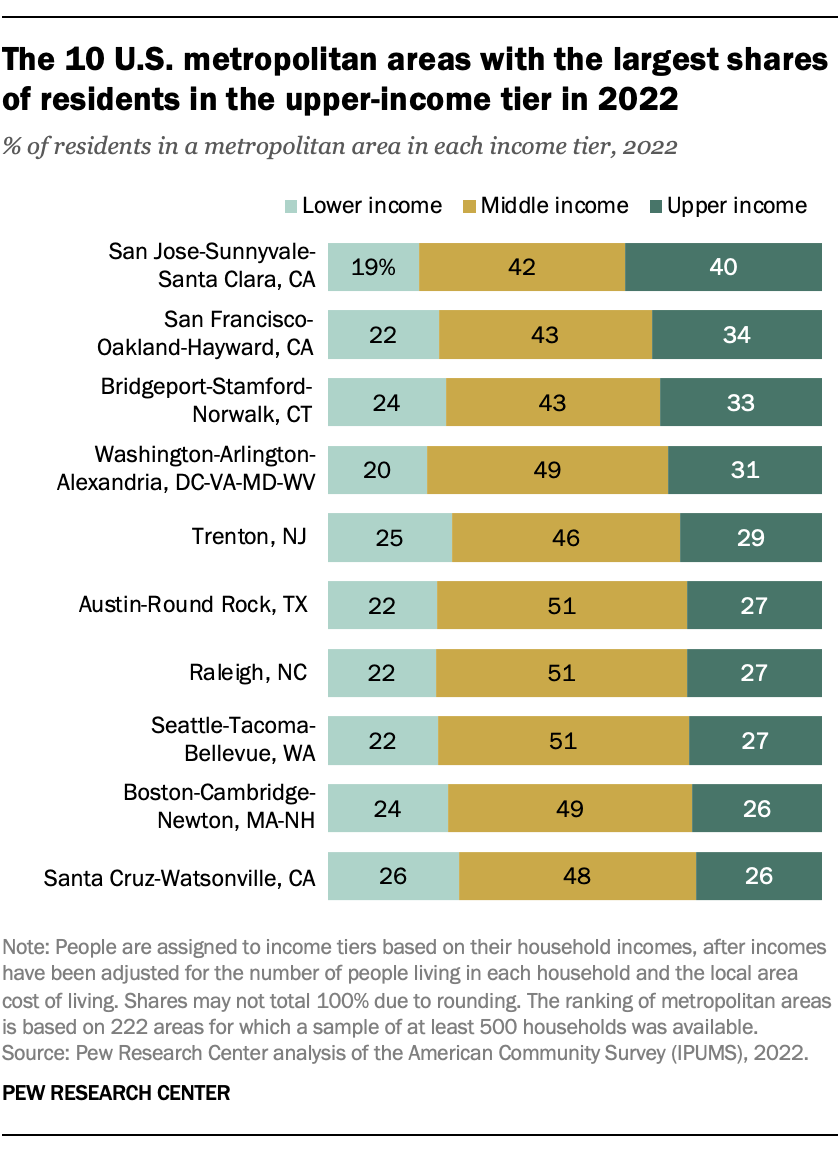
The 10 U.S. metropolitan areas with the highest shares of residents in the upper-income tier are mostly large, coastal communities. Topping the list is San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, California, a technology-driven economy, in which 40% of the population lived in upper-income households in 2022. Other tech-focused areas on this list include San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward; Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue; and Raleigh, North Carolina.
Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk, Connecticut, is a financial hub. Several areas, including Washington, D.C.-Arlington-Alexandria and Boston-Cambridge-Newton, are home to major universities, leading research facilities and the government sector.
Notably, many of these metro areas also have sizable lower-income populations. For instance, about a quarter of the populations in Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk; Trenton, New Jersey; Boston-Cambridge-Newton; and Santa Cruz-Watsonville, California, were in the lower-income tier in 2022.
