It’s possible that I shall make an ass of myself. But in that case one can always get out of it with a little dialectic. I have, of course, so worded my proposition as to be right either way (K.Marx, Letter to F.Engels on the Indian Mutiny)
Tuesday, August 11, 2020
LA REVUE GAUCHE - Left Comment: Alberta Seperatism Not Quite Stamped Out
LA REVUE GAUCHE - Left Comment: Alberta Seperatism Not Quite Stamped Out: Well that didn't take long. Starting with Bouquets of Grey documenting Edmonton East Conservative Campaign Manager Gordon Stamp, a pe...
FROM 2005 THE LAST TIME ALBERTA FACED A SEPARATIST CHALLENGE, THEN FROM KENNEY AND HARPER AS REFORM PARTY HACKS WHO RAISED FIREWALL ALBERTA
FROM 2005 THE LAST TIME ALBERTA FACED A SEPARATIST CHALLENGE, THEN FROM KENNEY AND HARPER AS REFORM PARTY HACKS WHO RAISED FIREWALL ALBERTA
Outbreak at Regina's K-Bro Linens: 18 employees test positive
The president of the union representing most workers at a Regina laundry facility expects the number of COVID-19 cases to rise among staff.
FORMERLY ALBERTA HOSPITALS PUBLIC LAUNDRY SERVICES
PRIVATIZED UNDER KLEIN NOW THE LARGEST HOSPITAL LAUNDRY SERVICE IN NORTH AMERICA
UNDERPAID NEW CANADIANS, MIGRANTS AND TEMP WORKERS ARE CLEANING HOSPITAL LAUNDRY IN COVID-19 CONDITIONS, LIKE THE MEAT PACKING INDUSTRY!!!
Author of the article:Ashley Martin • Regina Leader-Post
Publishing date:Aug 10, 2020 •
The president of the union representing most workers at a Regina laundry facility expects the number of COVID-19 cases to rise among staff.
FORMERLY ALBERTA HOSPITALS PUBLIC LAUNDRY SERVICES
PRIVATIZED UNDER KLEIN NOW THE LARGEST HOSPITAL LAUNDRY SERVICE IN NORTH AMERICA
EVEN THE ORACLE OF OMAHA WARREN BUFFETS BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY IS INVESTED IN IT
UNDERPAID NEW CANADIANS, MIGRANTS AND TEMP WORKERS ARE CLEANING HOSPITAL LAUNDRY IN COVID-19 CONDITIONS, LIKE THE MEAT PACKING INDUSTRY!!!
Author of the article:Ashley Martin • Regina Leader-Post
Publishing date:Aug 10, 2020 •

An employee pictured working at K-Bro Linens in Regina in 2016. DON HEALY / Regina Leader-Post
The president of the union that represents most workers at a Regina laundry facility expects the number of COVID-19 cases among employees will rise.
“I believe there’s probably going to be more than that,” said Norm Neault, president of the United Food and Commercial Workers Union local 1400, which counts among its members the majority of K-Bro Linen Systems staff in Regina.
Neault made that prediction Monday morning, when he was only aware of a handful of positive cases.
Late Monday afternoon, the Ministry of Health issued a news release that 18 employees have now tested positive for COVID-19.
On Saturday, all 11 new cases reported in Regina were among K-Bro employees or their close contacts. Most of the cases were identified through contact tracing, although some came through calls to Healthline 811.
In addition to 141 unionized members, Neault said there are 20-some non-unionized employees at the Regina shop.
Jackie Belanger, general manager of the Regina facility, said there are approximately 70 people working per shift.
The president of the union that represents most workers at a Regina laundry facility expects the number of COVID-19 cases among employees will rise.
“I believe there’s probably going to be more than that,” said Norm Neault, president of the United Food and Commercial Workers Union local 1400, which counts among its members the majority of K-Bro Linen Systems staff in Regina.
Neault made that prediction Monday morning, when he was only aware of a handful of positive cases.
Late Monday afternoon, the Ministry of Health issued a news release that 18 employees have now tested positive for COVID-19.
On Saturday, all 11 new cases reported in Regina were among K-Bro employees or their close contacts. Most of the cases were identified through contact tracing, although some came through calls to Healthline 811.
In addition to 141 unionized members, Neault said there are 20-some non-unionized employees at the Regina shop.
Jackie Belanger, general manager of the Regina facility, said there are approximately 70 people working per shift.

K-Bro Linen Systems is pictured in Regina on Monday, Aug. 10, 2020. There was widespread COVID-19 testing last week at the facility after some workers tested positive for the virus. TROY FLEECE/Regina Leader-Post
On Friday, Ministry of Health stated in an emailed news release that “a number of employees” at K-Bro Regina had tested positive.
Neault said two or three employees had initially tested positive. By Friday, all staff had been tested — most on site.
“Every employee has been tested and anyone who has tested positive and anyone who was in close contact with them is in self-isolation,” said Belanger.
About 30 employees did not come to work on Monday, according to the union.
Regina’s COVID-19 case numbers have climbed in the past week. On Aug. 3, there were seven active cases; a week later, on Monday, Aug. 10, there were 30 active cases reported.
As precautions during COVID-19, Neault said employees have been wearing masks and gloves, and physically distancing between workstations. Break times have been staggered. Employees take a screening questionnaire, and temperatures are checked before entering the facility.
Belanger said employees’ health and safety is the “highest priority,” and prior to the pandemic K-Bro had higher-than-standard health and safety protocols.
K-Bro is an Edmonton-based company with locales in Saskatoon, Prince Albert and other provinces. Much of the Regina facility is mechanized, said Neault, with people operating the machinery that cleans and folds linens.
The Health Ministry said a microbiologist determined there was no safety concern in regards to the linens that were processed in the facility.
This outbreak is “certainly an eye-opener for that facility, for that employer, and certainly for Regina,” said Neault. “We really have to be careful in these times and I think people let their guards down and (outbreaks) may happen.”
The UFCW also has members working at grocery stores, including the Regina Superstores at Golden Mile and Rochdale.
Even one case is “too many,” said Neault, “especially when you have facilities where you have that many people working there and how easily COVID can spread. … It’s got to be a concern to the public as well.”
Neault said UFCW negotiated sick pay in these members’ most recent contract; employees receive partial pay if they’re sick.
At this point, Neault said the company hasn’t offered and the union hasn’t asked for a wage top-up for employees who are off sick due to COVID-19.
amartin@postmedia.com
On Friday, Ministry of Health stated in an emailed news release that “a number of employees” at K-Bro Regina had tested positive.
Neault said two or three employees had initially tested positive. By Friday, all staff had been tested — most on site.
“Every employee has been tested and anyone who has tested positive and anyone who was in close contact with them is in self-isolation,” said Belanger.
About 30 employees did not come to work on Monday, according to the union.
Regina’s COVID-19 case numbers have climbed in the past week. On Aug. 3, there were seven active cases; a week later, on Monday, Aug. 10, there were 30 active cases reported.
As precautions during COVID-19, Neault said employees have been wearing masks and gloves, and physically distancing between workstations. Break times have been staggered. Employees take a screening questionnaire, and temperatures are checked before entering the facility.
Belanger said employees’ health and safety is the “highest priority,” and prior to the pandemic K-Bro had higher-than-standard health and safety protocols.
K-Bro is an Edmonton-based company with locales in Saskatoon, Prince Albert and other provinces. Much of the Regina facility is mechanized, said Neault, with people operating the machinery that cleans and folds linens.
The Saskatchewan government in 2013 contracted K-Bro to provide linen service to hospitals and health facilities across the province.
The Health Ministry said a microbiologist determined there was no safety concern in regards to the linens that were processed in the facility.
This outbreak is “certainly an eye-opener for that facility, for that employer, and certainly for Regina,” said Neault. “We really have to be careful in these times and I think people let their guards down and (outbreaks) may happen.”
The UFCW also has members working at grocery stores, including the Regina Superstores at Golden Mile and Rochdale.
Even one case is “too many,” said Neault, “especially when you have facilities where you have that many people working there and how easily COVID can spread. … It’s got to be a concern to the public as well.”
Neault said UFCW negotiated sick pay in these members’ most recent contract; employees receive partial pay if they’re sick.
At this point, Neault said the company hasn’t offered and the union hasn’t asked for a wage top-up for employees who are off sick due to COVID-19.
amartin@postmedia.com
'Like gold': Canadian canola prices spike as shippers find back door to China
Reuters
Rod Nickel and Hallie Gu
Publishing date:Aug 09, 2020
WINNIPEG — Canadian canola prices have soared to the highest in nearly two years, despite a diplomatic dispute between Ottawa and Beijing, as exporters find roundabout ways to reach top oilseed buyer China.
Chinese authorities have since March 2019 blocked canola shipments by two Canadian exporters, an action they took after Canadian police detained a Huawei Technologies executive in late 2018 on a United States warrant.
The dispute however, has not spoiled China’s appetite for canola, which is mainly processed into vegetable oil. While China is buying less from Canada directly, it has bought canola oil instead from Europe and the United Arab Emirates, with some of that oil made from Canadian canola, traders said.
ICE canola futures on Tuesday hit the highest nearby price since October 2018. Prices of China’s rapeseed oil, another name for canola oil, have also rallied, partly because of limited Canadian supply.
“Profits are extravagant. Anyone who has the resources to import (canola oil) will definitely buy,” said a manager with a China-based canola importer.
“It is like gold oil now.”
Canadian canola exports to China fell 45% year over year during the 11-month period through June, however total canola exports have jumped 9%, helped by a tripling of sales to France and double the shipments to the UAE.
Canada is the world’s biggest canola producer, and the yellow-flowering plant earned farmers C$8.6 billion ($6.42 billion) last year, the most of any crop.
China meanwhile boosted canola oil imports from Europe, Russia and Australia, with some of that oil made from Canadian canola, said another China-based trader.
The price rally left farmer Mary-Jane Duncan-Eger, who grows canola near Regina, Saskatchewan, “super-mystified,” considering that Canada is heading for a bumper crop.
To lock in high prices, she pre-sold 50% of her anticipated harvest, up from the 30% she usually pre-sells at this time of year.
“I’m pretty happy. As long as someone is buying it, I don’t care who.”
GLOBAL MULTILATERAL AGRIBUSINESS OLIGOPOLIES
Global canola oil demand has prompted Canadian crushers – who include Archer Daniels Midland Co and Bunge Ltd – to process canola at a brisk pace, said Brian Comeault, commodity risk manager with Cargill Ltd’s Canadian marketing service MarketSense.
Exporters are also selling more seed to the UAE, where crushers produce oil to sell to China, he said.
Bad crop weather and insect attacks in Europe have also lifted prices.
Rapeseed production in the European Union and Britain is expected near the 13-year low seen in 2019.
CANOLA WAS ONCE RAPESEED BUT TODAY IT IS A GMO (R)(TM)
This has led European importers to scour other countries for supplies, especially those with weaker currencies that make purchases more profitable, consultancy Strategie Grains said in a report.
“Canadian canola has the biggest edge,” it said. “Competition among importing countries will probably be fierce over the coming months.” ($1 = 1.3387 Canadian dollars)
(Reporting by Rod Nickel in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Hallie Gu in Beijing, Gus Trompiz in Paris and Michael Hogan in Hamburg Editing by Marguerita Choy)
Reuters
Rod Nickel and Hallie Gu
Publishing date:Aug 09, 2020
WINNIPEG — Canadian canola prices have soared to the highest in nearly two years, despite a diplomatic dispute between Ottawa and Beijing, as exporters find roundabout ways to reach top oilseed buyer China.
Chinese authorities have since March 2019 blocked canola shipments by two Canadian exporters, an action they took after Canadian police detained a Huawei Technologies executive in late 2018 on a United States warrant.
The dispute however, has not spoiled China’s appetite for canola, which is mainly processed into vegetable oil. While China is buying less from Canada directly, it has bought canola oil instead from Europe and the United Arab Emirates, with some of that oil made from Canadian canola, traders said.
ICE canola futures on Tuesday hit the highest nearby price since October 2018. Prices of China’s rapeseed oil, another name for canola oil, have also rallied, partly because of limited Canadian supply.
“Profits are extravagant. Anyone who has the resources to import (canola oil) will definitely buy,” said a manager with a China-based canola importer.
“It is like gold oil now.”
Canadian canola exports to China fell 45% year over year during the 11-month period through June, however total canola exports have jumped 9%, helped by a tripling of sales to France and double the shipments to the UAE.
Canada is the world’s biggest canola producer, and the yellow-flowering plant earned farmers C$8.6 billion ($6.42 billion) last year, the most of any crop.
China meanwhile boosted canola oil imports from Europe, Russia and Australia, with some of that oil made from Canadian canola, said another China-based trader.
The price rally left farmer Mary-Jane Duncan-Eger, who grows canola near Regina, Saskatchewan, “super-mystified,” considering that Canada is heading for a bumper crop.
To lock in high prices, she pre-sold 50% of her anticipated harvest, up from the 30% she usually pre-sells at this time of year.
“I’m pretty happy. As long as someone is buying it, I don’t care who.”
GLOBAL MULTILATERAL AGRIBUSINESS OLIGOPOLIES
Global canola oil demand has prompted Canadian crushers – who include Archer Daniels Midland Co and Bunge Ltd – to process canola at a brisk pace, said Brian Comeault, commodity risk manager with Cargill Ltd’s Canadian marketing service MarketSense.
Exporters are also selling more seed to the UAE, where crushers produce oil to sell to China, he said.
Bad crop weather and insect attacks in Europe have also lifted prices.
Rapeseed production in the European Union and Britain is expected near the 13-year low seen in 2019.
CANOLA WAS ONCE RAPESEED BUT TODAY IT IS A GMO (R)(TM)
SO IT'S CALLED CANOLA (C)(R)(TM)
This has led European importers to scour other countries for supplies, especially those with weaker currencies that make purchases more profitable, consultancy Strategie Grains said in a report.
“Canadian canola has the biggest edge,” it said. “Competition among importing countries will probably be fierce over the coming months.” ($1 = 1.3387 Canadian dollars)
(Reporting by Rod Nickel in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Hallie Gu in Beijing, Gus Trompiz in Paris and Michael Hogan in Hamburg Editing by Marguerita Choy)
STUPIDEST IDEA EVER
Edmonton’s Mask Exemption Cards And ‘Honour System’ Met With Criticism
The city is not asking people to explain why they need the cards or keeping track of who has one.
By Melanie Woods

