Rasti Delizo is a global affairs analyst, veteran Filipino socialist activist and former vice-president of the Bukluran ng Manggagawang Pilipino (BMP, Solidarity of Filipino Workers).
In the first of a three-part series, Delizo talks to Federico Fuentes from LINKS International Journal of Socialist Renewal about what underpins US-China tensions and the dangers posed for the Asia-Pacific region.
Growing US-China tensions in the Asia-Pacific region are causing concern. How should we understand the growing rivalry even while the two economies are so integrated?
Fundamentally, the increasingly intense US-China rivalry that broadly defines this first half of the 21st century is the logical consequence of global capitalism’s permanent process of capital accumulation amid universal conditions of uneven and combined development.
In this mode of production, the leading monopoly capitalist states compete with each other, principally to gain huge economic windfalls through political-security engagements and manoeuvres. They aim to safeguard their steadily rising control of international markets, with endless extraction and transfer of surplus value from non-monopoly capitalist states at the global periphery.
This capitalist logic compels the imperialist core to guarantee financial superprofits for their respective oligarch-owned national monopolies. To protect their huge net appropriation of surplus value, these imperialist powers deploy their superior military forces to secure geostrategic aims. This is the historic materialist basis for inter-imperialist conflicts and wars since the last century.
These profit- and power-seeking thrusts are chiefly pursued through international competitions to increase the dominance of their spheres of influence. This largely occurs through a perennial (re)partitioning of “territorial divisions” of labour based on particular production processes inside systemically dominated countries and regions. This combined approach aims to enhance the foreign policy agendas of powerful capitalist states.
To achieve this, the imperialist great powers wage strategic struggles for supremacy over the world order’s key correlated domains, including major geographical spaces. These cover the vital functions, activities and concerns relating to crucial economic-political-social-cultural-diplomatic-military-technological fields.
The imperialist states not only aim to sustain advantages already held by their own domestic monopolies operating within foreign markets, but exclusively deploy their military capabilities to thwart adversaries and gain a security monopoly to protect their market interests in parts of the world. This foreign policy dialectic typifies imperialist behaviour.
This materialist nature and long enduring status of the capitalist global system innately characterises and shapes the international setting’s volatile equilibrium. Accordingly, it is these inter-imperialist dynamics that frequently throw the worldwide correlation of class forces into disarray and put them onto a defensive footing.
Undoubtedly, this dilemma is already a disruptive phenomenon that strongly underpins today’s confrontational US-China relationship, particularly through their strategic domains in the immense Asia-Indo-Pacific area.
This is the case even as their entwined economies remain connected and financially integrated as part of the globalised architecture and structures of the almost half-century-old neoliberal capitalist project. This is another paradox of the modern international order, whose superstructure is propped up by the overarching imperialist world system.
The systemic and conjunctural international context acutely propels rising hostilities between Washington and Beijing as the top imperialist powers. These ramifications are defined, determined and driven by universally destructive conditions that are primarily generated by the still decaying phase of monopoly-finance capitalism. For as long as the epoch of capitalist imperialism lingers, the blowbacks from its negative features keep damaging and impairing global humanity’s wellbeing.
The deepening of capitalism’s contradictions are causing harsh shifts in the capitalist global order, with catastrophic consequences. The degeneration of the world’s status quo is unquestionably due to the crumbling neoliberal capitalist project, built on a globalised infrastructure of exploitative-oppressive mechanisms.
Yet, and in a coherent way, all of these processes are still geared towards bracing the world system’s imperialist core and its incessant siphoning off of superprofits — via unequal exchange mechanisms — from dependent countries of the semi-colonial and maldeveloped periphery.
The paramount capitalist powers — US imperialism (still the world’s foremost imperialist state) and Chinese social-imperialism (the US’s direct strategic contender) — are now mutually locked in an intensifying transglobal competition.
But was there a critical trigger for this confrontation?
