He was an anthropologist, an anarchist, and a provocative polemicist.
September 3, 2020

David Graeber, who died of undisclosed causes on Wednesday at the age of 59, was a prominent anthropologist who taught at the London School of Economics—and famously, an anarchist—but he disliked being referred to as “the anarchist anthropologist,” as he inevitably was. Most people, he thought, misunderstood what anarchism meant. Even those who didn’t associate it with running street battles and wanton crimes against property dismissed it as farcically utopian. “Most people don’t think anarchism is a bad idea, they think it’s insane,” he told me. “Yeah, sure it would be great not to have prisons and police and hierarchical structures of authority, but everybody would just start killing each other. That wouldn’t work, right?”
Graeber thought it could. His Kansas-born father had enlisted with the Republicans in the Spanish Civil War, alongside anarchists who had briefly run Barcelona according to their principles. (Graeber’s mother had her own left-wing bona fides, once starring in an International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union musical that improbably became a Broadway hit SEE PINS AND NEEDLES). Indeed, Graeber believed that it was much of contemporary life, lived in the grip of economic and political realities no one bothered to question, that was truly insane. He made his name by assaulting what he saw as its central pillars, both in his brilliant, idiosyncratic writing and in his participation and leadership of large-scale, left-wing street demonstrations in Quebec City, Philadelphia, New York, and Genoa, Italy.
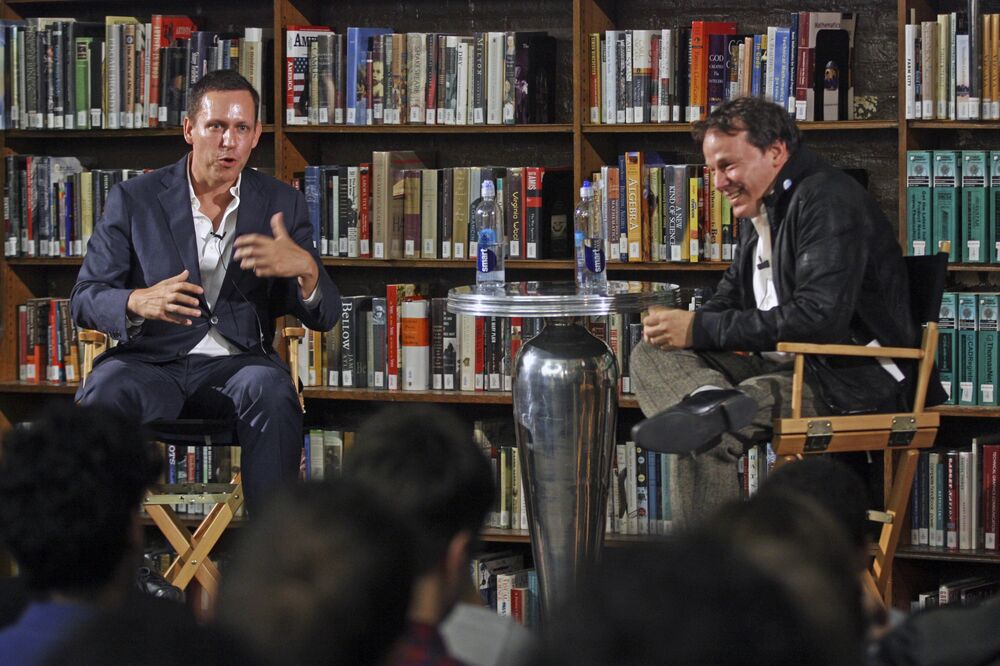

Silicon Valley entrepreneur Peter Thiel and David Graeber debate the future of technology in New York on Sept. 19, 2014.
PHOTOGRAPHER: HIROYUKI ITO/REDUX
The most influential of those was in fall 2011. Graeber was one of a core of organizers who, in a series of interminable meetings run according to anarchist principles—all decisions had to be made by consensus, no matter the size of the group—planned what would become the months-long occupation of a small private park near Wall Street named Zuccotti Park. It was Graeber who, among other things, suggested they call themselves “the 99%.” In the following weeks, Graeber, in interviews and essays, provided some of the most articulate encapsulations of the ideas animating the nebulous movement known as Occupy Wall Street.
His book Debt: The First 5,000 Years, published a few months earlier, would become an intellectual touchstone for the occupation, arguing that the concept of debt, whether applied by ancient despots, colonial powers, or modern investment banks peddling mortgage-backed securities, had a long and sordid past. “If history shows anything,” Graeber wrote, “it is that there’s no better way to justify relations founded on violence, to make such relations seem moral, than by reframing them in the language of debt—above all, because it immediately makes it seem that it’s the victim who’s doing something wrong. Mafiosi understand this.” Graeber’s book includes a description of 18th century English debtors’ prisons, where aristocratic inmates served out their brief sentences being waited on by liveried servants, while poor debtors were shackled to the walls of filthy, tiny cells. In the wake of the housing collapse and Too Big to Fail, the resonance was hard to miss.
I profiled Graeber for Bloomberg Businessweek during Occupy Wall Street, and he was already starting to think about other things: Why were the fruits of technological innovation so lame? Why are so many jobs so unfulfilling? Why do we still work so much? He’d tackle these topics in future essays, books, and “work rants.” Were the arguments sometimes simplistic? Yes. Were straw men avoided and opposing points of view soberly weighed? They were not. Graeber was a polemicist, and a delightful one. To read his writing was to find oneself suddenly ping-ponging through thousands of years of history, so that the Hindu Vedas are in conversation with the stand-up comedian Steve Wright, the divorce proceedings of George W. Bush’s brother Neil open a window into the African Lele people’s concept of blood debt, and where corporations, emerging from Medieval canon law, “are the most peculiarly European addition to that endless proliferation of metaphysical entities so characteristic of the Middle Ages—as well as the most enduring.”
In 2015, the year after Ferguson, Mo., broke out in angry demonstrations after a white police officer shot and killed a young black man named Michael Brown, Graeber wrote a piece in Gawker entitled “Ferguson and the Criminalization of American Life.” Citing a recent U.S. Department of Justice investigation of the Ferguson Police Department, he pointed out that, at the time, more than three-quarters of the residents of Ferguson had warrants outstanding for their arrest, most for such things as unpaid parking tickets or unmowed lawns. Because those fines made up a significant chunk of the city’s operating budget, there was institutional pressure to issue as many citations as possible and to make the fines costly. The police, in other words, were acting as the enforcement arm of a shakedown operation. “What the racism of Ferguson's criminal justice system produced is simply a nightmarish caricature of something that is beginning to happen on every level of American life,” Graeber wrote. “Most Americans no longer feel that the institutions of government are, or even could be, on their side. Because increasingly, in a very basic sense, they're not.”
David Graeber was known as a leader in the Occupy Wall Street movement
By Ashley Boucher September 03, 2020

David Graeber
HIROYUKI ITO/GETTY IMAGES
David Graeber, an anthropologist and professor, has died. He was 59.
Graeber died on Wednesday in Venice after he was taken to a hospital by ambulance, CNN reported Thursday. His cause of death has not been released.
"Yesterday the best person in a world, my husband and my friend .@davidgraeber died in a hospital in Venice," his wife Nika Dubrovsky wrote on Twitter.
Known for anarchist views and as a leader in the Occupy Wall Street movement, Graeber was a professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics. He also previously taught at Yale University and Goldsmiths, University of London.
Yesterday the best person in a world, my husband and my friend .@davidgraeber died in a hospital in Venice.— Nika Dubrovsky (@nikadubrovsky) September 3, 2020
We are very shocked and saddened to learn of David Graeber's death. David was a hugely influential anthropologist, political activist and public intellectual. He will be greatly missed as a friend and colleague. His brilliant work will be read by generations to come. pic.twitter.com/wnZp4xGOaT— LSE Anthropology (@LSEAnthropology) September 3, 2020
"We are very shocked and saddened to learn of David Graeber's death," the London School of Economics said in a statement shared on Twitter. "David was a hugely influential anthropologist, political activist and public intellectual. He will be greatly missed as a friend and colleague. His brilliant work will be read by generations to come."
Graeber was the author of Bull— Jobs: A Theory, which was published in 2018 following a viral 2013 Strike! Magazine essay on the same topic. He also wrote Debt: The First 500 Years, The Utopia of Rules, The Democracy Project and several more.