TWITTER/@VANESAFLYNN_One of the "mask exemption" cards being distributed by the City of Edmonton.
YOU IMMEDIATELY BREAK SOCIAL DISTANCING WHEN BEING HANDED THE CARD OR BEING THE GIVER OF THE CARD!!!
As cities across Canada introduce mandatory indoor mask bylaws to fight the spread of COVID-19, many people are adjusting to the new normal of wearing masks to the grocery store, mall or library.
But Edmonton residents who aren’t comfortable wearing a mask now have another option in the form of “mask exemption” cards. Unlike fake cards distributed by conspiracy theorists and anti-mask groups, these ones come with the city’s official endorsement.
The cards are orange and roughly the size and shape of a standard business card. “I cannot wear a mask or face covering,” they read, alongside the City of Edmonton logo.
WATCH: Can you be medically exempt from wearing a mask? Story continues below.
They’re part of the city’s indoor mask plan introduced earlier this month. The bylaw requires masks or face coverings inside all public indoor spaces such as grocery stores, malls and libraries in the city. But cardholders are exempt.
“If someone identifies as having some type of ailment, for example, that would limit their ability to wear a mask effectively or be detrimental to their health, they can get these cards that are now being issued,” city councillor Jon Dziadyk told HuffPost Canada. “It’s an official document from the City of Edmonton.”
The goal of the cards is to give people a way to acknowledge their inability to wear a mask if they are challenged in a city business or indoor space where it’s required.
Thousands of cards are being distributed by city staff at recreation centres across the city. Dziadyk said residents don’t have to justify or explain their reason for needing one, and that the program relies on the “honour system.”
RELATED
No, Most Masks Will Not Reduce Your Oxygen Intake
“People can come up, and request a card and they can volunteer the reasons why they’re exempt, but they’re not going to be pressed into explaining a medical reason,” he said. “It would be hard to have an exhaustive list of reasons for people being exempted.”
Dziadyk cited many reasons people may not be able to wear a face covering, including breathing issues, anxiety or religious reasons. He said over 1,000 cards have been handed out since the program launched Saturday.
But Dziadyk also acknowledged the public has been divided on the program.
“It’s not a perfectly administered program — I get that,” he said.
Critics have pointed to the “honour system” method of distributing the cards, suggesting that it could be easily exploited and essentially makes the mandatory mask bylaw “useless.”
You are creating more tension, not alleviating it. These should be issued by medical doctors if there are legitimate medical reasons. (<0 .5="" a="" href="https://twitter.com/CityofEdmonton?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw" of="" population="">@CityofEdmonton
staff can not evaluate legitimacy of requests and have now been placed in a difficult position. #yegcc— Sue Huff (@suehuff) August 9, 2020
Jon, I know you’re an advocate of business and small biz in #yeg, so why would you advocate for this? This just made the mask bylaw ineffective. Most small businesses wanted this bylaw.— Cherie Klassen 🏳️🌈🐶🚠 (@cherlk) August 9, 2020
This still puts so much responsibility on each business employee to monitor this. We see convenience store employees who usually work alone already overwhelmed and don’t confront the patrons. Just like the bus drivers don’t argue about not having fares.— LaraWearAMaskZorro (@LaraPinchbeck) August 8, 2020
As a person with a compromised immune system, I felt safe to go out for the first time in ages because of the level of compliance. Thanks for providing a loophole for *ssholes.— William Briar (@WilliamBriar) August 8, 2020
There’s also the issue of the various “non-official” mask exemption cards that have been circulating across Canada in recent months.
In mid-July, images circulated online of fake “mask exemption” cards bearing the Canadian Red Cross logo. The humanitarian organizations has listed “mask exemption cards” on its website on a list of misinformation hoaxes, adding that it is not at all involved in issuing medical mask exemption cards.
Ontario Premier Doug Ford condemned the fake cards.
“This isn’t the time to put up fraudulent cards to get away and be able to go into a store,” said Ford. “Just be responsible, don’t be a scammer.”
Far-right media organization Rebel Media is also selling “mask exemption cards”, which specifically reference Toronto’s local mask bylaw, for $10 on its website.
Dziadyk said if there’s evidence the cards are being abused, city council can amend the bylaw. He said the City of Edmonton is working with local businesses to spread awareness about how to identify the legitimate Edmonton cards.
“I hope that the sort of official look would distinguish [the Edmonton cards] from [...] illegitimate cards, non-official cards,” Dziadyk said.
He said Edmonton city council will be meeting later this week to discuss the mask bylaw and other COVID-19 measures.
I hope that the sort of official look would distinguish [the Edmonton cards] from [...] illegitimate cards, non-official cards.Edmonton city councillor Jon Dziadyk
But even the “official” card won’t get you everywhere in Edmonton. On Friday, a ministerial order clarified Transport Canada’s rules around masks when flying. A passenger must provide a legitimate doctor’s note in order to be exempt from wearing a mask on an airplane.
According to WestJet, if travellers want to fly without a mask, they must provide a medical note that:
has been issued by a medical professional.
is on official letterhead.
is dated.
clearly states the passenger’s name and that they have a medical condition that prevents them from wearing a mask.
In the wake of news about Edmonton’s mask exemption cards, the airline doubled down on its stance Monday.
In support of @Transport_gc's interim order, effective Aug 11 any guest who is unable to wear a mask due to a medical condition must present an official medical note from a physician specifying their exemption to the regulation to be permitted to fly. https://t.co/TFU2HCAfdQpic.twitter.com/P5NzUXVKUH— WestJet (@WestJet) August 10, 2020
Passengers without an official doctor’s note will be denied boarding.
Melanie WoodsAssociate Editor, HuffPost Canada
Edmonton’s Mask Exemption Cards And ‘Honour System’ Met With Criticism
The city is not asking people to explain why they need the cards or keeping track of who has one.
AND HANDING THEM OUT AT PUBLIC AND PRIVATE GYMS!!!
CALL 311 AND TELL THEM NO
CALL 311 AND TELL THEM NO
OR CONTACT THE MAYOR AND CITY COUNCIL
DIRECTLY SEE BOTTOM OF PAGE FOR CONTACTS
NO ONE SHOULD BE EXEMPT!!
COVID-19
Effective August 1, 2020, wearing a mask or face covering will be mandatory in all indoor public places and public vehicles. Learn more at edmonton.ca/COVID-19.
DIRECTLY SEE BOTTOM OF PAGE FOR CONTACTS
NO ONE SHOULD BE EXEMPT!!
COVID-19
Effective August 1, 2020, wearing a mask or face covering will be mandatory in all indoor public places and public vehicles. Learn more at edmonton.ca/COVID-19.
By Melanie Woods