The answer flows from the intrinsic tendency of capitalism to negate many of its own gains and contradictions over time. Indeed, the bourgeois socioeconomic system consistently induces a long drawn-out sublation of its own antagonisms. As a result, this dialectical materialist process further impels an overall progression of capitalism’s productive forces by elevating the system into its more advanced stages.
This international process of negating negative economic conditions (to enhance world capitalism) began in the early 1990s. The US — having overcome its prime adversary of the now dissolved Soviet Union — launched potent measures to create a neoliberal post-Cold War global economic regime to widen its international base of capital accumulation. Feeling a false triumph over capitalism’s historic ideological enemy, US capital became highly motivated to seek out and amass even more superprofits from beyond its shores by 1992.
Among its decisive moves was helping develop China as a major world economy. By that time, China already contained the world’s largest population, estimated at about 1.143 billion — and, thus, was a mammoth market in itself. However, its economic standing in the early 1990s still ranked outside of the world’s core of top ten capitalist economies.
US imperialism sought to dominate China’s blossoming capitalist economy. Washington intended to monopolise the Asian giant’s internal growth processes together with its maturing development agenda. Within a decade, US foreign policy had steered Beijing’s integration into the neoliberal globalisation framework, inserting China’s rising economy into the World Trade Organization (WTO) by December 2001.
Another key aim of US foreign policy was remoulding China into yet another bourgeois-democratic state; this was premised upon the latter’s alignment with US capitalism’s economic interests. China was to be assimilated into the Washington-led “liberal international order” — a collection of states upholding US imperialism’s narrative of a so-called “rules-based international order” (to justify US imperialism’s global hegemony).
US foreign policy trajectory rested on a conviction that Chinese capitalism’s advance would inevitably raise China into a highly prosperous society, with more liberal political rules and social values by the early decades of the 21st century.
For at least a quarter-century — from 1992 until around 2017 — US capital exploited (and monopolised) its sway over China’s party-directed state capitalism. The US’s domestic market was opened to Chinese products to boost China’s economic growth and expansion.
At the same time, the US massively increased its own exports of financial capital plus higher quality commodities, particularly advanced technologies, to China’s internal market (while keeping US high-tech designs in the hands of US-owned technological monopolies).
There was also an acute trend of US manufacturing firms offshoring their production to China during this era, due to China’s depressed wages, generous state-subsidies and lower currency valuation. Greenlit by Washington, the World Bank provided further market-oriented technical advice to Beijing — as a result of China insertion into the worldwide ecosystem of neoliberal globalisation — to fast-track its capitalist maturation.
All of these economic adjustments and financial modifications led to a higher concentration of capitalist production and capital for China’s development paradigm. A fundamental result was that China became the centre of gravity for international capital by the early 2010s, while swiftly accelerating its military capabilities.
As US capitalism strove to assist with upgrading China’s capitalist potential over at least two consecutive decades — to help overcome the latter’s earlier economic disadvantages and weaknesses — the US economy conversely suffered a major economic decline. In contrast to China’s ascendancy in the past decade, significant areas of the US economy have regressed and waned.
US imperialism now suffers from some fundamental defects impacting its long-term national economic growth. These deficiencies encompass among others: widening income-based social inequalities, swelling public sector debts, a decades-long shrinking of its manufacturing sector, a diminishing agricultural capacity and sustainability, and conceivable challenges to the dollar as the world’s premier reserve currency since the end of the Bretton Woods monetary regime in 1971.
Moreover, the lingering atrophy of the US’s manufacturing and industrial base, since at least the 1980s and ’90s, is linked to the aftermath and impacts of the free trade features of neoliberal globalisation.
So, as the tension-riven US-China linkage proceeds, its symbiotic relationship manifests a unique form of an international “negation of the negation”. In essence, the intensification of the world economy’s neoliberal globalisation process, at least with the end of the Cold War in 1991, produced a new interstate dynamic. This international relations dialectic led to one powerful bourgeois state imparting some of its economic competencies to an ascending state; but it led to China rapidly gaining innovative economic capabilities that, in time, transformed it into a pathbreaking global power.
