Operation Absolute Resolve and the Realpolitik of American Empire
January 7, 2026

Image by Dominik Vanyi.
The inherent fallacy of the political scientist is that she cannot test her theory. There are, of course, no controlled experiments (unless you’re running a country like an economic laboratory for neoliberal policies. See Chile 1973). Thus, making hypotheses or predicting the outcome in politics is a fool’s game. However, you can count on a constant reality in the game of geopolitics—self-preservation through pragmatic politics that secure a State’s national interests, or what is known as realpolitik. While made infamous by the notorious “statesman” (read war criminal) Henry Kissinger, pragmatism has helped preserve more States than ideology has throughout history. States, as systems of control and centralized power operated by an elite class, seek self-preservation above all. While ideology can help to win over a populace for more effective governance, geopolitics requires a pragmatic approach in a landscape dictated by force. In other words, politics has always been a game of power and nothing else.
While it is hard to determine the true geopolitical strategy behind Operation Absolute Resolve, which brazenly abducted the sovereign president of Venezuela, we can take a look at patterns and trends over the last few years, as well as the current geopolitical landscape, to deduce the pragmatic politics behind the assault. Setting aside the rhetoric from the White House as political posturing and saber-rattling, we can analyze what Operation Absolute Resolve accomplishes for the U.S. empire in the current moment. Beyond the immediate short-term goals of resource extraction and control, a closer look at what this operation does for the US on multiple fronts helps one better understand its move in the game of geopolitics. While the US is undoubtedly the world’s most influential rogue state, as it unapologetically prioritizes its interests over International Law in shaping the world order, it does not act irrationally. Instead, the US empire acts through strategic, well-calculated measures to preserve corporate and military interests. Whenever the US engages in open violations of International Law, such as the strikes in Libya, invasion of Iraq, bombing of EL Salvador, and so many others, we can assume it does so weighing the consequences of international blowback with the geopolitical and economic benefits it would gain.
The following interventions outline some of the main areas in which the US empire has benefited following Operation Absolute Resolve. It situates this operation within the current geopolitical landscape and asks: What are its long-term implications and the messages it conveys? What are the short-term and long-term impacts of this operation?
A clear message to China: The Western Hemisphere Belongs to the US
Just hours before his abduction, President Maduro had concluded his first scheduled meeting with a Chinese delegation. The manner in which the operation was conducted was an affront to diplomatic and consular immunity, as it disregarded the presence of Chinese diplomats. It sends a message to the broader Chinese government that the US is above international Law and the established diplomatic channels respected by other countries.
The meeting between Maduro and the diplomats sought to strengthen collaboration between Venezuela and China, which has invested nearly $70 billion over the past 20 years. China, Venezuela’s largest oil importer, has been strengthening its ties across the region over the years through its Belt and Road initiative, becoming Latin America’s largest trade partner. In 2024, trade in the region reached $518 billion, with more than 20 countries having signed on to the Belt and Road Initiative. Only a few months before the operation, China and Peru inaugurated the Chancay seaport just north of Lima. The nearly $4Billion project is a deep seaport that looks to cut travel time between regions and serve as the gateway to the mineral wealth across the hemisphere.
One of the surprising elements of China’s growth in the 21st century is that it has done so without military interventions or resource wars. Rather, China has relied on investments and economic diplomacy to secure essential trade routes, partners, and significant reserves of its growing economy. At the same time, the US has continued to put pressure on its regional security, strengthening military ties with Japan and Korea, while reaffirming it commitment to defend Taiwan’s sovereignty. That this operation happened while China remains unable to exert its influence over the South China Sea and establish a decisive foreign policy with Taiwan 80 miles off its coast speaks volumes to the contrast between the regional powers.
Operation Absolute Resolve reasserts US dominance over the hemisphere. “Under our new national security strategy, American dominance in the Western Hemisphere will never be questioned again, won’t happen,” said Trump shortly after the operation. This aligns with the national security blueprint, known as the Trump Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, issued by the White House in early December, which described the Western Hemisphere as a “Homeland Security Zone” given its strategic and economic significance to the well-being of the US.
Reaffirms the Military Power of the US
Operation Absolute Resolve’s effective, surgical brevity reflects the only sector of the American empire that remains unrivaled: its military. With China set to overtake the US by 2030 as the largest economy in the world, and US’s declining influence in the tech world as it falls behind the development of advanced supercomputers and large learning machine, this operation is a reminder to the world that the US not only stands alone with regard to military strength, but that it can be used to overcome its shortcomings.
As the US army’s invasion of Panama in 1989 served to get the “Vietnam syndrome” out of the general public in the US through a swift military victory, the brazen and highly successful abduction of a sovereign president in such a manner gets the US out of the Afghan and Libyan syndrome, while winning over the isolationist “America first” MAGA base. The praise for the operation from many across the MAGA base indicates that the popular isolationist ‘America First’ position was less rooted in concerns for domestic issues and more about the efficacy and ability to project strength onto the global community. It demonstrates a level of warfare that makes other regional powers seem weak in comparison, projecting its domestic chauvinism onto the global stage. With Russia now entering its 5th year of war against Ukraine, and China’s inability to exert full control of the South China Sea, the US reminds its rivals that it remains well ahead in regional, if not global, influence.
The US still maintains the largest number of aircraft carriers at sea, remains the world’s largest weapons manufacturer, and operates nearly 1000 military bases worldwide, most recently reactivating the Naval Station Roosevelt Roads in Puerto Rico, which returned to service after 20 years. Together with the bombing of Iran’s nuclear facilities in June of 2025, the Trump regime reminds the world that it is the US doctrine and not International Law that dictates the world order.
Not all about oil
Venezuela’s oil production has fallen to about 1/3 of what it was at the beginning of Chavez’s presidency. The same goes for many of its other commodities, namely natural gas, with sanctions, mismanagement and the fracturing of PDVSA leading to weakening industries. Much has been made of Venezuela’s holding the world’s largest oil reserves, an amount larger than those of the US and Saudi Arabia combined. However, these reserves are untapped, located in a region known as the Orinoco Belt in the southeastern part of the country with very little infrastructure. Accessing these ultra-crude oil reserves would require sophisticated mapping technology and drilling equipment that would take years to deploy. Thus, discussions of oil center on its potential to meet the country’s long-term needs rather than to satisfy the empire’s immediate energy requirements.
The inaccessibility of Venezuela’s resources is, of course, a consequence of the technological gap between the North and South countries, with the former still maintaining a disproportionate grip on patents and technologies for mineral extraction. Combined with sanctions and blockades, the extraction of mineral and oil reserves in the global south is always going to depend on its relationship with the North.
