Coronavirus forcing countries to reevaluate security paradigms
While global arms expenditures have been rising annually, many militaries have been caught off guard by the COVID-19 pandemic. Will governments start to reframe their security agendas?

The US military is well-equipped to repel conventional threats, but it's certainly not up to the task of containing biological hazards like the coronavirus pandemic, according to Christopher Preble of the Cato Institute, a Washington-based libertarian think tank. Neither the US military nor the Navy are safe from the pathogen, as a recent COVID-19 outbreak aboard the USS Theodore Roosevelt aircraft carrier, with its crew of 5,000, made clear.
As the outbreak continues to spread in the US, the health care infrastructure in many states is unable to cope. "Americans are now warming to the idea of investing more in the health care system," Preble, Cato's vice president for defense and foreign policy studies, told DW. But he believes this attitude could change once the pandemic passes.
Read more: Crises are fueling the global arms trade: SIPRI report
It is not just in the US where military preparedness for pathogens is seen as limited. Russian defense expert Alexander Golz also believes his country's leadership is not taking adequate measures to counter the outbreak. "Generals are always preparing to fight the wars of the past," he said.
Golz, deputy editor-in-chief of the Ezhednevny Zhurnal online platform, said President Vladimir Putin met with representatives of the military-industrial complex when the pandemic first hit Russia. They expected Putin would "discuss ways to reorganize the economy to ramp up the production of drugs, protective clothing and face masks," he told DW. But, to his surprise, the focus instead was on how the production and export of arms could be ensured.
'Watershed moment'
However, the coronavirus pandemic may help shift the framework of military thinking. Joe Biden, Donald Trump's presumed Democratic rival in the November US presidential election, has announced plans to create a special cabinet post to focus on the threats posed by pandemics and climate issues, should he be elected.
Chris Murphy, a Democratic Senator from Connecticut, told the German Marshall Fund (GMF) that the US must redefine its security agenda and consider pandemics, climate change and environmental damage as serious security threats. Speaking with the GMF podcast mini-series "Post-Pandemic Order," he backed the idea of a new defense budget with different priorities, simply because "there are other agencies besides the Department of Defense that protect this country."
Read more: Climate change leads to more violence against women, girls
"The crisis we are experiencing now is a watershed moment — also for our understanding of our security policies," said Ulrich Schlie, a professor of security and strategy studies at the University of Bonn. Schlie, who for years headed the planning division of Germany's Defense Ministry, told DW it was time to adapt a "broader notion of security" that goes beyond typical military considerations and arms spending.
Conventional defense spending still important
In Schlie's view, countries should plan for a variety of security threats, including pandemics, migration-related challenges and other phenomena, alongside "funds for conventional armies." He urged EU member states to coordinate more closely when to comes to security affairs.
Schlie did not, however, recommend spending less on conventional defense capabilities to free up resources for other threats, pointing out that one "should not play one off against the other." He stressed that NATO should remain viable, and said that in order to meet the danger of pandemics and other non-military threats NATO members on both sides of the Atlantic should increase their overall spending.
SIPRI: Germany significantly increases military spending
More and more money is going toward the world's militaries, with the US and China leading the way. But no other top-spending country has increased its military expenditure year-over-year as much as Germany.