TWITTER/@VANESAFLYNN_One of the "mask exemption" cards being distributed by the City of Edmonton.
YOU IMMEDIATELY BREAK SOCIAL DISTANCING WHEN BEING HANDED THE CARD OR BEING THE GIVER OF THE CARD!!!
As cities across Canada introduce mandatory indoor mask bylaws to fight the spread of COVID-19, many people are adjusting to the new normal of wearing masks to the grocery store, mall or library.
But Edmonton residents who aren’t comfortable wearing a mask now have another option in the form of “mask exemption” cards. Unlike fake cards distributed by conspiracy theorists and anti-mask groups, these ones come with the city’s official endorsement.
The cards are orange and roughly the size and shape of a standard business card. “I cannot wear a mask or face covering,” they read, alongside the City of Edmonton logo.
WATCH: Can you be medically exempt from wearing a mask? Story continues below.
They’re part of the city’s indoor mask plan introduced earlier this month. The bylaw requires masks or face coverings inside all public indoor spaces such as grocery stores, malls and libraries in the city. But cardholders are exempt.
“If someone identifies as having some type of ailment, for example, that would limit their ability to wear a mask effectively or be detrimental to their health, they can get these cards that are now being issued,” city councillor Jon Dziadyk told HuffPost Canada. “It’s an official document from the City of Edmonton.”
The goal of the cards is to give people a way to acknowledge their inability to wear a mask if they are challenged in a city business or indoor space where it’s required.
Thousands of cards are being distributed by city staff at recreation centres across the city. Dziadyk said residents don’t have to justify or explain their reason for needing one, and that the program relies on the “honour system.”
RELATED
No, Most Masks Will Not Reduce Your Oxygen Intake
“People can come up, and request a card and they can volunteer the reasons why they’re exempt, but they’re not going to be pressed into explaining a medical reason,” he said. “It would be hard to have an exhaustive list of reasons for people being exempted.”
Dziadyk cited many reasons people may not be able to wear a face covering, including breathing issues, anxiety or religious reasons. He said over 1,000 cards have been handed out since the program launched Saturday.
But Dziadyk also acknowledged the public has been divided on the program.
“It’s not a perfectly administered program — I get that,” he said.
Critics have pointed to the “honour system” method of distributing the cards, suggesting that it could be easily exploited and essentially makes the mandatory mask bylaw “useless.”
You are creating more tension, not alleviating it. These should be issued by medical doctors if there are legitimate medical reasons. (<0 .5="" a="" href="https://twitter.com/CityofEdmonton?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw" of="" population="">@CityofEdmonton
Jon, I know you’re an advocate of business and small biz in #yeg, so why would you advocate for this? This just made the mask bylaw ineffective. Most small businesses wanted this bylaw.— Cherie Klassen 🏳️🌈🐶🚠 (@cherlk) August 9, 2020
This still puts so much responsibility on each business employee to monitor this. We see convenience store employees who usually work alone already overwhelmed and don’t confront the patrons. Just like the bus drivers don’t argue about not having fares.— LaraWearAMaskZorro (@LaraPinchbeck) August 8, 2020
As a person with a compromised immune system, I felt safe to go out for the first time in ages because of the level of compliance. Thanks for providing a loophole for *ssholes.— William Briar (@WilliamBriar) August 8, 2020
There’s also the issue of the various “non-official” mask exemption cards that have been circulating across Canada in recent months.
In mid-July, images circulated online of fake “mask exemption” cards bearing the Canadian Red Cross logo. The humanitarian organizations has listed “mask exemption cards” on its website on a list of misinformation hoaxes, adding that it is not at all involved in issuing medical mask exemption cards.
Ontario Premier Doug Ford condemned the fake cards.
“This isn’t the time to put up fraudulent cards to get away and be able to go into a store,” said Ford. “Just be responsible, don’t be a scammer.”
Far-right media organization Rebel Media is also selling “mask exemption cards”, which specifically reference Toronto’s local mask bylaw, for $10 on its website.
Dziadyk said if there’s evidence the cards are being abused, city council can amend the bylaw. He said the City of Edmonton is working with local businesses to spread awareness about how to identify the legitimate Edmonton cards.
“I hope that the sort of official look would distinguish [the Edmonton cards] from [...] illegitimate cards, non-official cards,” Dziadyk said.
He said Edmonton city council will be meeting later this week to discuss the mask bylaw and other COVID-19 measures.
I hope that the sort of official look would distinguish [the Edmonton cards] from [...] illegitimate cards, non-official cards.Edmonton city councillor Jon Dziadyk
But even the “official” card won’t get you everywhere in Edmonton. On Friday, a ministerial order clarified Transport Canada’s rules around masks when flying. A passenger must provide a legitimate doctor’s note in order to be exempt from wearing a mask on an airplane.
According to WestJet, if travellers want to fly without a mask, they must provide a medical note that:
has been issued by a medical professional.
is on official letterhead.
is dated.
clearly states the passenger’s name and that they have a medical condition that prevents them from wearing a mask.
In the wake of news about Edmonton’s mask exemption cards, the airline doubled down on its stance Monday.
In support of @Transport_gc's interim order, effective Aug 11 any guest who is unable to wear a mask due to a medical condition must present an official medical note from a physician specifying their exemption to the regulation to be permitted to fly. https://t.co/TFU2HCAfdQpic.twitter.com/P5NzUXVKUH— WestJet (@WestJet) August 10, 2020
Passengers without an official doctor’s note will be denied boarding.
Melanie WoodsAssociate Editor, HuffPost Canada
YOU CAN EMAIL THE MAYOR AND COUNCILLORS VIA THE CITY CLERK EMAIL
For More Information
Office of the City Clerk
3rd floor, City Hall
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB T5J 2R7
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB T5J 2R7
| Telephone |
780-496-8178
|
|---|---|
| Fax | 780-496-8175 |
| city.clerk@edmonton.ca |
Office of the Councillors
2nd Floor, City Hall
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB T5J 2R7
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB T5J 2R7
| Telephone |
780-496-8110
|
|---|---|
| Fax | 780-496-8113 |
Office of the Mayor
2nd Floor, City Hall
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB
T5J 2R7
1 Sir Winston Churchill Square
Edmonton, AB
T5J 2R7
| Telephone |
780-496-8100
|
|---|---|
| Fax | 780-496-8292 |
The seven years of neglect, and 13 minutes of chaos, that destroyed Beirut
Special report: Speaking to Lebanese port officials, government sources, firefighters and eyewitnesses, and reviewing a dozen documents, Bel Trew, Oliver Carroll, Samira el-Azar and Richard Hall trace the paper trail of negligence and incompetence that led up to the devastating explosion
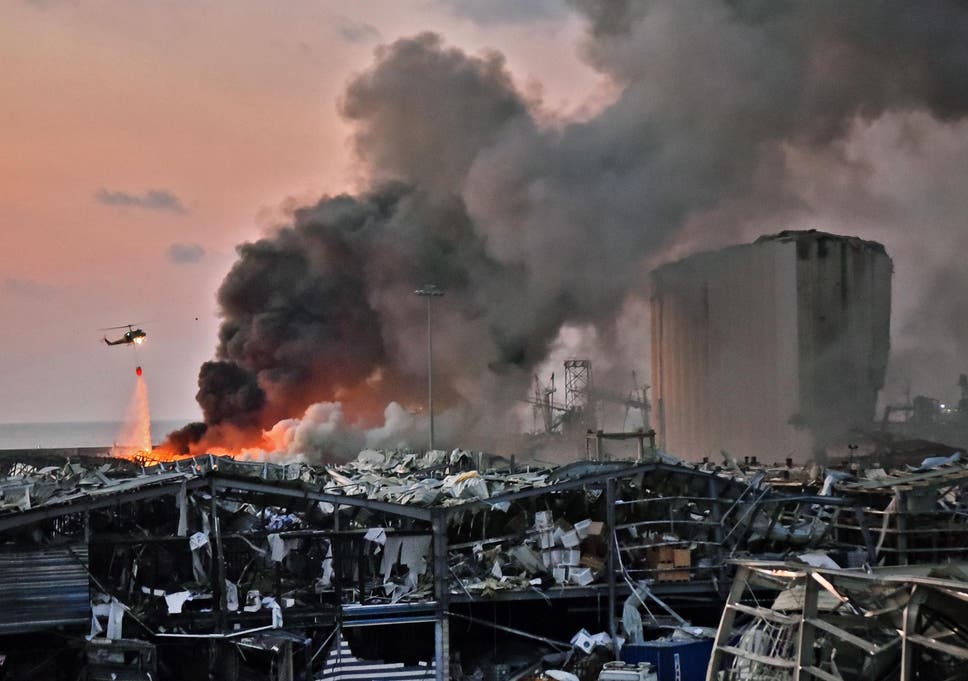