Finally, we can assume that there have been coordinated efforts behind the scenes by some, if not all, of Venezuela’s allies and the US, who themselves engage in their own form of realpolitik while remaining true to any “anti-imperialist” ideology. Putin has been notably quiet on Operation Absolute Revolve, as of this writing, having not called for the release of Maduro. A longtime ally of Maduro, Putin had for years reiterated his support for Chavez’s heir, supplying the country with defensive anti-aircraft weapons, the same that failed to deter the US invasion. We can only deduce from this that some concessions may have been given to Russia as negotiations with the US and Ukraine enter their next phase. The same can be assumed about China, although, given that the US and China are not engaged in public negotiations over territorial disputes, we can see why China’s response has been more direct. For people worldwide, including the genuine anti-imperialist movement, the manner in which the operation was conducted indicates the empire’s reluctance to engage in direct confrontation with popular fronts. The time spent on clandestine training, covert operations, and infiltration indicates the empire’s apprehension about symmetric and even classic asymmetric warfare. Only time will reveal more of the strategic benefits Operation Absolute Resolve may have had, or perhaps make it another page in colonial hubris.
The United States in Venezuela and Beyond

Image by Planet Volumes.
About a month ago, I was worried about an awful lot of saber-rattling that was going on in the Trump administration. That rattling became a reality with the invasion of Venezuela and more threats issued against other countries, first against Colombia, then Mexico, Cuba, and the dreamiest of all dreamworlds, the annexation of Greenland, which is still under the protective flag of Denmark.
Panama was the subject of some saber-rattling as well, so the threat against them appears to not be as serious. However (somewhat presciently), I said the following:
Panama has momentarily escaped Trump’s threats, primarily by promising to rethink the contract it has with CK Hutchison to run the canal. The president is worried that the Hong Kong-based company (and its subsidiary, Panama Ports Company) is giving too much power to China in a region where “rightfully” the US must dominate, as set forth in documents like the Monroe Doctrine and backed up by Teddy Roosevelt’s “Big stick” diplomacy. For the time being, Panama is working on a back-up plan in case a new contract with CK Hutchison falls through. Trump is still looming in the background, but things are stable, at least for the time being.
Nicolás Maduro has likely worn out his welcome as president of Venezuela. The US and some other states recognized Juan Guaidó as president, that failed, then Edmundo González probably won the most recent presidential election but Maduro was sworn in as president this year anyway. Lacking access to opinion polls, it seems that few people actually like Maduro because the continuation of policies introduced by Hugo Chávez has been carried out without much forethought, plunging Venezuela’s economy into a tailspin.
That said, if the US continues to threaten Venezuela, that is likely to bring people in the country together against Trump, more than it unites people against Maduro, as disliked as he may be. Decades ago, scholars like Benedict Anderson and Tom Nairn argued that nationality, nationalism, and one’s sense of belonging to a nation run much deeper in identity than anyone could imagine. It’s more important to defend Venezuela than it is to get rid of a president whose time has come and gone.
Yeah, all of that. You see, it’s not the Monroe Doctrine anymore, but the Donroe Doctrine, according to the president.
Columbia seems to be in the sights of the Trump administration, again under the auspices of dealing with the drug trade in Columbia even though the cartelization of cocaine trafficking was a much bigger deal back in the 1980s and early 1990s, and the current anti-drug obsession was supposed to be about illicit synthetic opioids coming into the United States (with fentanyl topping the list) and the flood of methamphetamines similarly getting cooked in other countries, then being sold in the US. None of that seems to matter anymore because the US is supposedly awash in coke right now. Time is of the essence, or so the government wants to argue.
There is also the precarious situation that Greenland finds itself at the moment. Vice President JD Vance and his spouse Usha visited Greenland not long ago, then White House “advisor” and blogger Katie Miller posted a map of Greenland in stars and stripes with the one word comment, “SOON.” Perhaps it was a joke of some kind, but the prime minister of Denmark warned that a military takeover of the island by an ally would signal the end of the NATO alliance. That’s a fairly big deal, and Vladimir Putin must certainly must be holding his thumb (in Eastern Europe, it’s like crossing one’s fingers) for that to happen.
Does the Trump administration recognize the dangers of saying that Greenland is “needed” by the US? Seems as though they are blind to that possibility, as they are to grabbing Venezuela and then claiming that the US will control the crude oil flowing out of that country. What happened to stopping the so-called “narco-terrorism” of the Maduro government? Oh, now it’s about oil.
Of course, the drug thing might all be just a cover story anyway. That was revealed when the former Honduran president, Juan Orlando Hernández, got pardoned by Trump, even though a trial found him guilty of helping to traffic 400 tons (metric tons—1000 kg each) of coke to the US, and his sentence was to serve 45 years in prison. But he said some nice things about Trump, so ignore what he was actually convicted of, right?
People of Venezuela were not big fans of Maduro. Gustavo Petro is probably on firmer ground with his constituents in Colombia. Forced to defend their country or not, people will resist American aggression. If the US wants to build better relations with other countries and their leaders other than Vladimir Putin, this is not the way to do it. The Monroe Doctrine affirmed US imperialistic ambitions in the 1820s. The Donroe Doctrine reinforces a more menacing foreign policy posture in 2026.
by Ted Snider | Jan 7, 2026 antiwar.com
At 4:21 in the morning of January 3, U.S. President Donald Trump posted that “The United States of America has successfully carried out a large scale strike against Venezuela and its leader, President Nicolas Maduro, who has been, along with his wife, captured and flown out of the Country.”
No one had anticipated such a military operation prior to the announcement, and no one anticipated the comments Trump would make later that morning in his press conference.
The press conference, and the comments that followed shortly after, contained several shocking statements.
The first was the announcement of the military operation itself. Once cloaked purely in the language of preventing drugs from flowing into the United States, the Trump administration had recently clarified its intention for regime change. In late November, Trump told Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro to resign and leave the country. In December, Secretary of State Marco Rubio said “It is clear that the current status quo with the Venezuelan regime is intolerable for the United States. So, yes, our goal is to change that dynamic.” Asked if his goal was to force Maduro to give up power, Trump said, “Well, I think it probably would… That’s up to him what he wants to do. I think it’d be smart for him to do that. But again, we’re gonna find out. If he wants to do something, if he plays tough, it’ll be the last time he’s ever able to play tough.” White House chief of staff Susie Wiles says that Trump’s Venezuela strategy is “to keep on blowing boats up until Maduro cries uncle.”
Maduro did not cry uncle. He continued to defy the U.S. and to call for the U.S. to abandon ambitions for its “crazy war.” So, the soft coup turned into a hard coup, and the U.S. launched a military attack on Venezuela, capturing Maduro and bringing him back to the U.S. to face drug charges.
But perhaps the most shocking moment in Trump’s press conference was his unexpected announcement that “We’re going to run the country until such time as we can do a safe, proper, and judicious transition. So we don’t want to be involved with, uh, having somebody else get in and we have the same situation that we had for the last long period of years.” During the Q&A, Trump added that “Venezuela has a lot of bad people in there, a lot of bad people that shouldn’t be leading. We’re not gonna take a chance that one of those people take over for Maduro.”