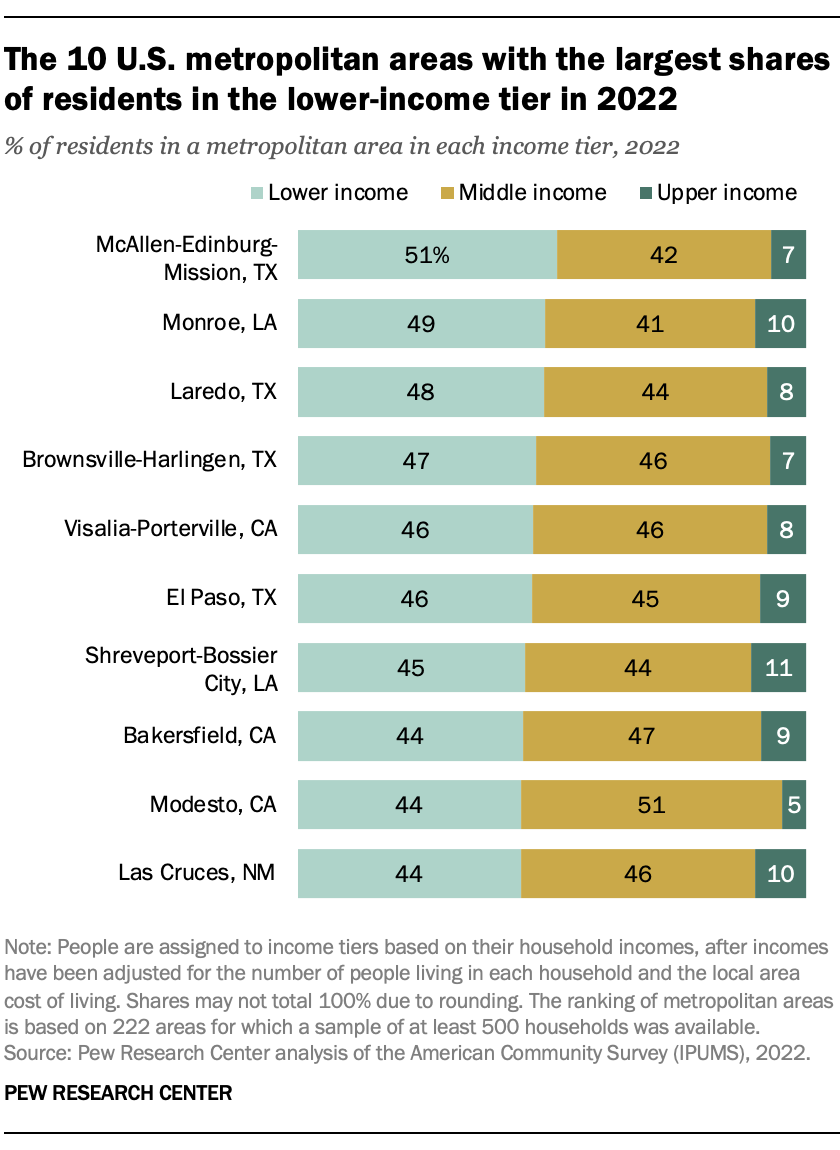
Most of the 10 U.S. metropolitan areas with the highest shares of residents in the lower-income tier are in the Southwest, either on the southern border of Texas or in California’s Central Valley. The shares of people living in lower-income residents were largely similar across these areas, ranging from about 45% to 50%.
About 40% to 50% of residents in these metro areas were in the middle class, and only about one-in-ten or fewer lived in upper-income households.
Compared with the nation overall, the lower-income metro areas in Texas and California have disproportionately large Hispanic populations. The two metro areas in Louisiana – Monroe and Shreveport-Bossier City – have disproportionately large Black populations.
Note: For details on how this analysis was conducted, refer to the methodology.


