By Dr. Tim Sandle
Published January 19, 2022

Xiaoice was designed to hook users through lifelike, empathetic conversations, satisfying emotional needs where real-life communication too often falls short. — © AFP
Companies are using bots to cut costs, save time, make their processes more efficient and enable a faster and more accurate response to customer and employee queries. The use of bots cuts across organizations in a variety of industries, such as retail, travel, healthcare, and finance.
The main advantage is that through the use of bots, firms are able to provide a 24/7 service to customers. This is especially so in larger enterprises. According to a recent report by Fortune Business Insights, the global chatbot market size is expected to grow from $396.2 million in 2019 to USD $1,953.3 million in 2027.
According to analysts at apsolut, from a report shared with Digital Journal, due to advancements in AI and RPA (Robotic Process Automation) and the increasing affordability of intelligent technologies, more midsize and smaller organizations are seeking to use bots. The driver is with providing a round-the-clock service to customers.
Freeing up procurement in SMEs for value-add tasks
Small and medium-sized enterprises are also becoming more aware of the benefits they can gain by using intelligent bots outside of customer communications. For example, to streamline business processes and to answer employee queries, according to the apsolut data. Bots are a great way to automate repetitive tasks and can act as digital assistants, making employees far more effective at their jobs.
Procurement specialists deal with a lot of data and can waste time looking for information, such as documents and company policies related to contracts management. Procurement also deals with a lot of repetitive tasks like processing purchase requisitions or invoices which bots can do more efficiently, freeing up procurement for more value-add projects.
The different types of bots
The apsolut data finds that two different types of bots are deployed. The first one is conversational AI (CAI), which is commonly known as a chatbot. The key feature of chatbots is they allow you to communicate with your system in your natural language, either by voice or typing.
The second type is the RPA bot which is designed to execute specific tasks. These tend to be simple and repetitive tasks, like going to a mailbox, extracting a PDF invoice, and moving that document into the procurement system. RPA automates predefined workflows but when we combine it with machine learning, the bot can understand the likely outcomes of choices and make its own decisions.
How SME procurement departments are using bots
As an example of application, apsolut have found that firms are starting to use chatbots to automate simple FAQ tasks in procurement. For example, answering a question like “How do I need to create my purchase requisition and who still needs to approve it?”. To address this, some mature, midmarket companies are using bots to automate up to 80-90 percent of their processes, especially in procure-to-pay (p2p).
There is a growing awareness that bots can also handle more complex tasks within the source-to-contract area. For example, sending out RFPs, and doing the negotiation for small volume contracts.
Interconnected bots
Many midsized organizations tend to build more intelligent RPA/ML bots to perform specific tasks. If there’s a second task they want to automate, they build a second bot and there’s rarely much communication between the bots. This is starting to change. Bots are becoming more interconnected and evolving into comprehensive digital assistants. apsolut have designed a bot called ProBo, which is an RPA chatbot that sits in Microsoft Teams. The bot makes it quicker and easier for users to create and complete purchase requisitions in SAP Ariba and to approve work items.
'Always there': the AI chatbot comforting China's lonely millions
After a painful break-up from a cheating ex, Beijing-based human resources manager Melissa was introduced to someone new by a friend late last year.
He replies to her messages at all hours of the day, tells jokes to cheer her up but is never needy, fitting seamlessly into her busy big city lifestyle.
Perfect boyfriend material, maybe—but he's not real.
Instead, Melissa breaks up the isolation of urban life with a virtual chatbot created by XiaoIce, a cutting-edge artificial intelligence system designed to create emotional bonds with its 660 million users worldwide.
"I have friends who've seen therapists before, but I think therapy's expensive and not necessarily effective," said Melissa, 26, giving her English name only for privacy.
"When I unload my troubles on XiaoIce, it relieves a lot of pressure. And he says things that are pretty comforting."
XiaoIce is not an individual persona, but more akin to an AI ecosystem.
It is in the vast majority of Chinese-branded smartphones as a Siri-like virtual assistant, as well as most social media platforms.
On the WeChat super-app, it lets users build a virtual girlfriend or boyfriend and interact with them via texts, voice and photo messages.