As a person to take over from Maduro, at least temporarily, the Trump administration has settled on Venezuela’s Vice President Delcy Rodríguez. In the press conference, Trump said that Rubio “just had a conversation with her, and she’s essentially willing to do what we think is necessary to make Venezuela great again. Very simple.”
That, too, was a stunning and unexpected move. The Trump administration had long argued that Maduro was an illegitimate leader who had lost Venezuela’s last election to the María Corina Machado led opposition. Rubio had nominated opposition Machado for her Nobel Prize, and she dedicated her prize to Trump. Following the coup, Machado declared that “Today we are prepared to assert our mandate and seize power.”
But Trump spurned Machado during the press conference, saying “it would be very tough for her to be the leader if she doesn’t have the support within, or the respect within the country. She’s a very nice woman, but she doesn’t have the respect within [Venezuela].”
It was stunning that Trump turned his back on democracy and on the election the U.S. had leaned so heavily on in its case against the legitimacy of the Maduro administration and on the opposition that they claim won that vote and settled on working with the Vice President whom they claim is not legitimately elected. In the days following the coup, Maduro’s government appears to still be in power.
But despite Trump’s claim that Rodríguez is willing to do whatever Washington tells her to do, Rodríguez appeared to remain loyal to Maduro and defiant. She maintained that “There is only one president in Venezuela, and his name is Nicolas Maduro.” She called America’s actions “barbarity.” Though she said that Venezuela is willing to “have respectful relations” with the United States, she insisted that they “will never return to being the colony of another empire.”
Prior to Rodríguez’ defiance, Trump had already declared in his press conference that the U.S. is “ready to stage a second and much larger attack if we need to do so.” He warned that “[a]ll political and military figures in Venezuela should understand what happened to Maduro can happen to them” and pointed out that Rodríguez will have to do whatever she’s told because “she really doesn’t have a choice.”
After her defiance, Trump warned that “if she doesn’t do what’s right, she is going to pay a very big price, probably bigger than Maduro.”
On January 5, Delcy Rodríguez issued a statement that sounded more conciliatory but preserved her main points. She continued to say, as both she and Maduro previously had, that Venezuela “consider[s] it a priority to move toward a balanced and respectful international relationship between the United States and Venezuela” and “to work together on a cooperation agenda aimed at shared development” but that that had to be done “within the framework of international law” and “based on sovereign equality and non-interference.” She insisted that there can be no “external threats,” and she continued to refer to Maduro as “President Nicolás Maduro.”
Though Rubio attempted to nuance Trump’s statement into a more palatable formulation, saying the U.S. would not be “running” Venezuela but would “running policy” in Venezuela – a difference so fine it is difficult to detect – Trump stuck to his harsher formula. Asked the next day who was in charge in Venezuela, Trump said that the U.S. would be “dealing with the people that just got sworn in.” But then he said, “Don’t ask me who’s in charge, because I’ll give you an answer, and it’ll be very controversial… We’re in charge.”
The press conference was shocking, not only for its dismissal of Venezuelan democracy, but for its dismissal of American democracy and the people’s representatives. When asked if Congress was notified about the military operation, Trump deferred to Rubio who said that “[t]his was not the kind of mission that you can do congressional notification on.” Trump then dismissed Congress, adding that it “has a tendency to leak… Congress will leak, and we don’t want leakers.” Despite the undemocratic precaution, news of the military action did leak: both “The New York Times and Washington Post learned of a secret US raid on Venezuela soon before it was scheduled to begin Friday night – but held off publishing what they knew to avoid endangering US troops.”
The press conference was also incredible for the legal justification it attempted to provide. Trump provided none. But Rubio and Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Dan Caine did. Caine said that the military operation was conducted “in support of a request from the Department of Justice,” that it was “an apprehension mission… to bring to justice two indicted persons.”
Rubio said the operation was “largely a law enforcement function. Remember, at the end of the day, at, at its core, this was an arrest of two indicted fugitives of American justice, and the Department of War supported the Department of Justice in that job.”
But there are two problems with that legal defense. The first is that, according to many international law experts, the argument doesn’t hold water. The American act was a crime of aggression that violated UN charter article 2(4) that prohibits states from using military force against another country or violating their sovereignty. Contrary to the UN charter, the U.S. attacked Venezuela without a resolution from the Security Council and without a necessity dictated by self-defense.
But even if the act of seizing and arresting Maduro was legitimized by the law enforcement defense, that would not legitimize the further acts of ruling Venezuela or seizing its oil.
And finally, the press conference, and the remarks that followed, were shocking for their scope and application beyond Venezuela.
Secretary of War Pete Hegseth said that America’s “adversaries remain on notice. America can project our will anywhere, anytime.” Asked if Colombian President Gustavo Petro had to “watch his ass” as Trump warned earlier, Trump replied, “He’s making cocaine, they’re sending it into the United States, so he does have to watch his.” On January 4, Trump said that Colombia’s Gustavo Petro is “making cocaine and selling it to the United States.” He then warned that “He’s not going to be doing it for very long.” Asked if the U.S. would conduct an operation against Colombia, he said “it sounds good to me.”
Trump also said that “Cuba is gonna be something we’ll end up talking about… we wanna help the people in Cuba.”
On Cuba, Rubio added, “when the president speaks, you should [Laughs] take him seriously. So, uh, suffice it to say, you know, Cuba is a disaster. It’s, it’s run by incompetent, senile men… So yeah, look, if I lived in Havana and I was in the government, I’d be concerned at least, a little bit.”
Trump further warned that “Mexico has to get their act together, because [drugs are] pouring through Mexico, and we’re going to have to do something” and that “we do need Greenland, absolutely. We need it for defense.”
Ted Snider is a regular columnist on U.S. foreign policy and history at Antiwar.com and The Libertarian Institute. He is also a frequent contributor to Responsible Statecraft and The American Conservative as well as other outlets. To support his work or for media or virtual presentation requests, contact him at tedsnider@bell.net.
