FILE - An Emirates jetliner comes in for landing at the Dubai International Airport in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Long-haul carrier Emirates successfully flew a Boeing 777 on a test flight Monday, Jan. 30, 2023, with one engine entirely powered by so-called sustainable aviation fuel. This comes as carriers worldwide try to lessen their carbon footprint.
JON GAMBRELL
Mon, January 30, 2023
Mon, January 30, 2023
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Long-haul carrier Emirates successfully flew a Boeing 777 on a test flight Monday with one of its two engines entirely powered by so-called sustainable aviation fuel. This comes as carriers worldwide try to lessen their carbon footprint.
Flight 2646 flew for just under an hour over the coastline of the United Arab Emirates, after taking off from Dubai International Airport, the world's busiest for international travel, and heading out into the Persian Gulf before circling to land. The second of the plane's General Electric Co. engines ran on conventional jet fuel for safety.
“This flight is a milestone moment for Emirates and a positive step for our industry as we work collectively to address one of our biggest challenges — reducing our carbon footprint," Adel al-Redha, Emirates' chief operation officer, said in a statement.
Emirates, a state-owned airline under Dubai's ruler Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, described the sustainable fuel as a blend “that mirrored the qualities of jet fuel.” It included fuel from Neste, a Finnish firm, and Virent, a Madison, Wisconsin-based company.
Virent describes itself as using plant-based sugars to make the compounds needed for sustainable jet fuel, while Neste's fuel comes from vegetable oils and animal fats. Those fuels reduce the release of heat-trapping carbon dioxide typically burned off by engines in flight.
Aviation releases only one-sixth the amount of carbon dioxide produced by cars and trucks, according to World Resources Institute, a nonprofit research group based in Washington. However, airplanes are used by far fewer people per day — meaning aviation is a higher per-capita source of greenhouse-gas emissions.
Airplane and engine manufacturers have been designing more-efficient models, in part to help keep down costs of jet fuel — one of the biggest expenses airlines face. Emirates, for instance, used over 5.7 million tons of jet fuel last year alone, costing it $3.7 billion out of its $17 billion in annual expenses.
But analysts suggest sustainable fuels can be three times or more the cost of jet fuel, likely putting ticket prices even higher as aviation restarts following the lockdowns during the coronavirus pandemic.
It wasn't immediately clear how much the fuel used in the Emirates' test on Monday cost per barrel. Jet fuel cost on average $146 a barrel at the end of last week, according to S&P Global Platts.
The UAE, a major oil producer and OPEC member, is to host the next United Nations climate negotiations, or COP28, beginning in November. Already, the seven sheikhdom federation has been criticized for nominating the CEO of Abu Dhabi's state oil company to lead the U.N. negotiations known as the Conference of the Parties — where COP gets its name.
___
Follow Jon Gambrell on Twitter at www.twitter.com/jongambrellAP.
Fight climate change without slowing growth: UAE's COP28 chief
Mohamad Ali Harissi
Mon, 30 January 2023
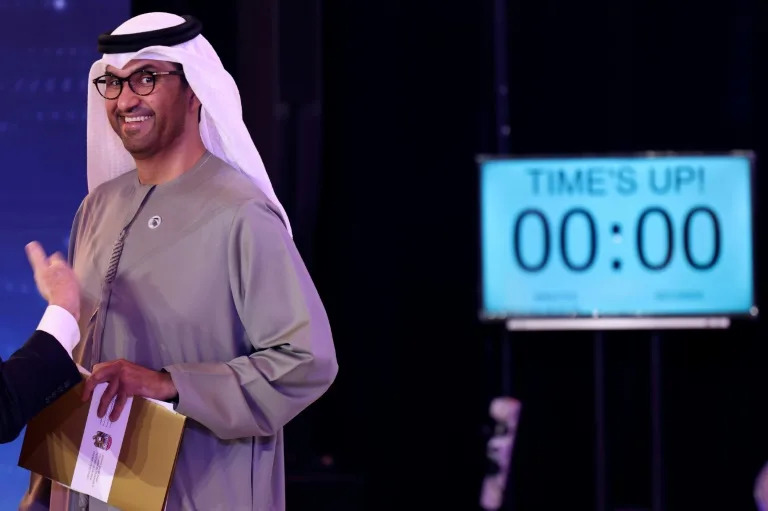

The fight against global warming should not be at the expense of economic growth, the United Arab Emirates' oil chief who will lead this year's UN climate talks said on Monday.