A helicopter puts out a fire at the scene of the explosion at the port of Lebanon’s capital ( AFP/Getty )
The Independent employs reporters around the world to bring you truly independent journalism. To support us, please consider a contribution.
Residents across central Beirut were peering quizzically at a mushroom cloud of grey above their heads when the sky cracked open and a tidal wave of pressure roared through.
It was like sound itself had imploded in everyone’s ears. The world simultaneously broke apart and snapped shut. Bodies were pulled into the air and thrown across rooms and streets. The facades of apartment blocks, offices and hospitals were peeled off and chewed into pieces.
The explosion unleashed warring tornadoes of pressure that wrestled everything off the walls and the floors, spitting shrapnel that cut through the air like bullets. The power of the blast instantly eviscerated windows, smacked down buildings, crumpled steel shutters and crushed cars like a giant’s fist.
“It was like an atomic bomb,” says Hala Okeili, 33, a yoga instructor who was less than a mile away from the port when disaster struck. “I thought they had started a war and someone was bombing us.”
The blast, which struck the Lebanese capital around 6.08pm on Tuesday, is being called one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in modern history. It killed at least 210 people, and injured 6,000 more. Dozens are still missing.
Investigations into what happened and who is responsible are underway: initial analysis points to nearly 3,000 tons of dangerously stored explosive ammonium nitrate catching on fire.
Watch more

Special report: Speaking to Lebanese port officials, government sources, firefighters and eyewitnesses, and reviewing a dozen documents, Bel Trew, Oliver Carroll, Samira el-Azar and Richard Hall trace the paper trail of negligence and incompetence that led up to the devastating explosion

A helicopter puts out a fire at the scene of the explosion at the port of Lebanon’s capital ( AFP/Getty )
The Independent employs reporters around the world to bring you truly independent journalism. To support us, please consider a contribution.
Residents across central Beirut were peering quizzically at a mushroom cloud of grey above their heads when the sky cracked open and a tidal wave of pressure roared through.
It was like sound itself had imploded in everyone’s ears. The world simultaneously broke apart and snapped shut. Bodies were pulled into the air and thrown across rooms and streets. The facades of apartment blocks, offices and hospitals were peeled off and chewed into pieces.
The explosion unleashed warring tornadoes of pressure that wrestled everything off the walls and the floors, spitting shrapnel that cut through the air like bullets. The power of the blast instantly eviscerated windows, smacked down buildings, crumpled steel shutters and crushed cars like a giant’s fist.
“It was like an atomic bomb,” says Hala Okeili, 33, a yoga instructor who was less than a mile away from the port when disaster struck. “I thought they had started a war and someone was bombing us.”
The blast, which struck the Lebanese capital around 6.08pm on Tuesday, is being called one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in modern history. It killed at least 210 people, and injured 6,000 more. Dozens are still missing.
Investigations into what happened and who is responsible are underway: initial analysis points to nearly 3,000 tons of dangerously stored explosive ammonium nitrate catching on fire.
Watch more

Entire Lebanon government resigns amid fury over explosion
A review of a dozen documents as well as interviews with Lebanese port officials, government sources, firefighters and eyewitnesses showed enormous incompetence in both the seven years leading up to the blast and the final 13 minutes before the city was destroyed.
Since 2014 authorities had so often warned about the dangerous nature of the materials being stored at the port that it became common practice to avoid Hangar 12, where the ammonium nitrate was being stored. Port officials may have even left the scene before they could brief first responders about the nature of the substances.
The firefighters, all of them thought to have died in the blast, arrived with inadequate provisions to put out the smouldering fire which may have started with fireworks.
The need for answers as to why it happened is urgent.
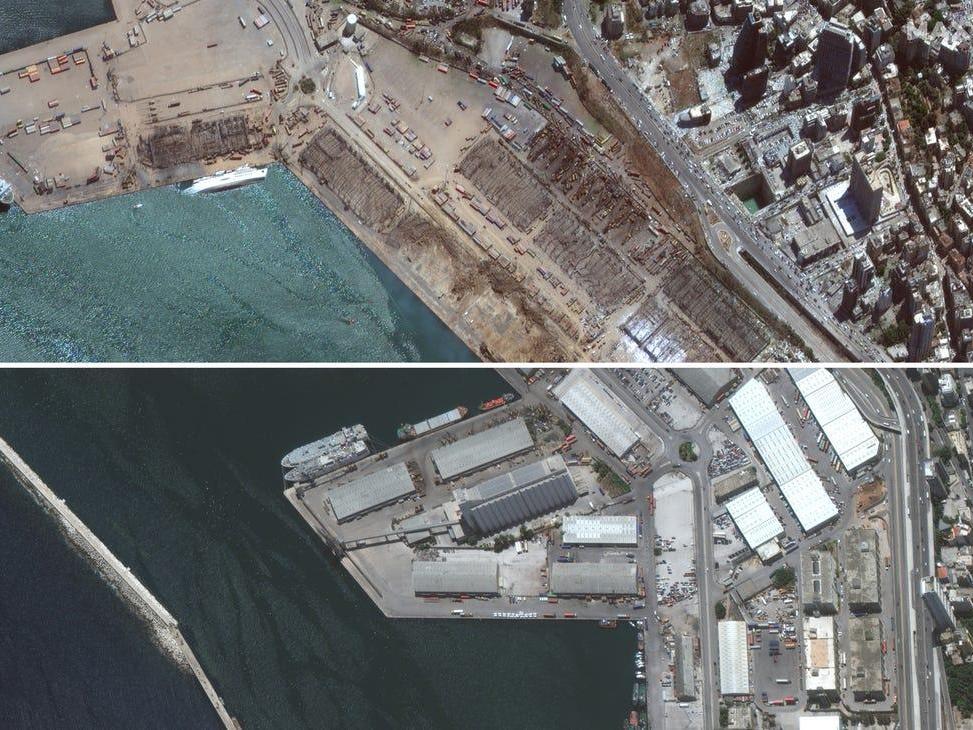