January 7, 2026
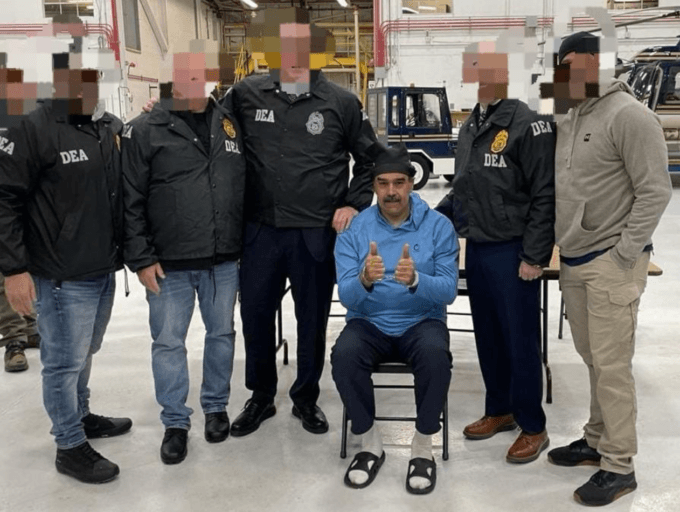

Photograph Source: Drug Enforcement Administration – Public Domain
We definitely should not be surprised that this happened. Venezuela is known for that addictive substance, used the world over. The use of this item will most certainly cause the death of untold millions, that much is true. The addiction requires that country to be invaded. Of course, I’m speaking of oil, but the controlled US media will say it’s about Fentanyl. As bizarre as the FIFA Peace Prize: up is down, down is up. If we can’t trust the FIFA Prize, what are we to think of the PEZ Genius Award, the Ramen Noodle New Literature Trophy and the Dr. Pepper Advances in Medicine Medal?
This muddled reality peddling is, of course, nothing new; the Iraqi weapons of mass destruction lie never found anyone to be responsible for the selling of those falsehoods. Colin Powell just became temporarily embarrassed. Hillary Clinton cackled about the death of Libya’s leader by a mob that sodomized him with a knife. A US emboldened knife, of course. Yeah, that guy was weird, as all these leaders are, but Libya was looking to create a pan-African currency and was plotting to remove itself from the petro-dollar stranglehold. That’s what got him killed, not having photos of Condoleezza Rice up on his walls and/or any generalized freakery. The subsequent descent of that nation from one that provided citizens with housing, free college (with stipends), into an open-air slave market was, I guess, funny to Clinton. Break things and plunder. America just looks forward and, like a dog kicking dirt on its last crap, runs to the next adventure, consequences be damned.
I won’t say that this time doesn’t feel a bit different and far more severe, however. Instead of the old method of toppling nations in a more sporadic fashion, this feels like a prelude to something much more massive. All of the American misbehavior we are used to is now on steroids, or if you will, on Pervitin. We have the current regime players putting pictures of Greenland on social media with US flags on top of it and the heading “Soon” by the nation. We have Rubio threatening Cuba that they are in hot water. We have Trump commenting that the leader of Mexico isn’t really in charge of her country, implying we should do something about it. My God, we can’t even keep our people on healthcare in this country, yet we can multi-task and threaten all of these nations and their leaders?
Things are not looking good here in the United States. We have so many homeless students that school districts are having to open up their parking lots for the kids and their parents to sleep in cars. We have a declining life expectancy. Many young people don’t even want to have children because one: They can’t afford them and two: They can’t imagine bringing them into a world so completely fucked up. And this is a nation that thinks it has the green light to move in to take over other countries? It’s as if you move every time your house gets dirty. This is filthy and deranged behavior.
One very bizarre aspect of this oligo-corporate kakistocracy is the fact that nothing is really being offered to the citizens. When we are speaking of the kind of funds it takes to prop up billionaires and to perform international take-overs of nations…you’d think there would be some chump change to toss at the masses to keep them fed, housed, and quiet. It’s not like the resources don’t exist. It’s as if Bezos didn’t have his funds from the month of June. His life wouldn’t change one bit. He would still have more than he could ever spend. The scarcity lie is just that–a lie. At some point, you have to wonder if cruelty isn’t the point. Those who revel in harming children probably low key get off on making vast numbers of people suffer as well. I think those of us with functioning empathy have completely underestimated the evil that simmers in so many of the rich and powerful. We are woefully unprepared for such enemies.
The fact that they are leading the citizens to such suffering might be their Achilles’ heel, however. People can turn a blind eye to many atrocities if they are comfortable, but this new paradigm does not even afford basic necessities. Americans watch ballrooms be built; they see filler-faced nightmare people oozing about, moving around in their private jets while watching loved ones fall deeper into debt and despair. They see international fiascos that they were told would be a thing of the past by Trump. I would say that isn’t sustainable. And all of this in a setting of…pedophilia ring cover-ups. The corruption and filth run deep.
This is a mask-off event, if you will. There isn’t even the slightest bit of subtlety. Those being told the economy is fine know they are broke when they try to purchase their groceries. They know their relative in the armed forces is being forced to be involved in foreign plunder, but barely gets by. Even the dimmest-witted of individuals will know the situation is wrong, even if they have no clue exactly who to blame. This is probably why we see such a rapid push to completely tighten up the news sources to all be a Pravda-style state media. Bari Weiss isn’t there for ratings, that’s for sure. The nation’s leaders are fine with an underfed and angry populace as long as they have no clue who to blame.
But word gets out…and a situation such as this is simply unsustainable, even for a FIFA Peace Award winner.
The US Justice Department, Fake Cartels,
and Maduro
A Shameful Sham
The Trump administration is increasingly resembling a government previously abominated by the current US president as entangling, bumbling, and prone to fantasies. President George W. Bush was well versed in baseless existential threats stemming from Mesopotamia, supposedly directed by the Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein. There was a critical problem in this assessment: in his dry drunk state, Bush was criminally wrong, proposing a doctrine in response to the attack by al-Qaeda on the United States on September 11, 2001 heavy on violence and slim on evidence.
The patchy formulation came to be known as the Bush Doctrine, permitting the United States to unilaterally and pre-emptively attack any country allegedly posing a threat to its security despite never evincing any genuine means of doing so. There would also be, Bush stated in his address to the nation, “no distinction between the terrorists who committed these acts [of 9/11] and those who harbor them.”
Such streaky reasoning eventually fastened upon Iraq’s alleged Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMDs), apparently at the ready to strike the US and its allies. If not Baghdad, then certainly an opportunistic terrorist proxy would be more than willing to deploy them. In his 2003 State of the Union Address, Bush solemnly stated that “the gravest danger facing America and the world, is outlaw regimes that seek and possess nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons.” Such weapons might be used “for blackmail, terror, and mass murder” or provided or sold “to terrorist allies, who would use them without the least hesitation.”
As the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq proceeded with its increasingly bloody bill of sale, there were no WMDs to be found. Saddam, foolishly as things would have it, destroyed or disarmed those weapons he had made free use of in the Iran-Iraq War. This hardly mattered. There was shoddy intelligence aplenty, including false claims that Iraq had tried to purchase 500 tons of yellowcake uranium powder from Niger, and cloudy lines of cooperation between Baghdad and al-Qaeda. With school boyish enthusiasm being shown by the evangelical UK Prime Minister, Tony Blair, the Saddam threat ballooned for Bush. Neoconservatives rejoiced at this chance of cratering, erasing and reforming the Middle East.