David Graeber
PIER MARCO TACCA/GETTY IMAGES
On his website, Graeber wrote that he tried to stay "actively engaged in social movements of one sort or another, insofar as I actually can, living in exile with a full-time job."
"I was involved in the initial meetings that helped set up Occupy Wall Street, for instance, and have been working with the Kurdish Freedom Movement in various capacities as well," he wrote, clarifying that while he has been credited with the "We are the 99 percent" slogan, coming up with the phrase was a group effort.

THEORY. UTOPIA. EMPATHY. EPHEMERAL ARTS – EST. 1990 –

David Graeber died suddenly at 59
Published on September 3, 2020 in Global movement/Void Network News
We are shocked by the news- our friend and comrade David Graeber died suddenly in Venice. Graeber’s death was confirmed on the morning of September 3 by his wife, Nika Dubrovsky. Dubrovsky tweeted, “Yesterday the best person in a world, my husband and my friend David Graeber died in a hospital in Venice.”
Graeber was the professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics and wrote the book Debt: The First 5000 Years which was published in 2011. His other books include 2015’s Utopia Rules and 2018’s Bullshit Jobs: A Theory. In addition to his involvement with Occupy Wall Street, Graeber was also known for his activism with the Global Justice Movement.
Void Network had a long friendship and collaboration with David organizing his talks in Greece and sharing ideas, plans and vision. He was the most intelligent anarchist theoretician of our era and we feel heart borken loosing a great friend and comrade.
Ashes to ashes / Dust to dust
Long Live Anarchy
________
Tasos Sagris
Void Network [Theory, Utopia, Empathy, Ephemeral Arts] – http://voidnetwork.gr
“A revolution on a world scale will take a very long time. But it is also possible to recognize that it is already starting to happen. The easiest way to get our minds around it is to stop thinking about revolution as a thing — “the” revolution, the great cataclysmic break—and instead ask “what is revolutionary action?” We could then suggest: revolutionary action is any collective action which rejects, and therefore confronts, some form of power or domination and in doing so, reconstitutes social relations—even within the collectivity—in that light. Revolutionary action does not necessarily have to aim to topple governments. Attempts to create autonomous communities in the face of power (using Castoriadis’ definition
here: ones that constitute themselves, collectively make their own rules or principles of operation, and continually reexamine them), would, for
instance, be almost by definition revolutionary acts. And history shows us that the continual accumulation of such acts can change (almost) everything.”
-Fragments of an Anarchist Anthropology
READ DAVID GRAEBER TEXTS here:
https://theanarchistlibrary.org/category/author/david-graeber
Graeber, who was a leading figure of the Occupy Wall Street movement, was 59.
04 SEPTEMBER 2020 PENGUIN BOOKS BLOG

David Graeber. Image: Getty
The writer, academic and political campaigner David Graeber has died at the age of 59.
The author of Bullshit Jobs (2018) and The Democracy Project (2014), Graeber was also a professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics and was a leading figure of the Occupy Wall Street movement. Known for his insightful critiques of capitalism, he popularised the phrase "we are the 99%".
Graeber’s editor at Penguin Press, Tom Penn, said:
“We are devastated to learn of the passing of David Graeber. A voice of boundless influence both in the academy and in political culture, David was a true radical, a pioneer in everything that he did. David's inspirational work has changed and shaped the way people understand the world.
“In his books, his constant, questing curiosity, his wry, sharp-eyed provoking of received nostrums shine through. So too, above all, does his unique ability to imagine a better world, borne out of his own deep and abiding humanity. We are deeply honoured to be his publisher, and we will all miss him: his kindness, his warmth, his wisdom, his friendship. His loss is incalculable, but his legacy is immense. His work and his spirit will live on.”
Bullshit Jobs was inspired by 2013 essay which went viral and described a society in which huge numbers of people were engaging in meaningless labour which resulted in psychological damage.
Graeber was also working on a new book, written with David Wengrove, The Dawn of Everything: a New History of Humanity, which is due to be published in autumn 2021.
Graeber's death was announced on Twitter by his wife, Nika Dubrovsky, who posted that he died in hospital in Venice. The cause of death has not yet been released.
The anarchist and author of bestselling books on capitalism and bureaucracy died in a Venice hospital on Wednesday

Sian Cain
@siancain
Thu 3 Sep 2020 16.18 BST
David Graeber, anthropologist and anarchist author of bestselling books on bureaucracy and economics including Bullshit Jobs: A Theory and Debt: The First 5,000 Years, has died aged 59.
On Thursday Graeber’s wife, the artist and writer Nika Dubrovsky, announced on Twitter that Graeber had died in hospital in Venice the previous day. The cause of death is not yet known.
Renowned for his biting and incisive writing about bureaucracy, politics and capitalism, Graeber was a leading figure in the Occupy Wall Street movement and professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics (LSE) at the time of his death. His final book, The Dawn of Everything: a New History of Humanity, written with David Wengrow, will be published in autumn 2021.
Caring too much. That's the curse of the working classes
David Graeber
Read more
The historian Rutger Bregman called Graeber “one of the greatest thinkers of our time and a phenomenal writer”, while the Guardian columnist Owen Jones called him “an intellectual giant, full of humanity, someone whose work inspired and encouraged and educated so many”. The Labour MP John McDonnell wrote: “I counted David as a much valued friend and ally. His iconoclastic research and writing opened us all up to fresh thinking and such innovative approaches to political activism. We will all miss him hugely.”
Tom Penn, Graeber’s editor at Penguin Random House, said the publishing house was “devastated” and called Graeber “a true radical, a pioneer in everything that he did”.
“David’s inspirational work has changed and shaped the way people understand the world. In his books, his constant, questing curiosity, his wry, sharp-eyed provoking of received nostrums shine through. So too, above all, does his unique ability to imagine a better world, borne out of his own deep and abiding humanity,” Penn said. “We are deeply honoured to be his publisher, and we will all miss him: his kindness, his warmth, his wisdom, his friendship. His loss is incalculable, but his legacy is immense. His work and his spirit will live on.”
Born in New York in 1961 to two politically active parents – his father fought in the Spanish civil war with the International Brigades, while his mother was a member of the international Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union – Graeber first attracted academic attention for his teenage hobby of translating Mayan hieroglyphs. After studying anthropology at the State University of New York at Purchase and the University of Chicago, he won a prestigious Fulbright fellowship and spent two years doing anthropological fieldwork in Madagascar.

David Graeber interview: ‘So many people spend their working lives doing jobs they think are unnecessary’
Read more
In 2005, Yale decided against renewing his contract a year before he would have secured tenure. Graeber suspected it was because of his politics; when more than 4,500 colleagues and students signed petitions supporting him, Yale instead offered him a year’s paid sabbatical, which he accepted and moved to the UK to work at Goldsmiths before joining LSE. “I guess I had two strikes against me,” he told the Guardian in 2015. “One, I seemed to be enjoying my work too much. Plus I’m from the wrong class: I come from a working-class background.”
His 2011 book Debt: The First 5,000 Years, made him famous. In it, Graeber explored the violence that lies behind all social relations based on money, and called for a wiping out of sovereign and consumer debts. While it divided critics, it attracted strong sales and praise from everyone from Thomas Piketty to Russell Brand.
Graeber followed it in 2013 with The Democracy Project: A History, a Crisis, a Movement, about his work with Occupy Wall Street, then The Utopia of Rules: On Technology, Stupidity and the Secret Joys of Bureaucracy in 2015, which was inspired by his struggle to settle his mother’s affairs before she died. A 2013 article, On the Phenomenon of Bullshit Jobs, led to Bullshit Jobs: A Theory, his 2018 book in which he argued that most white-collar jobs were meaningless and that technological advances had led to people working more, not less.
“Huge swaths of people, in Europe and North America in particular, spend their entire working lives performing tasks they believe to be unnecessary. The moral and spiritual damage that comes from this situation is profound. It is a scar across our collective soul. Yet virtually no one talks about it,” he told the Guardian in 2015 – even admitting that his own work could be meaningless: “There can be no objective measure of social value.”
Why is the world ignoring the revolutionary Kurds in Syria?
David Graeber
Read more
An anarchist since his teens, Graeber was a supporter of the Kurdish freedom movement and the “remarkable democratic experiment” he could see in Rojava, an autonomous region in Syria. He became heavily involved in activism and politics in the late 90s. He was a pivotal figure in the Occupy Wall Street movement in 2011 – though he denied that he had come up with the slogan “We are the 99%”, for which he was frequently credited.
“I did first suggest that we call ourselves the 99%. Then two Spanish indignados and a Greek anarchist added the ‘we’ and later a food-not-bombs veteran put the ‘are’ between them. And they say you can’t create something worthwhile by committee! I’d include their names but considering the way police intelligence has been coming after early OWS organisers, maybe it would be better not to,” he wrote
David Graeber dies aged 59: "One of the most original anthropologists"
Cnaan Liphshiz