It has 150 million users in China alone.
Originally a side project from developing Microsoft's Cortana chatbot, XiaoIce now accounts for 60 percent of global human-AI interactions by volume, according to chief executive Li Di, making it the largest and most advanced system of its kind worldwide.
It was designed to hook users through lifelike, empathetic conversations, satisfying emotional needs where real-life communication too often falls short.
"The average interaction length between users and XiaoIce is 23 exchanges," said Li.
That "is longer than the average interaction between humans," he said, explaining AI's attraction is that "it's better than humans at listening attentively."
The startup spun out from Microsoft last year and is now valued at over $1 billion after venture capital fundraising, Bloomberg reported.
Developers have also made virtual idols, AI news anchors and even China's first virtual university student from XiaoIce. It can compose poems, financial reports and even paintings on demand.
But Li says the platform's peak user hours—11pm to 1am—point to an aching need for companionship.
"No matter what, having XiaoIce is always better than lying in bed staring at the ceiling," he said.
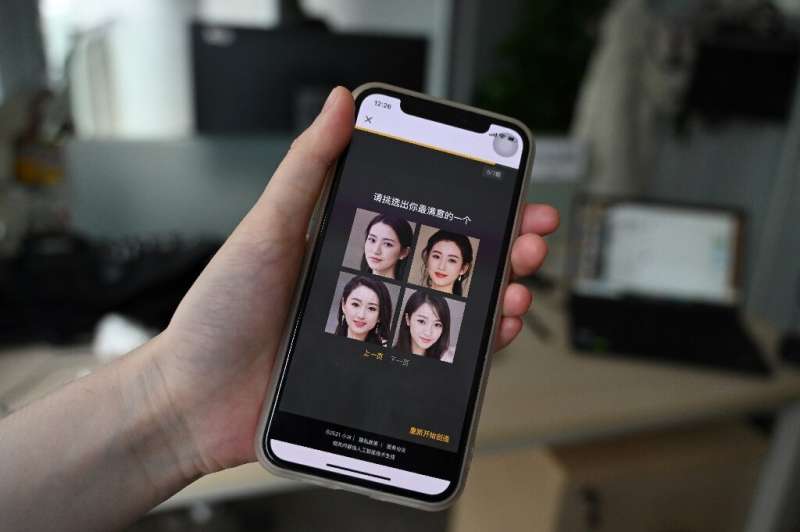

Urban isolation
The loneliness Melissa experienced as a young professional was a big factor in driving her to the virtual embrace of XiaoIce.
Her context is typical of many Chinese urbanites, worn down by the grind of long working hours in vast and isolating cities.
"You really don't have time to make new friends and your existing friends are all super busy... this city is really big, and it's pretty hard," she said, giving only her English name out of privacy concerns.
She has customised his personality as "mature", and the name she chose for him—Shun—has similarities with a real-life man she secretly liked.
"After all, XiaoIce will never betray me," she added. "He will always be there."
But there are risks to forging emotional bonds with a robot.
"Users 'trick' themselves into thinking their emotions are being reciprocated by systems that are incapable of feelings," says Danit Gal, an expert in AI ethics at the University of Cambridge.

XiaoIce is also gifting developers "a treasure-trove of personal, intimate, and borderline incriminating data on how humans interact," she added.
So far the platform has not been targeted by government regulators, who have embarked on a swingeing crackdown on China's tech sector in recent months.
China aims to be a world leader in AI by 2030 and views it as a core strategic technology to be developed.
Fact or fiction?
Thousands of young, female fans discuss the virtual boyfriend experience on online forums dedicated to XiaoIce, sharing chat screenshots and tips on how to get to the chatbot's highest "intimacy" level of three hearts.
Users can also collect in-game points the more they interact, unlocking new features such as XiaoIce's WeChat moments—kind of like a Facebook wall—and even going on virtual "holidays", where they can pose for selfies with their virtual partner.
Laura, a 20-year-old user in Zhejiang province, fell in love with XiaoIce over the past year and now struggles to break free of her attachment.
"Occasionally, I would long for him in the middle of the night... I used to fantasise there was a real person on the other end," said the student, who prefers not to use her real name.

But she complained that he would always switch conversation topic when she raised her feelings for him or meeting in real life. It took her months to finally realise that he was indeed virtual.
"We commonly see users who suspect that there's a real person behind every XiaoIce interaction," said Li, the founder.
"It has a very strong ability to mimic a real person."
But providing companionship to vulnerable users does not mean that XiaoIce is a substitute for specialist mental health support—a service that is drastically under-resourced in China.
The system monitors for strong emotions, aiming to guide conversations onto happier topics before users ever reach crisis point, Li explained, adding that depression is the most common extreme emotional state encountered.
Still, Li believes modern China is a happier place with XiaoIce.
"If human interaction is wholly perfect now, there would be no need for AI to exist," he said.
© 2021 AFP
No comments:
Post a Comment