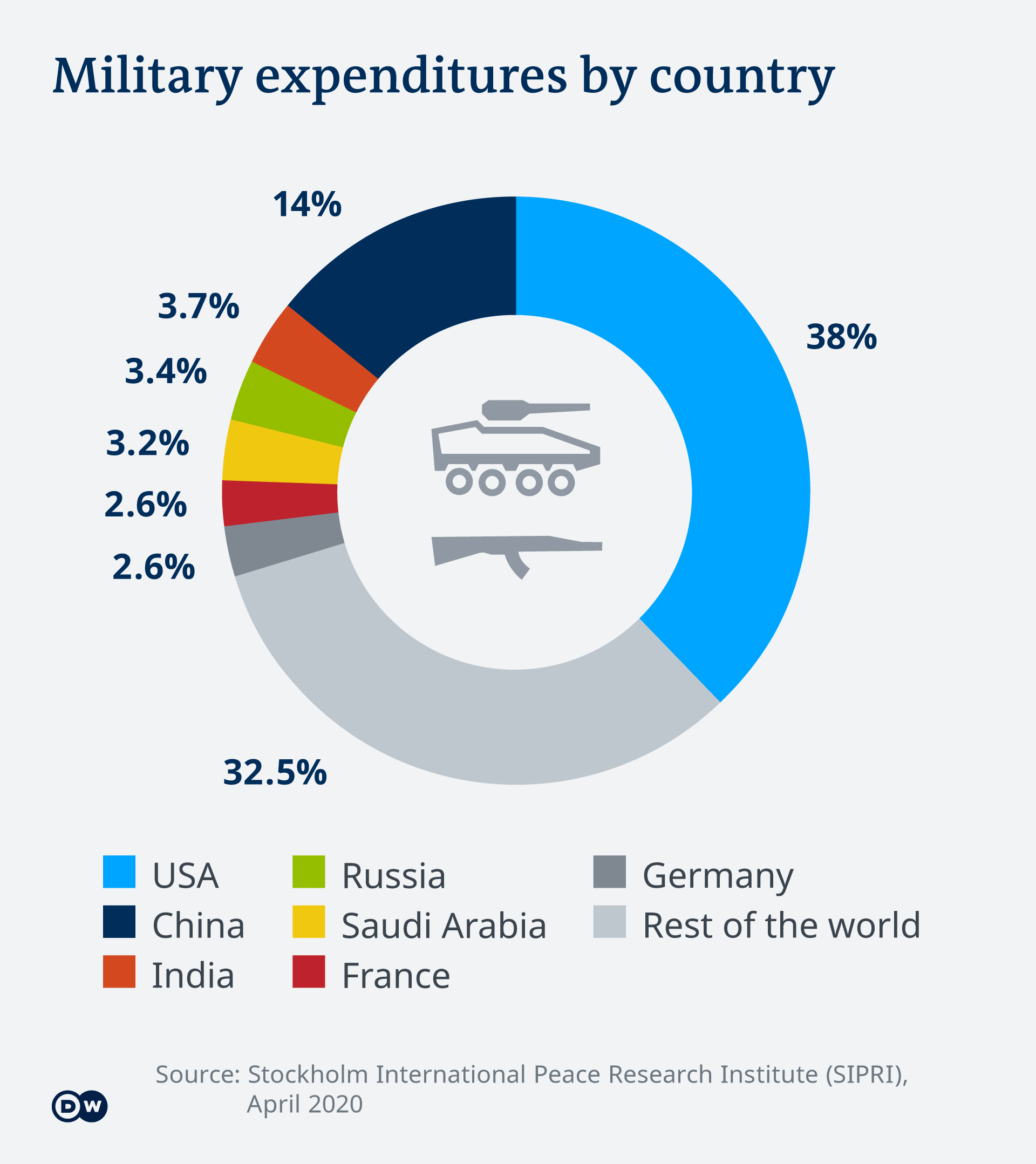
Global military expenditure reached $1.9 trillion (€1.7 trillion) in 2019, the highest annual sum in real terms since 1988. That sum marked an increase of 3.6% over 2018, the largest annual increase since 2010, according to the latest figures from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
In Germany, spending rose by 10% to $49.3 billion — the largest defense budget increase among the world's top 15 states when it comes to military expenditures.
"There's been pressure on Germany to increase its military expenditure since before the Trump administration," said Max Mutschler from the Bonn International Center for Conversion (BICC), a peace and conflict research institute. "The impact of this pressure is now becoming clear. However, one has to say that expenditure is still well below the 2% mark."
At a NATO summit in Wales in 2014, members agreed to meet a goal of spending at least 2% of their GDP on defense within the next decade. Last year, Germany's military expenditure amounted to 1.38% of its GDP.
NATO flexes muscles in Poland
Russia seen as a growing threatNATO commitments aside, SIPRI researcher Diego Lopes da Silva also attributed the increase in Germany's defense budget to the geopolitical situation in Europe and the fact that, "Russia is once again being considered as more of a threat." In 2019, almost 4% of Russia's GDP went to military spending, amounting to $65.1 billion.
Da Silva pointed out that Germany is not alone, and that many other NATO states are monitoring developments in Russia with a watchful eye.
Of the 15 countries in the world with the highest defense budgets, six are NATO members: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom and the United States. Their combined military expenditure makes up for almost half of the world's total figure. In 2019, the total military expenditure of NATO's 29 member states was some $1.04 trillion, a figure that didn't surprise Mutschler."Military expenditure is based on worst-case scenarios," he told DW, explaining that while the public often perceives economic conflict between states to be in the foreground, the threat of military conflict remains very present in the background.
"With regard to the tension between the US and China, we do not know if there will be an armed conflict or not. So the militaries in both countries are preparing for this eventuality, and they're very good when it comes to lobbying for more funds," he said.