The Baffler presents "No Future for You: David Graeber versus Peter Thiel" at General Society of Mechanics and Tradesmen on Friday night, September 19, 2014.This image:The anthropologist David Graeber in a debate.(Photo by Hiroyuki Ito/Getty Images)Hiroyuki Ito
(JTA) — David Graeber, an anthropologist and self-described anarchist, has died. He was 59.
A well-known figure in far-left circles in the United States and the United Kingdom, Graeber was the author of several books, including “Bullshit Jobs: A Theory,” which was ranked at number 13 in the Los Angeles Times’ July 2018 list of bestsellers in the hardcover nonfiction category.
He died in Venice, Italy, on Wednesday, The Guardian wrote in an obituary. The paper had no information on the cause of death.
The New York-born Graeber was a professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics known for “his biting and incisive writing about bureaucracy, politics and capitalism,” the obituary said.
“His iconoclastic research and writing opened us all up to fresh thinking and such innovative approaches to political activism,” said John McDonnell, a Labour lawmaker who had served as second-in-command under former party leader Jeremy Corbyn, according to the Guardian. “We will all miss him hugely.”
In recent years, Graeber had come out in defense of Corbyn, who has faced allegations of anti-Semitism, including by the current and previous chief rabbis of the U.K.
“What actually threatens Jews, the people who actually want to kill us, are Nazis,” he said in one video. The allegations against Corbyn represented the “weaponization” of anti-Semitism, he said in another.
The post David Graeber, anarchist anthropologist who defended Corbyn, dies at 59 appeared first on Jewish Telegraphic Agency.

September 04, 2020
David Graeber, Occupy activist and anthropologist, dies at 59

NEWS
OBITUARIES
David Graeber, Occupy activist and anthropologist, dies at 59
David Graeber, the anthropologist who played a pivotal role in Occupy Wall Street and devoted his academic career to the study of societal inequality and “bullshit jobs,” died September 2 at the age of 59.
Graeber’s death was confirmed on Twitter by his wife, Nika Dubrovsky, who said he died at a hospital in Venice, Italy. No cause of death was given.
Graeber was known for his outspoken politics. He was a founding member of the Anti-Capitalist Convergence, an anarchist group formed in the late 1990s with various chapters throughout North America. He nonetheless rejected the label of anarchist — at least sometimes — noting in his Twitter bio “I see anarchism as something you do not an identity so don’t call me the anarchist anthropologist.”
Born in 1961 in New York, Graeber was brought up in [a revolutionary milieu. His father, Kenneth, served in the Spanish Civil War and was a member of the Youth Communist League. Ruth, his mother, was a garment worker, who acted in the lead role in “Pins and Needles,” a production by the Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union. According to a Guardian profile from 2015, Graeber began identifying as an anarchist at the age of 16. “Anarchy wasn’t dinner table conversation,” he told The New York Times in 2005, “but it was on the horizon.”
A graduate of Phillips Academy Andover, Graeber received his B.A. from the SUNY Purchase in 1984 and earned his master’s and doctorate in anthropology from the University of Chicago, securing a Fulbright fellowship to conduct field research in Madagascar for his doctoral thesis. In 1998, he became an assistant professor at Yale. But in 2005, the school decided not to keep him on for the next academic year. The school gave no reason at the time, but he believed that it was because of his politics.
Graeber rallied supporters to write letters on his behalf (some 4,500 signed petitions supporting him, including prominent anthropologists Marshall Sahlins, Laura Nader, Michael Taussig, and Maurice Bloch), but agreed to take a paid sabbatical from the school in exchange for dropping his appeal.
“So many academics lead such frightened lives,” he told The Times of his decision. “The whole system sometimes seems designed to encourage paranoia and timidity. I wasn’t willing to live like that.”
Graeber acknowledged that, as an anarchist in an Ivy Tower, he was “challenging the way universities are run,” but said he had hoped to live as an activist in New York and a scholar in New Haven.
In 2011, Graeber’s activism crescendoed when he became involved with the Occupy Wall Street protesters at Zuccotti Park. Graeber is often credited with creating that movement’s most recognizable slogan, “We are the 99%.”
“We wanted to demonstrate we could do all the services that social service providers do without endless bureaucracy,” Graeber told The Guardian four years after the Occupy protests began. “People kept giving us money but we weren’t going to put it in the bank. You have all these rules and regulations. And Occupy Wall Street can’t have a bank account. I always say the principle of direct action is the defiant insistence on acting as if one is already free.”
As an anthropologist, Graeber was known for his work on value theory, or how societies determine what is important. His 10 books covered the topics of the value theory, global justice and the Occupy Movement’s experiment in direct democracy. His best-known books included “Debt: The First 5000 Years” and 2018’s “Bullshit Jobs: A Theory,” inspired by his 2013 article “On the Phenomenon of Bullshit Jobs.”
“Bullshit jobs” are, essentially, any kind of work that could be automated or that serves no essential purpose, but are kept in place anyway, despite leaving their workers feeling unfulfilled. “Huge swaths of people, in Europe and North America in particular, spend their entire working lives performing tasks they believe to be unnecessary,” Graeber told The Guardian. “The moral and spiritual damage that comes from this situation is profound. It is a scar across our collective soul. Yet virtually no one talks about it.”
At the time of his death, Graeber had been a professor at the London School of Economics for seven years. In London, he continued his activism, addressing the climate change group Extinction Rebellion in a demonstration at Trafalgar Square in late 2019. He was a supporter of Jeremy Corbyn’s Labour Party, and his pinned tweet was a graph alleging falsehoods in various British publications surrounding their coverage of the Labour’s alleged antisemitism problem.
as for the Guardian, we will never forget that during the “Labour #antisemitism controversy”, they beat even the Daily Mail to include the largest percentage of false statements, pretty much every one, mysteriously, an accidental error to Labour’s disadvantage pic.twitter.com/XiwYsVMOiZ— David Graeber (@davidgraeber) December 26, 2019
He was not shy to disagree with those he allied with either. His final tweet criticized a statement from the UK chapter of Extinction Rebellion’s Twitter account for being exclusionary.
I don’t know who writes these tweets but they should be fired. This is either awful PR or intentionally trying to alienate someone for internal political reasons. If you’re non-ideological, doesn’t that mean you’re not socialist OR pro-capitalist? Why leave one of the two out? https://t.co/vYxmZqsckD— David Graeber (@davidgraeber) September 2, 2020
For all of his critiques of managerialism and society’s broader flaws, Graeber described himself as ultimately hopeful about the future, telling the New Statesman he was a “professional optimist.”
Coming out in support of a Universal Basic Income, he predicted that in 50 years, the capitalist system would be obsolete. Yet, he was guarded about any replacement. “It could be something even worse. It’s therefore imperative that we end this taboo around trying to figure out something that might be better.”

Occupy Wall Street: A Year Later brittany Oct 19, 2012

David Graeber Apr 8, 2015

Anarchic Revolution and Traditional Judaism
PJ Grisar is the Forward’s culture reporter. He can be reached at Grisar@Forward.com.
His books on debt and "bullshit jobs" made him world famous. David Graeber was one of the most original critics of capitalism that today's left has.

