UK
More misery for commuters as rail operators brace for budget cutsTORY AUSTERITY
Matt Oliver
Thu, 28 December 2023

Ticket revenues are £4bn below pre-pandemic levels - Yui Mok/PA Wire
Millions of rail passengers face fresh misery in 2024 after train companies were told to find savings that could lead to reduced services and more overcrowding.
The Government, which nationalised rail franchises during the Covid pandemic, has ordered providers to slash their costs from April.
According to industry sources, the scale of the savings being sought is as much as £2bn to £3bn per year, with companies being asked to put forward initial suggestions within weeks.
Whitehall insiders suggested the request was part of the routine budgeting process and that subsidies for the rail industry remained high compared to pre-pandemic levels, after increased working from home hit demand.
But on Thursday, experts said the cuts, first reported by the Financial Times, would result in worse services, deterring passengers just as greater demand appeared to be returning.
They warned the scale of the savings being asked for would almost certainly force train operators to run services with fewer carriages or less frequently, raising the risk of busier trains and more overcrowding.
William Barter, an independent rail consultant with expertise in operations and planning, said there were anecdotal signs passenger growth had recovered further in the most recent quarter as more employers asked staff to work in offices for at least three days per week.
But he added: “The problem with cuts like this is that railways have very high levels of fixed costs - such as rolling stock - and very low levels of variable costs, so to make any significant savings you have to take out a lot of variable costs.
“That means quality of service goes down, which depresses passenger growth and revenues.
“If you really want to reduce the amount of subsidies being paid, the best way to do that would actually be to find ways to increase revenues - we should be going all-out to get people back on the trains.
“But if more people are having to stand for long-distance journeys, you are just going to achieve the complete opposite.”
Christian Wolmar, a railway historian and host of the Calling All Stations podcast, said: “I have spoken to people in government who say you absolutely can’t make these cuts without there being some kind of reduction in services, and some the ones already imposed have eaten into timetables to some extent.
“You have got places where you now have half-hourly trains instead of services every 20 minutes and others where they have cut back on carriages. So there is going to be a severe impact from this.”
He claimed the need for fresh savings had grown after ministers were forced to backtrack on proposals to close nearly 1,000 ticket offices following a public outcry.
However, a Whitehall insider noted that subsidies for the rail industry had jumped enormously since the pandemic, when lockdowns and remote working hit demand for travel and the Government stepped in to prop up train providers.
Only £9.2bn of ticket revenues were collected in the 2022/23 financial year, more than £4bn below pre-pandemic levels. Over the same period, subsidy levels jumped from £5.1bn to £11.9bn.
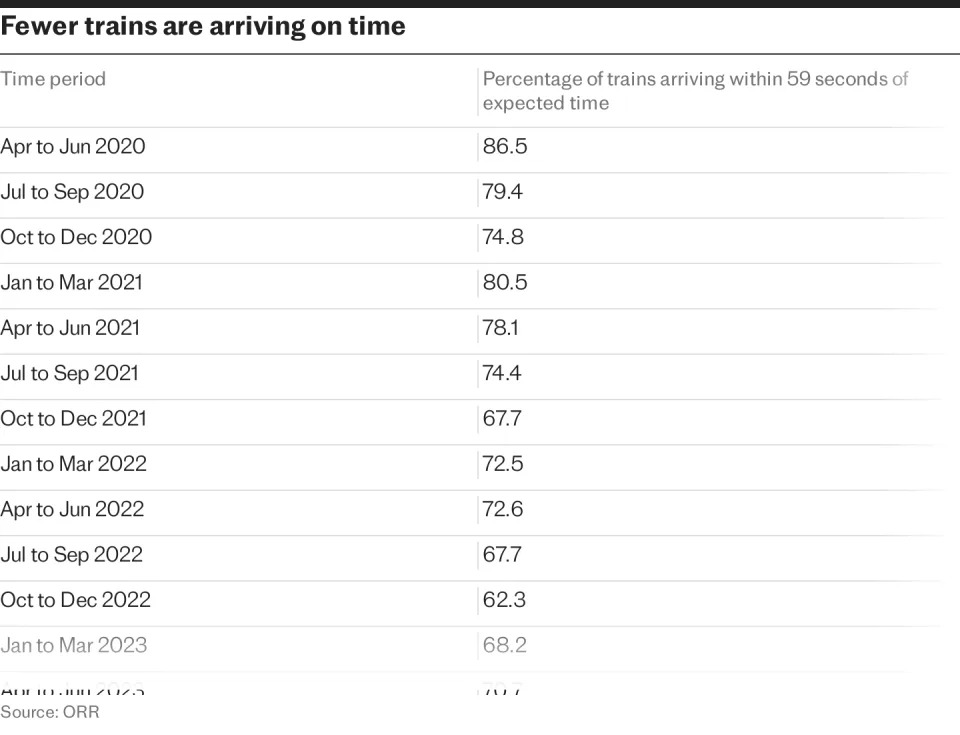
It comes amid widespread concern that services are getting worse, with figures showing roughly one in seven rail passengers could expect to stand when travelling between cities in England and Wales last year.
Delays are also common. In the three months to the end of September 2023, two fifths of train departures were late, according to the Office of Rail and Road.
Meanwhile plans to reform the way the railways have been stuck in the sidings since May 2021, when a review recommended the creation of ‘Great British Railways’, a quango that would be responsible for managing tracks and trains.
Those proposals have been delayed under Rishi Sunak, the Prime Minister, as well as plans to create a government-backed ticketing system and smartphone app to simplify fares for passengers.
On Thursday, the Department for Transport insisted that more budget cuts should not lead to worse services.
A spokesman said: “We have been upfront about the need to reform our railways in order to make them financially sustainable, and we expect operators to maintain services while ensuring passengers are provided better services at no additional cost to the taxpayer.”
Last week, ministers announced rail fares would rise by 4.9pc next year. That is below the normal 9pc increase that would have taken place, had the rise been index-linked to inflation
Matt Oliver
Thu, 28 December 2023