The Donroe Doctrine, childishly envisaged and clumsily applied, has an unmistakable analogue with that of Bush. In repurposing the Monroe Doctrine for the Western Hemisphere, excluding threatening foreign interests in Latin America and extinguishing governments adversarial or unsympathetic to the United States, Trump scorns the evidence. A fundamental reason for abducting President Nicolás Maduro of Venezuela, by way of example, was accusing him of being a narco-terrorist amenable to nasty foreign interests. Elevating his stature as a threat, he was accused of being a figure of the Cartel de los Soles (Cartel of the Suns).
This pattern stretches back to the first Trump administration, when a grand jury indictment alleged that Maduro, along with other officials, “participated in a corrupt and violent narco-terrorism conspiracy between the Venezuelan Cártel de Los Soles and the Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias de Colombia”. Five years later, when the Treasury Department retrieved the initial text, the Cartel was designated a “terrorist organization”. Come November 2025, US Secretary of State Marco Rubio directed the State Department to do the same.
With an eerie sense of the past cantering into the present, we find the US Justice Department conceding that there was no link between Maduro and this sinister cartel. This stands to reason, given that the group does not exist as a tangible organisation. The allegation has long been contentious, but those close to Trump were not willing to be swayed by that dullest compendium of subject matter unfashionably called “the facts”.
Believers in virgin births, tooth fairies and Sky Gods sometimes intrude into the making of American foreign policy, and Rubio, in justifying extrajudicial killings of those on board alleged narco-vessels in the Caribbean Sea by US military forces had this to say: “We will continue to reserve the right to take strikes against drug boats that are bringing drugs toward the United States that are being operated by transnational criminal organisations, including the Cartel de los Soles.”
The 2020 indictment mentioned the cartel no fewer than 32 times. The new indictment makes a mere two references to a term that has ceased to be an entity and become a concept, revised as a “patronage system run by those at the top.” It does not feature as an organisation along with the list of alleged “narco-terrorists” outlined in the fourth paragraph.
Those versed in the slippery argot of drug trafficking in Latin America have concluded that the Cartel de los Soles is a colloquialism minted by Venezuelan media to out despoiled officials sporting the sun insignia on their uniforms. It became a matter of usage in the 1990s, making it less a description of organisational reality than identifying a broader system of corruption.
From the outset, Venezuelan figures such as interior and justice minister Diosdado Cabello dismissed the cartel as the product of a fevered imagination. In August last year, he coolly remarked that US officials, when bothered, would name the target of their indignation “the head of the Cartel de los Soles”. The organisation makes no appearance in the United Nations’ annual World Drug Report, preferring to reference Mexico’s Sinaloa Cartel, and Brazil’s Primeiro Comando Capital (PPC) and Comando Vermelho (CV). The US Drug Enforcement Agency’s annual National Drug Threat Assessment makes reference to the Venezuelan Tren de Aragua, “a violent criminal organization founded between 2012 and 2013” that “mainly operates within Venezuelan migrant communities” in the United States. No favours are done naming the Cartel de los Soles, however.
The rewritten indictment against Maduro reveals how presidential doctrines can be used to force evidence upon a Procrustean bed, sawing or extending it to fit the set dimensions of a dogma. The crime of aggression against Iraq in 2003 was based upon forged evidence, implausible links and flimsy assumptions. The crime of aggression against Venezuela on January 3 reprised the performance. Instead of a uranium hoax, we got the Cartel of the Suns.
Venezuela vs. the Empire
January 7, 2026

Photograph by Nathaniel St. Clair
The USA is descending into a state of general lawlessness, at home and abroad. From using domestic special ops paramilitary units (ICE) to kidnap people off the streets of America and send them abroad, the US government is now deploying secret special ops military units (Delta Force) to snatch foreign heads of governments from their homes and sending them to jail in the US.
Political human trafficking has become the rule of law in America under the current Trump administration!
Before 2025, the two political parties engaged in a crescendo of lawfare actions against each other, employing the FBI, the courts and even the CIA behind the scene to destroy each other. Both parties engaged in abuse of the rule of law, pardoning family, rich friends, and business partners to protect themselves and their personal relations, rendering a travesty of the fiction that in America no one is above the law. Senior politicians of both enriched themselves, becoming multi-millionaires after leaving office after arranging special deals while in.
The recent US invasion of Venezuela a gross violation of international law. A hypocritical disrespect for sovereign boundaries that US neocon ideologues and their echo chamber captured US media have leveled at Russia in Ukraine the past four years.
Trump himself has publicly admitted the invasion of Venezuela was intended to secure US economic control of Venezuela’s natural resources, especially its oil reserves. In other words, good old fashion naked US imperialism, intended to grab another country’s natural resources.
The excuse was the nonsense charges of narco drug trafficking—i.e. the US neocons’ substitute excuse for WMD’s, weapons of mass destruction, used before in Iraq, Syria, Libya to justify US military intervention.
WMDs couldn’t be levied at Venezuela. Wouldn’t work. Nor would past excuses for US imperial intervention like ‘Remember the Maine’. ‘Tonkin Gulf’. Or ‘Killing Incubator Babies’. The neocons needed a new fake excuse for US imperial military intervention in Venezuela. So they looked into their magic bag of false flags, fake excuses, and CIA lies and pulled out ‘Narco drug trafficking’. That works better for Latin America imperial interventions—as former president of Panama, Noriega, found out in 1989.
Watch out Colombia president Gustavo Petro who defended Venezuela sovereignty and criticized Trump’s Venezuela action. And heed the warning Mexico president, Sheinbaum! You’re the next Trump targets. Ditto Cuba.
Does Greenland have a president Trump can threaten? Wonder what that excuse will be. Maybe the US must invade because ‘Chinese ships are melting the ice cap’.
And make no mistake. Trump’s not only engaged in naked military imperialism in Venezuela to enact regime change. His big mouth ‘spilled the beans’ that the US plans to install a new colonialism as well. Within 24 hrs. he declared publicly the US intends to ‘rule’ Venezuela directly until such time as a proper puppet regime can be put in place. Direct rule constitutes a colonial form of imperialism.
As the saying goes, the truth is often spoken from the mouth of a drunkard. And Trump is a big mouth bragger, drunk with power. And he’s saying directly what the US neocon imperialist elite behind him (Rubio, Walz, Graham, CIA spooks, etc.) are really thinking and planning.
In an attempt to cover up Trump’s careless blurting out the blunt truth, Trump neocon cronies like Rubio quickly rushed to the US media echo chamber to try to put lipstick on the ‘US will rule’ pig, saying the US has no such plans.
Another Trump neocon, Walz, former NSA to Trump and now ambassador to the UN, in his emergency speech to the UN argued the kidnapping of Venezuela president, Maduro, was not about creating colonial rule; it wasn’t even a military operation—according to Walz. It was just a police operation. Some police operation, accompanied by a fleet of 17 US warships, aircraft carriers, submarines, and 10,000 marines stationed in nearby Trinidad island!
