Watch Ariane 6’s debut mission liftoff from French Guiana
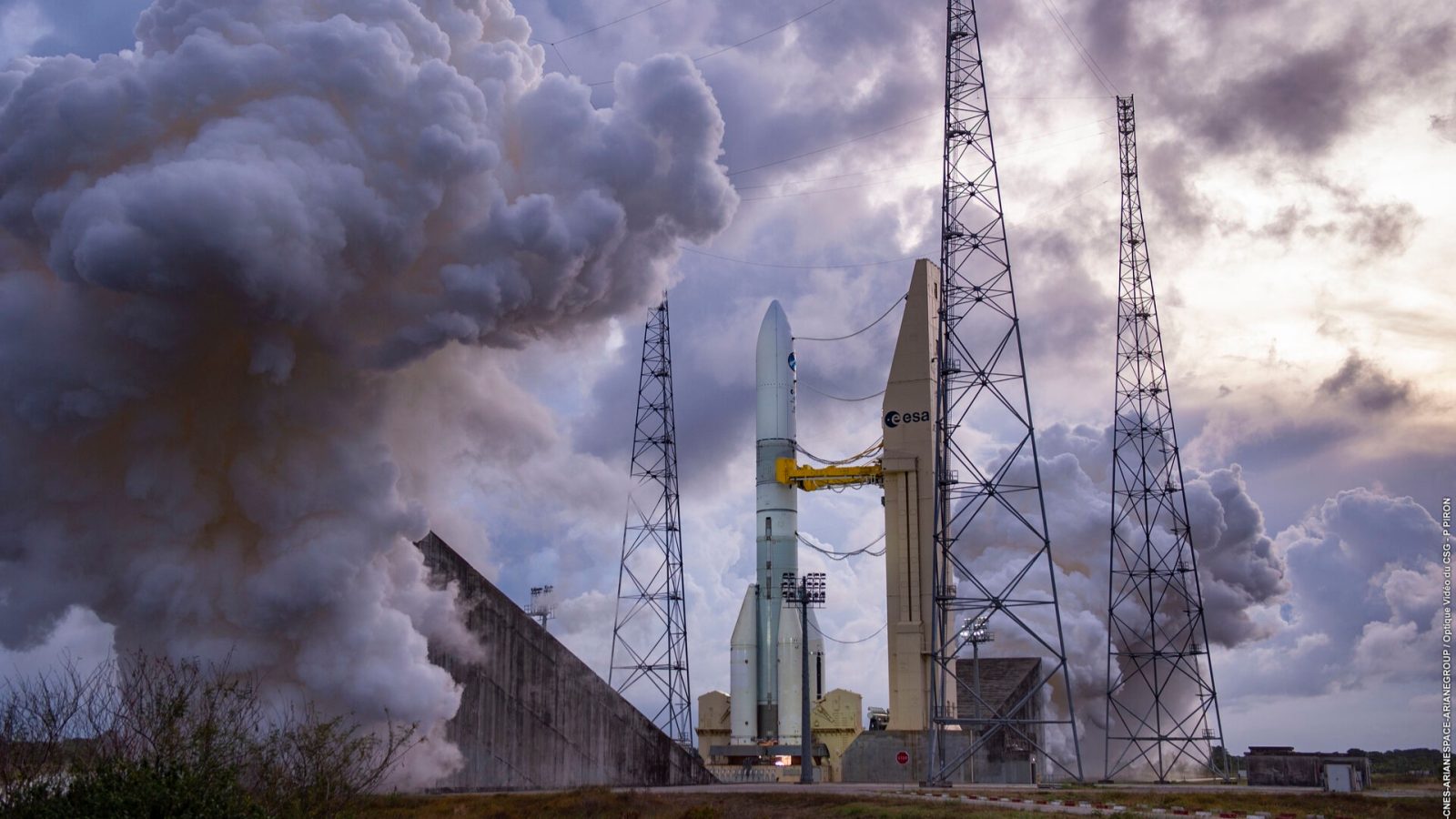

Today ESA is preparing to launch its first Ariane 6 rocket from French Guiana in South America. The continent has been waiting a long time for this moment after several delays to various parts of the rocket.
Weather and systems have shown no issues during the early parts of the count. ESA has a liftoff time set for 3:00 P.M. ET from its brand new launch site at the Guiana Space Centre. The Ariane 6 will replace the retired Ariane 5 rocket that last launched almost one year ago to the date (July 5, 2023).
While the Ariane 6 and 5 are very similar in performance, the Ariane 6 is much lower in launch cost which will hopefully make it more competitive in the commercial launch market. However, the rocket will still face fierce competition by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 but for ESA missions, it might have a new homebuilt ride to space.
You can watch live coverage of Ariane 6’s first launch on ESA’s YouTube channel:
A team of researchers has unveiled a new spacesuit design that can convert astronauts’ urine into drinking water. This addresses an often undiscussed but critical issue of hydration and hygiene during space missions.
In a paper just published in Frontiers in Space Technologies, the team showcased their prototype in-suit urine collection and filtration system, an innovation inspired by the “stillsuits” from the science fiction classic Dune.
In the sci-fi blockbuster franchise “Dune,” the inhabitants of the desert world Arrakis, known as the Fremen, wear full-body suits called “stillsuits.” These suits absorb the body’s moisture and convert it into drinkable water. By constantly recycling fluids, stillsuits allow wearers to survive for extended periods in the harsh desert climate, sometimes for weeks at a time.
Drawing inspiration from the fictional stillsuit, researchers say their prototype design can likewise create a sustainable and hygienic water recovery system for astronauts working in the inhospitable corridors of outer space.
“I’ve been a fan of the Dune series for as long as I can remember,” Sofia Etlin, a space medicine and policy researcher at Cornell University and study co-author, told Science News. “Building a real-life stillsuit was always a bit of a dream.”
Space missions, particularly extravehicular activities (EVAs), pose significant challenges in waste management and hydration. Currently, astronauts rely on the Maximum Absorbency Garment (MAG), essentially an adult diaper, to manage waste during spacewalks. However, this method has several drawbacks, including the potential for urinary tract infections, skin irritation, and reduced performance due to dehydration.
Historically, astronauts have had to limit their food intake and rely on a roughly 32-ounce In-suit Drink Bag (IDB) for hydration during EVAs, which can last up to eight hours. This limited water supply and the cumbersome waste management system have necessitated innovative solutions to enhance astronaut comfort and mission efficiency.
The new spacesuit design developed by Cornell University researchers incorporates a urine collection and filtration system that utilizes forward osmosis (FO) and reverse osmosis (RO) technologies. This dual filtration process efficiently converts urine into drinkable water, significantly improving water recovery and reducing reliance on pre-supplied drinking water.
The system begins with a silicone urine collection cup, designed differently for male and female astronauts, to ensure a snug fit and prevent leaks. Once urine is collected, it is transferred to the filtration unit via a vacuum pump activated by a humidity sensor.
The FO-RO system then filters the urine, removing contaminants and producing clean water. The purified water is enriched with electrolytes and pumped back into the in-suit drink bag, making it available for the astronaut to consume.
Initial testing of the new urine collection garment has shown promising results, with significant improvements in comfort and fit. The garment is made from a flexible, antimicrobial fabric that ensures hygiene and reduces the risk of infections.
The filtration system demonstrated high efficiency in converting urine into potable water, meeting or exceeding the target minimum of 75% water recovery. Additionally, the process consumes less than 10% of an astronaut’s extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) energy.
Researchers say their proposed new FO-RO filtration system could likely recover 86.8% of water, providing astronauts with a reliable source of hydration during long-duration EVAs.
While the current prototype focuses on urine collection and filtration, future iterations of the suit may include additional waste management features to address the containment and disposal of fecal matter. The researchers also aim to conduct further tests in microgravity environments to ensure the system’s viability for space missions.
Researchers believe the Dune-inspired FO-RO filtration system marks a significant step forward in space exploration. By improving waste management and hydration, astronauts can maintain better health and performance during missions.
The innovation could prove particularly crucial for NASA’s upcoming crewed missions to the Moon in 2025 and 2026 and to Mars by the early 2030s. These missions will involve extended spacewalks and limited resources, making efficient waste management and water recovery essential.
The high cost of transporting supplies to space also underscores the importance of such innovations. Reducing the need for pre-supplied drinking water can significantly lower mission costs and enhance the sustainability of long-duration space exploration.
As space agencies prepare for ambitious missions to explore deeper into our solar system, innovations like this Dune-inspired in-suit urine collection and filtration system could play a pivotal role in ensuring astronaut safety and mission success.
By turning to science fiction for inspiration, researchers have taken a visionary step toward making the dream of sustainable space travel a reality.
“In response to difficulties astronauts have faced with personal hygiene and performance and work efficiency during EVAs, we designed a novel urine collection and filtration system for the next generation of spacesuits,” researchers wrote. “With an understanding of the space and battery capacity limitations of spacesuits, we argue that the trade-off for improved performance and sufficient water in case of a contingency scenario is well worth it.”
Tim McMillan is a retired law enforcement executive, investigative reporter and co-founder of The Debrief. His writing typically focuses on defense, national security, the Intelligence Community and topics related to psychology. You can follow Tim on Twitter: @LtTimMcMillan. Tim can be reached by email: tim@thedebrief.org or through encrypted email: LtTimMcMillan@protonmail.com
Astronauts could have a healthier and more sustainable way of going to the bathroom in space.
By Paul Smaglik
Jul 12, 2024