US still well ahead of China
According to the SIPRI report, in 2019 the US was responsible for 38% of global military expenditure, totaling $732 billion. The increase over its 2018 budget alone amounted to the equivalent of Germany's total expenditure in 2019.
Those funds went to cover some 16,000 extra military personnel, along with the modernization of its conventional weaponry and nuclear arsenal. But experts also see the increase as a response to China, which ranks in second place after the US when it comes to military spending. Beijing's budget contributed 14% of global military expenditure in 2019 and rose by more than 5% to $261 billion.
China has been increasing its military expenditure steadily since 1994, but its budget has jumped by 85% since 2010. However, in terms of percentage of GDP, this has not changed considerably and almost always lies at 1.9%.
India surpasses Saudi Arabia
On the Asian continent, the military expenditure of China's rival, nuclear power India, is also considerable, rising last year by almost 7% to $71.1 billion.
"The tension with neighboring countries Pakistan and China are the main reasons that the Indian government has increased its expenditure so dramatically," said Siemon Wezeman, a senior researcher with SIPRI.
For its part, Saudi Arabia lies well ahead of other Middle Eastern countries, spending $61.9 billion in 2019 — though this was actually a 16% decrease in comparison with the previous year. The figure was a surprising development, according to the SIPRI report, considering the Saudi kingdom's ongoing military operations in Yemen and increasing tensions with Iran.
German weapons for Saudi Arabia
Emerging economies spend much less
Military expenditure in other countries pales by comparison to the global top spenders. South American states spent "only" $53 billion in 2019, and Brazil alone was responsible for half of that.
Southeast Asian countries totaled around $41 billion, and the entire continent of Africa spent some $42 billion, though there were considerable fluctuations depending on the states. Uganda, for example, increased its budget by 52%, while Burkina Faso decreased its expenditure by 22%.
The authors of the SIPRI report attributed the differences in expenditure to the current geopolitical situation in sub-Saharan Africa, and whether or not states are directly involved in a military conflict.
AFTER PANDEMICS; CLIMATE CHANGE
WORLD WATER CONFLICTS: THE GLOBAL HOTSPOTS