Rubio added the US only wants to bring Maduro to New York to stand trial, as he conveniently avoided any mention that the USnavy is continuing to blockade all shipping from Venezuela. The US has no further military plans! Really? Anyone wanna buy a bridge from the man?
This is crass, US gunboat imperialism reminiscent of the early 20th century when the US invaded Latin American countries by the dozens. It is also a harbinger of US plans to impose some new form of colonialism on Venezuela, and who knows what other Latin American countries who dare to try to walk an independent path from the US Empire.
Trump and his crony neocons will try to cover up their plans for some new kind of colonialism if they can with CIA managed new elections this spring, the outcome of which is already pre-determined. The US designated next president, Machado, is already packing her bags and on her way to Caracas, no doubt with an escort of US agents of course who’ll accompany her throughout the forthcoming phony election campaign.
US imperialism has never given up on regime change in Venezuela for the past quarter century. Just like it has never with Iran for nearly half a century. Nor Cuba for the past 65 years.
The Bush administration in 2002 thought it had achieved regime change deposing then Venezuelan president, former General Chavez. He nationalized US oil interests in the country. The most unholy of capitalist sins! But the deposing of Chavaz was short lived as he was rescued and re-installed as president by the people and Armed forces of Venezuela quickly.
Under Obama the CIA continued deep financial and other aid to opposition movements to overturn Venezuelan elections, to little avail. Venezuelan public support was too great despite the US launching a classic economic war on Venezuela, wrecking its currency, stoking inflation, preventing its sale of oil exports and receipt of necessary medical and food imports. Their candidates kept losing national elections nonetheless.
Under Trump in 2018-19 the CIA efforts intensified, seizing Venezuelan gold in western banks and Venezuela’s CITGO oil distribution company in the US and giving the money from its sale to Venezuelan opposition movements. Still no success in regime change via electoral intervention.
US CIA and regime change ops were temporarily put on hold with the arrival of the Covid recession in the US in 2020, followed by US chaotic exit from Afghanistan in 2021, and implementation in 2022 of bigger US plans to engineer a proxy war in Ukraine against Russia.
Once Trump returned to office in January 2025, however, Venezuelan regime change was placed on the US foreign policy front burner once again. This time the Empire planned to do it right—which meant not relying solely on CIA electoral interference in Venezuela, as in the past, but taking the gloves off and doing regime change by means of US special ops intervention and direct US military action!
The Emperor removed his clothes and waded in waist deep. Perhaps over his head, as time will only tell!
One should not lose sight of the bigger picture behind the Venezuelan invasion.
It is not a standalone, one off operation. I’m sure the governments of Colombia, Mexico and Cuba will agree. The Venezuela operation is part of US neocon forces and imperialists refocusing on the Empire’s western hemisphere base that it had partly neglected while preoccupied in the middle east and eastern Europe (Ukraine and Caucasus). The Empire had let the western hemisphere go unattended. In the interim, when it was preoccupied on the other side of the world, and while planning long term to engage China in Taiwan, other challengers to Empire intervened quietly in Latin America. China in particular.
In the past decade, China invested heavily as part of its global ‘Belt and Road’ infrastructure building program in Latin America. It bought up ports in Panama and started other projects there. It struck deals in Mexico to build the largest EV auto plant in north America that might then export under free trade to the US auto market. It started building ports in Ecuador and Peru. It had plans to build a railroad link from that latter country through the Amazon to Brazil. And it loaned Venezuela more than $100 billion for infrastructure projects and oil infrastructure modernization. Most important, it also started buying large quantities of Venezuela oil.
The US imperialists want that oil. The US pumps 13m barrels a day, the most in the world, and is sucking its own fracking wells dry in the next decade. Moreover, it needs more oil to sell to its European allies since the US chased the Russians out of Europe. Where to get it? Next door Venezuela of course.
The Trump administration, and US neocon imperialists’, have turned back to the western hemisphere to try to restore US economic hegemony over the region. That meant driving China and its investments out of Latin America, and especially Venezuela to secure its future oil supplies.
In the first year of Trump’s term in office, the US threatened Mexico with US drones and special ops; in response Mexico canceled its EV deal with China.
It threatened Panama with a repeat of the US 1989 invasion; Panama canceled its projects with China and US private equity took over its ports.
It threatened Ecuador and Peru. Propped up its client in Argentina with a new $40 billion loan, supported recent right wing government shifts in Chile and Boliva, threatened Brazil if it prosecuted Trump’s buddy, Bolsonaro for his attempting a coup, and threatened Venezuela continually, amassing military forces offshore, blowing up more than 80 fishing boats in the region, and sending in more CIA forces on the ground into that country. The US delta force special ops snatching of Maduro and his wife is just the latest tactic. Stand by. There’s more to come!
Lawless operations by Trump in the hemisphere are only beginning. I predict he will ‘seize’ Greenland one way or another, and soon. The objective there is the same as throughout Latin America. In the case of Greenland it’s about preventing China (and Russia) arctic shipping access down Greenland’s western coast on the way to the Atlantic ports and trade. Panama was quickly cut off for the Chinese. Now the Arctic passage will be as well.
All the Trump intimidation and insulting of Canada is also about the US shoring up its Arctic strategy which has lagged badly in competition with Russia. The latter’s arctic strategy development and implementation is well ahead of the US’s. Russia has a fleet of more than 40 advanced icebreakers. The US has two. Trump’s ridiculing of Canada has been about forcing that country to develop an arctic military presence and strategy—along with the US in Greenland and Alaska. Trump wants Canada to pay part of the US cost. Canada’s new prime minister, in his first visit to the White House earlier in 2025, pledged to do so. The Trump ridicule and intimidation immediately stopped.
Trump’s and the US empire’s plans to refocus more to the western Hemisphere is not this writer’s conjecture. It’s been obvious as Trump’s 2024 election campaign. The strategic shift was recently spelled out clearly in the Trump administration’s recently publication, ‘National Security Strategy of the United States of America, November 2025. It’s on the White House website. Read it. Especially discussion about the western hemisphere.
Trump says it’s all about Making America Great Again. What he really means it’s about Making American the Great Bully Again. That other American imperialist president, Teddy Roosevelt, bragged about ‘speak softly and carry a big stick’? Trump is a perverted facsimile of Roosevelt. His motto is ‘brag boldly and carry a stick’ so long as it’s against someone smaller than you.
The US Empire is restructuring and refocusing its resources—immediately on the western hemisphere and longer term on the western Pacific where it’s now rearming and shoring up its allies to contain and confront China. That’s a longer term objective. Western hemisphere comes first.
Japan has been encouraged and has begun to remilitarize. The US is pumping military arms at an accelerating rate into the key countries—Taiwan, Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, and South Korea. Four years ago, these countries purchased less than $1 billion a year each in US military equipment. In 2024, all were buying more than $4 billion a year, and in 2025 no doubt the data will show that’s accelerated further, especially for Taiwan. US imperial plans are longer term in that region. The western Hemisphere is shorter term.