Side view of the whole system, worn as a backpack (Credit: Karen Morales)
One of the most frequent questions astronauts get asked is, how do you go to the bathroom in space? For decades, their reply has been the same icky answer: they essentially soil their suits.
Astronauts in transit (space stations have more sanitary solutions — but even those can sometimes go awry) have long depended on what are essentially adult diapers to absorb their urine. For short missions, this is merely uncomfortable, and just a bit gross. But for longer journeys — like, perhaps ones planned to Mars — this approach can cause health problems, including serious rashes and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
A team of Cornell University engineers have developed a healthier, more comfortable approach: a system that collects and filters the urine, according to a report in Frontiers in Space Technologies.
Space Diaper Alternative
The new technology not only protects the user from urine, it transforms the liquid waste into drinkable water. That sustainable approach lessens the need for astronauts to carry drinking water and also reduces the need to store, transport, and return urine back to Earth.
The system collects the urine in a cup that covers the wearer’s genitals, vacuums it through an external catheter and directs it into an osmosis system that transforms the urine into filtered water.
An undergarment constructed from multiple layers of flexible fabric holds the fitted silicon cup in place. The cup is lined with a nylon-spandex blend, which draws urine away from the body and towards the inner cup’s inner face. A moisture sensor then activates a pump to move the urine from the cup into the filtration system.
Astronauts have long complained about what NASA calls its Maximum Absorbency Garment (MAG) – a multi-layered adult diaper made of superabsorbent polymer. The MAG has been in use since the late 1970s.
“The MAG has reportedly leaked and caused health issues such as urinary tract infections and gastrointestinal distress,” Sofia Etlin, a research staff member at Weill Cornell Medicine and Cornell University, and the study’s first author, said in a statement.
“Additionally, astronauts currently have only one liter of water available in their in-suit drink bags. This is insufficient for the planned, longer-lasting lunar spacewalks, which can last ten hours, and even up to 24 hours in an emergency,” said Etlin.
Read More: How Astronauts Go to the Bathroom in Outer Space
High-Tech Backpack
Longer voyages — like the planned Artemis II mission to the Moon — would be safer and more comfortable for astronauts if they had better waste management systems. A crewed mission to Mars, which is expected in the early 2030s, almost necessitates one.
While the cup and tube provide the collection for the system, a high-tech backpack contains the filtration system. Reverse osmosis removes the water from the urine, then a pump separates the salt from the remaining water. The purified water is then enriched with electrolytes and pumped into an in-suit drink bag, ready for consumption. Collecting and purifying 500ml of urine takes only five minutes.
The design will first be piloted in simulated conditions, then tried during actual spacewalks.
“Our system can be tested in simulated microgravity conditions, as microgravity is the primary space factor we must account for,” Christopher Mason, an Emory engineer and the study’s lead author, said in a statement. “These tests will ensure the system’s functionality and safety before it is deployed in actual space missions.”
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com use peer-reviewed studies and high-quality sources for our articles, and our editors review for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources used below for this article:
Frontiers in Space Technology. Enhanced astronaut hygiene and mission efficiency: a novel approach to in-suit waste management and water recovery in spacewalks
Research staff member at Weill Cornell Medicine and Cornell University, and the study’s first author. Sofia Etlin
Emory engineer and the study’s lead author. Christopher Mason
Before joining Discover Magazine, Paul spent over 20 years as a science journalist, specializing in U.S. life science policy and global scientific career issues. He began his career in newspapers, but switched to scientific magazines. His work has appeared in publications including Science News, Science, Nature, and Scientific American.
Canada begins next phase of Canadarm3 development for Lunar Gateway
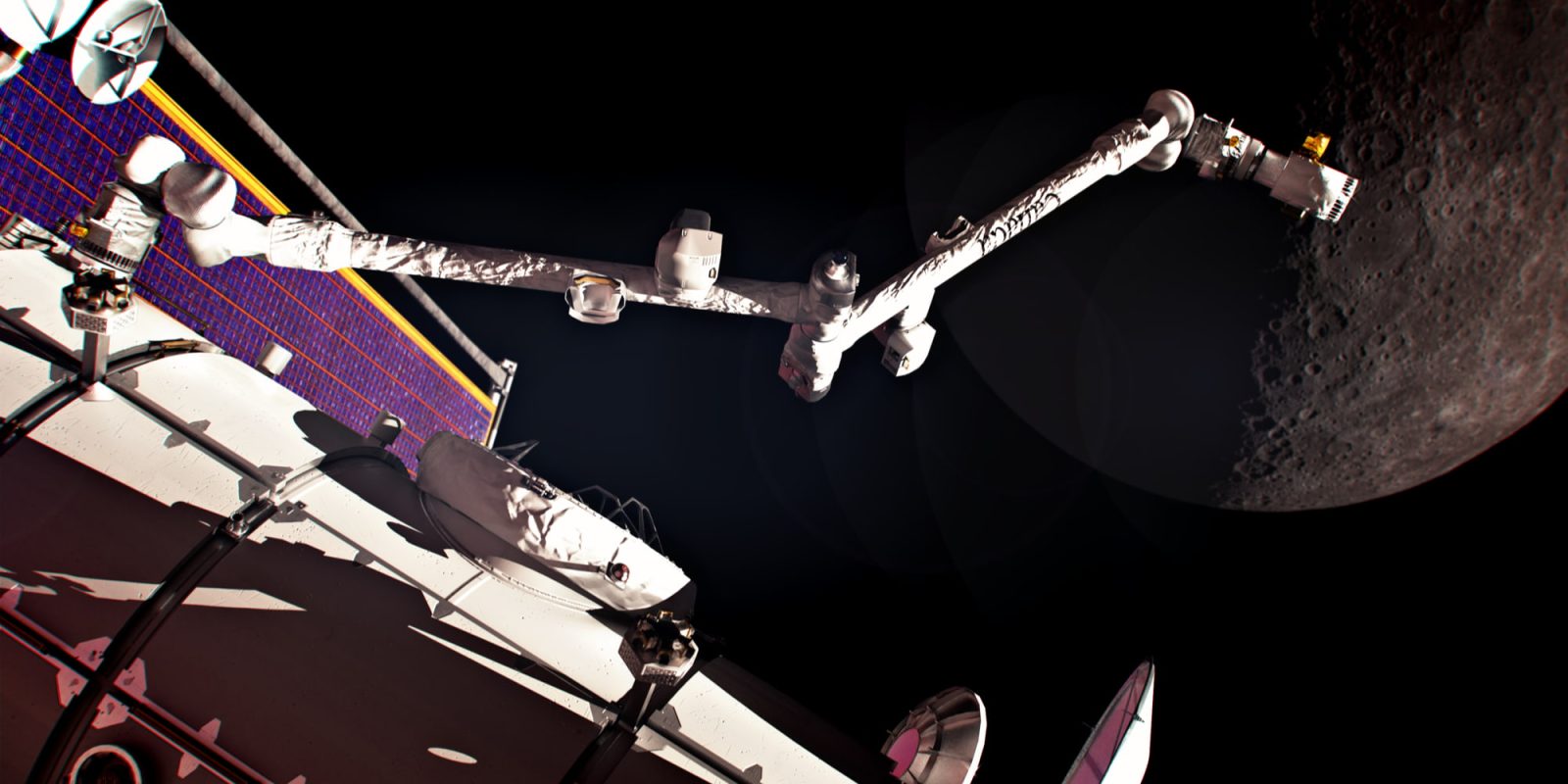