Water conflicts worldwide
Water conflicts have more than doubled over the last 10 years compared to previous decades, research shows. Sometimes the essential resource is at the root of these clashes but more often than not, disputes over water alone will not spark violence. Instead, water can act as an accelerant when mixed together with other problems, such as poverty, inequality and hunger.

Pakistan's tireless fight over water with India
The Indus river, shared by India and Pakistan, has long been a point of contention. The countries divided up the rights to the river and its tributaries in the 1960 Indus Waters Treaty. But tensions have flared recently. Pakistan says India has stopped water flowing into the Islamic Republic and accuses its neighbor of using water as a weapon in the ongoing dispute over Kashmir.

Nigeria faces ongoing water challenges
Water-related violence in Nigeria is responsible for more casualties than militant Islamist group Boko Haram. In the country's north, where the group has been waging war since 2010, they're also demanding the government provide clean water. Elsewhere, a lack of rain in their own grazing areas, is causing Muslim Fulani herders to move onto land owned by Christian farmers, leading to clashes.

India's water crisis spans from its ongoing conflict over the Indus river with Pakistan to droughts that have repeatedly caused severe water shortages across the country. Delayed monsoon rains have recently added to the crisis, with estimates showing that 40% of India's population may not have access to drinking water by 2030.

Iran's multiple water disputes
Population growth, urbanization, poor infrastructure and governance have been driving water tensions in Iran. But the country has also seen discord with Afghanistan over how to share the Helmand River's waters. Iran is concerned about its neighbor's Kamal Khan Dam, expected to be completed in 2020, as it will restrict water flow to one of its provinces. Some fear the dispute could turn violent.

In Mali, farmers and herders have been fighting over scarce water and land resources, against a backdrop of ethnic tensions, armed groups and population rise. In 2019, a combination of these factors led to mass killings in the Inner Niger Delta, a central Malian wetland. Government plans to build dams that may affect over a million farmers, herders and fishers in the Delta could make things worse.

Iraq's multifaceted water crisis
Iraq's ongoing water crisis is complex. Droughts, decreasing annual rainfall, changing weather patterns and pollution all play a role. The state has faced repeated criticism over its failure to properly manage water resources and further destabilizing the country. In late 2019, Iraq's prime minister resigned amid mass protests, partly over lack of access to electricity and clean water.
Author: Sarah Mewes
CHINESE SOLDIERS TRAIN FOR EPIDEMIC IN BAVARIA

Special delivery
This Chinese armored medical evacuation vehicle arrived by ship at the port in Hamburg, before being shipped to southern Germany and the Bavarian town of Feldkirchen. A total of 92 Chinese and 120 German soldiers are taking part in the Combined Aid 2019 exercise, along with 120 men and women in supporting roles.

No ordinary exercise
The armored medical evacuation vehicle and other Chinese army supplies were brought here to Feldkirchen, where the exercise is taking place until July 17. It's the first of its kind in Germany in the history of German-Chinese military cooperation. In 2016, 38 Bundeswehr medical orderlies took part in a previous exercise in China.

Folding hospital
The exercise is simulating a fictitious UN deployment. The scenario: Cholera has broken out in several refugee camps, and there are many wounded people elsewhere. The Chinese soldiers brought their own mobile hospital along with them for the exercise. It can be pulled out and folded up like an accordion

Ready in no time
"It's impressive how fast the mobile equipment from the Chinese People's Liberation Army can be set up," said a Bundeswehr report. "The modern Chinese tents are up and ready within a few minutes, and the medical equipment is put in place just as quickly."

In the 2016 joint exercise, training focused on treating and providing for earthquake victims. China has plenty of experience in this area. Following earthquake disasters in 2008, 2010 and 2012, it had to take care of between 40,000 and 50,000 injured people each time. The 2019 exercise only involves medical staff, but it's being seen as a first step toward limited military cooperation.
Tricky translation
During the joint exercise, participants either speak English, or use an interpreter. The German army has said the exercise is helping to establish international cooperation, in preparation for a possible cross-border outbreak of disease.