As such, US capitalism became debilitated to a significant extent while Chinese capitalism — eliminating its erstwhile economic features and weaknesses — was energised. The resulting synthesis of this momentous global shift is the advent of a new period of international struggles and conflicts.
This time around, the result of this still evolving new global content displays yet another pivotal inter-imperialist contest, primarily between Washington and Beijing. Today’s unprecedentedly changing global order is a direct product of the epoch of the imperialist-dominated capitalist world system.
This fast arising great power conflict plays out across the global order’s twin arenas of geoeconomic and geopolitical competition. In this manner, Washington and Beijing’s distinct but antagonistic geostrategies now aggressively compete against each other to attain a relatively greater hegemony over the globalised capitalist system and its interconnected geographic spaces. They seek to constantly expand their respective spheres of influence and domination to control the most important regions of our planet for their very absolute great power agendas.
In fact, their imperialist foreign policies are resolutely geared toward coopting and coercing foreign states in furtherance of the great power’s nationally defined core strategic interests.
Their central objectives include: a) gain and extend market access within and beyond the national frontiers of a contiguous range of countries; b) sway the domestic policies of foreign regimes and eventually convert them into puppet-states; c) firmly secure long-term military basing rights plus regular troop-visit arrangements in exchange for security guarantees on a pretext of “potential internal and external threats”; and, d) integrate these countries into existing and newly-created regional economic and security alliances controlled by the imperialist powers.
These conjoined measures comprise the basic components of any imperialist great power’s “sphere of influence and control”. Operationally fused together across regions, these spheres of influence augment the force projection capabilities of any imperialist foreign policy at the international level.
So, in effect, these imperialist spheres of influence act as strategically developed geographical buffer zones sandwiched between contending great powers. Already, most of the countries within these buffer zones passively act as tripwire-states to heighten the geopolitical aims of world imperialism.
The materialist context of this global setting now reflects an intensification of the US-China dyadic conflict. When amplified, it expresses a fresh inter-imperialist struggle on the world stage.
This is not unlike previous worldwide imperialist tensions and confrontations, which twice led to universal catastrophes in the first half of the 20th century (but with a varied set of dynamics). As an international phenomenon, the Washington-Beijing rivalry clearly reveals that it is yet once more a mere by-product of the imperialist world system’s integral contradictions.
What then is specifically behind US military strategy in the region?
We have to understand Washington’s prevailing international strategy to better understand its military posture toward Beijing.
As the driving force of its overarching foreign policy, US imperialism’s economic-based grand strategy has always been predicated by an overall national security outlook shaped by certain historical periods. The US’s national security-obsessed foreign policy perspective remains impelled by its leading monopoly capitalist position within the global system of capital accumulation.
On this basis, several key aspects have buttressed US foreign policy since 1945. This set of integral elements centre on asserting Washington’s global imperatives to sustain US capital.
These include the following: a) retaining the US’s profitable dominance over the capitalist world economy; b) safeguarding its nuclear deterrence capabilities; c) maintaining its diplomatic leadership role across various intergovernmental and regional organisations; d) employing its military powers to achieve unilateral political-security objectives; and, e) aggressively pursuing policies of containment and degradation of the international Communist movement, global working-class forces and their allies.
When this array of external policy measures are projected onto a specific geographic area, they materialise into a coherent geostrategy.
In this regard, we will also need to recognise how US foreign policy reflects Washington’s National Security Strategy (NSS) framework. Being a periodically reevaluating national security vision set by the White House, the NSS analyses, assesses and evaluates existing and/or potential global security threats and challenges to the US’s strategic interests.
Likewise, the US’s NSS thrusts overlap with a parallel national defense strategy (NDS) set by the Department of War. Acting in a supplementary manner to the NSS, the NDS concentrates on the US military’s operational role in addressing the US’s declared global menaces.