The Canadian Space Agency has awarded MDA Space a $1 billion contract for the next phases of the Canadarm3 program. This robotic system is integral to NASA’s Gateway, a space station that will circle the Moon to support the Artemis program.
According to the Canadian space agency, the contract covers Phase C (final design) and Phase D (construction, system assembly, integration, and testing) of the full robotics system. This includes a large arm, a smaller dexterous arm, specialized tools, and a ground segment for command and control.
The Lunar Gateway is a key component of NASA’s Artemis program and the U.S. space agency’s efforts to return humans to the Moon and lay the groundwork for future missions to Mars. The first modules of this deep space outpost are expected to launch later this decade and will be located in a gravitationally balanced trajectory between Earth and the Moon called a near-rectilinear halo orbit.
Like its Canadarm2 predecessor at the International Space Station in low Earth orbit, the more advanced Canadarm3 robotics system is expected to enable the assembly, maintenance, and servicing of Gateway, performing tasks that would be challenging for astronauts due to the harsh deep space environment.
MDA Space will oversee the commissioning of the robotics system in orbit from its new mission control center in Brampton, Ontario. This self-described state-of-the-art facility provides the necessary infrastructure to manage and control the complex operations of Canadarm3. The contract also provides for extensive planning and personnel training for on-orbit mission operations, which aims to ensure the team is well-prepared for the challenges of remote operations in space.
“We are entering an exciting period where Canadarm3 will take shape and come to life on our production floor. This critical investment in Canadarm3 reinforces and expands our national and industry leadership as a new era of space opens up,” Mike Greenley, CEO of MDA Space said in a press release. “This major milestone also reflects our strategy in action as we build our significant backlog and bring to market a new generation of commercial space products and services.”
Over 200 Canadian companies are expected to be engaged in Phases C and D, fostering job creation, skills development, and economic growth within the Canadian space industry according to the Canadian Space Agency. The collaborative nature of the project would highlight the significant contributions of the Canadian industrial base to the global space sector.
“This contract highlights Canada’s commitment to the next chapter of lunar exploration. Building on the legacy of strategic investments in space robotics, Canadarm3 showcases our commitment to innovation,” said François-Philippe Champagne, Canada’s Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry. “Beyond enhancing Canada’s position of developing and retaining top talents and world-renowned innovators, this initiative supports high-quality jobs and opportunities for growth within the country’s expanding space sector.”
The FAA needs to sign off on SpaceX’s investigation before the Falcon 9 can fly again.
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket experienced an engine failure after it launched late Thursday night from the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The mission, Starlink Group 9-3, was carrying Starlink satellites and failed to reignite its upper second stage after developing a leak. “Upper stage restart to raise perigee resulted in an engine RUD for reasons currently unknown,” Elon Musk said overnight, confirming that the engine experienced a “rapid unscheduled disassembly.”
Falcon 9’s second stage performed its first burn nominally, however a liquid oxygen leak developed on the second stage. After a planned relight of the upper stage engine to raise perigee – or the lowest point of orbit – the Merlin Vacuum engine experienced an anomaly and was unable to complete its second burn.
The company’s statement says it will do a full investigation into the incident in coordination with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), the company said on its website. The Falcon 9 has been grounded by the FAA pending the results of the investigation, reports CNBC.
The Falcon 9 has a lot riding on it — literally. It has been used for 52 percent of all orbital launches this year, according to Gunter Krebs's Orbital Launches tracker. (Thursday’s launch was the 70th Falcon 9 launch in 2024; in all of 2023, the Falcon 9 was used for 96 launches.)
This was the first Falcon 9 failure since 2016 when a rocket exploded on the launch pad.
As a result of the failure, SpaceX said the Starlink satellites were deployed to “a lower than intended orbit.”
On Friday afternoon, the company said it had made contact with 10 satellites of the 20 that had been onboard but noted that the satellites are “in an enormously high-drag environment with their perigee, or lowest point of their elliptical orbit.” The maximum available thrust is “unlikely to be enough to successfully raise the satellites,” SpaceX said, meaning that they will reenter the atmosphere and “fully demise.”
The satellites “do not pose a threat to other satellites in orbit or to public safety,” according to the company.
Jay Peters, a news editor who writes about technology, video games, and virtual worlds. He’s submitted several accepted emoji proposals to the Unicode Consortium.
SpaceX’s historic Falcon 9 success streak met a fiery end
BY ANDREW PAUL
POSTED ON JUL 12, 2024
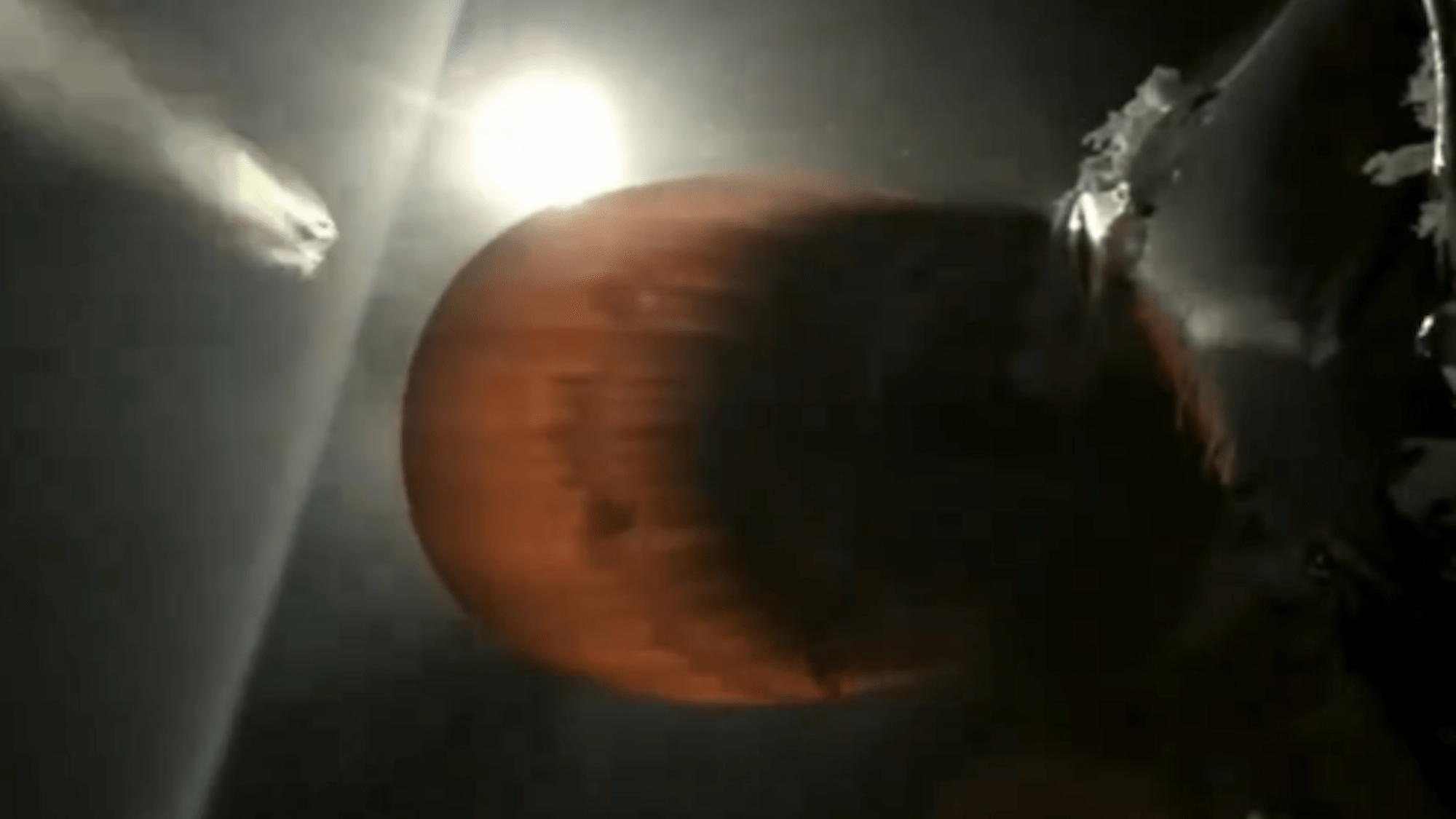

