The Geopolitics Of The Central Caucasus – Analysis
By Natalie Tavadze
For years, to avoid the confusion between Georgia the country, and Georgia the U.S. state, international media referred to the former as a post-Soviet entity. It seemed that only in the wake of the 2008 Georgian-Russian war (when Americans were finally assured that it was not their state being attacked) did the country rise to global attention. Nowadays, it appears that Georgia, next to its immediate neighbors Armenia and Azerbaijan (together forming the Central Caucasus), draws attention due to its role in the so-called Middle Corridor (TITR). However, it eluded the attention of many that the area has long obtained three distinctive geopolitical roles owing to its location. These were: a bridge of economic interactions, a buffer between Europe, Russia, and the Middle East, and a border of different civilizations.
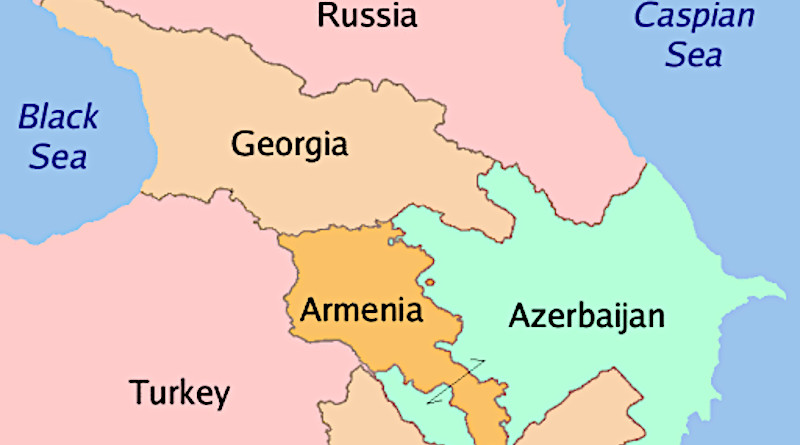
There were reasons why it evaded the notice of many, but first and foremost, we should mentally map the area. The Central Caucasus, comprised of Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan, is a historically constructed, complex political concord, embodying a geopolitical tapestry woven over centuries and forming a culturally, ethnically, linguistically, and religiously diverse area stretched between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
In the geopolitical discourse, as explained by Saul Bernard Cohen, an eminent American geographer, the axiom stands firm: “Geopolitics is a product of its time.” Each historical period has produced a geopolitical model offering a lens through which to interpret the world map and the world order of that time. In imperialist geopolitical writings of the 19th to early 20th centuries when a state’s greatness lay in its maritime power and/or in domination of the Heartland (the territory ruled by the Russian Empire and later by the Soviet Union), the distance of the Central Caucasus from the Anglo-American space resulted in little to no mention of the region.
Whilst the strategic location of the Central Caucasus temporally escaped the attention of imperialist writers, historically, the region carried geopolitical importance for three major Eastern powers: The Persian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian Empire. Already in the early 1800s, the region acted as a buffer zone between Orthodox Christianity and the Muslims of the Middle East. Russia’s expansion into the Caucasus in the sixteenth century additionally carried economic considerations, evident in projects like the Trans-Caspian railway, which facilitated access to Central Asia and control over Caspian oil supplies. Next to its geographical advantages, the Central Caucasus was a boon for natural resources. Besides Petroleum, the region is rich in copper ore. The minerals also attracted foreign investors and as of 1870, Rothschild and Shell was extracting oil, while Siemens mined copper.
After World War II, the political picture drastically changed and a new international system emerged, with multipolarity giving way to bipolarity. During the Cold War, geopolitics became associated with the two leading ideologies of that time: Communism and Western Democracy. Geopoliticians, thus, were mostly preoccupied with the rivalry between the two blocs of the West and the East. When the Soviet Union established its rule over the Central Caucasian states, the region once again became extraneous to the interests of international observers and witnessed its geopolitical role as a bridge for regional and international trade routes reduced to serving the southeastern border of Europe with Communist Russia and the Middle East.
By the 1980s, however, “winds of change” were blowing on the Eastern side of the Iron Curtain, and with Mikhail Gorbachov’s policies of glasnost and perestroika, the Cold War was nearing its logical end, giving way to a new world order. Simultaneously, geopolitical concepts were updated to understand the new world map and where geopolitical pivots had moved, which came to be known as the New World Order in an academic context. While some rejoiced in triumph of the Western ideology and others coined a neologism “Geo-economics” to explain the substantial penetration of economics into geopolitics, a drastically different approach was undertaken by Samuel P. Huntington to explain the geopolitical setting and patterns of this “new world.” He emphasized cultural differences as the primary basis for identity and conflict, predicting that nations would align along cultural lines rather than ideological or economic ones, leading to conflicts at local and global levels. Huntington identified several fault lines, including the Balkans, the Caucasus, and the Middle East, as areas where clashes between civilizations were likely.
