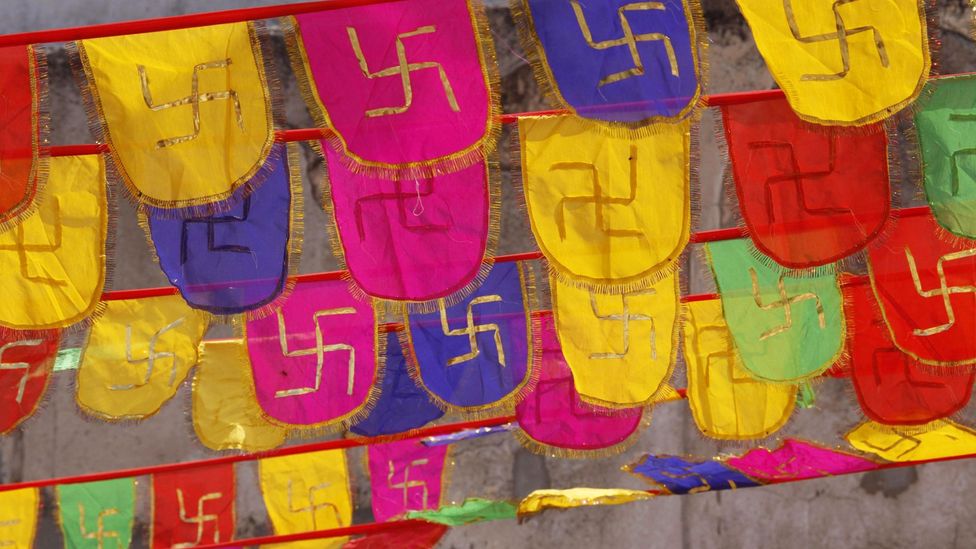
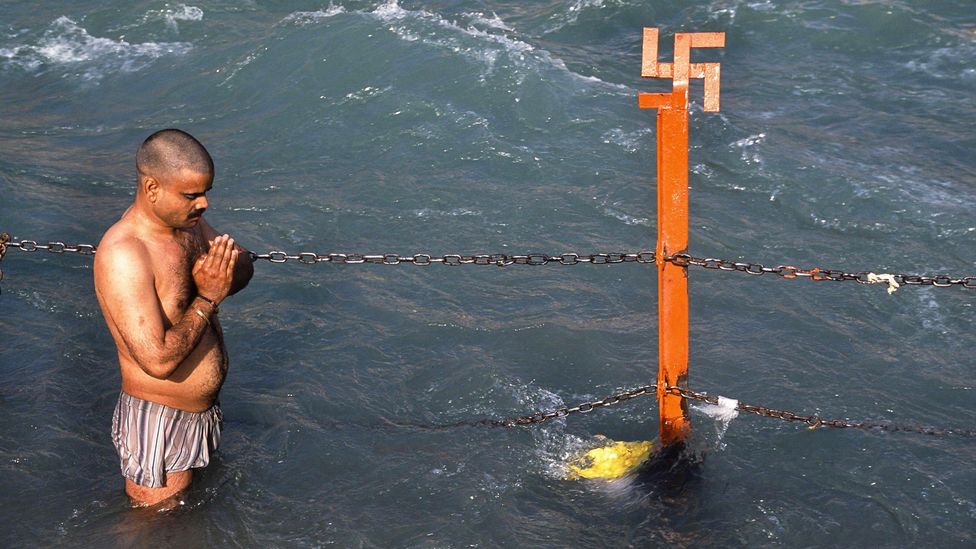
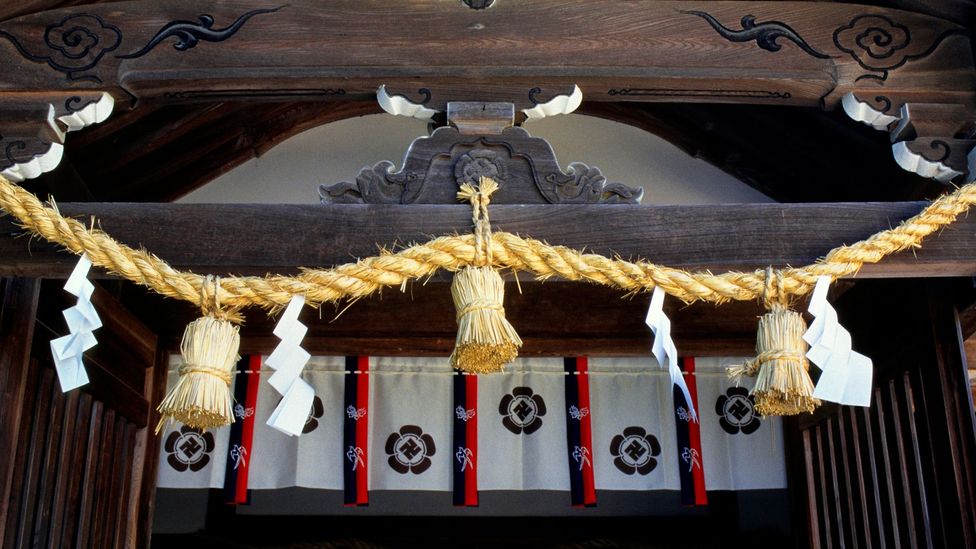
Asian faiths try to save swastika symbol corrupted by Hitler
The symbol is a millennia-old sacred symbol in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism that represents peace and good fortune, and was also used widely by Indigenous people worldwide in a similar vein.