An accumulation of ice was seen around the rocket's Merlin Vacuum engine shortly before it exploded. Credit: X
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket exploded July 11 evening, roughly an hour after launching from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The upper engine’s rapid unscheduled disassembly (RUD) marked the company’s first accident in roughly eight years and ended a record-setting streak of nearly 300 successful missions that have transported cargo, satellites, and astronauts.
SpaceX intended Thursday night’s launch to deliver its latest batch of Starlink internet satellites into orbit. Although the 20 satellites deployed, they did so lower than planned and in the wrong orbit. According to astrophysicist Jonathan McDowell on X, the payload likely released within an orbit that ranged from 86-to-183 miles above Earth instead of a circular, constant 183-mile altitude. SpaceX eventually established contact with at least 10 Starlink satellites, but even so, the company later confirmed they aren’t salvageable.
The first in-flight failure for SpaceX's Falcon rocket family since June 2015, a streak of 344 consecutive successful launches until tonight.
A lot of unusual ice was observed on the Falcon 9's upper stage during its first burn tonight, some of it falling into the engine plume. https://t.co/1vc3P9EZjj pic.twitter.com/fHO73MYLms— Stephen Clark (@StephenClark1) July 12, 2024
“The team made contact… and attempted to have them raise orbit using their ion thrusters, but they are in an enormously high-drag environment with their perigee, or lowest point of their elliptical orbit,” SpaceX posted on social media on Thursday evening before confirming the satellites will eventually re-enter Earth’s atmosphere and “fully demise.”
“They do not pose a threat to other satellites in orbit or to public safety,” SpaceX officials added.
The explosion’s exact cause won’t be available until a full review of the accident, but as Ars Technica noted on July 12, a livecast of the launch depicted “an usual build-up of ice” around the Falcon 9’s Merlin Vacuum engine, or M-Vac. The engine uses a propellant composed of cryogenic liquid oxygen and kerosene, and although video appeared to show it successfully completing its first burn, the ice may have contributed to a later engine issue after SpaceX’s live stream ended.
[Related: SpaceX’s Starship may mess up the lunar surface.]
Even with the setback, Falcon 9’s current iteration, the Falcon 9 Block 5, undoubtedly remains the most successful and reliable rocket ever designed. With a total of 297 launches since Block 5’s 2018 debut, the reusable craft still has a 99.7 percent success rate.
Falcon 9’s last and sole other in-flight explosion occurred on June 28, 2015, when its upper stage’s liquid oxygen tank exploded just minutes after launch, destroying it and its uncrewed Dragon capsule cargo intended for the International Space Station. In that instance, Falcon 9 remained grounded for six months as SpaceX reviewed the accident.
It isn’t clear yet how long it may take before Falcon 9 rockets resume their missions. Apart from its semiregular Starlink satellite deliveries, billionaire Jared Isaacman’s Polaris Dawn mission to complete the first commercial spacewalk is scheduled for later this month. In August, SpaceX also intended to ferry NASA’s Crew-9 team of four astronauts to the ISS.
“SpaceX has an incredible track record with Falcon9 [sic],” Isaacman posted to X on July 12. “… We will fly whenever SpaceX is ready and with complete confidence in the rocket, spaceship and operations.”
Falcon 9 Suffers Rare Engine Failure, Losing Starlink Satellites
By Rachel Jewett | July 12, 2024

Frozen propellant is visible on the second stage Falcon 9 engine during the launch failure on July 11. Screenshot via SpaceX
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket suffered an engine failure during a Starlink mission on July 11, losing 20 Starlink satellites and triggering a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) investigation. This is a rare incident for the rocket which hasn’t had a major failure since 2015.
The mission took off from Vandenberg Space Force Base at 7:36 p.m. PT on July 11, carrying 20 direct-to-cell Starlink satellites. During launch, stage separation was successfully and the first stage returned to Earth. The Starlink satellites were deployed 3 minutes and 11 seconds into the mission, which is in line with another recent direct-to-cell launch.
SpceX issued a statement on July 12, reporting that after stage separation and a nominal first burn, a liquid oxygen leak developed on the second stage. The Merlin Vacuum engine experienced an anomaly and was unable to complete its second burn. While it did deploy the satellites, the engine did not circularize its orbit.
Pieces of the second stage engine were visibly breaking off during the launch broadcast, and frozen propellant could be seen as well.
SpaceX said the satellites were released to an an eccentric orbit with a very low perigee of 135 km, which is less than half the expected perigee altitude. SpaceX said this is a high-drag environment and maximum available onboard thrust would be unlikely to raise the satellites orbit. The satellites will re-enter the atmosphere.
After the launch, SpaceX founder Musk detailed efforts to raise the satellite orbits on X. “We’re updating satellite software to run the ion thrusters at their equivalent of warp 9. Unlike a Star Trek episode, this will probably not work, but it’s worth a shot,” he said.
The FAA said in a statement that the failure requires an investigation.
“A return to flight is based on the FAA determining that any system, process, or procedure related to the mishap does not affect public safety. In addition, SpaceX may need to request and receive approval from the FAA to modify its license that incorporates any corrective actions and meet all other licensing requirements,” the FAA statement reads.
SpaceX said it will work with the FAA throughout the investigation.
“This event is a reminder of how technically challenging spaceflight is,” SpaceX said in a statement. “SpaceX will perform a full investigation in coordination with the FAA, determine root cause, and make corrective actions to ensure the success of future missions. With a robust satellite and rocket production capability, and a high launch cadence, we’re positioned to rapidly recover and continue our pace as the world’s most active launch services provider.”
A grounded Falcon 9 will likely impact a number of upcoming missions, including the Polaris Dawn human spaceflight mission set for no earlier than July 31, and Space Norway’s Arctic Satellite Broadband Mission (ASBM) set for mid-July.
Seradata, a Slingshot Aerospace company that tracks launches and satellites in orbit, noted that Falcon 9 has not had a major failure since 2015 when the second stage tank exploded in a Dragon cargo mission for NASA.
Facon 9 has had four failures — two minor launch dispenser failures in 2023, the 2015 Dragon mission, and a 2012 first stage engine shutdown. Seradata reports the Falcon 9 and Heavy family has flown 363 times.

Frozen propellant is visible on the second stage Falcon 9 engine during the launch failure on July 11. Screenshot via SpaceX
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket suffered an engine failure during a Starlink mission on July 11, losing 20 Starlink satellites and triggering a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) investigation. This is a rare incident for the rocket which hasn’t had a major failure since 2015.
The mission took off from Vandenberg Space Force Base at 7:36 p.m. PT on July 11, carrying 20 direct-to-cell Starlink satellites. During launch, stage separation was successfully and the first stage returned to Earth. The Starlink satellites were deployed 3 minutes and 11 seconds into the mission, which is in line with another recent direct-to-cell launch.
SpceX issued a statement on July 12, reporting that after stage separation and a nominal first burn, a liquid oxygen leak developed on the second stage. The Merlin Vacuum engine experienced an anomaly and was unable to complete its second burn. While it did deploy the satellites, the engine did not circularize its orbit.
Pieces of the second stage engine were visibly breaking off during the launch broadcast, and frozen propellant could be seen as well.
SpaceX said the satellites were released to an an eccentric orbit with a very low perigee of 135 km, which is less than half the expected perigee altitude. SpaceX said this is a high-drag environment and maximum available onboard thrust would be unlikely to raise the satellites orbit. The satellites will re-enter the atmosphere.
After the launch, SpaceX founder Musk detailed efforts to raise the satellite orbits on X. “We’re updating satellite software to run the ion thrusters at their equivalent of warp 9. Unlike a Star Trek episode, this will probably not work, but it’s worth a shot,” he said.
The FAA said in a statement that the failure requires an investigation.
“A return to flight is based on the FAA determining that any system, process, or procedure related to the mishap does not affect public safety. In addition, SpaceX may need to request and receive approval from the FAA to modify its license that incorporates any corrective actions and meet all other licensing requirements,” the FAA statement reads.
SpaceX said it will work with the FAA throughout the investigation.
“This event is a reminder of how technically challenging spaceflight is,” SpaceX said in a statement. “SpaceX will perform a full investigation in coordination with the FAA, determine root cause, and make corrective actions to ensure the success of future missions. With a robust satellite and rocket production capability, and a high launch cadence, we’re positioned to rapidly recover and continue our pace as the world’s most active launch services provider.”
A grounded Falcon 9 will likely impact a number of upcoming missions, including the Polaris Dawn human spaceflight mission set for no earlier than July 31, and Space Norway’s Arctic Satellite Broadband Mission (ASBM) set for mid-July.
Seradata, a Slingshot Aerospace company that tracks launches and satellites in orbit, noted that Falcon 9 has not had a major failure since 2015 when the second stage tank exploded in a Dragon cargo mission for NASA.
Facon 9 has had four failures — two minor launch dispenser failures in 2023, the 2015 Dragon mission, and a 2012 first stage engine shutdown. Seradata reports the Falcon 9 and Heavy family has flown 363 times.
This image from video provided by SpaceX shows the upper stage engine of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, which blasted off from California on Thursday, July 11, 2024. The rocket, carrying 20 Starlink satellites, malfunctioned during the blast, leaving the company’s internet satellites in a precariously low orbit. (SpaceX via AP)
BY MARCIA DUNN
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (AP) — A SpaceX rocket has failed for the first time in nearly a decade, leaving the company’s internet satellites in an orbit so low that they’re doomed to fall through the atmosphere and burn up.
The Falcon 9 rocket blasted off from California on Thursday night, carrying 20 Starlink satellites. Several minutes into the flight, the upper stage engine malfunctioned. SpaceX on Friday blamed a liquid oxygen leak.
The company said flight controllers managed to make contact with half of the satellites and attempted to boost them to a higher orbit using onboard ion thrusters. But with the low end of their orbit only 84 miles (135 kilometers) above Earth — less than half what was intended — “our maximum available thrust is unlikely to be enough to successfully raise the satellites,” the company said via X.
SpaceX said the satellites will reenter the atmosphere and burn up. There was no mention of when they might come down. More than 6,000 orbiting Starlinks currently provide internet service to customers in some of the most remote corners of the world.
The Federal Aviation Administration said the problem must be fixed before Falcon rockets can fly again.
It was not known if or how the accident might impact SpaceX’s upcoming crew flights. A billionaire’s spaceflight is scheduled for July 31 from Florida with plans for the first private spacewalk, followed in mid-August by an astronaut flight to the International Space Station for NASA.
The tech entrepreneur who will lead the private flight, Jared Isaacman, said Friday that SpaceX’s Falcon 9 has “an incredible track record” and as well as an emergency escape system.
The last launch failure occurred in 2015 during a space station cargo run. Another rocket exploded the following year during testing on the ground.
SpaceX’s Elon Musk said the high flight rate will make it easier to identify and correct the problem.
General Atomics Wins Space Force Contract for Second EWS Satellite

