The Permian Is Drowning in Its Own Wastewater
- The Permian basin's massive oil production from hydraulic fracturing generates huge amounts of wastewater, and the industry is running out of safe places to dispose of it.
- The Texas Railroad Commission has restricted new disposal wells due to widespread increases in reservoir pressure, leading to drilling hazards, ground deformation, and seismic activity.
- Potential solutions, such as treating the water for release into rivers, face regulatory hurdles and would add significant, unwelcome costs to producers operating below $60 per barrel West Texas Intermediate.
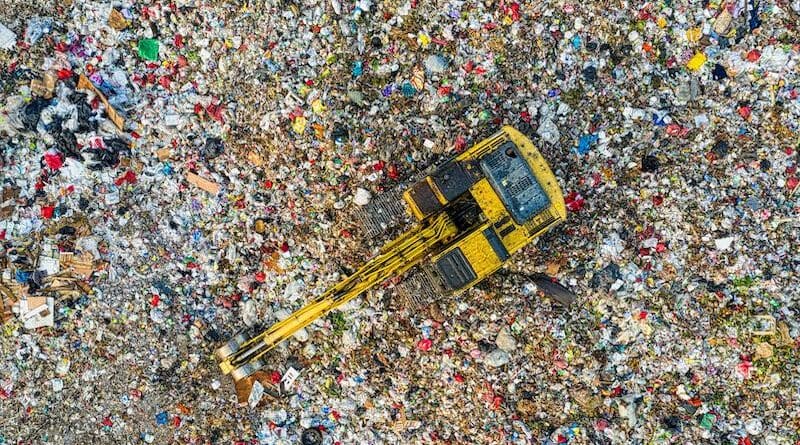
The Permian Basin is the largest contributor to U.S. oil production, accounting for nearly half of total production in both 2024 and 2025. But success comes at a price, and in the Permian’s case, the price is huge amounts of wastewater—and the industry is running out of places to store it.
Hydraulic fracturing, which is the dominant way of extracting oil in the Permian, is a water-intensive process. Fracking involves injecting chemicals and sand into the horizontal well to open up the oil-bearing rock and keep it open. The longer the laterals got, the more water needed to be injected. This water, which is mixed with chemicals, then gets disposed of in special wells. But there are too many of those, and they are overflowing, according to reports.
The first signs of serious trouble emerged earlier this year, when the Texas Railroad Commission sent out notices to companies applying for licenses for wastewater disposal wells in the basin, stating that there were ground pressure issues caused by wastewater disposal. The number of new ones was to be restricted.
Wastewater disposal, the Railroad Commission wrote in the letters sent out in May, “has resulted in widespread increases in reservoir pressure that may not be in the public interest and may harm mineral and freshwater resources in Texas.” The RRC added that “Drilling hazards, hydrocarbon production losses, uncontrolled flows, ground surface deformation, and seismic activity have been observed.”
It is difficult to find a solution to this problem without compromising oil production, and while local communities may not have a big problem with that, the industry will. So decision-makers in relevant positions are considering options. One of these, per a recent Bloomberg report, is releasing the water—after treating it—into local rivers.
The report cited regulatory filings concerning the issue of permits to energy companies to treat their wastewater and then release it into the Pecos River near New Mexico. Texas Pacific Land Corp. and NGL Energy Partners were two of the companies named as potential receivers of such a permit. At least one of these could be awarded by the end of March 2026, the Bloomberg report also said, citing Texas Pacific Land Corp.
If the wastewater problem is to be solved, however, more such permits would be needed—unless opposition to them emerges and spreads. There is also the issue of additional costs, Bloomberg noted. Treating the water to make it of suitable quality to be poured into a river would add to oil producers’ costs, and this is not the time to have more costs pile up for most producers, with West Texas Intermediate firmly below $60 per barrel. What’s more, Bloomberg reports that the safety of the whole procedure of releasing treated water into rivers has not yet been confirmed.
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has already signaled it will not be handing out wastewater-to-river permits like candy. The watchdog told Bloomberg it was monitoring the water quality at four locations along the Pecos River and two locations in its Red Bluff Reservoir—while considering the first of those permits.
The Wall Street Journal, meanwhile, reported that while regulators are looking for solutions to the wastewater problem, pressure is building in the rock, suggesting it may come to affect production. There is so much wastewater across the Permian that it is moving into old wellbores, causing geysers that cost a lot to clean up, the publication said, adding that pressure in injection reservoirs in some parts of the Permian has reached 0.7 pounds per square inch per foot. This is 0.2 pounds higher than the threshold over which liquid can flow up to the surface and potentially affect drinking water.
The Wall Street Journal noted that drillers in the Delaware Basin are pumping between 5 and 6 barrels of fluid for every barrel of oil they recover. That, it appears, is a lot, and the practice, as suggested by these reports, is unsustainable. The current solutions also appear to be falling short, mostly consisting of switching from deep disposal wells to shallower ones to avoid changes in seismic activity, as reported by the U.S. Geological Survey.
The shallow disposal wells have fixed the seismic problem and are currently receiving three-quarters of all wastewater produced in the Permian, the WSJ reported, noting, like Bloomberg, the unwanted water geysers that the migrating water is causing. One of these costs $2.5 million to plug, with the Texas Railroad Commission also shutting the injection wells that it suspected were leading to leaks, the Wall Street Journal wrote.
Meanwhile, the industry is trying to fortify its wells against wastewater seeping from injection wells, which also leads to additional costs. “Bit by bit, it adds cost, it adds complexity, it adds mechanical challenges,” one Chevron executive told the WSJ. On top of this, the wastewater is seeping into the oil and gas reservoirs, and there seems little that anyone can do about it except spend more to remove it. The issue with excess wastewater in Texas remains a challenge to an industry that is pumping almost half of the nation’s oil.
By Irina Slav for Oilprice.com