Beirut port, before and after Tuesday’s explosion (Maxar Technologies)
The boat that was lost
None of the crew aboard the Russian-owned ship would have guessed seven years ago that their journey, which started in the Black Sea, would ultimately end with the decimation of the Lebanese capital of Beirut more than 1,000km away.
The story began on 23 September 2013. The Rhosus, a 27-year-old cargo ship, set sail from the Georgian port of Batumi with a 2750-ton cargo of ammonium nitrate, an explosive substance frequently used in fertilisers and bombs.
The ship was never supposed to dock in Beirut. A landing docket given to The Independent shows the intended end recipient was an explosives company in Mozambique.
The vessel’s origins are shadowy, like much in the global shipping industry. It was managed by a company registered in the Marshall Islands, and set sail under a Moldovan flag. It was controlled by a small-scale Russian businessman and Cyprus resident named Igor Grechushkin, according to documents reviewed by The Independent.
Russian citizen Boris Prokoshev eventually took charge of the vessel when it made a stop in Tuzla, Turkey.
Trouble was already brewing aboard the ship.
Captain Prokoshev and crew members demand their release from the arrested cargo vessel in 2014 (Reuters)
Captain Prokoshev was greeted by an entirely new Ukrainian crew after the old one unexpectedly stormed out because they had not been paid for four months.
But it was only when the Prokoshev finally met the owner in Pireaus, Greece, during an October fuel stop, that he began to understand the scale of Grechushkin’s financial problems.
“It was bizarre – after first signing off on the supplies, he then refused to pay for two-thirds of them,” Prokoshev tells The Independent. “Then he ordered us to make an additional stop in Beirut to pick up another consignment.”
The Rhosus set sail for Beirut on 15 November and arrived, in the captain’s estimation, approximately four days later. The exact circumstances before landing are disputed. According to lawyers acting for creditors of the vessel, the Rhosus experienced technical problems forcing it to enter the port, where it then failed a safety inspection.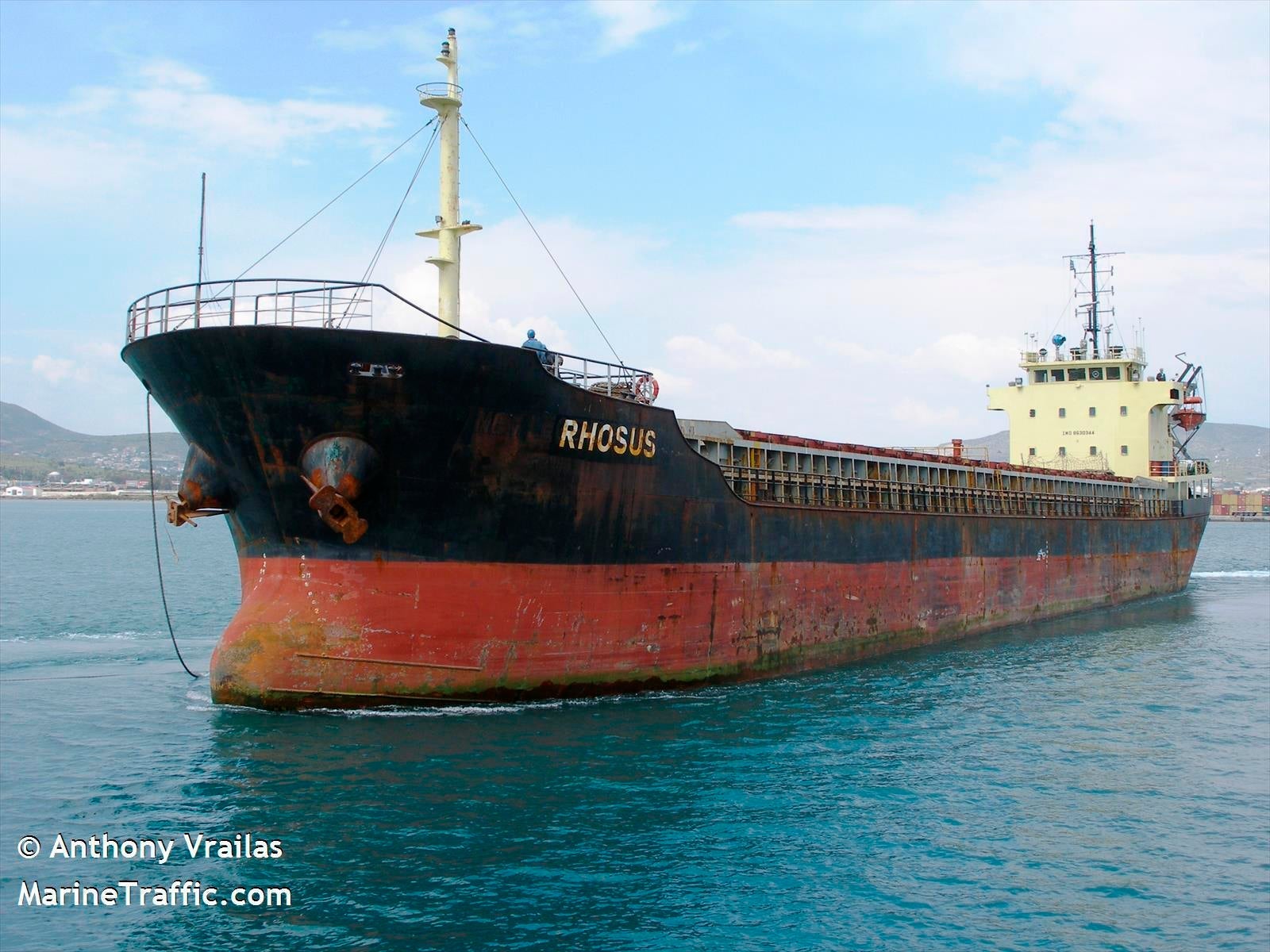
The Rhosus is seen in Volos, Greece (AP)
But Prokoshev tells The Independent he was able to dock in Beirut to take on an extra load of heavy road-making equipment, which he eventually decided could not safely be stowed onboard. Following a “heated” discussion with Grechushkin, the captain agreed to travel on to Larnaca in Cyprus.
But by this point, Lebanese port officials were demanding unpaid fines and port fees, and refused to let them leave. In Prokoshev’s account, Grechushkin then made a decision to “abandon” the ship and its 10-man crew to their fate. Some time in late November, Lebanese authorities impounded the vessel.
The crew quickly ran out of provisions. “If it wasn’t for our Beirut agent, we’d have starved,” Prokoshev tells The Independent.
‘Dangerous’ cargo left behind
After months of furious lobbying by Ukranian diplomats, the majority of the Rhosus crew was allowed to return home in early 2014. But Prokoshev and a skeleton staff were kept on, effectively held hostage by Lebanese authorities as they worked out what to do with the ship.
The captain was even forced to sell off the fuel to pay for lawyers, who applied for the crew’s release on “compassionate grounds”. A Lebanese court eventually agreed, but only after taking consideration of the “imminent danger the crew was facing given the nature of the cargo”.
By the time of their release, the crew was owed over $240,000 (£190,600) in unpaid wages.
The Lebanese authorities knew from the very start just how volatile the shipment was. The next six years were marked by numerous warnings that could have averted disaster had they been acted upon. Instead, a toxic mix of corruption and mismanagement that plagues every public institution in Lebanon paved the way for tragedy.
Read more

A review of a dozen documents as well as interviews with Lebanese port officials, government sources, firefighters and eyewitnesses showed enormous incompetence in both the seven years leading up to the blast and the final 13 minutes before the city was destroyed.
Since 2014 authorities had so often warned about the dangerous nature of the materials being stored at the port that it became common practice to avoid Hangar 12, where the ammonium nitrate was being stored. Port officials may have even left the scene before they could brief first responders about the nature of the substances.
The firefighters, all of them thought to have died in the blast, arrived with inadequate provisions to put out the smouldering fire which may have started with fireworks.
The need for answers as to why it happened is urgent.

Beirut port, before and after Tuesday’s explosion (Maxar Technologies)
The boat that was lost
None of the crew aboard the Russian-owned ship would have guessed seven years ago that their journey, which started in the Black Sea, would ultimately end with the decimation of the Lebanese capital of Beirut more than 1,000km away.
The story began on 23 September 2013. The Rhosus, a 27-year-old cargo ship, set sail from the Georgian port of Batumi with a 2750-ton cargo of ammonium nitrate, an explosive substance frequently used in fertilisers and bombs.
The ship was never supposed to dock in Beirut. A landing docket given to The Independent shows the intended end recipient was an explosives company in Mozambique.
The vessel’s origins are shadowy, like much in the global shipping industry. It was managed by a company registered in the Marshall Islands, and set sail under a Moldovan flag. It was controlled by a small-scale Russian businessman and Cyprus resident named Igor Grechushkin, according to documents reviewed by The Independent.
Russian citizen Boris Prokoshev eventually took charge of the vessel when it made a stop in Tuzla, Turkey.
Trouble was already brewing aboard the ship.

Captain Prokoshev and crew members demand their release from the arrested cargo vessel in 2014 (Reuters)
Captain Prokoshev was greeted by an entirely new Ukrainian crew after the old one unexpectedly stormed out because they had not been paid for four months.
But it was only when the Prokoshev finally met the owner in Pireaus, Greece, during an October fuel stop, that he began to understand the scale of Grechushkin’s financial problems.
“It was bizarre – after first signing off on the supplies, he then refused to pay for two-thirds of them,” Prokoshev tells The Independent. “Then he ordered us to make an additional stop in Beirut to pick up another consignment.”
The Rhosus set sail for Beirut on 15 November and arrived, in the captain’s estimation, approximately four days later. The exact circumstances before landing are disputed. According to lawyers acting for creditors of the vessel, the Rhosus experienced technical problems forcing it to enter the port, where it then failed a safety inspection.

The Rhosus is seen in Volos, Greece (AP)
But Prokoshev tells The Independent he was able to dock in Beirut to take on an extra load of heavy road-making equipment, which he eventually decided could not safely be stowed onboard. Following a “heated” discussion with Grechushkin, the captain agreed to travel on to Larnaca in Cyprus.
But by this point, Lebanese port officials were demanding unpaid fines and port fees, and refused to let them leave. In Prokoshev’s account, Grechushkin then made a decision to “abandon” the ship and its 10-man crew to their fate. Some time in late November, Lebanese authorities impounded the vessel.
The crew quickly ran out of provisions. “If it wasn’t for our Beirut agent, we’d have starved,” Prokoshev tells The Independent.
‘Dangerous’ cargo left behind
After months of furious lobbying by Ukranian diplomats, the majority of the Rhosus crew was allowed to return home in early 2014. But Prokoshev and a skeleton staff were kept on, effectively held hostage by Lebanese authorities as they worked out what to do with the ship.
The captain was even forced to sell off the fuel to pay for lawyers, who applied for the crew’s release on “compassionate grounds”. A Lebanese court eventually agreed, but only after taking consideration of the “imminent danger the crew was facing given the nature of the cargo”.
By the time of their release, the crew was owed over $240,000 (£190,600) in unpaid wages.
The Lebanese authorities knew from the very start just how volatile the shipment was. The next six years were marked by numerous warnings that could have averted disaster had they been acted upon. Instead, a toxic mix of corruption and mismanagement that plagues every public institution in Lebanon paved the way for tragedy.
Read more