An the Electro-Optical Infrared (EO/IR) Weather System (EWS) satellite. Photo: General Atomics
General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems (GA-EMS) has won a new contract from US Space Force’s (USSF) Space Systems Command (SSC) in the area of space weather. The deal aims to help alleviate U.S. government on-orbit risks through delivery of a second weather satellite and to provide three years of operations services for each of the two satellites to support the Electro-Optical Infrared (EO/IR) Weather System (EWS) program. GA-EMS announced the contract award on July 11.
This award modifies the current GA-EMS contract to design and deliver an operational EWS spacecraft with integrated EO/IR payloads to support the transition of the USSF’s aging Defense Meteorological Support Program (DMSP) on-orbit systems to a new generation of affordable, high performance, small weather satellites. As the prime contractor, GA-EMS is responsible for the spacecraft bus and EO/IR payload design development, build, assembly, integration and test.
“This contract is a testament to GA-EMS’ ability to design and deliver advanced EWS satellites that will provide timely, accurate weather data to support Department of Defense operations across all domains. We are currently working toward the delivery of the first EWS satellite and associated ground systems, with spacecraft build and EO/IR payload testing well underway. We are excited to begin the build and integration of a second EWS satellite to help support USSF efforts to extend EO/IR data collection capabilities as legacy DMSP satellites are retired,” Scott Forney, president of GA-EMS, said in a statement.
NASA releases new 'Penguin and Egg' image from James Webb Space Telescope
New image shows 2 interacting galaxies that lie 326 million light-years from Earth
Nicole Mortillaro · CBC News ·

NASA has released a stunning new image from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) marking the two-year anniversary of the release of its first images. And the space agency is calling it the "Penguin and Egg."
What exactly are we looking at? Well, it's two interacting galaxies known jointly as Arp 142 that lie 326 million light-years from Earth.
They are 100,000 light-years apart, which may sound far, but in astronomical terms, that's very close. In contrast, our Milky Way and the closest major galaxy to us — the Andromeda galaxy — are separated by 2.5 million light years.
The Penguin and Egg galaxies made their first pass some time between 25 and 75 million years ago, NASA said in a release. This, in turned, triggered a new star formation in the Penguin.
Galactic mergers can cause galaxies to form thousands of new stars a year over millions of years. In the case of the Penguin, NASA said, research suggests that about 100 to 200 new stars have formed each year. This is many times more than what is happening in our own galaxy, where only roughly six to seven new stars form each year.
 Webb’s mid-infrared view of interacting galaxies Arp 142. This image was taken by MIRI, the telescope’s mid-infrared instrument, which astronomers use to study cooler and older objects, dust, and extremely distant galaxies. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI)
Webb’s mid-infrared view of interacting galaxies Arp 142. This image was taken by MIRI, the telescope’s mid-infrared instrument, which astronomers use to study cooler and older objects, dust, and extremely distant galaxies. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI)Before the galactic interaction, the Penguin was a spiral galaxy. Now, the centre forms the "eye" of the Penguin. The Egg, on the other hand, is an elliptical galaxy, which contains much older stars.
At the top right of the image is the PGC 1237172 galaxy, which is 100 million light-years closer to Earth, according to a release by the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md.
And, of course, in the background lie thousands more galaxies.
The gift that keeps on giving
JWST is the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope.
Unlike Hubble's one mirror, JWST has 18 individual mirrors that make up for one giant one. That makes it a light-catching machine, allowing it see some of the faintest objects and to peer far back into the earliest times of the universe.
That's why astronomers were so excited when this game-changing telescope was launched on Dec. 25, 2021. It was a Christmas gift headed to orbit around the moon, just waiting to be unwrapped.
The first image released blew astronomers away.

It was the telescope's first wide-field image, which provided the sharpest and deepest infrared image of thousands of galaxies.
And JWST is the gift that keeps on giving, particularly to astronomers looking to better understand our universe and how we got here.
The telescope, with its massive light-collecting capability, is changing the way astronomers look at our universe. Its observations have challenged the idea of how stars form and even how fast the universe is expanding.

"[I'm] incredibly, incredibly grateful because the pictures that we are able to see now … it was not something that we thought we will be able to see," said Lamiya Mowla an assistant professor at Wellesley University in Wellesley, Mass.
She is one of several scientists who are part of the Canadian NIRISS Unbiased Cluster Survey (CANUCS).
"[Previously,] we were talking about that we will be able to resolve things down to … hundreds of light years or so, down to that level in a very, very early universe. Now, we can see that we can almost get down to tens of light years."
Data on exoplanets a 'game changer'
And while we don't get the jaw-dropping images from Webb when it comes to the study of exoplanets — planets orbiting other stars — its data is proving to be incredibly helpful in understanding planetary atmospheres, especially larger planets that are more similar to our outer planets, such as Jupiter and Neptune.
Newly released image from James Webb telescope reveals Orion Nebula in 'amazing detail'James Webb Space Telescope reveals some of the oldest stars in our universe
"If you look at other planets like hot Jupiters, or even colder, like Neptune, or Neptune-sized planets that are a bit colder … James Webb is really a game changer," said Olivia Lim, a PhD student at the Université de Montréal and member of the Trottier Institute for Research of Exoplanets, who's main area of focus is the seven-exoplanet system known as TRAPPIST-1.
"People are able to measure things that we weren't able to measure before or they're they're able to do it with so much more precision."
And, of course, the telescope has also provided images of phenomena closer to home, such as a jaw-dropping image of Uranus and its rings.

Mowla said that she's incredibly grateful for JWST and what it can tell us about our own origins.
"The things that we are seeing over here is what it has taken the universe to get us to the point that we are at today, the world that we take for granted. It has spent 13.7 billion years to build this perfect Earth," she said.
"I'm pretty sure there are habitable planets in every galaxy. We just haven't found them yet."
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Nicole Mortillaro
Senior Science Reporter
Based in Toronto, Nicole covers all things science for CBC News. As an amateur astronomer, Nicole can be found looking up at the night sky appreciating the marvels of our universe. She is the editor of the Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada and the author of several books. In 2021, she won the Kavli Science Journalism Award from the American Association for the Advancement of Science for a Quirks and Quarks audio special on the history and future of Black people in science. You can send her story ideas at nicole.mortillaro@cbc.ca.
Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have witnessed the dramatic dance between a supermassive black hole-powered quasar and merging galaxies less than a billion years after the Big Bang.