9/4/2020
And now this news: David Graeber died in Venice.
He was 59 years old.
There are not many left-wing radicals who do not allow left-wing radicalism to degenerate into clowning, but rather mean it, and who at the same time become global superstars and bestselling authors.
"Anarchist" he called himself - or was named - but whether he really was one can be debated.
He was simply of the opinion that people would cultivate solidarity with one another and take care of one another if they were not cooped up in repressive structures, and he was convinced that "power corrupts".
He did not feel he belonged to other leftist tendencies or even parties, so perhaps he was more of an anarchist for lack of a better alternative.
Graeber still had something of the habitus of earlier revolutionaries and intellectuals, the self-indulgent pomposity of some academic leftists was not his thing, he was much more modest there.
Perhaps that has something to do with his origin.
Graeber grew up in a left-wing Jewish working class family, his father fought in the Spanish Civil War.
The American anthropologist, who had been teaching in London for years, was made world-famous and a figure on the international left by the financial crisis ten years ago.
His book of debt. The first 5,000 years was an event, of course also because gambling banks, loans and government budget deficits were the topic of the hour.
Graeber dismantled a few myths and looked at what seemed to be taken for granted with a new, sharp look.
Social relations determined by money produce violence, dehumanization, slavery, he wrote.
Payment relationships established hierarchical relationships between power and powerlessness.
Where everyone is in debt, many only run for survival.
Myths of origin, such as the economy loves, such as the fairy tale that earlier societies simply exchanged use values, Graeber brushed off the table: Such societies never existed.
People have always used equivalents to facilitate exchange.
But money, in the form of banknotes and coins, was very rare until the early modern period.
You didn't need a lot of it if everyone wrote to them and settled no more than twice a year.
Graeber also pointed to the moral questions that come with debt.
To this day we believe that a debtor is somehow "morally obliged" to repay his debts.
But why at all?
After all, the creditor has lent him money, is hoping for a return - the interest - but at the same time knows about the risk of a loan default. But why is it primarily the debtor that we give moral persecution to?
"A wonderful and helpful book", a "liberation", Frank Schirrmacher celebrated at the time in the
FAZ on a whole page of the book, which contributed not insignificantly to Graeber's fame in Germany.
Revolutions, wars, upheavals: they almost always have to do with over-indebtedness.
Of course, I could object to Graeber that debt relationships in premodern societies are not comparable to the investment credit that led to exponential economic growth in capitalism.
All of this was a wonderful thing to discuss with him, and he was speaking at what felt like fifteen thousand words a minute in his New York working class accent.
Source: zei
David Graeber, a writer and activist famous for popularizing the phrase’We are the 99%’ died
MORTIMER NELSON SEP 04, 202O\

Graeber was a professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics and a keen criticism of capitalism and bureaucracy and his Anarchist view.
His book “Bullshit Jobs: A Theory” was inspired by an essay from 2013 and made word of mouth. Graeber is a large herb Much of society was working in meaningless jobs that ultimately resulted in psychological consequences. His book “Debt: The First 5,000 Years” focused on the history of how people use credit systems to buy and sell goods.
“David was a very influential anthropologist, political activist and public intellectual,” said Laura Bear, director of the Department of Anthropology at the London School of Economics, in a CNN statement.
“He will be greatly missed as a friend and colleague in our department. The community of our staff and students will not be the same now. But his great work will be read over the next generations.”
Graeber’s wife Nika Dubrovsky wrote about his death. From a post on Twitter.
“Yesterday the best man in the world, my husband and my friend. @davidgraeber died in a hospital in Venice,” she wrote.
The hospital’s press room told CNN that Graeber was in Venice on Wednesday and was not feeling well and his family called an ambulance. His signature has not yet been revealed.
Graeber was born and raised in New York by working class parents. He wrote on his website. His father was a plate stripper who fought as part of an international brigade in the Spanish Civil War, and his mother was a clothing worker who starred female in the musical “Finn and Needle”.
He said on his website that he entered anthropology “after being discovered by some Maya archaeologists because of the strange hobby I developed to translate Maya hieroglyphs.” He earned a bachelor’s degree in anthropology from the State University of New York in 1984.
READ Netanyahu to condone undisclosed plans to sell US arms to UAE: report
Having worked in several places, including Chicago and Madagascar, Graeber became a professor at Yale University. The university’s decision not to continue his contract in 2004 was controversial at the time, and Graeber and others suggested that the decision may have been motivated by his anarchist activism.
Graeber worked at London University’s Goldsmiths from 2007 to 2013 before becoming a professor at the London School of Economics.
Graeber has been involved in the alternative globalization movement since 2000 and was part of the initial meeting that launched Occupy Wall Street. He was credited with popularizing the movement’s slogan “We are 99%”, but pointed out that he did not come up with it.
“No, I personally didn’t come up with the slogan’We are 99%’,” he wrote. “At first we offered to call ourselves 99%. Then two Spanish Indigna and Greek anarchists added “us” and later a non-bomb food veteran put “are” between them. And They say you can’t. Make something worthwhile on the committee!”
CNN’s Brian Ries and Valentina DiDonato contributed to this report.