Now, in addition to its geographically determined strategic function as a buffer and bridge on two axes – West-East and North-South, the region’s ethnoreligious mosaic was also put under the spotlight of geopolitical works and international actors. Geographically situated between Orthodox and Islamic civilizations, the region has fostered a diverse ethno-religious mosaic. Despite religious differences, examples of religious tolerance can be found in cities like Derbent, Dagestan, and Tbilisi, Georgia. Additional emphasis is given to the role of customs, which in the Caucasus is referred to as ‘adat.’ It is argued that customs (or adats) in the region are stronger than confessions, and even contend for superiority over the latter. The custom-based relationship between the peoples of religion facilitated their peaceful coexistence, tolerance, and mutual understanding. The historical background of peaceful coexistence and distinct patterns of Caucasian, custom-based relations between different religions and ethnicities, provided the understanding behind the harmonious relationship between the Caucasian people.
The Russian Effect
The demise of the Soviet Union, however, did not mean the end of the Cold War rationale. Russia – as the heir of the Soviet Union – after disappointing the hopes of anticipated democratization was still considered a power whose influence had to be contained. Zbigniew Brzezinski, like many of his contemporaries and those before him, assumed that Russia at some point in post-Cold War history, whether voluntarily or not, would choose the path of Western development, a hope that remains unrealized to this day. The reasons behind this can be traced back to the Russian understanding of the world system, which has been incautiously neglected by Western academia and which is vividly illustrated by the Russian geopolitical school: Eurasianism. All important contributors to the development of Russian Geopolitics (Nikolai Trubetzkoy, Peter Savitsky, Lev Gumilev, Aleksandr Dugin) emphasized Eurasia’s distinct cultural-geographic and socio-historical pattern and rejected Western universal ideas of the cultural and historic development of mankind. It was believed that it was Russia’s mission to unify Eurasia and maintain this unity, asserting that it was the destiny of the Eurasian people to be concerted.
It is important to understand that Eurasianinism and Moscow’s approaches toward the Caucasus correspond to each other. In this regard, the Central Caucasus is considered as Russia’s backyard. Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Armenia, the Black Sea, and the Caspian Sea constitute strategic dimensions for Russia. The latter is determined to dominate the region and uses the “ethnic card” to keep the countries of the Central Caucasus off balance. From the Russian standpoint, any foreign influence in its “near abroad” is seen through the prism of its national security. Such a menace should be thwarted by any means, as Moscow made clear more than once that it does not entertain any notion of conceding territories of its utmost geopolitical interests.
As the successor of the Soviet Union, Russia experienced the heaviest losses in terms of territory, resources, influence, economy, as well as international image. Its borders were pushed back from the west, south, and east. To add fuel to the fire, the divorce of the Central Caucasian states from Russian influence and the emergence of newly independent states in Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan with nationalist-minded political elites reinforced the fears of a resurgence of the deep-rooted Russian-Turkish rivalry over influence in the region. A prominent Eurasianist Alexandr S. Panarin argued, that “the geopolitical concessions which post-Soviet Russia made to the West are the maximum Russia will ever concede. Any further attack by the West Belt in the form of further enlargement of NATO or by playing the Ukrainian, Georgian, Azeri, or Central Asian ‘cards’ would mean that the aforementioned concessions by Russia were like the concessions to Hitler at Munich.”
Dominating the Caucasus for Russia also translates into being closer to the Mediterranean and Balkans. Some of the imperialist-minded politicians, such as Vladimir Zhirinovsky, expressed the ambition of obtaining access to a warm water port on the Indian Ocean. Needless to say, conceding the vital Caspian Sea resources it could potentially lose with the opening of the market to the west – along with flows of Western investment following the breakup of the USSR – would substantially weaken Russia.
The Caucasian Chalk Circle
In the context of the so-called emerging New World Order, Russia was at first left on the periphery, while Turkey and Iran were the first countries affected by geopolitical turbulence. Entering the ‘Mittlespiel’ of this ‘Great Chess Game,’ the United States and the European Union quickly exploited the opportunity to increase their influence in the region of the Central Caucasus. Hence the latter soon became a space of competition between original geopolitical players and so-called ‘newcomers.