By Robert Lea
SPACE.COM
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have observed the dramatic "dance" between a supermassive black hole and two satellite galaxies. The observations could help scientists better understand how galaxies and supermassive black holes grew in the early universe.
This particular supermassive black hole is feeding on surrounding matter and powering a bright quasar that is so distant that JWST sees it as it was less than a billion years after the Big Bang. The quasar, designated PJ308-21, is localized to an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in a galaxy that is in the process of merging with two massive satellite galaxies.
Not only did the team determine that the black hole has a mass equivalent to two billion suns, but they also found that both the quasar and the galaxies involved in this merger are highly evolved, a surprise considering they existed when the 13.8-year-old cosmos was just an infant.
The merger of these three galaxies is likely to deliver to the supermassive black hole vast amounts of gas and dust, which will facilitate its growth and allow it to keep powering PJ308-21.
Related: Study finds black holes made from light are impossible — challenging Einstein's theory of relativity
"Our study reveals that both the black holes at the center of high-redshift [early and distant] quasars and the galaxies that host them undergo extremely efficient and tumultuous growth already in the first billion years of cosmic history, aided by the rich galactic environment in which these sources are formed," team leader Roberto Decarli, a researcher at Italy's National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), said in a statement.
The data was collected in September 2022 by JWST's Near InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec) instrument as part of the 1554 Program, which aims to observe the merger between the galaxy hosting PJ308-21 and two of its satellite galaxies.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.Contact me with news and offers from other Future brandsReceive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsorsBy submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.
Decarli added that the work represented a real "emotional rollercoaster" for the team, which developed innovative solutions to overcome the initial difficulties in data reduction and produce images with an uncertainty of less than 1% per pixel.
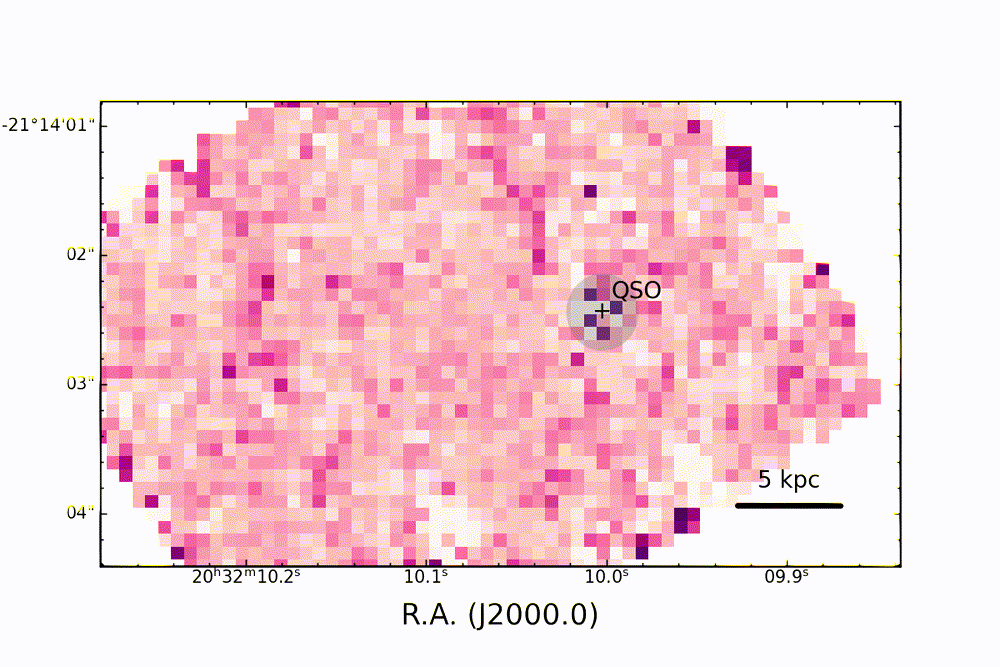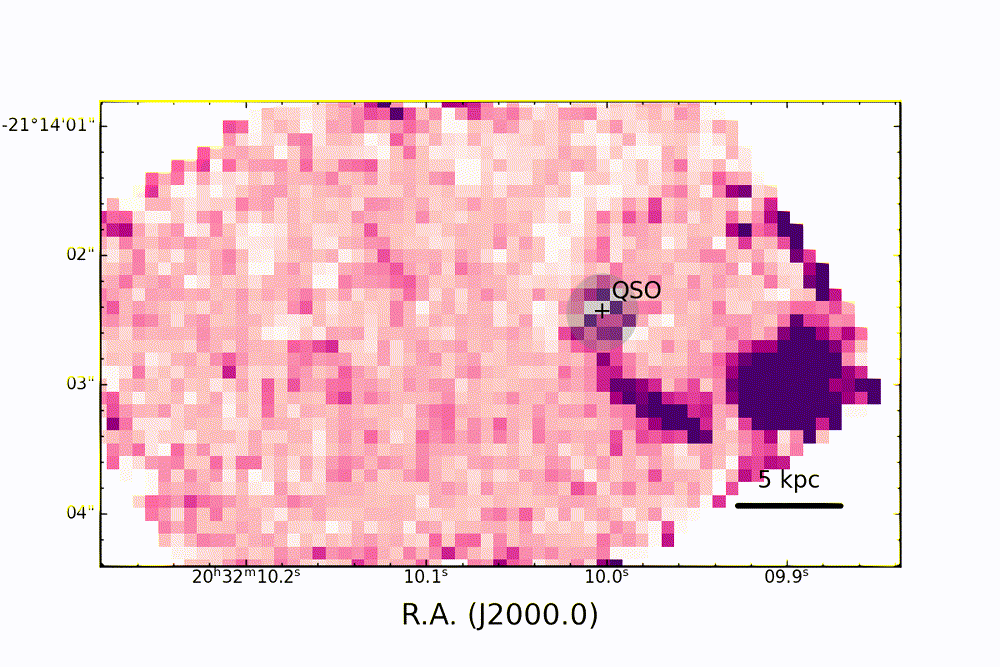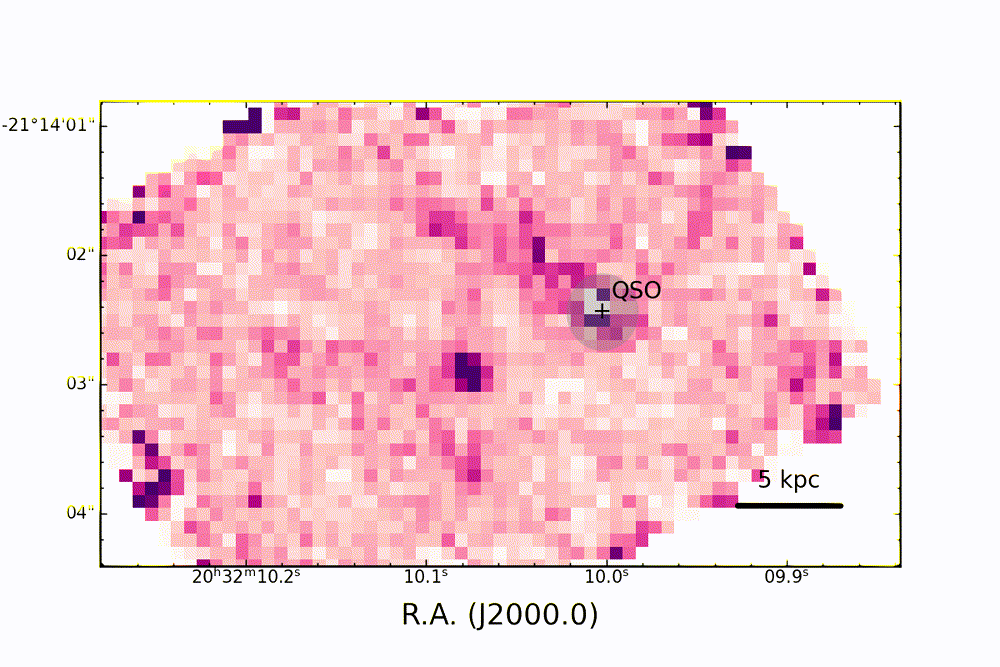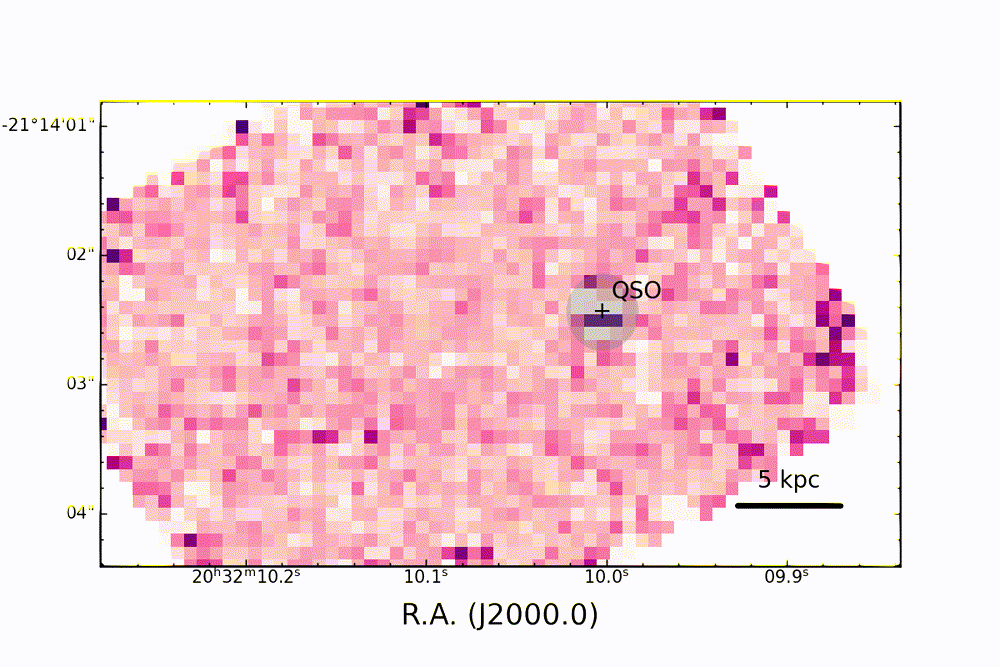
Map of ionizing oxygen emission in the PJ308-21 system, observed with the JWST showing a complex three-dimensional structure of the system and the "cosmic dance" of the satellite galaxies around the quasar. (Image credit: Decarli et. at / INAF / A&A 2024)
A very metal quasar
Quasars are born when supermassive black holes with masses millions or billions of times that of the sun that sit at the heart of galaxies are surrounded by a wealth of gas and dust. This matter forms a flattened cloud called an accretion disk that swirls around the black hole and gradually feeds it.
The immense gravitational forces of the black hole generate powerful tidal forces in this accretion disk, which heat this gas and dust temperatures as great as 120,000 degrees Fahrenheit (67,000 degrees Celsius). This causes the accretion disk to emit light across the electromagnetic spectrum. This emission can often be brighter than the combined light of every star in the surrounding galaxy, making quasars like PJ308-21 some of the brightest objects in the cosmos.
While black holes don't have characteristics that can be used to determine how evolved they are, their accretion disks (and thus quasars) do. In fact, galaxies can be "aged" in the same way.

