`It's always in Canada's interests to try to elevate... humanitarian rights.'
Peter MacKay, foreign affairs minister
A conflict that the international community has exasperated by its lack of involvement but its overflowing of crocodile tears. And would the discovery of oil reserves in the region and its neighbour Chad have anything to do with this? Nah.
 Sat Apr 29, 1:40 PM ET
Sat Apr 29, 1:40 PM ETLaura Cacho of Working Assets hands a protester a sign during a mass rally against the war in Iraq on Saturday, April 29, 2006 in New York, NY. (AP Photo/Adam Rountree)
The international community has had plenty of opportunity to intervene with armed force, to create a barrier between the refugee camps and the conflicting forces in the region. But like Rawanda the original colonial powers in the region pull the strings behind the scenes, exerting their great power influence over the region. In this case the US and Canada have less to say about this than say oh Britain and France the original Imperialist powers in the region.
The Sudan Wars were a series of conflicts in the Sudan part of Africa in the late 19th Century. The conflicts erupted between the British and the Muslims Africans in the Sudan in 1881 because of religious disputes and the British attempt to end the "new" slavery trade. Muslim fundamentalists instigated a rebellion against the British, driving them and their Egyptian armies from Sudan. Britain atoned for the loss in 1898, militarily reclaiming control of the Sudan. Following this engagement, competition between Britain and France for the south of Sudan led to military conflict, ended by diplomatic avenues which partitioned the disputed area. Both events demonstrate the intensifying struggle to control Africa, and the conflict between the European powers in the race of imperialism. This conflict gave rise to the beginning of World War I. Sudan Wars
French Equatorial Africa (Introduction)
Chad • Congo • Gabon • Central African Republic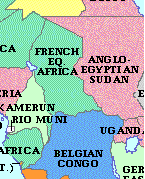
French Equatorial Africa was a former administrative grouping of four French territories in west central Africa. It was first formed in 1910 by the federation of three French imperial colonies — Gabon, Middle Congo, and Ubangi-Shari-Chad — comprising a total area of 969,112 square miles (2,500,000 sq km). Chad was separated from Ubangi-Shari in 1920 to form a fourth colony.
In 1934, French Equatorial Africa was transformed into a unified territory of France, but in 1946 it was re-divided into four separate overseas territories (TOM — territoires d'outre-mer).
The federation ended in 1959 after the territories had chosen — in 1958 — to become self-governing republics of the French Community. Middle Congo was renamed Republic of the Congo, and Ubangi-Shari became the Central African Republic. All four republics attained their independence in 1960.
In the case of Africa, this human element is seen in the variety of forces that affected or moulded her history and experience. Lydia Polgreen summarized the roots of Africa’s present burden: Africa was a land carved for a colonial feast. For her, “it is a truism of Africa that the borders bequeathed by white colonial powers, drawn in the 19th-century scramble for Africa at the convenience of London, Paris and Brussels, became the Blackman’s burden”. And if the inherited colonial- nation state has been the Blackman’s burden, it has also been the African despot’s best friend, a powerful tool when wielded by crafty hands. In fact, the excesses of African dictators, from Mobutu Sesse Seko to Robert Mugabe, from Sani Abacha to Charles Taylor, were enabled, to a greater or lesser degree, by the inherent conflicts created by artificial state boundaries that allowed a powerful central government to play tribal, ethnic and religious groups against one another. Aligned to that, colonialism destroyed some African cultural values and structures that would have conduced to the emergence of accountability in governance. This is well depicted by the fact that until now as Ali Mazrui argued, “Africa has borrowed Western tastes without Western skills, Western consumption patterns without Western production techniques, urbanization without industrialization, secularization (erosion of religion) without scientification.” African Poverty as Failure of Leadership
Beware of war for humanity or humanitarianism, behind the rehtoric lies the profit motive. And it is the only motive that drives war, whether for good or evil.
What the postcolonial left who oppose intervention and the liberal internationalists who support intervention in Darfur (but oppose it in the Middle East) share is a common concern about the conditions of the Third World. They are likely to agree that the West is fully or partially responsible for the deterioration of those conditions. Unlike those on the right like the current President of the U.S., their foreign policy ideas transcend crass national self interests and are burdened by their moral consciences. Where they disagree however is in what role the West can play in alleviating the global south’s conditions. Where the liberals want the West to intervene to save the poor Africans from killing themselves (which can be understood in a post-Rwanda context as either humanitarianism or on the other extreme, a neo-imperial continuation of the white man’s burden), the postcolonial left want the West out of the third world. Since the West is responsible for the poverty, war and low rates of democratic and human development in places like Africa, the Middle East and beyond – vis-à-vis colonialism and neo-colonialism – they should just butt out. SkarredBlogAlso See: War and the Market State
Find blog posts, photos, events and more off-site about:
war, genocide, Darfur, Sudan, Canada, US, humanitarianism, France, Britain, colonies, colonialism, Imperialism, oil, uranium, post-colonialism, Africa, UN

No comments:
Post a Comment