Sultan Al Jaber, the UAE' special envoy for climate change and CEO of oil giant ADNOC, said the energy transition needed to make the planet "wealthier and healthier".
"We need to hold back the global rise in temperatures to 1.5 degrees (Celsius), without slowing economic growth," he told a graduation ceremony at the Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence.
"We need to drive an inclusive energy transition that leaves no one behind, especially in the Global South. We need to make our planet wealthier and healthier at the same time."
Al Jaber's appointment as president of COP28 has been criticised by activists who said it threatens the "legitimacy" of the global forum against climate change.
The minister of industry and advanced technology is a veteran of COP meetings and heads a leading renewable energy company. His appointment was welcomed by US climate envoy John Kerry.
On Monday, France's economy minister urged delegates to get behind Al Jaber and focus on "concrete decisions".
"Don't misunderstand the challenge of COP28," Bruno Le Maire said in Abu Dhabi.
"The challenge of COP28 is not to know who is in charge of the COP. The key challenge of the COP28 are the results, the concrete decisions."
- 'Single winner' -
The French minister, who also visited Qatar as part of his trip to the Gulf, said he had been reassured by Al Jaber and members of the UAE government regarding their approach to the climate conference.
"I think all the participants to the COP28 should ... try to support the efforts of the presidency of COP28 so that at the end of COP28 the single winner will be our planet."
The last UN climate talks, in Egypt in November, ended with a landmark deal to create a "loss and damage" fund to cover the costs that developing countries face from climate-linked natural disasters and impacts like rising sea levels.
But observers were left disappointed that little progress was made on reducing planet-heating emissions from fossil fuels.
The UAE, one of the world's biggest oil producers, argues that crude remains indispensable to the global economy and is needed to finance the energy transition.
The Gulf monarchy is pushing the merits of carbon capture -- removing carbon dioxide as fuel is burned, or from the air.
It is also spending billions to develop enough renewable energy to cover half of its needs by 2050, when it is targeting net-zero domestic carbon emissions -- which do not include pollution from exported oil.
mah/th/ho/fz
Mohamad Ali Harissi
Mon, 30 January 2023

The fight against global warming should not be at the expense of economic growth, the United Arab Emirates' oil chief who will lead this year's UN climate talks said on Monday.
Sultan Al Jaber, the UAE' special envoy for climate change and CEO of oil giant ADNOC, said the energy transition needed to make the planet "wealthier and healthier".
"We need to hold back the global rise in temperatures to 1.5 degrees (Celsius), without slowing economic growth," he told a graduation ceremony at the Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence.
"We need to drive an inclusive energy transition that leaves no one behind, especially in the Global South. We need to make our planet wealthier and healthier at the same time."
Al Jaber's appointment as president of COP28 has been criticised by activists who said it threatens the "legitimacy" of the global forum against climate change.
The minister of industry and advanced technology is a veteran of COP meetings and heads a leading renewable energy company. His appointment was welcomed by US climate envoy John Kerry.
On Monday, France's economy minister urged delegates to get behind Al Jaber and focus on "concrete decisions".
"Don't misunderstand the challenge of COP28," Bruno Le Maire said in Abu Dhabi.
"The challenge of COP28 is not to know who is in charge of the COP. The key challenge of the COP28 are the results, the concrete decisions."
- 'Single winner' -
The French minister, who also visited Qatar as part of his trip to the Gulf, said he had been reassured by Al Jaber and members of the UAE government regarding their approach to the climate conference.
"I think all the participants to the COP28 should ... try to support the efforts of the presidency of COP28 so that at the end of COP28 the single winner will be our planet."
The last UN climate talks, in Egypt in November, ended with a landmark deal to create a "loss and damage" fund to cover the costs that developing countries face from climate-linked natural disasters and impacts like rising sea levels.
But observers were left disappointed that little progress was made on reducing planet-heating emissions from fossil fuels.
The UAE, one of the world's biggest oil producers, argues that crude remains indispensable to the global economy and is needed to finance the energy transition.
The Gulf monarchy is pushing the merits of carbon capture -- removing carbon dioxide as fuel is burned, or from the air.
It is also spending billions to develop enough renewable energy to cover half of its needs by 2050, when it is targeting net-zero domestic carbon emissions -- which do not include pollution from exported oil.
mah/th/ho/fz