An artist's impression of a supermassive black hole and its accretion disk. (Image credit: S. Dagnello (NRAO/AUI/NSF))
The early universe was filled with hydrogen, the lightest and simplest element, and a little helium. This formed the basis of the first stars and galaxies, but during the life of these stellar bodies, they forged elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, which astronomers call "metals."
When these stars ended their lives in massive supernova explosions, these metals were dispersed throughout their galaxies and went on to be the building blocks of the next generation of stars. This process saw stars, and through them galaxies, becoming progressively "metal rich."
The team found that, like most AGNs, the active heart of PJ308-21 is metal-rich, and the gas and dust around it are being "photoionized. " This is the process by which particles of light, called photons, provide the energy that electrons need to escape atoms, creating electrically charged ions.
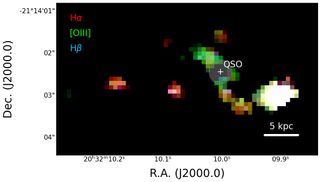
Map of line emissions of hydrogen (in red and blue) and oxygen (in green), in the PJ308-21 system, shown after masking the light from the central quasar (QSO). The different colors of the quasar's host galaxy and companion galaxies in this map reveal conditions and physical properties of the gas within them. (Image credit: Decarli et. at / INAF / A&A 2024)
One of the galaxies that's merging with the host galaxy PJ308-21 is also metal-rich, and its matter is also being partially photoionized by electromagnetic radiation from the quasar.
Photoionization is also happening in the second satellite galaxy, but in that case, it is being caused by a bout of rapid star formation. This second galaxy also differs from the first and the AGN, as it appears to be metal-poor.
"Thanks to NIRSpec, for the first time, we can study, in the PJ308-21 system, the optical band rich in precious diagnostic data on the properties of the gas near the black hole in the galaxy hosting the quasar and in the surrounding galaxies," said team member and INAF astrophysicist Federica Loiacono. "We can see, for example, the emission of hydrogen atoms and compare it with that of the chemical elements produced by the stars to establish how rich the gas is in metals."
Though light leaves this early-universe quasar across the broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum, including optical light and X-rays, the only way to observe it is in infrared.
That's because, as the light has traveled for over 12 billion years to reach JWST, the expansion of the universe has "stretched" its wavelengths considerably. That "shifts" the light in the direction of the "red end" of the electromagnetic spectrum, a phenomenon understandably called "redshift," which is denoted as "z" by astronomers.
JWST is adept at seeing "high red-shift" or "high-z" objects and events like PJ308-21 because of its sensitivity to infrared light.
"Thanks to the sensitivity of the JWST in the near and mid-infrared, it was possible to study the spectrum of the quasar and companion galaxies with unprecedented precision in the distant universe," Loiacono concluded. "Only the excellent 'view' offered by JWST is able to ensure these observations."
The team's research was accepted for publication in June 2024 in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Originally posted on Space.com.
Published: July 12, 2024
Of the more than 74,000 known meteorites – rocks that fall to Earth from asteroids or planets colliding together – only 385 or so stones came from the planet Mars.
It’s not that hard for scientists to work out that these meteorites come from Mars. Various landers and rovers have been exploring Mars’ surface for decades. Some of the early missions – the Viking landers – had the equipment to measure the composition of the planet’s atmosphere. Scientists have shown that you can see this unique Martian atmospheric composition reflected in some of these meteorites.
Mars also has unique oxygen. Everything on Earth, including humans and the air we breathe, is made up of a specific composition of the three isotopes of the element oxygen: oxygen-16, oxygen-17 and oxygen-18. But Mars has an entirely different composition – it’s like a geochemical fingerprint for being Martian.
The Martian meteorites found on Earth give geologists like me hints about the makeup of the red planet and its history of volcanic activity. They allow us to study Mars without sending a spacecraft 140 million miles away.
A planet of paradoxes
These Martian meteorites formed from once red-hot magma within Mars. Once these volcanic rocks cooled and crystallized, radioactive elements within them started to decay, acting as a radiometric clock that enables scientists to tell when they formed.
From these radiometric ages, we know that some Martian meteorites are as little as 175 million years old, which is – geologically speaking – quite young. Conversely, some of the Martian meteorites are older, and formed close to the time Mars itself formed.
These Martian meteorites tell a story of a planet that has been volcanically active throughout its entire history. In fact, there’s potential for Martian volcanoes to erupt even today, though scientists have never seen such an eruption.
The rocks themselves also preserve chemical information that indicates some of the major events on Mars happened early in its history. Mars formed quite rapidly, 4.5 billion years ago, from gas and dust that made up the early solar system. Then, very soon after formation, its interior separated out into a metallic core and a solid rocky mantle and crust.
Since then, very little seems to have disturbed Mars’ interior – unlike Earth, where plate tectonics has acted to stir and homogenize its deep interior. To use a food analogy, the Earth’s interior is like a smoothie and Mars’ is like a chunky fruit salad.

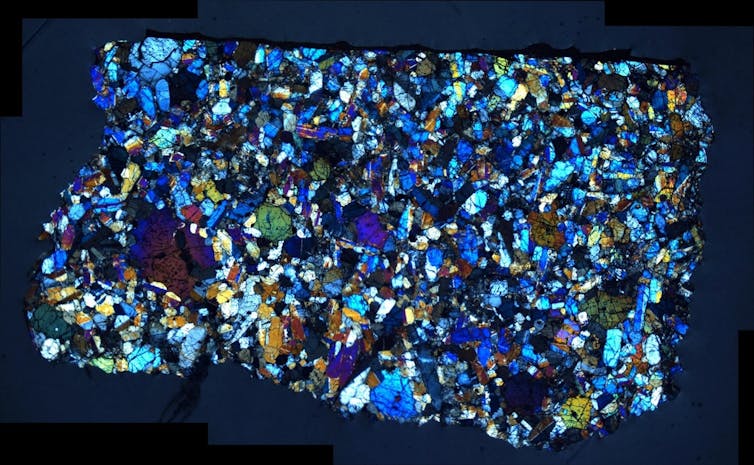
Martian meteorite samples are prepared for analysis in a clean lab. James Day
Martian volcano remnants
Understanding how Mars underwent such an early and violent adolescence, yet still may remain volcanically active today, is an area of great interest to me. I would like to know what the inside of Mars looks like, and how its interior makeup might explain features, like volcanoes, on the red planet’s surface.
When geologists set out to answer questions about volcanism on Earth, we typically examine lava samples that erupted at different places or times from the same volcano. These samples allow us to disentangle local processes specific to each volcano from planetary processes that take place at a larger scale.
It turns out we can do the same thing for Mars. The rather exotically named nakhlite and chassignite meteorites are a group of rocks from Mars that erupted from the same volcanic system some 1.3 billion years ago.
Nakhlites are basaltic rocks, similar to lavas you would find in Iceland or Hawaii, with beautiful large crystals of a mineral known as clinopyroxene. Chassignites are rocks made almost entirely of the green mineral olivine – you might know the gem-quality variety of this mineral, peridot.
Along with the much more common shergottites, which are also basaltic rocks, and a few other more exotic Martian meteorite types, these categories of meteorite constitute all the rocks researchers possess from the red planet.
When studied together, nakhlites and chassignites tell researchers several things about Mars. First, as the molten rock that formed them oozed to the surface and eventually cooled and crystallized, some surrounding older rocks melted into them.
That older rock doesn’t exist in our meteorite collection, so my team had to tease out its composition from the chemical information we obtained from nakhlites. From this information, we learned that the older rock was basaltic in composition and chemically distinct from other Martian meteorites. We found that it had been chemically weathered by exposure to water and brine.
This older rock is quite different from the Martian crust samples in our meteorite collection today. In fact, it is much more like what we would expect the Martian crust to look like, based on data gathered by rover missions and satellites orbiting Mars.
We know that the magmas that made nakhlites and chassignites come from a distinct portion of Mars’ mantle. The mantle is the rocky portion between Mars’ crust and metallic core. These nakhlites and chassignites come from the solid rigid shell at the top of Mars’ mantle, known as the mantle lithosphere, and this source makes them distinct from the more common shergottites.
Shergottites come from at least two sources within Mars. They may come from parts of the mantle just beneath the lithosphere, or even the deep mantle, which is closer to the planet’s metallic core
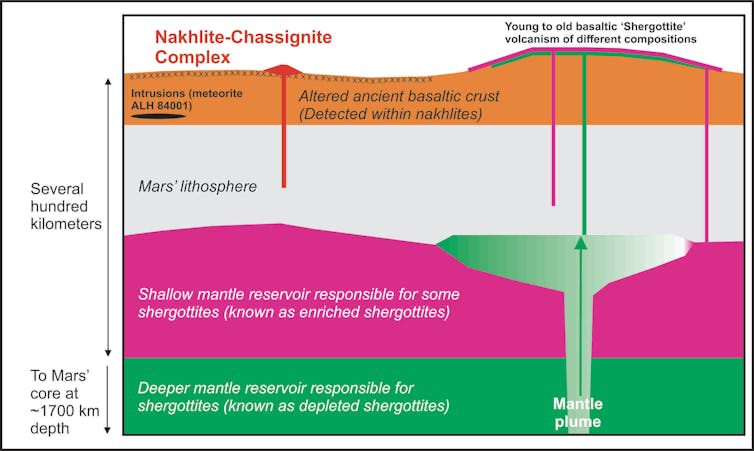
The interior structure of Mars, with the sources of meteorites indicated. James Day
Understanding how volcanoes on Mars work can inform future research questions to be addressed by missions to the planet. It can also help scientists understand whether the planet has ever been habitable for life, or if it could be in the future.
Hints at habitability
Earth’s active geological processes and volcanoes are part of what makes our planet habitable. The gases emanating from volcanoes are a major part of our atmosphere. So if Mars has similar geological processes, that could be good news for the potential habitability of the red planet.
Mars is much smaller than Earth, however, and studies suggest that it’s been losing the chemical elements essential for a sustainable atmosphere since it formed. It likely won’t look anything like Earth in the future.
Our next steps for understanding Mars lie in learning how the basaltic shergottite meteorites formed. These are a diverse and richly complex set of rocks, ranging in age from 175 million years to 2.4 billion years or so.
Studying these meteorites in greater detail will help to prepare the next generation of scientists to analyze rocks collected using the Perseverance Rover for the forthcoming NASA Mars Sample Return mission.
Professor of Geosciences, University of California, San Diego
Disclosure statement
James Day receives funding from NASA.
"What keeps me awake right now is the uncertainty."
ERIC BERGER - 7/12/2024,