Mortimer Nelson
Evil tv buff. Troublemaker. Coffee practitioner. Unapologetic problem solver. Bacon ninja. Thinker. Professional food enthusiast.
David Graeber Dead: Anthropologist & Anti-Capitalist Thinker Behind ‘We Are the 99%’ Slogan Dies at 59
Twitter/David GraeberDavid Graeber pictured on his Twitter page in December 2019.
David Graeber, the anthropologist who was influential in the Occupy Wall Street movement and is believed to have coined the phrase, “We are the 99%,” has died at age 59.
Graeber’s death was confirmed on the morning of September 3 by his wife, Nika Dubrovsky. Dubrovsky tweeted, “Yesterday the best person in a world, my husband and my friend . @davidgraeber died in a hospital in Venice.”
Graeber was a professor of anthropology at the London School of Economics and wrote the book Debt: The First 5000 Years which was published in 2011. His other books include 2015’s The Utopia of Rules and 2018’s Bullshit Jobs: A Theory. In addition to his involvement with Occupy Wall Street, Graeber was also known for his activism with the Global Justice Movement. On his Twitter page, Graeber described himself as “an anthropologist, sometimes I occupy things & such. I see anarchism as something you do not an identity so don’t call me the anarchist anthropologist.”
Here’s what you need to know:
1. Graeber Said on August 28 That He Was ‘Under the Weather’ but Was Starting to Feel Better
On August 28, Graeber said in a YouTube video that he had been feeling “a little under the weather” but was beginning to feel better. The same day, Graeber tweeted that he had “not been in tip-top shape.”
On August 31, Dubrovsky tweeted a photo from Venice with the caption, “Venice. Dark, wet and chilly.” Graeber was active on Twitter until the day before his death.
In August 2020, Graeber was interviewed in a special edition of the street newspaper The Big Issue. The special edition was edited by British singer Jarvis Cocker.
According to Graeber’s LinkedIn page, he is a graduate of SUNY Purchase and attained a Ph.D. in anthropology from the University of Chicago in 1996. Graeber’s first teaching job was as an assistant professor of anthropology at Haverford College. In 1998, Graeber began working as an associate professor at Yale University. He remained in that role until June 2007. Since September 2007, Graeber had been teaching at the University of London’s School of Economics, according to LinkedIn. A profile on SUNY Purchase’s website referred to Graeber as “one of the most brilliant minds of his generation.”
2. Graeber Suspected His Teaching Contract at Yale Was Discontinued Because of His ‘Radical Actions’
Getty
A 2011 Rolling Stone article attributed the phrase “We are the 99%” to Graeber in a piece on the Occupy Wall Street movement. The phrase had been mentioned by economist Josep Stiglitz’s in a May 2011 article for Vanity Fair. Rolling Stone reported that Graeber suspected his teaching job at Yale was discontinued because of his “radical actions.” The article also said he decamped to Austin, Texas, four days after the physical protest began in Zuccotti Park in New York City.
In a March 2015 interview with The Guardian, Graeber referred to the Occupy movement as an “experiment in a post-bureaucratic society.” Graeber said demonstrators wanted to show the public that people could perform the functions of a bank without bureaucracy. He said during the protests there was a plastic bag in Zuccotti Park holding $800,000 in donations because “Occupy Wall Street can’t have a bank account.” Graeber said, “I always say the principle of direct action is the defiant insistence on acting as if one is already free.”
3. Graeber Previously Described Himself as an ‘Eternal Optimist’
In 2018, Graeber told the New Statesman that he was born in New York to self-educated parents. His father, Kenneth, fought on the side of the Republicans in the Spanish Civil War, Graeber said. Later, his mother, Ruth, worked as a garment worker and was active in the International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union, he said. Graeber said in the interview that he was raised in an environment that embraced anarchism.
Graeber told the New Statesman that he thought of himself as an “eternal optimist.” He added that he felt that in 50 years a new system would be in place that was not capitalist. Graeber warned, “It could be something even worse. It’s therefore imperative that we end this taboo around trying to figure out something that might be better. If we don’t get something better, it will be something worse – it won’t be the same.”
4. Graeber Married His Wife Nika Dubrovsky in April 2019
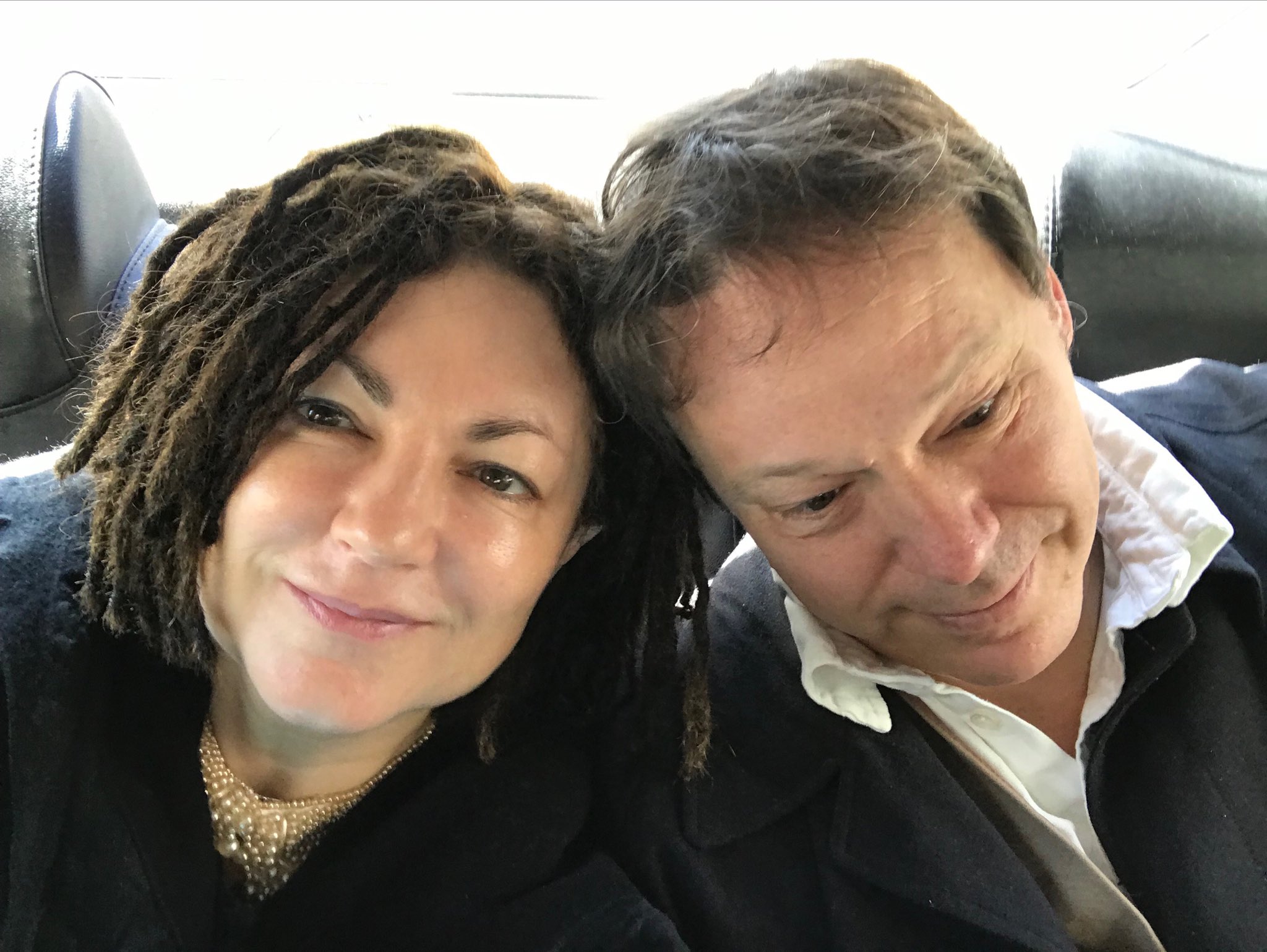

Twitter/Nika DubrovskyGraeber pictured with his wife on their wedding day in April 2019.
Graeber married Nika Dubrovsky in April 2019. On April 25, Dubrovsky tweeted a photo of the couple with the caption, “Going for a wedding.” Graeber retweeted the photo and added, “I’ve never been married before.” He also said, “I have never been more moved than that someone who actually knows me would want to be with me forever.”
Graeber has tweeted in the past that his wife is a native of St. Petersburg, Russia, and grew up in the Soviet-era. Graeber tweeted that his wife struggled to watch the United Kingdom’s public broadcaster the BBC because it reminded her too much of the Soviet propaganda of her youth. In 2019, the couple founded Yes Women, an art group that sought justice for ostracized women in the former East Germany.
5. Graeber Is Being Mourned on Social Media by His Peers as One of the Greatest Minds of His Generation
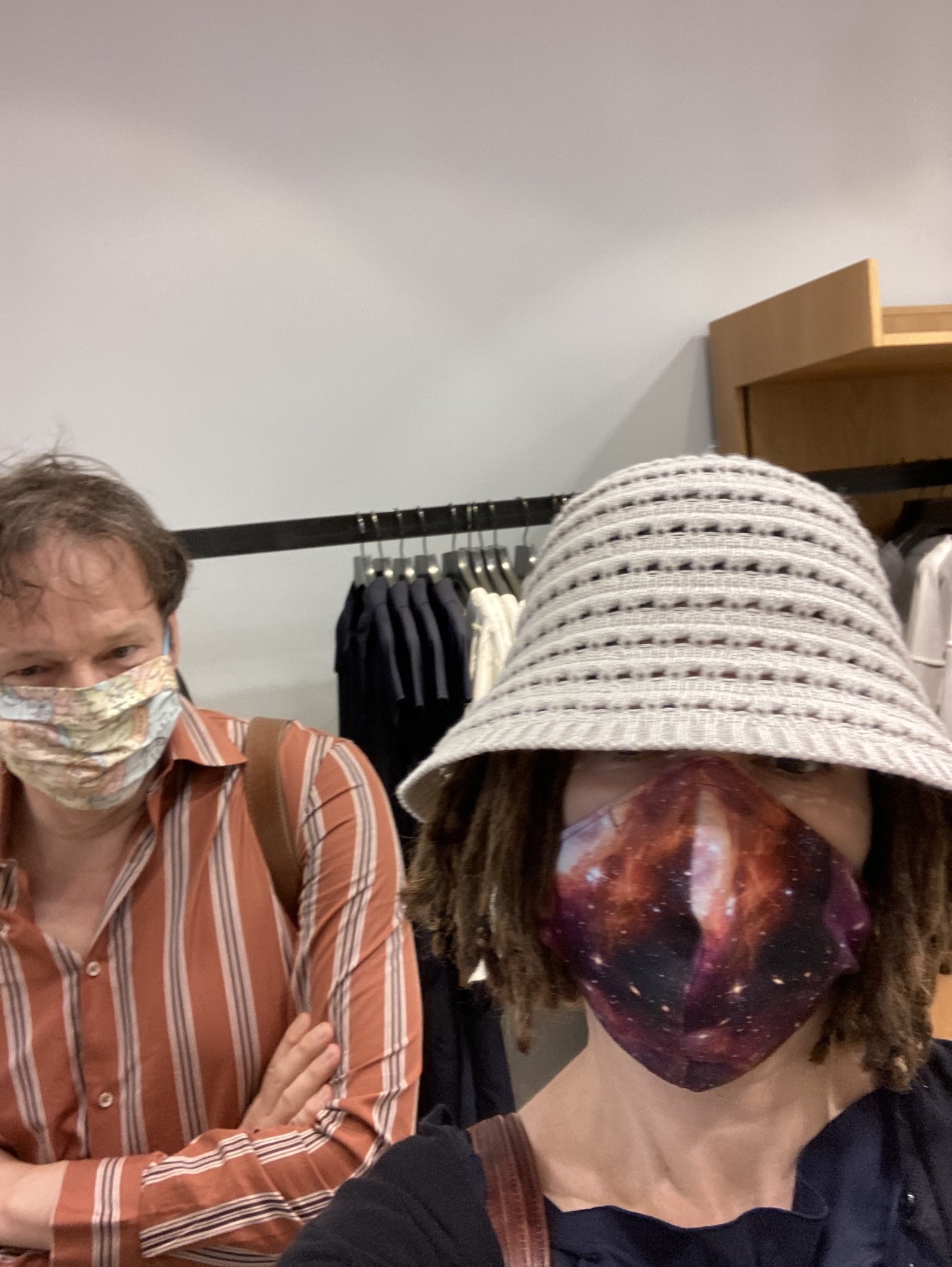