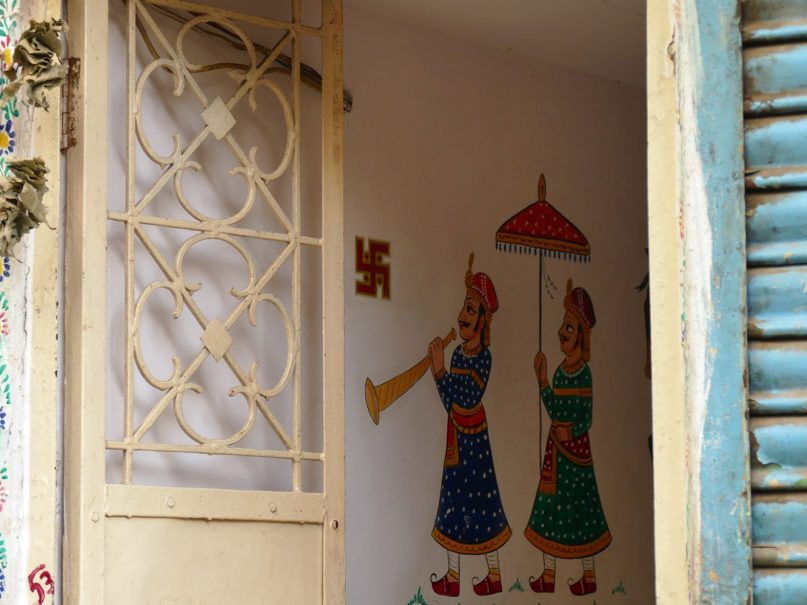 A swastika decorates an entryway in India. Photo by Rabbi Joshua Hammerman
A swastika decorates an entryway in India. Photo by Rabbi Joshua Hammerman“My decoration said ‘Happy Diwali’ and had a swastika on it,” said Deo, a physician, who was celebrating the Hindu festival of lights.
The equilateral cross with its legs bent at right angles is a millennia-old sacred symbol in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism that represents peace and good fortune, and was also used widely by Indigenous people worldwide in a similar vein.
But in the West, this symbol is often equated to Adolf Hitler’s hakenkreuz or the hooked cross – a symbol of hate that evokes the trauma of the Holocaust and the horrors of Nazi Germany. White supremacists, neo-Nazi groups and vandals have continued to use Hitler’s symbol to stoke fear and hate.
RELATED: The swastika and the 4 H’s
Over the past decade, as the Asian diaspora has grown in North America, the call to reclaim the swastika as a sacred symbol has become louder. These minority faith communities are being joined by Native American elders whose ancestors have long used the symbol as part of healing rituals.
Deo believes she and people of other faiths should not have to sacrifice or apologize for a sacred symbol simply because it is often conflated with its tainted version.
“To me, that’s intolerable,” she said.
Yet to others, the idea that the swastika could be redeemed is unthinkable.
Holocaust survivors in particular could be re-traumatized when they see the symbol, said Shelley Rood Wernick, managing director of the Jewish Federations of North America’s Center on Holocaust Survivor Care.
