Webb captures a cosmic tarantula
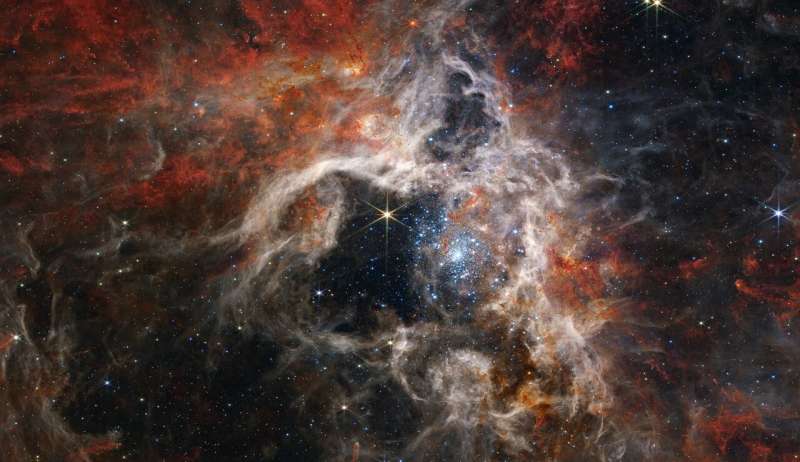

Thousands of never-before-seen young stars are spotted in a stellar nursery called 30 Doradus, captured by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. Nicknamed the Tarantula Nebula for the appearance of its dusty filaments in previous telescope images, the nebula has long been a favorite for astronomers studying star formation. In addition to young stars, Webb reveals distant background galaxies, as well as the detailed structure and composition of the nebula's gas and dust
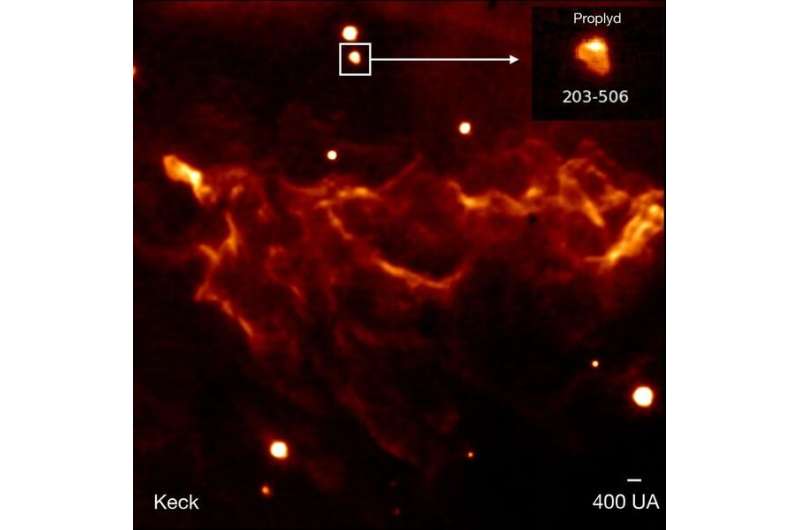
At only 161,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy, the Tarantula Nebula is the largest and brightest star-forming region in the Local Group, the galaxies nearest to our Milky Way. It is home to the hottest, most massive stars known. Astronomers focused three of Webb's high-resolution infrared instruments on the Tarantula. Viewed with Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the region resembles a burrowing tarantula's home, lined with its silk. The nebula's cavity centered in the NIRCam image has been hollowed out by blistering radiation from a cluster of massive young stars, which sparkle pale blue in the image. Only the densest surrounding areas of the nebula resist erosion by these stars' powerful stellar winds, forming pillars that appear to point back toward the cluster. These pillars contain forming protostars, which will eventually emerge from their dusty cocoons and take their turn shaping the nebula.
Webb's Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) caught one very young star doing just that. Astronomers previously thought this star might be a bit older and already in the process of clearing out a bubble around itself. However, NIRSpec showed that the star was only just beginning to emerge from its pillar and still maintained an insulating cloud of dust around itself. Without Webb's high-resolution spectra at infrared wavelengths, this episode of star formation-in-action could not have been revealed.