World leaders pledge €250m to help Lebanon after Beirut explosion
The first warning was raised before the cargo was even offloaded in an internal memo dated February 2014 and seen by The Independent.
In it Colonel Joseph Skaf, head of the Lebanese narcotics control division, warned Beirut’s anti-smuggling department that the material was “highly dangerous and a threat to public safety”.
Baroudi & Associates, which represented the Russian vessel’s crew, reportedly sent letters in July 2014 to officials at Beirut port and the ministry of transportation “warning of the dangers of the materials carried on the ship”.
In the end shortly after the crew’s departure from Lebanon, the dangerous cargo was transferred to warehouse number 12.
The Rhosus, without crew or an owner, would remain in Beirut’s docks before sinking “two or three years later”.
For Prokoshev it was the end of a nightmare, and an event he had long shelved in his mind, until news broke of the blast last week. For the citizens of Beirut this would mark the start of theirs.
A damning paper trail
Six years on, it was common knowledge in Beirut’s port that Hangar 12 was “dangerous”, port employees told The Independent.
Not everyone knew exactly what was inside. The rank and file believed it housed confiscated weapons. People steered clear.
At the official level, the contents of the hangar were very well known. In fact concerns about the stockpile were raised at least eight times since 2014, according to documents seen by The Independent and interviews with officials.
Fireworks were even moved into the hangar, despite the dangers, according to one port source.
The paper trail is damning.
In a letter dated 20 May 2016, the then head of the customs department Shafik Merhi wrote to a judge at the Urgent Matters Court asking for permission to sell or export the dangerous stockpile to a Lebanese company. He mentions that it was jeopardising the safety of the port and the workers.
A year later in a 28 October 2017 letter to the same court, Badri Daher, the new head of the customs department, repeats the same plea.
In this communique, seen by The Independent, he writes that it follows similar letters sent in 2014, 2015, twice in 2016 and earlier in 2017. Shortly before his arrest, Daher, who is among more than a dozen port officials currently under investigation, said he received no proper instructions of what to do.
In December 2019, the State Security requested an investigation into dangerous substances in Hangar 12 and completed its findings in January. It informed the presidency and the prime minister a few months later.
President Michel Aoun admitted that nearly three weeks before the blast – on 20 June – he was handed that report and informed that the dangerous material had been there for seven years.
He said he immediately ordered the military and security officials “to do what is needed”.
Prime Minister Hassan Diab, whose government resigned on Monday, received the same letter on the same day and sent it on to the Supreme Defence Council for advice within 48 hours.
But still nothing was done.
The matter was even raised just 11 days before the blast when the public works minister, Michel Najjar, told Al Jazeera he first learnt about the dangerous stockpile.
Because of a new coronavirus lockdown in place at the time, Najjar said there was a short delay and so he spoke to the port’s general manager, Hassan Koraytem, about the matter on the Monday 24 hours before the blast.
The port manager said he would send all the relevant documentation so everyone could look into the matter. But it was too late.
Thirteen minutes that sealed the city’s fate
On the afternoon of Tuesday 4 August, port electrician Joe Akiki, 23, called his mother to say he was starting the night shift.
Most of the port workers clock off at 4pm each day. And so there were comparatively few people on the ground when, a few hours later, a fire started.
Shortly before 6pm local time, Akiki stood on the roof of a building which was part of Beirut’s imposing grain silo. He started filming black smoke billowing out of warehouse 12, which was about 40m away in front of him.
In the clip, the camera pans across left to right across the battered hangar. Faint sirens, perhaps belonging to the incoming fire crew, can be heard sounding in the background.
Joe Akiki films the burning warehouse from on top of the silo minutes before the blast
Around the same time, at 5:55pm, a member of the fire department operations room just east of the port received a call from the Beirut police department saying there was a fire in one of the warehouses.
Fires at the port are not uncommon, he told The Independent. But the way it was reported and handled was unusual. The fire department employee who received the call said no one mentioned ammonium nitrate or explained to them which hangar was affected.
A 10-person team – nine male firefighters and female paramedic – was dispatched to the scene arriving just two minutes later.
There, unusually, there was no port crew to greet them, show them the site and hand them the key. It took them some time to work out the location of the fire.
Fire department officials told The Independent had they known the contents of the warehouse and its location or even been given a key, they would have had more time to assess the danger and the contents of the hanger, possibly put out the initial fire, order an evacuation or just scramble to safety.
Instead the firefighters wasted precious minutes that could have saved lives – their lives – trying to locate and break into the warehouse.
“Each minute counts in our work. If they just had more information,” said fire department chief Fadi Mazboudi.
At some point an unknown person, likely a port worker, began filming from the exact same spot where Akiki was standing. The clip that was shared online and verified by Bellingcat shows the smoke thickening to a deep charcoal. The crackle of dozens of what appear to be fireworks can be heard, popping in time with bright white and red sparks.
The person filming begins to retreat from the fire as it grows. A man screams as a large explosion sends them scrambling across the roof.
Across town, just before 6pm, that initial blast was heard by many residents who took to social media to tweet pictures of the column of smoke towering in the sky.
As the minutes trickled by more people came out of their homes, businesses, and shops, or looked out their window to find out what was going on.
Just 600m south of Hangar 12, Cherine el-Zein, an interior designer and activist, started filming the cloud above the port and telling people they should shut the doors and windows because of the smoke.
Cherine el-Zein films the moment the explosion destroys swathes of Beirut
A few minutes along Armenia Street to her right, Carmen Khoury, 46, a university administrator, stopped buying water and stepped out of the shop with a woman she did not know to look for fighter jets.
Back at Hanger 12, Sahar Fares, 27, the female medic accompanying the all-male fire crew had herself already started filming.
From the footage – broadcast by the BBC and verified by The Independent – it is possible to geolocate her to an area just below where Akiki was standing on top of the grain silo.
Her video shows the warehouse on fire, with her colleagues in uniform looking up at the burning building. She sent this clip to her fiance Gilbert Karaan at 6.03pm, according to Mazboudi. Worried, Gilbert spoke to her on the phone, urging her leave. He was still on the call when, disoriented, she started to run towards the grain silo.
A minute later at 6.04pm, Akiki, presumably scared and confused, sent his three-second clip with no explanation to a WhatsApp group chat: the last time his friends would ever hear from him.
By this point the firefighters realised the enormity of the situation that they had walked into blind. The fire was much bigger than they anticipated.
And so a few seconds before 6.08pm, firefighters Elia Khizami and Charbel Karam called their superiors demanding immediate back-up. They warned they only had “three tons of water” which wasn’t enough to control such a massive fire.
But before anyone within the fire department could scramble together a single piece of equipment, Hangar 12 detonated.
Fares was still on the phone to her fiance and running for safety when the line cut.
The sky above her imploded into a brilliant and billowing roar of orange and deep red, which set off a white ring of pressure consuming everything in its path.
The fire department employee who took the original phone call is thrown metres in the air in his office, which is ripped open.
For Carmen Khoury, just a few hundred metres away from the epicentre, it felt like hell had been unleashed.
“An iron rod swung down and knocked me off my feet. I found myself pinned under a car, with the woman beside me bleeding,” she says, describing the horrific moment.
“I have lived through two wars, and I have never experienced a blast quite like that. For a second I thought the world had come to an end.”
The city torn in two
For nearly one whole minute everything on Armenia street was quiet – in a kind of sharp inhalation of breath before the surge of pain.
Cherine el-Zein’s video capturing the moment is black; the only sounds heard are the hiss of gas and the persistent bleat of car alarms.
Then as people regain consciousness the screams start. The sirens begin.
“What just happened? My daughter is inside the shop, my daughter is inside the shop,” shouts one man in desperation. In the distance a woman says something incomprehensible and quietly whimpers.
Across Beirut, blood-soaked bodies staggered through the dust and smoke and glass and mess. Many asked themselves if a war had started.
View from the ocean of Beirut’s devastated port after warehouse explosion
Hala Okeili, who was approaching Armenia street in her car, says everything was instantly destroyed.
“Our neighbours, faces I recognised. Young people bleeding from every single part of their bodies.”
Citizens started making frantic phone calls to family members across the city. People report experiencing hour-long lapses in memory.
Medical workers at the nearest hospital St George, which was gutted by the blast, were forced to pull their own colleagues and patients from under the fallen masonry. With the emergency room destroyed, the generator broken and parts of the building structurally unsound, they started treating the newly injured in the car park with the light of their mobile phones.
Citizens on motorcycles began to ferry the shell-shocked injured, many hastily patched up by well-wishers, to hospitals outside the city, as those close to downtown Beirut were each capacity.
At the port, the explosion had clawed a 43m-deep crater, overturned cruise ships like beached whales, destroyed half of Lebanon’s main grain silo, and left just the rickety ribs of the warehouses.
Days later, rescue workers issued diminishing percentages of the likelihood of finding survivors there. Angry families gathered at the site demanding bulldozers check under the warehouses in case anyone made it an underground network of tunnels and store rooms.
In succession the bodies of Fares, Akiki and Khizami are found within the rubble, many of them incinerated and in pieces. But the rest of the team, including Karam, remain missing.
‘Hang up the nooses’
Very quickly in the aftermath of the blast, the shattered streets of Beirut begin to simmer with rage. Protesters armed with nooses demand accountability and help from their government whose officials are woefully absent in the rescue and clean-up operation manned by volunteers.
Among the crowds are Khoury and El-Zein, who protest despite having been hospitalised. The unidentified woman pinned under the car with Khoury doesn’t make it.
A nation’s grief turns to fury.
“There’s not one form of death they haven’t used with us,” says Sara Assaf, a Lebanese activist at one rally. She says this was no accident, but the result of years of endemic corruption at every level of public life by the country’s leaders.
“They killed us financially. They killed us economically. They killed us physically. They killed us morally. They killed us chemically.”
Since the explosion, everyone has passed the buck. President Aoun insisted on Friday he is not responsible, saying that he didn’t know where the ammonium nitrate was placed or “the level of danger”.
Watch more