The NDS also provides strategic goals and parameters to the US’s armed forces via a National Military Strategy (NMS). In turn, the NMS — determined and managed by the Chairperson of the Joint Chiefs of Staff — develops the requisite military plans for achieving strategic objectives set forth by the NDS in support of the NSS. The synergised NSS-NDS-NMS national security policy configuration is effectively the US’s geostrategy.
This somewhat teleological approach not only seeks to advance US foreign policy’s aims. Its geostrategy is equally intended to foil and counteract emergent international risks, which could jeopardise the US’s global hegemonic status. Therefore, this geostrategic mode of US foreign policy pursues a unified integration of “all facets of US power needed to achieve the nation’s security goals”.
US imperialism’s geostrategy for the Asia-Indo-Pacific is further primed by the 2022 Indo-Pacific Strategy (IPS) document. This anti-Beijing policy framework emphasises Washington’s central economic-political-security concentration on this area’s two colossal maritime zones — the Indian and Pacific oceans — which flank China.
The IPS asserts that “the United States is an Indo-Pacific power” that “has long recognized the Indo-Pacific as vital to our security and prosperity”. The IPS states, “the US is determined to strengthen our long-term position in and commitment to the Indo-Pacific”.
Furthermore, the IPS affirms, “the US is committed to an Indo-Pacific that is free and open, connected, prosperous, secure, and resilient”. To realise this goal, the US “will strengthen our own role while reinforcing the region itself”.
The IPS — in convergence with the overarching NSS-NDS-NMS scheme of US foreign/national security policy — intensifies the current US geostrategy to surmount China’s soaring powers. Yet, there remains a contextual reality behind Washington’s scope of external security issues and concerns. Perceived international perils and predicaments — seen as barriers to the US’s manoeuvre space — are clearly identified by various fractions of its capitalist ruling-class elites.
This relatively tiny minority presides over the continued growth of US imperialism’s economic and financial monopolies. In consequence, the top echelons of the US’s combined national security-external relations apparatus are obliged to carry out the reactionary impositions of US foreign policy, under the edict of US monopoly-finance capital.
The US’s foreign policy agenda is primarily monopolised by an interconnected military-industrial-legislative-intelligence think tank complex directed by the country’s oligarchic elites. Preserving the US’s general class character, specifically the need to secure the socioeconomic wellbeing of its reigning oligarchs, will define US imperialism’s evolving external policy framework and attitude toward China.
Even so, the US’s foreign policy-national security elites still affirm China as an adversarial strategic competitor. In similar terms, Washington views Beijing as “the only competitor with both the intent to reshape the international order and, increasingly, the economic, diplomatic, military, and technological power to advance that objective.”
These US foreign policy positions mirror the strategic guidelines framed by the US’s operating NSS. Steered by the axioms of its geostrategic framework, the 2022 US NSS directly names China — followed by Russia — as US imperialism’s topmost strategic competitors, which need to be dually targeted. However, as of early September 2025, the US’s official national defense strategy still remains under review, pending final approval.
On September 5, just one week before the longstanding name of the US Department of Defense was officially reverted to its original title, the “Department of War”, the first draft of a Trump 2.0 National Defense Strategy paper was completed. Based on some initial news reports, the new US NDS 2025 [which was finalised by December, after this interview was conducted — FF] is set to replace some of the major aspects of the Biden-era NSS-NDS–NMS geostrategy.
According to these reports, the Donald Trump regime’s NDS 2025 will see a “major” and “radical” shift in the US’s comprehensive defense strategy. If these reports are correct, then the forthcoming NDS 2025 is set to align with Trump’s “America First” foreign policy, on account of a reprioritised focus for the US’s national security posture.