Why the Trump administration wants to reduce its presence in Europe and NATO and extricate from its former commitment in Ukraine should be viewed in the context of this more fundamental shift to the hemisphere and the western Pacific. That’s also spelled out in the ‘National Security Strategy’ document.
So what’s the deeper reason for the Empire’s strategic shift now accelerating under Trump?
The answer to that most fundamental question is to be found in the accelerating costs of maintaining the US global empire as previously structured. It can no longer afford it, simply put.
According to its own budget data, the US now spends more than $1 trillion a year on the Pentagon alone. But that’s not all its ‘defense’ spending. At least as much ‘defense’ spending is squirreled away in other parts of the budget. When adding other defense cost like Veterans affairs, Homeland Security, nuclear weapons development, CIA and intelligence ops, foreign military aid, foreign military base expenses, rising pay for its1.4m military forces and top heavy, bloated senior officer corps, plus the defense share of interest payments on the US national debt, the total actual US defense spending in 2025 was more than $2.1 trillion!
With US annual budget deficits of $1.5 trillion a year, a national debt of $38 trillion, and interest payments on the latter already $1.1 trillion a year and rising—the US empire can no longer continue its costs as previously structured.
So it’s consolidating—back to the western Hemisphere and the Pacific basin.
That’s the bigger picture and context for the current events in Venezuela and what’s yet to come there—and throughout the western hemisphere—as the US resorts to direct military action to re-establish direct control and unchallenged hegemony in its back yard once again.

Photograph by Nathaniel St. Clair
The USA is descending into a state of general lawlessness, at home and abroad. From using domestic special ops paramilitary units (ICE) to kidnap people off the streets of America and send them abroad, the US government is now deploying secret special ops military units (Delta Force) to snatch foreign heads of governments from their homes and sending them to jail in the US.
Political human trafficking has become the rule of law in America under the current Trump administration!
Before 2025, the two political parties engaged in a crescendo of lawfare actions against each other, employing the FBI, the courts and even the CIA behind the scene to destroy each other. Both parties engaged in abuse of the rule of law, pardoning family, rich friends, and business partners to protect themselves and their personal relations, rendering a travesty of the fiction that in America no one is above the law. Senior politicians of both enriched themselves, becoming multi-millionaires after leaving office after arranging special deals while in.
The recent US invasion of Venezuela a gross violation of international law. A hypocritical disrespect for sovereign boundaries that US neocon ideologues and their echo chamber captured US media have leveled at Russia in Ukraine the past four years.
Trump himself has publicly admitted the invasion of Venezuela was intended to secure US economic control of Venezuela’s natural resources, especially its oil reserves. In other words, good old fashion naked US imperialism, intended to grab another country’s natural resources.
The excuse was the nonsense charges of narco drug trafficking—i.e. the US neocons’ substitute excuse for WMD’s, weapons of mass destruction, used before in Iraq, Syria, Libya to justify US military intervention.
WMDs couldn’t be levied at Venezuela. Wouldn’t work. Nor would past excuses for US imperial intervention like ‘Remember the Maine’. ‘Tonkin Gulf’. Or ‘Killing Incubator Babies’. The neocons needed a new fake excuse for US imperial military intervention in Venezuela. So they looked into their magic bag of false flags, fake excuses, and CIA lies and pulled out ‘Narco drug trafficking’. That works better for Latin America imperial interventions—as former president of Panama, Noriega, found out in 1989.
Watch out Colombia president Gustavo Petro who defended Venezuela sovereignty and criticized Trump’s Venezuela action. And heed the warning Mexico president, Sheinbaum! You’re the next Trump targets. Ditto Cuba.
Does Greenland have a president Trump can threaten? Wonder what that excuse will be. Maybe the US must invade because ‘Chinese ships are melting the ice cap’.
And make no mistake. Trump’s not only engaged in naked military imperialism in Venezuela to enact regime change. His big mouth ‘spilled the beans’ that the US plans to install a new colonialism as well. Within 24 hrs. he declared publicly the US intends to ‘rule’ Venezuela directly until such time as a proper puppet regime can be put in place. Direct rule constitutes a colonial form of imperialism.
As the saying goes, the truth is often spoken from the mouth of a drunkard. And Trump is a big mouth bragger, drunk with power. And he’s saying directly what the US neocon imperialist elite behind him (Rubio, Walz, Graham, CIA spooks, etc.) are really thinking and planning.
In an attempt to cover up Trump’s careless blurting out the blunt truth, Trump neocon cronies like Rubio quickly rushed to the US media echo chamber to try to put lipstick on the ‘US will rule’ pig, saying the US has no such plans.
Another Trump neocon, Walz, former NSA to Trump and now ambassador to the UN, in his emergency speech to the UN argued the kidnapping of Venezuela president, Maduro, was not about creating colonial rule; it wasn’t even a military operation—according to Walz. It was just a police operation. Some police operation, accompanied by a fleet of 17 US warships, aircraft carriers, submarines, and 10,000 marines stationed in nearby Trinidad island!
Rubio added the US only wants to bring Maduro to New York to stand trial, as he conveniently avoided any mention that the USnavy is continuing to blockade all shipping from Venezuela. The US has no further military plans! Really? Anyone wanna buy a bridge from the man?
This is crass, US gunboat imperialism reminiscent of the early 20th century when the US invaded Latin American countries by the dozens. It is also a harbinger of US plans to impose some new form of colonialism on Venezuela, and who knows what other Latin American countries who dare to try to walk an independent path from the US Empire.
Trump and his crony neocons will try to cover up their plans for some new kind of colonialism if they can with CIA managed new elections this spring, the outcome of which is already pre-determined. The US designated next president, Machado, is already packing her bags and on her way to Caracas, no doubt with an escort of US agents of course who’ll accompany her throughout the forthcoming phony election campaign.
US imperialism has never given up on regime change in Venezuela for the past quarter century. Just like it has never with Iran for nearly half a century. Nor Cuba for the past 65 years.
The Bush administration in 2002 thought it had achieved regime change deposing then Venezuelan president, former General Chavez. He nationalized US oil interests in the country. The most unholy of capitalist sins! But the deposing of Chavaz was short lived as he was rescued and re-installed as president by the people and Armed forces of Venezuela quickly.
Under Obama the CIA continued deep financial and other aid to opposition movements to overturn Venezuelan elections, to little avail. Venezuelan public support was too great despite the US launching a classic economic war on Venezuela, wrecking its currency, stoking inflation, preventing its sale of oil exports and receipt of necessary medical and food imports. Their candidates kept losing national elections nonetheless.