The first warning was raised before the cargo was even offloaded in an internal memo dated February 2014 and seen by The Independent.
In it Colonel Joseph Skaf, head of the Lebanese narcotics control division, warned Beirut’s anti-smuggling department that the material was “highly dangerous and a threat to public safety”.
Baroudi & Associates, which represented the Russian vessel’s crew, reportedly sent letters in July 2014 to officials at Beirut port and the ministry of transportation “warning of the dangers of the materials carried on the ship”.
In the end shortly after the crew’s departure from Lebanon, the dangerous cargo was transferred to warehouse number 12.
The Rhosus, without crew or an owner, would remain in Beirut’s docks before sinking “two or three years later”.
For Prokoshev it was the end of a nightmare, and an event he had long shelved in his mind, until news broke of the blast last week. For the citizens of Beirut this would mark the start of theirs.
A damning paper trail
Six years on, it was common knowledge in Beirut’s port that Hangar 12 was “dangerous”, port employees told The Independent.
Not everyone knew exactly what was inside. The rank and file believed it housed confiscated weapons. People steered clear.
At the official level, the contents of the hangar were very well known. In fact concerns about the stockpile were raised at least eight times since 2014, according to documents seen by The Independent and interviews with officials.
Fireworks were even moved into the hangar, despite the dangers, according to one port source.
The paper trail is damning.
In a letter dated 20 May 2016, the then head of the customs department Shafik Merhi wrote to a judge at the Urgent Matters Court asking for permission to sell or export the dangerous stockpile to a Lebanese company. He mentions that it was jeopardising the safety of the port and the workers.
A year later in a 28 October 2017 letter to the same court, Badri Daher, the new head of the customs department, repeats the same plea.
In this communique, seen by The Independent, he writes that it follows similar letters sent in 2014, 2015, twice in 2016 and earlier in 2017. Shortly before his arrest, Daher, who is among more than a dozen port officials currently under investigation, said he received no proper instructions of what to do.
In December 2019, the State Security requested an investigation into dangerous substances in Hangar 12 and completed its findings in January. It informed the presidency and the prime minister a few months later.
President Michel Aoun admitted that nearly three weeks before the blast – on 20 June – he was handed that report and informed that the dangerous material had been there for seven years.
He said he immediately ordered the military and security officials “to do what is needed”.
Prime Minister Hassan Diab, whose government resigned on Monday, received the same letter on the same day and sent it on to the Supreme Defence Council for advice within 48 hours.
But still nothing was done.
The matter was even raised just 11 days before the blast when the public works minister, Michel Najjar, told Al Jazeera he first learnt about the dangerous stockpile.
Because of a new coronavirus lockdown in place at the time, Najjar said there was a short delay and so he spoke to the port’s general manager, Hassan Koraytem, about the matter on the Monday 24 hours before the blast.
The port manager said he would send all the relevant documentation so everyone could look into the matter. But it was too late.
Thirteen minutes that sealed the city’s fate
On the afternoon of Tuesday 4 August, port electrician Joe Akiki, 23, called his mother to say he was starting the night shift.
Most of the port workers clock off at 4pm each day. And so there were comparatively few people on the ground when, a few hours later, a fire started.
Shortly before 6pm local time, Akiki stood on the roof of a building which was part of Beirut’s imposing grain silo. He started filming black smoke billowing out of warehouse 12, which was about 40m away in front of him.
In the clip, the camera pans across left to right across the battered hangar. Faint sirens, perhaps belonging to the incoming fire crew, can be heard sounding in the background.
Joe Akiki films the burning warehouse from on top of the silo minutes before the blast
Around the same time, at 5:55pm, a member of the fire department operations room just east of the port received a call from the Beirut police department saying there was a fire in one of the warehouses.
Fires at the port are not uncommon, he told The Independent. But the way it was reported and handled was unusual. The fire department employee who received the call said no one mentioned ammonium nitrate or explained to them which hangar was affected.
A 10-person team – nine male firefighters and female paramedic – was dispatched to the scene arriving just two minutes later.
There, unusually, there was no port crew to greet them, show them the site and hand them the key. It took them some time to work out the location of the fire.
Fire department officials told The Independent had they known the contents of the warehouse and its location or even been given a key, they would have had more time to assess the danger and the contents of the hanger, possibly put out the initial fire, order an evacuation or just scramble to safety.
Instead the firefighters wasted precious minutes that could have saved lives – their lives – trying to locate and break into the warehouse.
“Each minute counts in our work. If they just had more information,” said fire department chief Fadi Mazboudi.
At some point an unknown person, likely a port worker, began filming from the exact same spot where Akiki was standing. The clip that was shared online and verified by Bellingcat shows the smoke thickening to a deep charcoal. The crackle of dozens of what appear to be fireworks can be heard, popping in time with bright white and red sparks.
The person filming begins to retreat from the fire as it grows. A man screams as a large explosion sends them scrambling across the roof.
Across town, just before 6pm, that initial blast was heard by many residents who took to social media to tweet pictures of the column of smoke towering in the sky.
As the minutes trickled by more people came out of their homes, businesses, and shops, or looked out their window to find out what was going on.
Just 600m south of Hangar 12, Cherine el-Zein, an interior designer and activist, started filming the cloud above the port and telling people they should shut the doors and windows because of the smoke.
Cherine el-Zein films the moment the explosion destroys swathes of Beirut
A few minutes along Armenia Street to her right, Carmen Khoury, 46, a university administrator, stopped buying water and stepped out of the shop with a woman she did not know to look for fighter jets.
Back at Hanger 12, Sahar Fares, 27, the female medic accompanying the all-male fire crew had herself already started filming.
From the footage – broadcast by the BBC and verified by The Independent – it is possible to geolocate her to an area just below where Akiki was standing on top of the grain silo.
Her video shows the warehouse on fire, with her colleagues in uniform looking up at the burning building. She sent this clip to her fiance Gilbert Karaan at 6.03pm, according to Mazboudi. Worried, Gilbert spoke to her on the phone, urging her leave. He was still on the call when, disoriented, she started to run towards the grain silo.
A minute later at 6.04pm, Akiki, presumably scared and confused, sent his three-second clip with no explanation to a WhatsApp group chat: the last time his friends would ever hear from him.
By this point the firefighters realised the enormity of the situation that they had walked into blind. The fire was much bigger than they anticipated.
And so a few seconds before 6.08pm, firefighters Elia Khizami and Charbel Karam called their superiors demanding immediate back-up. They warned they only had “three tons of water” which wasn’t enough to control such a massive fire.
But before anyone within the fire department could scramble together a single piece of equipment, Hangar 12 detonated.
Fares was still on the phone to her fiance and running for safety when the line cut.
The sky above her imploded into a brilliant and billowing roar of orange and deep red, which set off a white ring of pressure consuming everything in its path.
The fire department employee who took the original phone call is thrown metres in the air in his office, which is ripped open.
For Carmen Khoury, just a few hundred metres away from the epicentre, it felt like hell had been unleashed.
“An iron rod swung down and knocked me off my feet. I found myself pinned under a car, with the woman beside me bleeding,” she says, describing the horrific moment.
“I have lived through two wars, and I have never experienced a blast quite like that. For a second I thought the world had come to an end.”
The city torn in two
For nearly one whole minute everything on Armenia street was quiet – in a kind of sharp inhalation of breath before the surge of pain.
Cherine el-Zein’s video capturing the moment is black; the only sounds heard are the hiss of gas and the persistent bleat of car alarms.
Then as people regain consciousness the screams start. The sirens begin.
“What just happened? My daughter is inside the shop, my daughter is inside the shop,” shouts one man in desperation. In the distance a woman says something incomprehensible and quietly whimpers.
Across Beirut, blood-soaked bodies staggered through the dust and smoke and glass and mess. Many asked themselves if a war had started.
View from the ocean of Beirut’s devastated port after warehouse explosion
Hala Okeili, who was approaching Armenia street in her car, says everything was instantly destroyed.
“Our neighbours, faces I recognised. Young people bleeding from every single part of their bodies.”
Citizens started making frantic phone calls to family members across the city. People report experiencing hour-long lapses in memory.
Medical workers at the nearest hospital St George, which was gutted by the blast, were forced to pull their own colleagues and patients from under the fallen masonry. With the emergency room destroyed, the generator broken and parts of the building structurally unsound, they started treating the newly injured in the car park with the light of their mobile phones.
Citizens on motorcycles began to ferry the shell-shocked injured, many hastily patched up by well-wishers, to hospitals outside the city, as those close to downtown Beirut were each capacity.
At the port, the explosion had clawed a 43m-deep crater, overturned cruise ships like beached whales, destroyed half of Lebanon’s main grain silo, and left just the rickety ribs of the warehouses.
Days later, rescue workers issued diminishing percentages of the likelihood of finding survivors there. Angry families gathered at the site demanding bulldozers check under the warehouses in case anyone made it an underground network of tunnels and store rooms.
In succession the bodies of Fares, Akiki and Khizami are found within the rubble, many of them incinerated and in pieces. But the rest of the team, including Karam, remain missing.
‘Hang up the nooses’
Very quickly in the aftermath of the blast, the shattered streets of Beirut begin to simmer with rage. Protesters armed with nooses demand accountability and help from their government whose officials are woefully absent in the rescue and clean-up operation manned by volunteers.
Among the crowds are Khoury and El-Zein, who protest despite having been hospitalised. The unidentified woman pinned under the car with Khoury doesn’t make it.
A nation’s grief turns to fury.
“There’s not one form of death they haven’t used with us,” says Sara Assaf, a Lebanese activist at one rally. She says this was no accident, but the result of years of endemic corruption at every level of public life by the country’s leaders.
“They killed us financially. They killed us economically. They killed us physically. They killed us morally. They killed us chemically.”
Since the explosion, everyone has passed the buck. President Aoun insisted on Friday he is not responsible, saying that he didn’t know where the ammonium nitrate was placed or “the level of danger”.
Watch more