Twitter/Nika DubrovskyGraeber and his wife pictured in Berlin, Germany, on August 4.
As news spread of Graeber’s death, his peers and fans took to Twitter to mourn him. Here are some of the most poignant messages of remembrance:
David Graeber was truly a friend of the women's struggle and the revolution in Rojava. The world has lost his presence, but his light lives on in every person who struggles for freedom. Rest in peace, comrade #davidgraeber pic.twitter.com/KVhs0WnaHs
— Kongra Star Women's Movement Rojava (@starrcongress) September 3, 2020
We have just learnt with great grief the death of @davidgraeber yesterday.
David, famous anthropologist scholar, was a great friend and supporter of the Kurdish Freedom Movement; traveling to Rojava, speaking about the revolution and participating to many demos.
Rest in Power! pic.twitter.com/Nvb8WOyg97
— Internationalist Commune of Rojava (@IntCommune) September 3, 2020
So terribly sad to hear about @davidgraeber's passing. People will be sharing a lot of his brilliant public intellectual work, but Graeber was an outstanding, unmatched theorist in anthropology. His ability to link the two forms of writing was awe inspiring.
— Arsalan Khan (@akkhan81) September 3, 2020
Oh David! @davidgraeber. They say only the good die young, but why did you have to be one of them?
There's even more bullshit in the world now that you are no longer with us.
It was a pleasure to know you, and it is a tragedy to say goodbye.
— Steve Keen (@ProfSteveKeen) September 3, 2020
Absolutely devastated to hear that @davidgraeber has lost his life. He was not just a brilliant mind but a brilliant human too. The harmonious entanglement of theory and practice in his existence was not only enlightening but a joy to witness. pic.twitter.com/YJp84ql5He
— Giran Ozcan (@GiranOzcan) September 3, 2020
I'm truly lost for words💔
David Graeber was a comrade of the Kurdish Women’s Movement, a defender of Rojava, a friend of the oppressed, and an important voice in our collective struggles for justice and freedom.
An honour to know you. Rest in light and power, heval David🌱✌🏽☀️ pic.twitter.com/tqsu4uqzxz— Dilar Dirik☀️ (@Dlrdrk1) September 3, 2020
I shed tears when I heard David Graeber had died.
Many people can be called clever, but he was a man whose genius intellect was matched by true courage and a passion for speaking up for politics based on kindness.
I only met him once but I loved him.
What a loss for humanity.
— Francesca Martinez (@chessmartinez) September 3, 2020
David Graeber was the rare combination of an intellectual giant and an unfailingly kind, decent, gentle soul who made lives around the world better however he could. I’m devastated for his loss
— Molly Crabapple🇵🇷 (@mollycrabapple) September 3, 2020
RIP David Graeber. I don’t think there’s a working social scientist who wouldn’t give their eye teeth to write something as galvanizing and invigorating as the first few chapters of “Debt”.
— Kieran Healy (@kjhealy) September 3, 2020
David Graeber, RIP. Profoundly important work, along with titans like Picketty, Lietaer, Chomsky, and Klein, opened my eyes and inspired so many of us to understand the operating system underlying not just our economy but our civilization.
— douglas rushkoff (@rushkoff) September 3, 2020
My heart is utterly broken over the news that my good friend and comrade David Graeber has passed away. It is impossible to process this… it seems completely unreal. There is simultaneously too much to say and no words, but let me attempt a few:
— Jason Hickel (@jasonhickel) September 3, 2020
I am so sorry. This is so shocking. I counted David as a much valued friend and ally. His iconoclastic research and writing opened us all up to fresh thinking and such innovative approaches to political activism. We will all miss him hugely. I send my deepest sympathy.
— John McDonnell MP (@johnmcdonnellMP) September 3, 2020
David Graeber, one of the key minds behind the Occupy Wall Street movement, has died at the age of 59. He was a leading voice in the global social justice movement.

Anthropologist and influential anarchist intellectual David Graeber passed away, his wife Nika Dubrovsky confirmed on Thursday. He was an important voice in prompting the 2011 Occupy Wall Street protest movement in New York City.
Dubrovsky and Graeber were on holiday in Venice, Italy, when the 59-year-old author and activist fell ill. The cause of his death has not been confirmed.
Graeber has frequently been dubbed an "anarchist anthropologist" but in his own Twitter bio, the London School of Economics professor said he saw "anarchism as something you do, not an identity," and urged people not to use the label of "anarchist anthropologist" to describe him.
Former Greek finance minister and economist Yanis Varoufakis lamented Graeber's honored his work on debt in a Twitter about the author.
On August 28, he addressed followers of his YouTube account saying he was "under the weather" and was still active on Twitter until September 2.
His sudden passing deals a blow to the global social justice movement which is heavily influenced by Graeber's ideas. Born and raised in New York City, Graeber identified himself as a son of working class parents and in his career, he sought to harness his anthropological training to better understand economics.
Occupy Wall Street and activism
In Graeber's bio on his own website, the anthropologist says he "only really became active in any meaningful way" after becoming involved with the Alter-Globalization movement in the beginning of 2000. He says was involved in the initial meetings that helped establish the Occupy Wall Street movement in the heart of New York's financial district.
"It might be said that all my work since has been exploring the relation between anthropology as an intellectual pursuit, and practical attempts to create a free society, free, at least, of capitalism, patriarchy, and coercive state bureaucracies," he added.
Dutch historian and author Rutger Bregman said Graeber would be remembered as ''one of the greatest thinkers of our time'.'
In a 2011 opinion article for The Guardian, Graeber wrote that he saw the movement as "the opening salvo in a wave of negotiations over the dissolution of the American Empire."

Graeber was an influential voice the 2011 Occupy Wall Street protest movement in New York City seen pictured here in 2012
From debt to 'bullshit jobs'
While his activism has centered on global economics, Graeber's academic career has centered on anthropology. He obtained a BA on the subject from State University of New York, at Purchase, in 1984 and later received a PhD in 1996 from the University of Chicago, based on anthropological fieldwork in highland Madagascar.
Seemingly incongruous, Graeber melded the economics and anthropology for his authored works. One of his most celebrated books, "Debt: The First 5,000 Years" he sought to explain the concept of debt across human civilization.
Read more: Global debt levels surging, but keep your calm
More recently, his book on "Bullshits job: a theory" explored how and why technology has created more unnecessary jobs than was predicted and identifying the capitalist system as the cause.
"Huge swathes of people, in Europe and North America in particular, spend their entire working lives performing tasks they secretly believe do not really need to be performed. The moral and spiritual damage that comes from this situation is profound. It is a scar across our collective soul," he explained in the essay upon which the book was based.
At the time of his passing, the US-born Graeber was active in the London School of Economics faculty of anthropology and resided in the city of London.
Criticisms
Graeber's work was heavily criticized by economists and leaders in the US business community. His books were often dismissed or rejected as leftist political rhetoric.
Economist and Bloomberg columnist Noah Smith described Graeber's book on debt as ''a sprawling, rambling, confused book, mostly about economic history, mixed with some political and moral philosophy.''
Book critic and scholar Paul W. Gleason took aim at Graeber's narrow focus on economic conditions as a sign of human fulfillment in his book about "bullshit jobs."
''While humans are social animals, Graeber focuses overwhelmingly on the meaning and purpose that come from creativity and achievement. He mostly neglects the meaning found in belonging. Families, churches, unions, neighborhoods or even nations, no less than workplaces, can all bestow identity and a sense of purpose,'' Gleason wrote.
Occupy author examines archeology of debt
Few books have provoked the kind of media hype, discussion and praise that David Graeber's "'Debt: The Last 5,000 Years" has in the past few weeks. DW looks at the movement and the man behind the book.