As such, the impending post-2025 US geostrategy will expect to refocus its geographical concentration. The US will emphasise the need to defend its strategic interests within the Western Hemisphere (comprising North, Central and South America, and including the Caribbean and parts of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans), as US imperialism’s primary sphere of influence and dominance. This hemisphere contains Brazil, Cuba, Greenland, Mexico, Panama and Venezuela, national territories that the Trump regime has negative designs on.
This potential change of course for US foreign relations will mean a reinvigoration of the US’s centuries-old Monroe Doctrine. In aiming to further dominate and exploit selectively targeted countries in the Western Hemisphere, this newfangled adventure seeks to monopolise the area’s ample lands, peoples and accompanying raw minerals.
Yet, despite its probable (and seemingly impending) foreign policy U-turn, US imperialism will continue to target China and Russia. Washington will intensify its endeavours at denying Beijing and Moscow’s respective strategic expansions across their primary spaces of manoeuvre around the Eastern Hemisphere’s Eurasian zone.
How is the US developing its military alliance, potentially in preparation for a war with China?
US imperialism is already gearing up to execute whatever latest geostrategy it decides upon given the volatile world situation. More specifically, US military prowess is expected to be harnessed against any discernible threats emanating from China’s rising military presence throughout the Asia-Indo-Pacific region.
Washington’s envisaged moves will aim to preserve the US’s economic regime of capital aggregation by securing US imperialism’s sustained superprofits from among the dominated peripheral economies. Furthermore, should a belligerent scenario break out in the future, the US will apply its military forces to thwart Chinese imperialism’s own militarist activities within this zone of the world.
In concrete terms, US imperialism’s bolstering geostrategy remains zeroed in on China’s naval and air presence across the Indian Ocean, the Southeast Asian Sea (also known as the South China Sea), and the Pacific Ocean.
To enhance its geopolitical posture, US imperialism has built upon its security alliances across the Asia-Indo-Pacific region. These regional security mechanisms — major components of Washington’s IPS — include AUKUS (Australia–United Kingdom–United States), the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, comprising Australia, India, Japan and the US), and the two trilateral security cooperation partnerships for this area (one involving Japan, South Korea and the US; the other involving Japan, the Philippines and the US).
In the absence of a NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)-type multilateral security arrangement in the Asia-Indo-Pacific, Washington acts as the security “hub” to all of its “spokes” in the region. US imperialism endures as the undisputed geostrategic commander of its puppet-states operating within the former’s widening military-sphere of influence in the eastern zone of the Eastern Hemisphere.
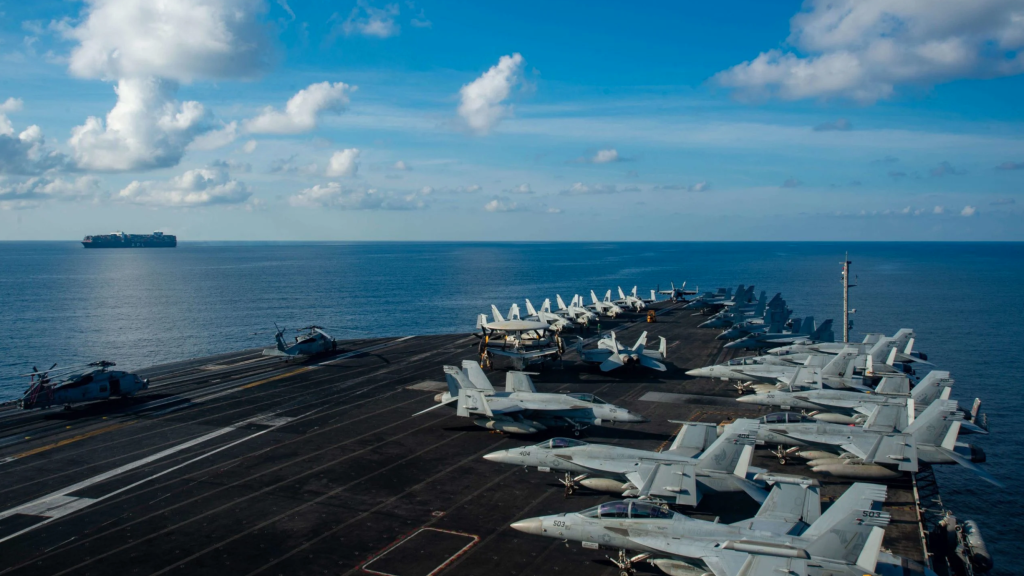
US imperialism’s designated military unit for any possible warfare with its Chinese counterpart(s) across this region is the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM). USINDOPACOM is the largest of the US’s six geographic commands.