“One of the hallmarks of trauma is that it shatters a person’s sense of safety,” said Wernick, whose grandparents met at a displaced persons’ camp in Austria after World War II. “The swastika was a representation of the concept that stood for the annihilation of an entire people.”
For her grandparents and the elderly survivors she serves, Wernick said, the symbol is the physical representation of the horrors they experienced.
“I recognize the swastika as a symbol of hate.”
New York-based Steven Heller, a design historian and author of “Swastika: Symbol Beyond Redemption?”, said the swastika is “a charged symbol for so many whose loved ones were criminally and brutally murdered.” Heller’s great-grandfather perished during the Holocaust.
“A rose by any other name is a rose,” he said. “In the end it’s how a symbol affects you visually and emotionally. For many, it creates a visceral impact and that’s a fact.”
The symbol itself dates back to prehistoric times. The word “swastika” has Sanskrit roots and means “the mark of well being.” It has been used in prayers of the Rig Veda, the oldest of Hindu scriptures. In Buddhism, the symbol is known as “manji” and signifies the Buddha’s footsteps. It is used to mark the location of Buddhist temples.
In China it’s called Wàn, and denotes the universe or the manifestation and creativity of God. The swastika is carved into the Jains’ emblem representing the four types of birth an embodied soul might attain until it is eventually liberated from the cycle of birth and death. In the Zoroastrian faith, it represents the four elements – water, fire, air and earth.