Ticket revenues are £4bn below pre-pandemic levels - Yui Mok/PA Wire
Millions of rail passengers face fresh misery in 2024 after train companies were told to find savings that could lead to reduced services and more overcrowding.
The Government, which nationalised rail franchises during the Covid pandemic, has ordered providers to slash their costs from April.
According to industry sources, the scale of the savings being sought is as much as £2bn to £3bn per year, with companies being asked to put forward initial suggestions within weeks.
Whitehall insiders suggested the request was part of the routine budgeting process and that subsidies for the rail industry remained high compared to pre-pandemic levels, after increased working from home hit demand.
But on Thursday, experts said the cuts, first reported by the Financial Times, would result in worse services, deterring passengers just as greater demand appeared to be returning.
They warned the scale of the savings being asked for would almost certainly force train operators to run services with fewer carriages or less frequently, raising the risk of busier trains and more overcrowding.
William Barter, an independent rail consultant with expertise in operations and planning, said there were anecdotal signs passenger growth had recovered further in the most recent quarter as more employers asked staff to work in offices for at least three days per week.
But he added: “The problem with cuts like this is that railways have very high levels of fixed costs - such as rolling stock - and very low levels of variable costs, so to make any significant savings you have to take out a lot of variable costs.
“That means quality of service goes down, which depresses passenger growth and revenues.
“If you really want to reduce the amount of subsidies being paid, the best way to do that would actually be to find ways to increase revenues - we should be going all-out to get people back on the trains.
“But if more people are having to stand for long-distance journeys, you are just going to achieve the complete opposite.”

Christian Wolmar, a railway historian and host of the Calling All Stations podcast, said: “I have spoken to people in government who say you absolutely can’t make these cuts without there being some kind of reduction in services, and some the ones already imposed have eaten into timetables to some extent.
“You have got places where you now have half-hourly trains instead of services every 20 minutes and others where they have cut back on carriages. So there is going to be a severe impact from this.”
He claimed the need for fresh savings had grown after ministers were forced to backtrack on proposals to close nearly 1,000 ticket offices following a public outcry.
However, a Whitehall insider noted that subsidies for the rail industry had jumped enormously since the pandemic, when lockdowns and remote working hit demand for travel and the Government stepped in to prop up train providers.
Only £9.2bn of ticket revenues were collected in the 2022/23 financial year, more than £4bn below pre-pandemic levels. Over the same period, subsidy levels jumped from £5.1bn to £11.9bn.
It comes amid widespread concern that services are getting worse, with figures showing roughly one in seven rail passengers could expect to stand when travelling between cities in England and Wales last year.
Delays are also common. In the three months to the end of September 2023, two fifths of train departures were late, according to the Office of Rail and Road.
Meanwhile plans to reform the way the railways have been stuck in the sidings since May 2021, when a review recommended the creation of ‘Great British Railways’, a quango that would be responsible for managing tracks and trains.
Those proposals have been delayed under Rishi Sunak, the Prime Minister, as well as plans to create a government-backed ticketing system and smartphone app to simplify fares for passengers.
On Thursday, the Department for Transport insisted that more budget cuts should not lead to worse services.
A spokesman said: “We have been upfront about the need to reform our railways in order to make them financially sustainable, and we expect operators to maintain services while ensuring passengers are provided better services at no additional cost to the taxpayer.”
Last week, ministers announced rail fares would rise by 4.9pc next year. That is below the normal 9pc increase that would have taken place, had the rise been index-linked to inflation