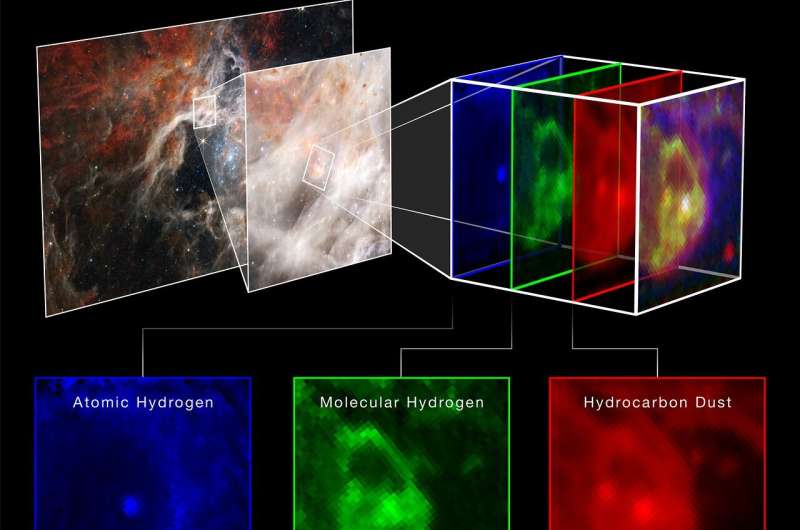
The region takes on a different appearance when viewed in the longer infrared wavelengths detected by Webb's Mid-infrared Instrument (MIRI). The hot stars fade, and the cooler gas and dust glow. Within the stellar nursery clouds, points of light indicate embedded protostars, still gaining mass. While shorter wavelengths of light are absorbed or scattered by dust grains in the nebula, and therefore never reach Webb to be detected, longer mid-infrared wavelengths penetrate that dust, ultimately revealing a previously unseen cosmic environment.
One of the reasons the Tarantula Nebula is interesting to astronomers is that the nebula has a similar type of chemical composition as the gigantic star-forming regions observed at the universe's "cosmic noon," when the cosmos was only a few billion years old and star formation was at its peak. Star-forming regions in our Milky Way galaxy are not producing stars at the same furious rate as the Tarantula Nebula, and have a different chemical composition. This makes the Tarantula the closest (i.e., easiest to see in detail) example of what was happening in the universe as it reached its brilliant high noon. Webb will provide astronomers the opportunity to compare and contrast observations of star formation in the Tarantula Nebula with the telescope's deep observations of distant galaxies from the actual era of cosmic noon.
Despite humanity's thousands of years of stargazing, the star formation process still holds many mysteries—many of them due to our previous inability to get crisp images of what was happening behind the thick clouds of stellar nurseries. Webb has already begun revealing a universe never seen before, and is only getting started on rewriting the stellar creation story.Webb reveals cosmic cliffs, glittering landscape of star birth
Provided by European Space Agency
NASA's Webb catches Tarantula Nebula
A stellar nursery nicknamed the Tarantula Nebula has been captured in crisp detail by NASA's Webb telescope, revealing hitherto unseen features that deepen scientific understanding, the agency said Tuesday.
Officially known as 30 Doradus, the region of space is characterized by its dusty filaments that resemble the legs of a hairy spider, and has long been a favorite for astronomers interested in star formation.
Thousands of young stars, distant background galaxies, and the detailed structure of the nebula's gas and dust structures were viewable for the first time thanks to Webb's high resolution infrared instruments.
Webb operates primarily in the infrared spectrum, because light from objects in the distant cosmos has been stretched into this wavelength over the course of the universe's expansion.
The telescope's primary imager, Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), found the cavity in the center of the nebula was hollowed out by radiation carried on stellar winds emanating from a cluster of massive young stars, which appear as pale blue dots.
Webb's Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), which analyzes light patterns to determine the composition of objects, caught one young star in the act of shedding a cloud of dust from around itself.
The same star was previously thought to be at a later stage of formation, already well on the way to clearing its dusty bubble.
The region was also imaged using the Mid-infrared Instrument (MIRI), which uses longer wavelengths of infrared to pierce through dust grains that absorb or scatter shorter wavelengths.
This faded the hot stars and clarified the cooler regions, revealing never-before-seen points of light within the stellar nursery, which indicate protostars that are still gaining mass.
Astronomic interest in the Tarantula Nebula stems from its similar chemical composition to gigantic star-forming regions observed a few billion years after the Big Bang, a period called the "cosmic noon" when star formation peaked.
At just 161,000 light-years away, Tarantula is a readily viewable example of this flourishing period of cosmic creation.
Webb should also provide scientists the opportunity to gaze at distant galaxies from the actual era of cosmic noon, and compare it to observations of Tarantula, to understand similarities and differences.
Operational since July, Webb is the most powerful space telescope ever built, with astronomers confident it will herald a new era of discovery.
ia/mlm