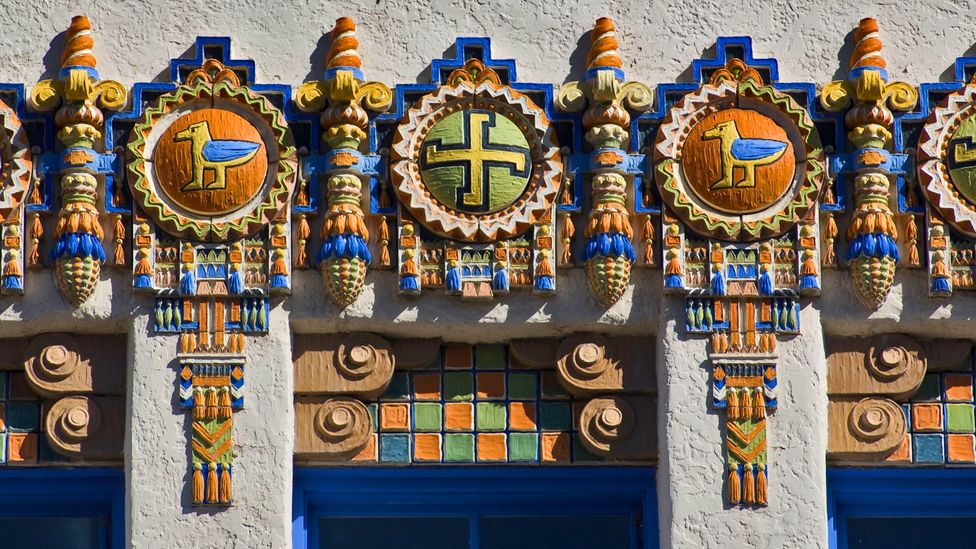
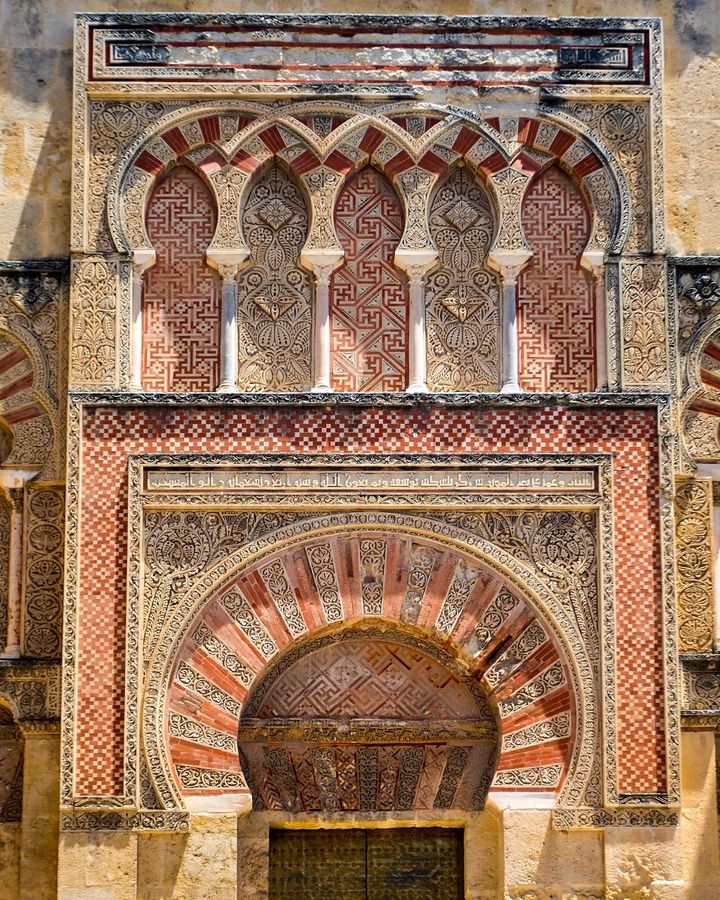
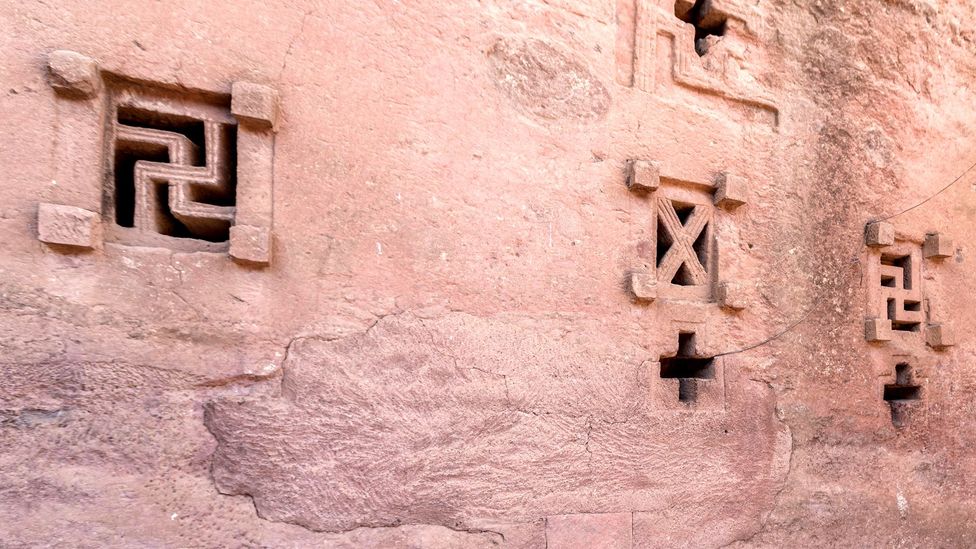
In India, the ubiquitous symbol can be seen on thresholds, drawn with vermillion and turmeric, and displayed on shop doors, vehicles, food packaging and at festivals or special occasions. Elsewhere, it has been found in the Roman catacombs, ruins in Greece and Iran, and in Ethiopian and Spanish churches.
The swastika also was a Native American symbol used by many southwestern tribes, particularly the Navajo and Hopi. To the Navajo, it represented a whirling log, a sacred image used in healing rituals and sand paintings. Swastika motifs can be found in items carbon-dated to 15,000 years ago on display at the National Museum of the History of Ukraine as well as on artifacts recovered from the ruins of the ancient Indus Valley civilizations that flourished between 2600 and 1900 BC.
The symbol was revived during the 19th century excavations in the ancient city of Troy by German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, who connected it to a shared Aryan culture across Europe and Asia. Historians believe it is this notion that made the symbol appealing to nationalist groups in Germany including the Nazi Party, which adopted it in 1920.