He doesn't stay in one place for long. One minute David Graeber is in London, where he teaches anthropology at Goldsmith College, the next he's in Frankfurt at Blockupy, then in Cologne and Berlin for book releases, next stop New York. It's no wonder that Graeber is so busy: He's published three books in 40 days.
The best-known of the three, "Debt: The First 5,000 Years," was described by journalist and political talk show host Maybritt Illner and culture presenter Dieter Moor as "perhaps the most important book of the year." With the three publications, the man whose slogan is "We are the 99 percent" - now deeply ingrained in the system-critical Occupy movement - has managed to attract more attention than any of his fellow-campaigners before him.
He's an activist, anarchist and anthropologist who appears in all the most influential feuilletons. But what does Graeber have to say for himself?
Chronicling the history of debt
In 400 pages, Graeber chronicles the history of debt and, with that, the history of humanity. He begins the book with a slick, but provocative sentence: "Debt doesn't have to be repaid."
He then goes on to describe the economic systems of various indigenous groups and the invention of coinage, finally landing in the present. The assumption that barter trade was initially in existence before it was simplified with the introduction of coinage and later the credit system is, he concludes, idiocy.
Credit systems were in existence long before the invention of money. People who live together in a community are constantly lending things and helping each another, so everyone owes a debt in one way or another. But these debts have nothing to do with money, argues Graeber.
Graeber shows that debt has a moral dimension. He finds it remarkable that the moral imperative that debt must be repaid is now considered more important than other moral and ethical obligations. Why else could it be that governments in poor countries prioritize debt repayments over the basic nutritional requirement of their citizens? Debt, says Graeber, is a moral principle merely enforcing the power of the ruling classes, leading to the repression of the masses.
This system can't function forever. When too many people are in debt, uprisings and revolutions occur. The solution? Debt cancellation, says Graeber.
Success story

FAZ editor Frank Schirrmacher described Graeber's book as a "revelation"
This demand is in keeping with Graeber's style, having in the past represented a number of radical positions. He has no allegiance to any political party, calls himself an anarchist, is a member of the union Industrial Workers of the World and has researched power and the meaning of history and slavery in Madagascar. Graeber taught at Yale until 2007 when his contract was controversially not renewed. Critics believe the decision was politically motivated.
The 51-year-old American has secured himself a place on the bestseller list of Germany's prominent news magazine Der Spiegel, reaching fourth place last month. The success story of the book began in fall 2011 with the English edition. The editor of the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, Frank Schirrmacher, wrote that the book was "a revelation because the author has shown that one is no longer obliged to react in the system of apparent economic rationality." This review made Graeber's risqué theses socially acceptable.
But the media hype really began when the German translation of the book was published in May, in conjunction with the release of Graeber's "Inside Occupy," a monograph about the Occupy movement. The book reveals much about Graeber's political background: He was involved in the Occupy protests as an organizer and follower right from the start, while simultaneously analyzing, promoting and shaping the movement.
All of the major German newspapers were talking about Graeber - Süddeutsche Zeitung, TAZ, the Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, Die Welt, Der Spiegel and Stern to name just a few. Most critiques of the book were benevolent. Graeber's theories were described as brilliant, illuminating, exciting. Graeber translated between worlds, between critics and supporters of the system, between academics and the media. He presented his complex theories in bite-size, easy to understand sections. He interrupts analyses to build strands of thought, while still remaining entertaining.
Playing by the rules
But it's not just the content of the book. It's Graeber, the person. The idea of the "99 percent" in the slogan "We are the 99 percent" comes from him. And even though he himself is one of the 99 percent, he knows the language of the one percent. He also knows the unwritten rules of getting heard in public.
On Maybritt Ilmer's talk show, Graeber was smartly dressed in a black suit-jacket. It was his 67th interview with the German press. Still, he remained polite, succinct and never looked bored. As radical as his thinking may be, his appearances are always in keeping with convention. He's well aware of how much conformity is necessary to inspire interest in non-conformist thinking. He's no madcap revolutionary; rather, he fits into the protocol of prime-time programming.
Above all, he's a figurehead for the so-called 99 percent. The media have bestowed a range of attributes upon him, from "mentor" to "brains" behind the Occupy movement, but also the moniker "intellectual superstar."
Reading his "Inside Occupy," one thing is clear: The last thing that Occupy wants is a leader. "Direct Action," basic democracy and no hierarchy are central to the movement. But Graeber is already easily available for the media. Just as he explains the history of debt, he can also easily formulate what Occupy is all about. Slogans such as "We explain why the system doesn't work" are more likely to be taken seriously when they come from the mouth of a Yale professor than from a 20-year-old with a hoodie and dreadlocks.
In the meantime, the media hype has trailed off, the financial system in still in place, and the reluctance to cancel debt hasn't changed. The revolution hasn't happened yet. Will it take another 5,000 years to rethink the financial system?
Author: Ruth Krause / hw
Editor: Kate Bowen
![]()
Looking Busy
The rise of pointless work.
By Michael Robbins THE NATION NOVEMBER 8, 2018