Strong together
The exercise "is also extremely relevant with regard to non-military disease prevention, as there is an international duty to protect the population against epidemics and pandemics," said the Bundeswehr. There's even a joint logo for Combined Aid 2019, incorporating the German and Chinese flags.
Author: Marco Müller
Read more: SIPRI: Weapons boom shows no signs of slowing
Read more: NATO and Russia: Maneuvers and countermaneuvers in the Baltic Sea
Read more: Crises are fueling the global arms trade: SIPRI report
DW RECOMMENDS
Coronavirus forcing countries to reevaluate security paradigms
While global arms expenditures have been rising annually, many militaries have been caught off guard by the COVID-19 pandemic. Will governments start to reframe their security agendas? (27.04.2020)
Opinion: Weapons don't fight pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic shows that we've got our security priorities wrong. Virus outbreaks, after all, cannot be contained by military force. Time for a security rethink, says Miodrag Soric. (27.04.2020)
Germany sells arms to members of Saudi-led Yemen coalition
Since 2019, Germany's government has approved arms exports worth over €1 billion to members of the Saudi-led coalition fighting Houthi rebels in Yemen. Critics says this exacerbates the fighting. (02.04.2020)
New technologies drive military spending: SIPRI
Military spending has surged across the globe, according to a new report published by SIPRI. With new advances in defense technologies, countries are spending more to gain an edge. (29.04.2019)
Merkel vows to hit 2% NATO spending target 'by early 2030s'
The German leader says NATO is even more essential to Germany and Europe now than during the Cold War. (27.11.2019)
Opinion: Weapons don't fight pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic shows that we've got our security priorities wrong. Virus outbreaks, after all, cannot be contained by military force. Time for a security rethink, says Miodrag Soric. (27.04.2020)
SIPRI: Germany significantly increases military spending
Though the US and China are leading the way, no other top-spending country has increased its expenditure year-over-year as much as Germany.
Germany sells arms to members of Saudi-led Yemen coalition
Since 2019, Germany's government has approved arms exports worth over €1 billion to members of the Saudi-led coalition fighting Houthi rebels in Yemen. Critics says this exacerbates the fighting. (02.04.2020)
SIPRI: Weapons boom shows no signs of slowing
Armaments production worldwide is continuing full speed ahead. According to a new study by a Swedish think tank, the 100 biggest weapons companies have once again increased their sales, with the US leading the way. (09.12.2019)
New technologies drive military spending: SIPRI
Military spending has surged across the globe, according to a new report published by SIPRI. With new advances in defense technologies, countries are spending more to gain an edge. (29.04.2019)
WWW LINKS
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2019 (PDF)
Date 26.04.2020 Author Miodrag Soric
Global military spending nearly $2T in 2019, U.S. accounts for one-third

The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute said on Monday that global military spending reached $1.9 trillion in 2019. Photo by Jesper Sundstrom/Swedish Armed Forces
April 27 (UPI) -- Global military spending grew 3.6 percent in 2019 to $1.9 trillion, with the United States accounting for $732 billion, or 38 percent of the global total.
U.S. military spending grew by 5.3 percent, equivalent to Germany's entire military budget for the year, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute said Monday in its annual report.
The five largest buyers were the United States, China, India, Russia and Saudi Arabia, whose purchases accounted for 62 percent of the total figure. The global expenditure was the largest annual percentage increase in a decade, representing 2.2 percent of global gross domestic product, or about $249 per person.
By the benchmarks of SIPRI, military spending includes all government spending on current military forces and activities, including salaries and benefits, operational expenses, arms and equipment purchases, military construction, research and development, and central administration, command and support. The dollar figures include the cost of more than weapons and armaments.
"Global military expenditure was 7.2 per cent higher in 2019 than it was in 2010, showing a trend that military spending growth has accelerated in recent years," SIPRI researcher Nan Tian said in a press release. "This is the highest level of spending since the 2008 global financial crisis and probably represents a peak in expenditure."
The study noted that China's military expenditures rose 5.1 percent to about $261 billion in 2019, or only about one-third of the U.S. figure. India's grew 6.8 percent to $71.1 billion. Russia saw a 4.5 percent increase to $65.1 billion, or nearly four percent of its GDP.
Beyond the top five, however, military spending increased all over the world. Bulgaria's military budget increased by 127 percent, largely because of payments for new fighter planes to replace its Soviet-era fleet. The 29 nations of NATO combined to spend more than $1.035 trillion in 2019, the report
Spending by South American countries was little changed, but armed conflict in central Africa increased Burkina Faso's military budget by 22 percent and Uganda's by 52 percent.