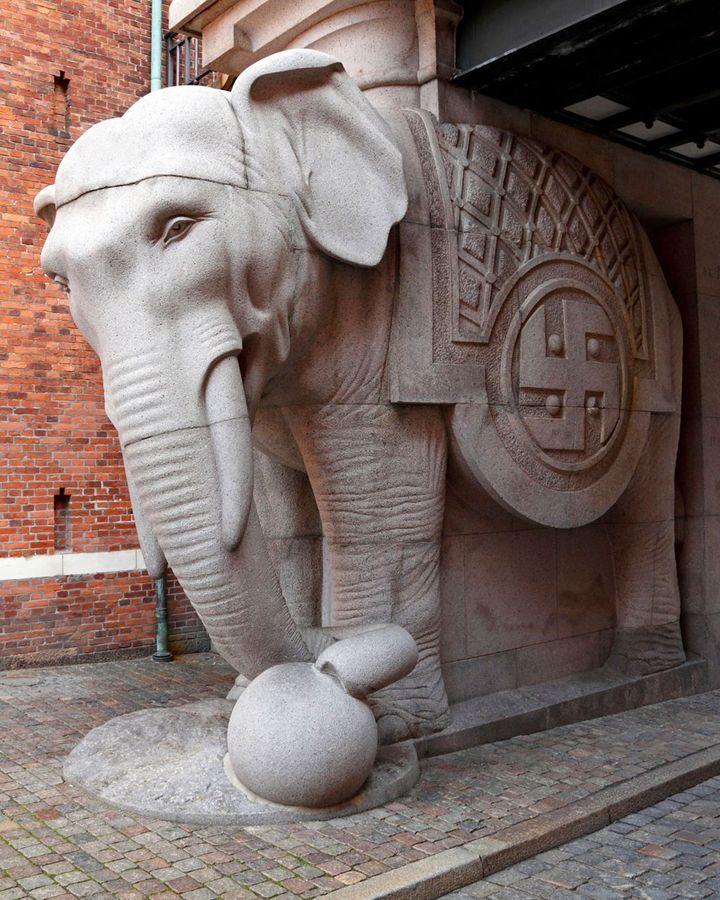
In North America, in the early 20th century, swastikas made their way into ceramic tiles, architectural features, military insignia, team logos, government buildings and marketing campaigns. Coca-Cola issued a swastika pendant. Carlsberg beer bottles came etched with swastikas. The Boy Scouts handed out badges with the symbol until 1940.
___
The Rev. T.K. Nakagaki said he was shocked when he first heard the swastika referred to as a “universal symbol of evil” at an interfaith conference. The New York-based Buddhist priest, who was ordained in the 750-year-old Jodoshinshu tradition of Japanese Buddhism, says when he hears the word “swastika” or “manji,” he thinks of a Buddhist temple because that is what it represents in Japan where he grew up.
“You cannot call it a symbol of evil or (deny) other facts that have existed for hundreds of years, just because of Hitler,” he said.
In his 2018 book titled “The Buddhist Swastika and Hitler’s Cross: Rescuing a Symbol of Peace from the Forces of Hate,” Nakagaki posits that Hitler referred to the symbol as the hooked cross or hakenkreuz. Nakagaki’s research also shows the symbol was called the hakenkreuz in U.S. newspapers until the early 1930s, when the word swastika replaced it.
Nakagaki believes more dialogue is needed even though it will be uncomfortable.
“This is peace work, too,” he said.
___
The Coalition of Hindus of North America is one of several faith groups leading the effort to differentiate the swastika from the hakenkreuz. They supported a new California law that criminalizes the public display of the hakenkreuz — making an exception for the sacred swastika.
Pushpita Prasad, a spokesperson for the Hindu group, called it a victory, but said the legislation unfortunately labels both Hitler’s symbol and the sacred one as swastikas.
This is “not just an esoteric battle,” Prasad said, but an issue with real-life consequences for immigrant communities, whose members have resorted to self-censoring.
Vikas Jain, a Cleveland physician, said he and his wife hid images containing the symbol when their children’s friends visited because “they wouldn’t know the difference.” Jain says he stands in solidarity with the Jewish community, but is sad that he cannot freely practice his Jain faith “because of this lack of understanding.”
He noted that the global Jain emblem has a swastika in it, but the U.S. Jain community deliberately removed it from its seal. Jain wishes people would differentiate between their symbol of peace and Hitler’s swastika just as they do with the hateful burning cross symbol and Christianity’s sacred crucifix.
 |
| EDMONTON SWASTIKA'S WOMENS HOCKEY TEAM PRE WWII |
Before World War II, the name “Swastika” was so popular in North America it was used to mark numerous locations. Swastika Park, a housing subdivision in Miami, was created in 1917, and still has that name. In 2020, the hamlet of Swastika, nestled in the Adirondack Mountains in upstate New York, decided to keep its name after town councilors determined that it predated WWII and referred to the prosperity symbol.