Lebanon president admits knowing about explosive stockpile weeks ago
Port officials, before their arrests, had expressed similar sentiments, saying they warned the courts, which did nothing. Najjar told Al-Jazeera “no minister knows what’s in the hangars or containers, and it’s not my job to know”.
Hassan Diab, in his resignation speech on Monday, blamed the political elite and his predecessors for hiding the problem for seven years.
The obvious question is why nothing at any point was practically done.
Many have even questioned the little action that was taken: the letters written by the port officials.
One document shown to The Independent – dated June 2014 before the shipment was even unloaded – apparently shows an Urgent Matters Court judge telling port officials that his court did not have the jurisdiction to authorise the sale of the ship or its contents.
Beirut protesters stormed government buildings (EPA)
Investigative journalist Riad Kobeissi says this proves that all the subsequent letters were completely pointless, since the court could not authorise what the customs officials were ultimately asking: to resell or reimport the stockpile of ammonium nitrate.
“Why keep writing the same letter over and over again? Why didn’t they go immediately to the security forces or higher up and press for action all those years ago?” he asks.
The Independent spoke to port officials but they declined to speak on this. The prime minister’s office did not reply to a request for comment.
The security forces manning the rescue effort directed The Independent to the confidential investigation team that is not speaking to the media. The merry-go-round continues.
And while the authorities continue to finger-point and deflect blame, more bodies are unearthed – many of them the first responders.
“I am numb, a lost ship, I have been unable to cry,” says a fellow firefighter describing how he lost 10 of his best friends by that hangar on Tuesday. A team he calls his family.
“They are national heroes and were sent to their certain deaths. We have lost everything. We will make them pay.”
Port officials, before their arrests, had expressed similar sentiments, saying they warned the courts, which did nothing. Najjar told Al-Jazeera “no minister knows what’s in the hangars or containers, and it’s not my job to know”.
Hassan Diab, in his resignation speech on Monday, blamed the political elite and his predecessors for hiding the problem for seven years.
The obvious question is why nothing at any point was practically done.
Many have even questioned the little action that was taken: the letters written by the port officials.
One document shown to The Independent – dated June 2014 before the shipment was even unloaded – apparently shows an Urgent Matters Court judge telling port officials that his court did not have the jurisdiction to authorise the sale of the ship or its contents.
Beirut protesters stormed government buildings (EPA)
Investigative journalist Riad Kobeissi says this proves that all the subsequent letters were completely pointless, since the court could not authorise what the customs officials were ultimately asking: to resell or reimport the stockpile of ammonium nitrate.
“Why keep writing the same letter over and over again? Why didn’t they go immediately to the security forces or higher up and press for action all those years ago?” he asks.
The Independent spoke to port officials but they declined to speak on this. The prime minister’s office did not reply to a request for comment.
The security forces manning the rescue effort directed The Independent to the confidential investigation team that is not speaking to the media. The merry-go-round continues.
And while the authorities continue to finger-point and deflect blame, more bodies are unearthed – many of them the first responders.
“I am numb, a lost ship, I have been unable to cry,” says a fellow firefighter describing how he lost 10 of his best friends by that hangar on Tuesday. A team he calls his family.
“They are national heroes and were sent to their certain deaths. We have lost everything. We will make them pay.”
China turns waste tires from "black pollution" to “black gold”
(People's Daily Online) August 04, 2020
China has made great efforts to turn waste tires, also known as "black pollution", into “black gold”, as part of efforts to promote the healthy development of the industry and effectively improve the efficiency of resource utilization.

(Photo/Pixabay.com)
There were about 330 million waste tires produced in 2019, with a total weight of over 10 million tons. Every year, the amount of waste tires produced by scrapping continues to grow at a rate of 6 to 8 percent, according to data.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology recently issued the standard conditions for the comprehensive utilization of waste tires, which put forward standard requirements for various aspects such as technical equipment and process, ecological environmental protection, product quality control and safety management.
“In the past, local refining workshops for waste tires were rampant, and waste gas was discharged directly into the air, causing serious damage to the environment," said Zhu Jun, president of China’s Tire Recycling Association (CTRA).
Zhu Jun added that in recent years, with key technologies continuing to tackle the problem and environmental protection management being strengthened, new pyrolysis technology has become an important direction that has been taken in the comprehensive utilization of waste tires.
Since the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the access conditions for the comprehensive utilization of waste tires in 2012, it has announced six batches of 80 enterprises that meet these conditions. "These enterprises represent the advanced level of the industry and play a leading role in the green recycling of waste tires,” Zhu said.
Under the guidance of the circular economy policy, in recent years, the comprehensive utilization industry of waste tires in China has developed rapidly, and the recycling utilization rate of waste tires has been increasing year by year.
In 2019, there were about 1,500 comprehensive utilization enterprises, and about 200 million waste tires were recovered and reused, with a recycling rate of about 60 percent.
Although many difficult challenges still need to be overcome, the surveyed enterprises in the industry are generally optimistic about the market prospects for the comprehensive utilization of waste tires. With the constant upgrading of national environmental policies and continuous industrial regulation, waste tires are being turned from "black pollution" to “black gold".
Case zero not always where first cluster is: WHO official
(Xinhua) 08:27, August 11, 2020
Dr. Michael Ryan(L), executive director of the World Health Organization (WHO) Health Emergencies Program, addresses a press conference, in Geneva, Switzerland, Feb. 18, 2020. (Photo by Chen Junxia/Xinhua)
Michael Ryan, executive director of the WHO Health Emergencies Program, has earlier said that although the first clusters of COVID-19 cases were reported in Wuhan of China, it doesn't necessarily mean that Wuhan is where the COVID-19 disease crossed from animals into humans.
GENEVA, Aug. 10 (Xinhua) -- A senior World Health Organization (WHO) official on Monday highlighted that while the first clusters of cases were picked up for epidemiologic research, case zero is not always where the first cluster is.
Michael Ryan, executive director of the WHO Health Emergencies Program, said at a virtual press conference that case zero can be in another place, and "that's why we have to keep an open mind."
"All hypotheses are on the table, if you follow the data in the science, you will find, hopefully, the point at which the disease crossed the species barrier," he said.

A funeral home worker wheels the body of a deceased person into a van outside Brooklyn Hospital Center in the Brooklyn borough of New York, the United States, on April 24, 2020. (Photo by Michael Nagle/Xinhua)
According to the WHO official, this novel coronavirus is proving exceptionally difficult to stop -- "it's difficult to recognize, it's difficult to distinguish between it and other syndromes unless we have adequate and immediate testing."
Noting that it took decades in other diseases to find the case zero, Ryan explained to reporters that it took years to do it in the case of MERS, and it has never been fully established in the case of SARS in terms of the actual events that cross the animal-human barrier.
"It does prove very difficult to find that initiation point where the disease crossed the animal-human species barrier, but it is important that we find that, because as long as the animal-human breach has not been discovered, there's always a chance that barrier can be breached again," he said.
Earlier this month at another press conference, Ryan also said that although the first clusters of COVID-19 cases were reported in Wuhan of China, it doesn't necessarily mean that Wuhan is where the COVID-19 disease crossed from animals into humans.
Wuhan is not necessarily the place where the COVID-19 disease crossed from animals into humans, said a senior WHO expert.
GENEVA, Aug. 3 (Xinhua) -- Although the first clusters of atypical pneumonia were reported in Wuhan, China, it doesn't necessarily mean that is where the COVID-19 disease crossed from animals into humans, a senior World Health Organization (WHO) expert said on Monday.
Dr. Michael Ryan, executive director of the WHO Health Emergencies Program, said at a routine COVID-19 briefing on Monday that a much more "extensive retrospective epidemiological study" should be taken to fully understand the links between the cases.

Senior students study in a classroom with transparent boards placed on each desk to separate each other as a precautionary measure against the spread of COVID-19 at Wuhan No. 23 Middle School in Wuhan, central China's Hubei Province, May 6, 2020. (Xinhua/Xiao Yijiu)
He stressed the need to start studies on the first reported human clusters in order to systematically look for the "first signal at which the animal-human species barrier was crossed," before moving to the studies on the animal side.
The WHO advance team that traveled to China in preparation for an international mission of identifying the zoonotic source of COVID-19 has concluded its mission recently, according to the WHO expert. Future studies will build on the initial investigations done by Chinese experts around the Wuhan seafood market.
Ryan also noted that WHO is moving forward with agreeing on the international team and ensuring that right expertise will be in place to work with the Chinese counterparts to design and implement further studies.
Where To Donate For Lebanon's Blast Survivors
Two blasts in the capital of Beirut killed over 100 people and left thousands more injured
Two blasts in the capital of Beirut killed over 100 people and left thousands more injured
.
By Brian Trinh
As the people of Beirut grapple with the fallout from two deadly blasts Tuesday, Canadians thousands of miles away might be wondering what they can do to help.
Canada’s Lebanese community is mobilizing to raise donations, specifically for the Lebanese Red Cross. The non-governmental organization is the main provider of ambulances in the country and its network for first-responders are mostly volunteers.
The tragedy marks a tough chapter for Lebanon as hospitals there were already dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic, plus there are rising food prices due to inflation and the country has a government mired with corruption allegations.
For more on other local nonprofits are open to donations, check out the video above.
THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT WILL MATCH YOUR $ DONATION TILL THE END OF THE MONTH!!!
GO TO UNICEF OR RED CROSS
RELATED
Canada To Send Up To $5 Million To Lebanon After Deadly Beirut Explosion
Lebanese-Canadians Band Together To Help Beirut Following Deadly Explosion
Refugee Teen Receives Laptop From Anonymous Donor Following HuffPost Story
By Brian Trinh
As the people of Beirut grapple with the fallout from two deadly blasts Tuesday, Canadians thousands of miles away might be wondering what they can do to help.
Canada’s Lebanese community is mobilizing to raise donations, specifically for the Lebanese Red Cross. The non-governmental organization is the main provider of ambulances in the country and its network for first-responders are mostly volunteers.
The tragedy marks a tough chapter for Lebanon as hospitals there were already dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic, plus there are rising food prices due to inflation and the country has a government mired with corruption allegations.
For more on other local nonprofits are open to donations, check out the video above.
THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT WILL MATCH YOUR $ DONATION TILL THE END OF THE MONTH!!!
GO TO UNICEF OR RED CROSS
RELATED
Canada To Send Up To $5 Million To Lebanon After Deadly Beirut Explosion
Lebanese-Canadians Band Together To Help Beirut Following Deadly Explosion
Refugee Teen Receives Laptop From Anonymous Donor Following HuffPost Story
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)