Under Trump in 2018-19 the CIA efforts intensified, seizing Venezuelan gold in western banks and Venezuela’s CITGO oil distribution company in the US and giving the money from its sale to Venezuelan opposition movements. Still no success in regime change via electoral intervention.
US CIA and regime change ops were temporarily put on hold with the arrival of the Covid recession in the US in 2020, followed by US chaotic exit from Afghanistan in 2021, and implementation in 2022 of bigger US plans to engineer a proxy war in Ukraine against Russia.
Once Trump returned to office in January 2025, however, Venezuelan regime change was placed on the US foreign policy front burner once again. This time the Empire planned to do it right—which meant not relying solely on CIA electoral interference in Venezuela, as in the past, but taking the gloves off and doing regime change by means of US special ops intervention and direct US military action!
The Emperor removed his clothes and waded in waist deep. Perhaps over his head, as time will only tell!
One should not lose sight of the bigger picture behind the Venezuelan invasion.
It is not a standalone, one off operation. I’m sure the governments of Colombia, Mexico and Cuba will agree. The Venezuela operation is part of US neocon forces and imperialists refocusing on the Empire’s western hemisphere base that it had partly neglected while preoccupied in the middle east and eastern Europe (Ukraine and Caucasus). The Empire had let the western hemisphere go unattended. In the interim, when it was preoccupied on the other side of the world, and while planning long term to engage China in Taiwan, other challengers to Empire intervened quietly in Latin America. China in particular.
In the past decade, China invested heavily as part of its global ‘Belt and Road’ infrastructure building program in Latin America. It bought up ports in Panama and started other projects there. It struck deals in Mexico to build the largest EV auto plant in north America that might then export under free trade to the US auto market. It started building ports in Ecuador and Peru. It had plans to build a railroad link from that latter country through the Amazon to Brazil. And it loaned Venezuela more than $100 billion for infrastructure projects and oil infrastructure modernization. Most important, it also started buying large quantities of Venezuela oil.
The US imperialists want that oil. The US pumps 13m barrels a day, the most in the world, and is sucking its own fracking wells dry in the next decade. Moreover, it needs more oil to sell to its European allies since the US chased the Russians out of Europe. Where to get it? Next door Venezuela of course.
The Trump administration, and US neocon imperialists’, have turned back to the western hemisphere to try to restore US economic hegemony over the region. That meant driving China and its investments out of Latin America, and especially Venezuela to secure its future oil supplies.
In the first year of Trump’s term in office, the US threatened Mexico with US drones and special ops; in response Mexico canceled its EV deal with China.
It threatened Panama with a repeat of the US 1989 invasion; Panama canceled its projects with China and US private equity took over its ports.
It threatened Ecuador and Peru. Propped up its client in Argentina with a new $40 billion loan, supported recent right wing government shifts in Chile and Boliva, threatened Brazil if it prosecuted Trump’s buddy, Bolsonaro for his attempting a coup, and threatened Venezuela continually, amassing military forces offshore, blowing up more than 80 fishing boats in the region, and sending in more CIA forces on the ground into that country. The US delta force special ops snatching of Maduro and his wife is just the latest tactic. Stand by. There’s more to come!
Lawless operations by Trump in the hemisphere are only beginning. I predict he will ‘seize’ Greenland one way or another, and soon. The objective there is the same as throughout Latin America. In the case of Greenland it’s about preventing China (and Russia) arctic shipping access down Greenland’s western coast on the way to the Atlantic ports and trade. Panama was quickly cut off for the Chinese. Now the Arctic passage will be as well.
All the Trump intimidation and insulting of Canada is also about the US shoring up its Arctic strategy which has lagged badly in competition with Russia. The latter’s arctic strategy development and implementation is well ahead of the US’s. Russia has a fleet of more than 40 advanced icebreakers. The US has two. Trump’s ridiculing of Canada has been about forcing that country to develop an arctic military presence and strategy—along with the US in Greenland and Alaska. Trump wants Canada to pay part of the US cost. Canada’s new prime minister, in his first visit to the White House earlier in 2025, pledged to do so. The Trump ridicule and intimidation immediately stopped.
Trump’s and the US empire’s plans to refocus more to the western Hemisphere is not this writer’s conjecture. It’s been obvious as Trump’s 2024 election campaign. The strategic shift was recently spelled out clearly in the Trump administration’s recently publication, ‘National Security Strategy of the United States of America, November 2025. It’s on the White House website. Read it. Especially discussion about the western hemisphere.
Trump says it’s all about Making America Great Again. What he really means it’s about Making American the Great Bully Again. That other American imperialist president, Teddy Roosevelt, bragged about ‘speak softly and carry a big stick’? Trump is a perverted facsimile of Roosevelt. His motto is ‘brag boldly and carry a stick’ so long as it’s against someone smaller than you.
The US Empire is restructuring and refocusing its resources—immediately on the western hemisphere and longer term on the western Pacific where it’s now rearming and shoring up its allies to contain and confront China. That’s a longer term objective. Western hemisphere comes first.
Japan has been encouraged and has begun to remilitarize. The US is pumping military arms at an accelerating rate into the key countries—Taiwan, Philippines, Australia, New Zealand, and South Korea. Four years ago, these countries purchased less than $1 billion a year each in US military equipment. In 2024, all were buying more than $4 billion a year, and in 2025 no doubt the data will show that’s accelerated further, especially for Taiwan. US imperial plans are longer term in that region. The western Hemisphere is shorter term.
Why the Trump administration wants to reduce its presence in Europe and NATO and extricate from its former commitment in Ukraine should be viewed in the context of this more fundamental shift to the hemisphere and the western Pacific. That’s also spelled out in the ‘National Security Strategy’ document.
So what’s the deeper reason for the Empire’s strategic shift now accelerating under Trump?
The answer to that most fundamental question is to be found in the accelerating costs of maintaining the US global empire as previously structured. It can no longer afford it, simply put.
According to its own budget data, the US now spends more than $1 trillion a year on the Pentagon alone. But that’s not all its ‘defense’ spending. At least as much ‘defense’ spending is squirreled away in other parts of the budget. When adding other defense cost like Veterans affairs, Homeland Security, nuclear weapons development, CIA and intelligence ops, foreign military aid, foreign military base expenses, rising pay for its1.4m military forces and top heavy, bloated senior officer corps, plus the defense share of interest payments on the US national debt, the total actual US defense spending in 2025 was more than $2.1 trillion!
With US annual budget deficits of $1.5 trillion a year, a national debt of $38 trillion, and interest payments on the latter already $1.1 trillion a year and rising—the US empire can no longer continue its costs as previously structured.
So it’s consolidating—back to the western Hemisphere and the Pacific basin.
That’s the bigger picture and context for the current events in Venezuela and what’s yet to come there—and throughout the western hemisphere—as the US resorts to direct military action to re-establish direct control and unchallenged hegemony in its back yard once again.