Swastika Acres, the name of a Denver housing subdivision, can be traced to the Denver Swastika Land Company. It was founded in 1908, and changed its name to Old Cherry Hills in 2019 after a unanimous city council vote. In September, the town council in Puslinch, Ontario, voted to change the name of the street Swastika Trail to Holly Trail.
Next month, the Oregon Geographic Names Board, which supervises the naming of geographic features within the state, is set to vote to rename Swastika Mountain, a 4,197-foot butte in the Umpqua National Forest. Kerry Tymchuk, executive director of the Oregon Historical Society, said although its name can only be found on a map, it made news in January when two stranded hikers were rescued from the mountain.
“A Eugene resident saw that news report and asked why on earth was this mountain called that in this day and age,” said Tymchuk. He said the mountain got its name in the 1900s from a neighboring ranch whose owner branded his cattle with the swastika.
Tymchuk said the names board is set to rename Mount Swastika as Mount Halo after Chief Halito, who led the Yoncalla Kalapuya tribe in the 1800s.
“Most people we’ve heard from associate it with Nazism,” Tymchuk said.
___
For the Navajo people, the symbol, shaped like a swirl, represents the universe and life, said Patricia Anne Davis, an elder of the Choctaw and Dineh nations.
“It was a spiritual, esoteric symbol that was woven into the Navajo rugs, until Hitler took something good and beautiful and made it twisted,” she said.
In the early 20th century, traders encouraged Native artists to use it on their crafts; it appeared often on silver work, textiles and pottery. But after it became a Nazi symbol, representatives from the Hopi, Navajo, Apache and Tohono O’odham tribes signed a proclamation in 1940 banning its use.
Davis views the original symbol that was used by many Indigenous people as one of peace, healing and goodness.
“I understand the wounds and trauma that Jewish people experience when they see that symbol,” she said. “All I can do is affirm its true meaning — the one that never changed across cultures, languages and history. It’s time to restore the authentic meaning of that symbol.”
___
Like Nakagaki, Jeff Kelman, a New Hampshire-based Holocaust historian, believes the hakenkreuz and swastika were distinct. Kelman who takes this message to Jewish communities, is optimistic about the symbol’s redemption because he sees his message resonating with many in his community, including Holocaust survivors.
“When they learn an Indian girl could be named Swastika and she could be harassed in school, they understand how they should see these as two separate symbols,” he said. “No one in the Jewish community wants to see Hitler’s legacy continue to harm people.”
Greta Elbogen, an 85-year-old Holocaust survivor whose grandmother and cousins were killed at Auschwitz, says she was surprised to learn about the symbol’s sacred past. Elbogen was born in 1938 when the Nazis forcibly annexed Austria. She went into hiding with relatives in Hungary, immigrated to the U.S. in 1956 and became a social worker.
This new knowledge about the swastika, Elbogen said, feels liberating; she no longer fears a symbol that was used to terrorize.
“Hearing that the swastika is beautiful and sacred to so many people is a blessing,” she said. “It’s time to let go of the past and look to the future.”
___
For many, the swastika evokes a visceral reaction unlike any other, said Mark Pitcavage, senior research fellow at the Anti-Defamation League’s Center on Extremism who for the past 22 years has maintained the group’s hate symbols database.
“The only symbol that would even come close to the swastika is the symbol of a hooded Klansman,” he said.
The ADL explains the sanctity of the swastika in many faiths and cultures, and there are other lesser-known religious symbols that must be similarly contextualized, Pitcavage said. One is the Celtic cross – a traditional Christian symbol used for religious purposes and to symbolize Irish pride – which is used by a number of white supremacist and neo-Nazi groups.
Similarly, Thor’s hammer is an important symbol for those who follow neo-Norse religions such as Asatru. But white supremacists have adopted it as well, often creating racist versions of the hammer by incorporating hate symbols such as Hitler’s hakenkreuz.
“In the case of the swastika, Hitler polluted a symbol that was used innocuously in a variety of contexts,” Pitcavage said. “Because that meaning has become so entrenched in the West, while I believe it is possible to create some awareness, I don’t think that its association with the Nazis can be completely eliminated.”
___
Associated Press religion coverage receives support through the AP’s collaboration with The Conversation US, with funding from Lilly Endowment Inc. The AP is solely responsible for this content.

.jpg)