With an area of operational responsibility (AOR) spanning the Indian and Pacific oceans — including landmass and archipelagic spaces of East Asia — the USINDOPACOM’s AOR covers about 38 countries, enveloping 52% of the earth’s surface and abode to more than 50% of the world’s population.
The USINDOPACOM comprises a unified fighting force containing combined component and sub-unified commands embodying air, naval, marine, and army units.
How do you view China’s role in the region and actions towards the US and regional neighbours?
For context, US imperialism initially attempted to contain China’s fast-growing sway around East and Southeast Asia in November 2011 via then-President Barack Obama’s “Pivot to Asia’. This came in the wake of China’s relatively rapid recovery after the September 2008 global capitalist crisis.
Being endogenous to the capitalist system, the Great Recession — an international financial meltdown that induced a long-term worldwide economic recession — was caused by a severe economic conjunction several years in the making. It was a confluence that combined the latest crisis of overproduction with risky practices linked to US capitalism’s vulnerable financialised structures.
Amid such a global economic landscape, many national economies got battered by this capitalist calamity. However, China was able to swiftly execute a state-led economic rebound through a mix of large-scale stimulus packages, expansionary monetary measures and a boosting of domestic consumption capacities.
At the same time, Beijing managed to win the economic and political confidence of its immediate neighbours, including Japan, South Korea and the majority of the ASEAN’s (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) member states, while increasing its investments and market shares in those countries.
Astonished by the Chinese economy’s capacity to overcome the Great Recession’s fallouts, while politically swaying many from the region, US capital felt exposed and threatened. Deeming a clear and present danger to its seriously weakened domestic conditions, US imperialism was compelled to regain its pre-2008 great power supremacy over the globalised capitalist system.
Soon afterward, the US assumed a new foreign policy stance to rebalance itself on the world stage. As a consequence, the main orientation of Washington’s external policy thrust was now aimed at counteracting Beijing’s emergent global ascendancy.
The US’s Pivot to Asia track was intensified during Trump’s first term in the White House and upheld, with certain adjustments, under Biden’s rule. The 2022 NSS actively guided US foreign policy’s grand strategy planning toward China.
As Washington toughened its anti-China stance, Beijing increasingly became aggravated with the former, obliging it to develop its own geostrategy to thwart the US’s expanding aims and powers in the Asia-Indo-Pacific theatre.
China’s external policy framework for an alternative mode of international relations is guided by the Communist Party of China’s (CPC) thrust in creating its “Community of a Shared Future for Mankind”.
Responding to the unfolding dynamics of its external strategic setting, and just less than three years after the US embraced its foreign policy shift toward Asia (to contain China), Beijing developed its own regional security agenda. Viewed as an “Asian security vision”, it featured concepts underpinning “common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable security”.
Beijing’s newly forged regional security outlook was presented by President Xi Jinping before the Fourth Summit of the Conference on Interaction and Confidence Building Measures in Asia (CICA) in Shanghai, China in May 2014.
After this was positively received by various Asian countries, China’s president reiterated his Asia-centred security agenda before the 86th Session of the INTERPOL General Assembly in Shanghai in September 2017. Following this reiteration, and broadening its scope to conform to a global perspective, Xi’s global security concept became China’s “new security vision” for at least the next half-a-decade.
US imperialism has been accelerating its attempts to impede China’s strategic rise. Since 2011, Washington’s deliberate shots and stabs against Beijing have relentlessly mounted. This situation forced China to react with a more developed security concept to guide its foreign policy: its Global Security Initiative (GSI).
Delivered by Xi before the Bo’ao Forum for Asia in April 2022, the GSI is a conceptual policy framework designed to advance Chinese imperialism’s national security agenda by means of an international focus opposing US imperialism’s longtime predominance in the Asia-Indo-Pacific.
The GSI is essentially a bid by China to vigourously chip away at and displace the hegemonic US-led security architecture spread across the Asia-Indo-Pacific, together with the latter’s concomitant regional political-security regime of pro-Washington puppet-states.
In addition to the GSI, China’s latest outward drive is the Global Governance Initiative (GGI). Both of these initiatives, which share a political-security nexus, further complement China’s two other multilateral enterprises: the Global Development Initiative (GDI) and Global Civilisation Initiative (GCI).
Xi proposed the GGI on September 1, 2025 during the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Plus Meeting in Tianjin, China. The GGI can be considered a correlated foreign policy concept (and linked to the GSI), anchored around key international political-security concerns. The GGI enhances the GSI in terms of China’s core strategic interests at the international level.
As a synergised and externally oriented security policy approach, the fused GSI-GGI framework provides China with a contemporary grand strategy. Flowing from this is the possibility for Beijing to materialise an associated geostrategy that can actively counter Washington’s anti-China geostrategy.
Common principles that accentuate China’s paired GSI and GGI concepts are: a) advance the creation of a multipolar world order on the basis of multilateralism (and not US unilateralism); b) abide by the international rule of law (not a US-defined rules-based international order); c) uphold the purposes and principles of the United Nations Charter while building “a more just and equitable global governance system” (not the hegemonism and power politics of Washington); and, d) advance a “people-centred approach” so as to “better safeguard the common interests of all countries” (and not the interests of a few states led by US imperialism).
Beijing’s increasingly assertive foreign policy gears China to escalate its “external struggles” (in the field of global diplomacy) to fight “unilateralism, protectionism, hegemonism, bullying and foreign interference, sanctions, and sabotage.”
This multi-pronged range of geopolitical strategies attempts to hide behind the facade of a “global governance” agenda in targeting US imperialism. The basic intention of China’s GSI-GGI geostrategy is to frustrate and cripple the US’s Indo-Pacific Strategy within the broader Asia-Pacific region.
To operationalise its new-crafted geostrategy, China also has a relatively new Foreign Relations Law (FRL). Passed in June 2023, the country’s first-ever FRL guarantees the leading role of the CPC in the overall design, formulation, planning, coordination and execution of Chinese foreign policy. By firmly bracing its foreign policy direction, especially toward the US imperialist-led bloc, Beijing’s FRL buttresses its combined GSI-GGI geostrategic framework.
To guarantee this effort, the FRL purposely affirms China’s “right” to implement “countermeasures” against foreign-bred actions that “violate international laws and fundamental norms of international relations”, including those that “undermine China’s sovereignty, security, or development interests.”
China’s 2023 FRL provides Chinese foreign policy with an added layer of legal justifications to pursue Beijing’s geostrategy to eventually supplant US imperialism’s hegemonic bourgeois-democratic international order.
What is China’s attitude towards multilateral institutions? What role does it see for itself inside such institutions that have often been dominated by US imperialism, but which Trump is today turning his back on?
Beijing strives to gain the influential support of at least three principal international organisations. Chinese imperialism does so by advancing its main foreign policy goals within the structures of these top-three-by-choice transnational formations.
Beijing’s priority multilateral institutions are the UN, the BRICS (Brazil/Russia/India/China/South Africa), and the SCO. While there are other global bodies that China synchronously maintains relations with (the World Trade Organisation, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, East Asia Summit, the G20, etc), there are fundamental factors that oblige China to prioritise this trio.