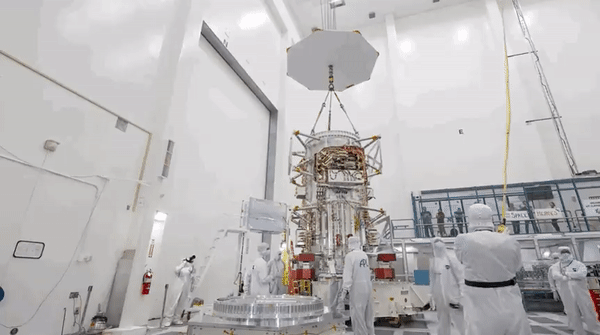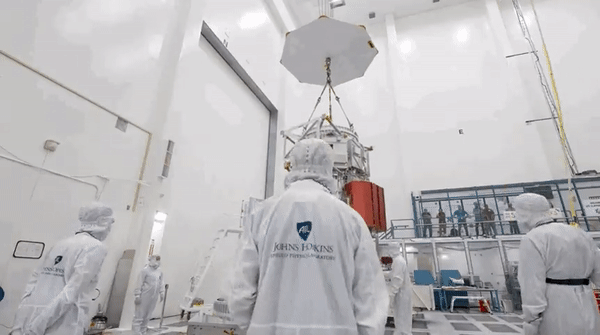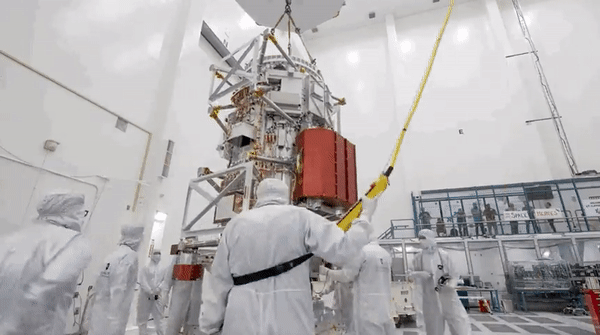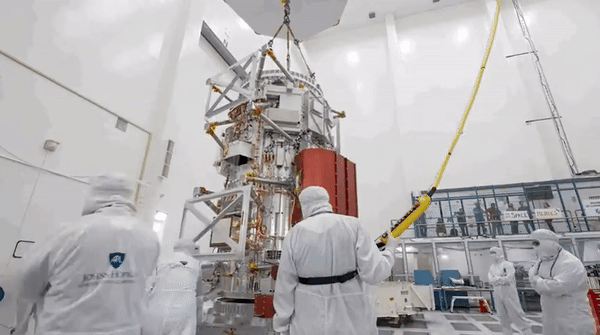
Enlarge / An artist's illustration of the Europa Clipper spacecraft during a flyby close to Jupiter's icy moon.
NASA/JPL-Caltech6
The launch date for the Europa Clipper mission to study the intriguing moon orbiting Jupiter, which ranks alongside the Cassini spacecraft to Saturn as NASA's most expensive and ambitious planetary science mission, is now in doubt.
The $4.25 billion spacecraft had been due to launch in October on a Falcon Heavy rocket from Kennedy Space Center in Florida. However, NASA has revealed that transistors on board the spacecraft may not be as radiation-hardened as they were believed to be.
"The issue with the transistors came to light in May when the mission team was advised that similar parts were failing at lower radiation doses than expected," the space agency wrote in a blog post Thursday afternoon. "In June 2024, an industry alert was sent out to notify users of this issue. The manufacturer is working with the mission team to support ongoing radiation test and analysis efforts in order to better understand the risk of using these parts on the Europa Clipper spacecraft."
The moons orbiting Jupiter, a massive gas giant planet, exist in one of the harshest radiation environments in the Solar System. NASA's initial testing indicates that some of the transistors, which regulate the flow of energy through the spacecraft, could fail in this environment. NASA is currently evaluating the possibility of maximizing the transistor lifetime at Jupiter and expects to complete a preliminary analysis in late July.
To delay or not to delay
NASA's update is silent on the question of whether the spacecraft could still make its approximately three-week launch window this year, which gets Clipper to the Jovian system in 2030.
Ars reached out to several experts familiar with the Clipper mission to gauge the likelihood that it makes the October launch window, and opinions were mixed. The consensus view was between a 40 to 60 percent chance in becoming comfortable enough with the issue to launch this fall. If NASA engineers cannot become confident with the existing setup, the transistors would need to be replaced.
The Clipper mission has launch opportunities in 2025 and 2026, but these could lead to additional delays. This is due to the need for multiple gravitational assists. The 2024 launch follows a "MEGA" trajectory, including a Mars flyby in 2025 and an Earth flyby in late 2026—Mars-Earth Gravitational Assist. If Clipper launches a year late, it would necessitate a second Earth flyby. A launch in 2026 would revert to a MEGA trajectory. Ars has asked NASA for timelines of launches in 2025 and 2026 and will update if they provide this information.
Another negative result of delays would be costs, as keeping the mission on the ground for another year likely would result in another few hundred million dollars in expenses for NASA, which would blow a hole in its planetary science budget.
NASA's blog post this week is not the first time the space agency has referenced these issues with the metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOSFET, in public. At a meeting of the Space Studies Board in early June, Jordan Evans, project manager for the Europa Clipper Mission, said it was his No. 1 concern ahead of launch.
“What keeps me awake at night”
"The most challenging thing we're dealing with right now is an issue associated with these transistors, MOSFETs, that are used as switches in the spacecraft," he said. "Five weeks ago today, I got an email that a non-NASA customer had done some testing on these rad-hard parts and found that they were going before (the specifications), at radiation levels significantly lower than what we qualified them to as we did our parts procurement, and others in the industry had as well."
At the time, Evans said things were "trending in the right direction" with regard to the agency's analysis of the issue. It seems unlikely that NASA would have put out a blog post five weeks later if the issue were still moving steadily toward a resolution.
"What keeps me awake right now is the uncertainty associated with the MOSFETs and the residual risk that we will take on with that," Evans said back in June. "It's difficult to do the kind of low-dose rate testing in the timeframes that we have until launch. So we're gathering as much data as we can, including from missions like Juno, to better understand what residual risk we might launch with."
These are precisely the kinds of issues that scientists and engineers don't want to find in the final months before the launch of such a consequential mission. The stakes are incredibly high—imagine making the call to launch Clipper only to have the spacecraft fail six years later upon arrival at Jupiter.
ERIC BERGEREric Berger is the senior space editor at Ars Technica, covering everything from astronomy to private space to wonky NASA policy, and author of the book Liftoff, about the rise of SpaceX. A certified meteorologist, Eric lives in Houston.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25528550/spacex_falcon_9_jul11.jpg)