Iran is one of the classical players in the Central Caucasus, however, due to its internal turbulence and international pressures, it was forced to temporarily retreat from the contest. The latest trends show the revitalization of Iran’s interests in the Central Caucasus. In the regional context, Iran is an ally of Armenia and Russia.
Turkey, as Brzezinski suggests, must not be alienated from geopolitical calculations, because a rejected Turkey can not only become strongly Islamic but will be able to upset the region’s stability. Turkey’s role in this contest, along with its geopolitical inclinations, is to counter-balance Russia’s domination over the region. That is why Brzezinski argues that political developments in Turkey and its orientation will be crucial for the states of the Central Caucasus.
The EU presence in the region is perceptible as well. In the framework of its Eastern Neighborhood Partnership, the Union encouraged countries of the region toward reform and as an accolade granted Georgia candidacy status. Furthermore, the location and the mentioned potential to provide transit roads allow Central Caucasus to serve as an energy security guarantee to Europe. In line with this, Europe needs to assist the region in its peaceful development and assure its security as a strategic partner.
Contrary to Armenia and Georgia, Azerbaijan does not openly express willingness to join either military or economic blocs. The country is neither pro-Russian, nor pro-Western, but emphasizes the importance of regional cooperation. Consequently, the countries are at different steps in the process of Europeanization. Nevertheless, the EU’s need for a reliable partner in the Central Caucasus is currently at odds with Turkey’s estrangement from the Union and Russia being non-responsive to sanctions.
The United States has long viewed the region, and especially Georgia as a strategic buffer zone to assist its interests in the Middle East, as well as against the expansion of terrorism. In 2016, Donald Rumsfeld, former US Secretary of Defense, highlighted the strategic location of Georgia in his article in The Wall Street Journal, by stating that “[Georgia] provides a barrier to the flow of jihadists from other parts of the former Soviet Union to the Middle East. And it will doubtless figure large in the strategies of any NATO consortium for securing the Black Sea and ‘New Europe’ against Russian adventurism.”
An additional newcomer to the regional chess game is China with its growing geopolitical influence, making the region’s importance even greater through participation in the Chinese Silk Road project and, since 2017, in the Trans-Caspian International Transport Route project.
The cultural dimension, specifically the ethno-religious factor, in a time of growing resurgence of nationalism and fundamentalism, is a factor directly influencing geopolitical considerations. Historical differences have shaped difficult relations between Turkey-Armenia and Armenia-Azerbaijan, leading to friendship between Russia and Armenia. Russia’s betrayal and mistreatment of Georgia has alienated the country from its northern neighbor, with whom it shares a common religion. Despite diverse religions, Georgia maintains a friendly relationship with Turkey and Iran, with the latter enjoying a somewhat positive attitude among all the Caucasian republics.
Its location and its experience as a borderland of various religions and ethnicities permit the region to be crucial in what is claimed to be the primary menace and security challenges of the 21st century- terrorism, further enhancing the Central Caucasus’s role as a border of civilizations.
As observed, the developments of the post-Soviet era brought new actors such as the US, EU, and China into the contest of imposing influence over the region, as well as extracting benefits from it. Such unfolding of events, however, runs contrary to the aspirations of the major neighboring geopolitical powers, such as Russia, Turkey, and Iran; the concentration of political interests of the great powers in such a small region emphasizes its favored geopolitical position and economic advantages.
Borrowing from Bertolt Brecht’s theatrical play The Caucasian Chalk Circle, the configuration of international interests in the region spotlights power conflicts. Such concentration of global powers in its turn shapes the foreign orientations of the countries of the Central Caucasus. In the realm of geopolitical discourse, a region can be geopolitically significant if it serves the geopolitical and economic benefits of major geopolitical players or has the potential to challenge such political-economic aspirations of great powers. The Central Caucasus, as a result of its strategic location and diversity, possesses both characteristics. Consequently, Central Caucasus stands amid a complex geopolitical landscape, and next to presenting economic opportunities for great powers, finds itself in the hotspot of 21st-century security considerations.
This article was published at Geopolitical Monitor.com

Geopoliticalmonitor.com is an open-source intelligence collection and forecasting service, providing research, analysis and up to date coverage on situations and events that have a substantive impact on political, military and economic affairs.
No comments:
Post a Comment