China maintains that the UN remains the central foundation of the international system. Yet, the UN is incrementally becoming more reliant on Beijing’s diplomatic contributions while warmly welcoming its many significant external policy initiatives. Subsequently, with this altering UN-based milieu, Chinese diplomacy is equally becoming more vocal about its intentions regarding the urgent need for a major overhaul — via substantive organisational reforms — of the world’s primary global body.
As one of the five UN Security Council permanent members holding veto powers — the Permanent 5 (P5) — China has only lately appreciated the need to maximise its powerful role within the UN. Being a member of the P5, Chinese social-imperialism is set to readily exploit UN global platforms to advance its anti-Washington foreign policy agenda.
Moreover, since the UN contains 193 member states, including sub-imperialist states plus the majority of the world’s peripheral countries, Beijing has a growing desire to win over a majority to its own strategic geopolitical project and shift the global balance of power in China’s favour.
Beijing is primed to take fuller advantage of the UN system as an international arena of great power struggle so as to reshape the global order in its favour. China’s function inside the UN is oriented to frustrating US imperialism’s diplomatic manoeuvres in global affairs. Beijing will gradually do so on top of the UN’s premier world stage.
On BRICS, China fathoms the alternative role that this intergovernmental organisation plays in current world affairs. With 10 member states and nine partner countries, BRICS now reflects about 4 billion people (more than half of the world’s population), spans an estimated 47 million square kilometres, and accounts for at least 40% of the global economy (in PPP terms).
Aspiring to counter US geostrategy on a global scale, China appreciates the similar perspective which the other BRICS member states share and advocate. Simultaneously, Beijing values the fact that BRICS countries have a presence within key regions.
As BRICS steadily expands its membership, it will amplify its global sway through an economic-political-diplomatic lens. With a joint stance opposing the US imperialist-led bloc, BRICS can be employed by China to advance its “global governance” schemes. This geostrategic direction can help build a powerful Chinese social-imperialist-led bloc, which could counter US hegemonism on a global scale in the near future.
With the SCO, China views it as a premier international organisation in the Eurasian sphere. The SCO comprises 10 member states, two observer states and 14 dialogue partners, with its Secretariat based in Beijing. With only one member state located in Europe, the rest of the SCO countries are located in parts of Asia (including a few spanning the Europe-Asia divide).
As a primary Eurasian political-security alliance, the SCO is seen as a transregional bulwark straddling the Eastern Hemisphere with a major focus on deepening political cooperation, ensuring and maintaining regional peace and security, enhancing international diplomacy, strengthening mutual trust and amity among the member states, and promoting a “new democratic, fair and rational” international political and economic order.
Furthermore, the SCO retains unique features positive to China. The SCO projects a Eurasia-wide stature and influence, espouses a critical anti-US imperialist policy agenda and maintains a distinctively pro-China stance. Given the current equilibrium, and its overall volatility, Beijing is confident the SCO is poised to become a highly effective regional political-security instrument to boost China’s geostrategic line.
This is undoubtedly why the CPC staged a very impressive People’s Liberation Army (PLA) parade in Beijing on September 3, 2025 — just two days after this year’s SCO meeting in Tianjin. Although this military show-of-force was to commemorate the 80th anniversary of the official end of World War II, it was aimed at Washington and its Western allies.
When Xi delivered his keynote address at Tiananmen Square, he was flanked by fellow SCO leaders (including Russian President Vladimir Putin and Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian) as well as Kim Jong Un, the leader of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (a non-SCO country).
In his speech, the CPC General Secretary stated, “Today, humanity is again faced with the choice of peace or war, dialogue or confrontation, win-win or zero-sum,” while emphasising the Chinese people “firmly stand on the right side of history”.
He affirmed that China is a great nation that “is never intimidated by bullies” — in apparent reference to the US imperialist-led bloc of Western states — and warned that China is “unstoppable”.