Sears Tower, Chicago, 1977. (AP / Charles Kelly)
Let’s just get this out of the way: All jobs are bullshit jobs. Even if you’re a public defender or work for Médecins Sans Frontières, insofar as your labor is determined by a system of abstract compulsion—insofar, that is, as it exists within capitalism—it’s bullshit. You know this.
REVIEWED
BULLSHIT JOBS: A THEORY
By David Graeber
In his new book, Bullshit Jobs: A Theory, David Graeber is interested in a particular variety of bullshit and work. In 2013, the anthropologist and anarchist (he hates to be called “the anarchist anthropologist”) published an essay slamming the proliferation of “pointless jobs” that seem to exist “just for the sake of keeping us all working.” The response was tremendous: It turns out that many people have jobs that they believe require them to do nothing of value (or to do nothing whatsoever while trying to appear to be doing something).
Graeber sifted through the responses and solicited additional input on Twitter in a quest to categorize the “five basic types of bullshit jobs” and document the absurdist travails of those who hold them. From such data, he constructed a working definition of the subject at hand:
[A] bullshit job is a form of paid employment that is so completely pointless, unnecessary, or pernicious that even the employee cannot justify its existence even though, as part of the conditions of employment, the employee feels obliged to pretend that this is not the case.
Graeber distinguishes these bullshit jobs from “shit jobs,” which serve a purpose but suck. Which is not to say that bullshit jobs don’t suck as well, but they suck precisely because they don’t serve a purpose. Much of the stress they produce—the “spiritual violence,” as Graeber terms it—results from the contortionist maneuvers that employees are forced to perform in order to pretend to be working when they have nothing to do. And as Graeber notes, this sense of purposelessness is widespread: To give just two examples, 37 percent of the UK respondents to a poll on the subject, and 40 percent of the Dutch ones, insisted that their work is utterly useless.
In 1930, John Maynard Keynes predicted that, by the end of the century, technology would have become so far advanced that developed economies would have a 15-hour workweek. So how did we get to our current state, almost two decades into the 21st century? It turns out that Keynes was only half right—technology has advanced spectacularly, but we are far from a 15-hour workweek. Keynes thought that the developed economies would adjust to a growth in productivity by decreasing workers’ hours. Instead, capital absorbed those gains but did not free up the now-superfluous human labor—a tendency that Karl Marx noticed long ago.
For Marx, this pattern is intrinsic to capital, whose constant expansion of its own value requires the reproduction of existing social relations. For Graeber, however, this pattern has less to do with capital’s prerogatives than with human agency; the problem “clearly isn’t economic: it’s moral and political,” he writes. Yet it would be truer to say that the problem is not merely economic, but also moral and political, and even truer to relate these spheres to one another, a point that Graeber himself makes later: “[E]very day it’s more difficult to tell the difference between what can be considered ‘economic’ and what is ‘political.’” But despite a muddled sense of causes and effects, Graeber’s book offers us an engaging—albeit at the same time tremendously disheartening—portrait of labor in 21st-century capitalism.
In his previous books, especially 2009’s Direct Action: An Ethnography and 2011’s Debt: The First 5,000 Years, Graeber’s ear for anecdote lent his activism the air of folktale. Debt’s opening vignette, for example, set at a garden party at Westminster Abbey, offers a charming little parable about our tacit beliefs and assumptions. At the party, Graeber suggests to an attorney he meets that the developing world’s debt should be abolished. “But,” she objects, “they’d borrowed the money! Surely one has to pay one’s debts.”
In Bullshit Jobs, Graeber similarly employs anecdote in order to illustrate just how much insanity we take for granted. Liberally drawing from the respondents to his original essay, he recounts stories that read like Philip K. Dick at his least plausible. Some are sad, others infuriating, and many are both. A number verge on the absurd: One woman’s job was to go around demanding IDs and proof of income from temporarily sheltered homeless people so that “the temporary homeless unit could claim back [the] housing benefit.” If homeless people couldn’t provide the necessary paperwork—as often happened—their caseworkers would kick them out. In another instance, a “subcontractor of a subcontractor of a subcontractor for the German military” describes driving for hours and filling out pages of paperwork simply to prevent a soldier from carrying his computer about 16 and a half feet down a hallway to his new office.
Most of the stories involve jobs that are also nightmarish in their unrelenting tedium. My favorite is the museum guard whose job was to protect an empty room, apparently to make sure no one started a fire in it. To ensure his vigilance, he was forbidden to read a book or even look at his phone.
All of these jobs sound terrible, but are they also bullshit? The people who have to do them think so. But Graeber’s reliance on subjective impressions of whether work produces value is the book’s major weakness. He brings up Marx’s distinction between productive and unproductive labor—between workers who produce surplus value and those who do not—simply to brush it off. And it is telling that he focuses on “information work” and what he calls “salaried paper pushers.” While he claims that these kinds of positions, rather than “waiters, barbers, salesclerks and the like,” account for “the bulk” of service jobs added to the economy since 1990, the US Bureau of Labor Statistics could have set him straight on this score. As Jason E. Smith pointed out in his review of Graeber’s book in The Brooklyn Rail, the bureau’s table of “occupations with the most job growth” actually does include waiters and retail salespeople, not to mention nurses, customer-service representatives, janitors, health aides, fast-food workers, cooks, and construction workers. Most service workers, in other words, are indeed providing valuable services—caring for others and feeding people.
Graeber’s picture of a Dickensian bureaucratization run amok has other problems as well. He correctly notes that our economic system has undergone profound transformations since the 1970s, with declining manufacturing and wages and a rising service and financial sector. But according to Graeber, these changes mean that the existing system isn’t exactly capitalism anymore, but rather a kind of “managerial feudalism”—one that involves “hierarchies,” “class loyalty,” and “moral envy”—that is the result of political will rather than structural determination. However, while one can surely find such attributes at work in the global economy, the system remains capitalist: predicated on the extraction of profit from the labor of others (even when such profit is mediated by financial markets). “Class loyalty” and “moral envy” are the products of such a system.
In his work, the Marxist theorist Moishe Postone (who died earlier this year) explored “the domination of people by time” under capitalism in ways that bolster some of Graeber’s claims. Postone’s discussion of the shift from the “variable” time of the Middle Ages, which was determined by the different kinds of human activity, to the clock time of the modern period, an invariable standard that dictates the workday, parallels Graeber’s own.
Yet there are important differences as well. In his discussion of value, Graeber (like some Marxists, it must be said) attributes to Marx a “labor theory of value” akin to David Ricardo’s, according to which the value of a given commodity is equal to the amount of labor that went into its production. But the point of Marx’s theory, as Postone makes clear, is precisely to refute this: Value for Marx is not a market mechanism focused on exchange relations, but a social mediation. It is that which compels workers to reproduce capitalism. For Marx, capitalism’s alienated social relations are not by-products of capital’s expansion of value—they are how capital gets valorized.
Also, capitalism—like feudalism—is a system of domination. But in comparison, feudal domination was overt and easy to comprehend—no peasant had to wonder what he was working for. This is why Marx’s theory can indeed help to explain the situation that Graeber rightly decries: because it is a theory about how social relations get reproduced, including those that seem irrational and unnecessary.
Despite Graeber’s focus on surface phenomena like hierarchy and envy, he is correct to conclude that the only thing keeping capitalism going is our refusal to stop it in its tracks through collective action. One of his respondents, whom he calls Lilian, captures the pathos of our continued submission to our own domination: “I get most of the meaning in my life from my job,” she writes. But the “meaning” of most jobs is meaninglessness itself.
Here we find Graeber exploring what is perhaps his true subject: not jobs that seem unnecessary, but the unnecessary compulsion of wage labor. In a free society—one in which your time and work are your own rather than commodities—Lilian’s sentiment would not necessarily be pathological. Work doesn’t need to be drudgery; we can find meaning in our jobs. But a society based on the production of value is by definition unfree, since we don’t really have a choice about whether to participate in it, and because work often becomes merely a tedious means of survival.
We have all experienced the truth of this. After college, I worked briefly as a temp doing data entry for a corporate law firm. I sat in a windowless room with a bunch of other temps, all of us squeezed together at a long table like students in a computer lab. We earned a little over the minimum wage. As often as I could, I would shirk my duties and surf the then-nascent Web. I had my spreadsheets minimized in a corner, ready to click should a paralegal come in to pick up something from the printer. But it was a fellow temp, who sat on my left, who objected to my wretched rebellion. “You’re not getting paid to surf the Web,” he informed me. I was just trying to reclaim a little of my time from those who were stealing it. And it wasn’t even a very effective protest, since I still had to sit in that depressing room and fill out enough spreadsheets to keep from getting fired. But my co-worker was simply expressing an assumption so commonplace that it hardly ever needs to be articulated: Your time does not belong to you.
Some of the first factories in London went bankrupt because laborers refused to work all day, every day. To the factory owners, this proved the workers were indolent loafers, so they reduced wages to the point that workers were forced to put in even more hours to survive. But this was really doing the workers a favor, the owners insisted, because otherwise they’d just get drunk and lie about. “Productive activity,” as André Gorz noted, began to be “cut off from its meaning, its motivations and its object and became simply a means of earning a wage.” Now we’ve all internalized this view of work.
Graeber doesn’t mention a project I recently learned about from Franco Berardi’s Futurability: The Age of Impotence and the Horizon of Possibility, but it represents the ne plus ultra of bullshit work. Berardi reprints an article—one of the most terrifying things I’ve ever read—that describes Candelia, a job-training center in France:
Sabine de Buyzer, working in the accounting department, leaned into her computer and scanned a row of numbers. Candelia was doing well. Its revenue that week was outpacing expenses, even counting taxes and salaries. “We have to be profitable,” Ms. de Buyzer said. “Everyone’s working all out to make sure we succeed.”
This was a sentiment any boss would like to hear, but in this case the entire business is fake. So are Candelia’s customers and suppliers, from the companies ordering the furniture to the trucking operators that make deliveries. Even the bank where Candelia gets its loans is not real.
The wages are imaginary, too. Nothing is produced in this “job” except the illusion of waged labor, but de Buyzer “welcomes the regular routine.” France has more than 100 of these “staged companies.”
This is the world we’ve inherited—one in which we reflexively inquire of strangers, “What do you do?” which means, of course, “How do you earn a living?” And this is so even when there’s no social need for everyone to be working all the time. Bullshit jobs are only one idiotic facet of this larger decoupling of work from meaningful activity. If the problem were managers and bureaucracy, then we would simply need to eliminate them. But if the problem is capitalism, then we need to change the world. The familiar slogan of Occupy Wall Street and the global justice movement of the early 2000s, both of which Graeber was involved in, was “Another world is possible.” We’re told this is idealistic and naive. But it’s not bullshit.
Michael Robbins is the author of two books of poetry and the essay collection Equipment for Living: On Poetry and Pop Music.
Taylor was in conversation with David Graeber, author of Bullshit Jobs and Professor of anthropology at the LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS