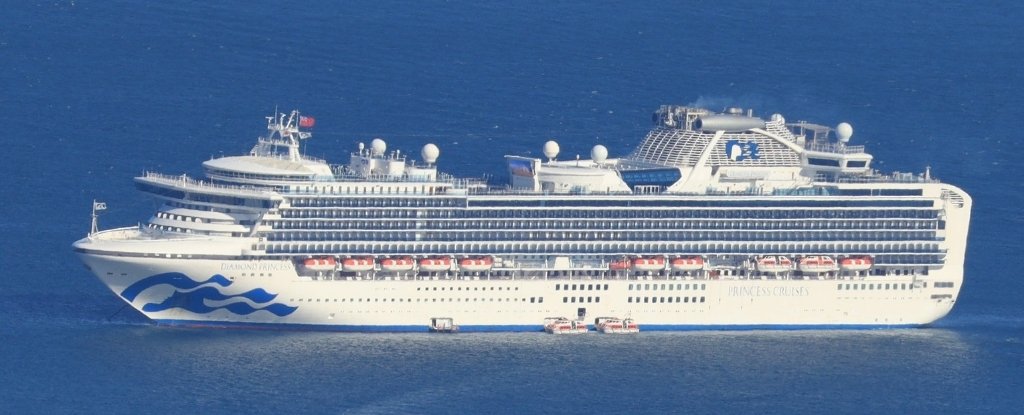
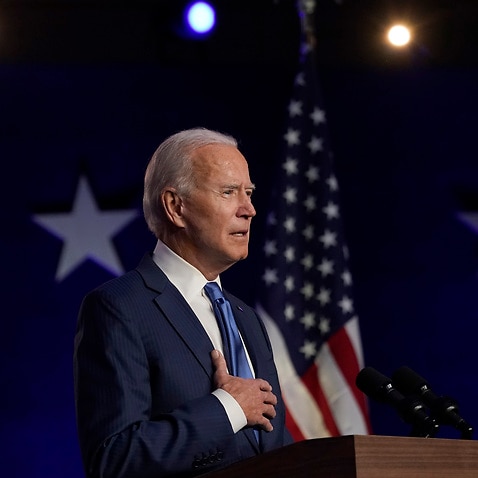
The Diamond Princess cruise ship was a superspreader site.
KELLY MACNAMARA, AFP
21 NOVEMBER 2020
At churches, on cruise ships, and even in the White House, superspreading events that can sicken dozens, even hundreds, of people have illustrated the potential for the coronavirus to infect in dramatic bursts.
Experts say these large clusters are more than just extreme outliers, but rather the pandemic's likely main engine of transmission.
And understanding where, when, and why they happen could help us tame the spread of the virus in the period before a vaccine may be widely available.
Research increasingly suggests that the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 does not fan out evenly across the population, but spreads at the extremes in an almost "all or nothing" pattern.
Many studies now suggest the majority of people with COVID-19 barely pass it on to anyone else, but when infections happen, they can be explosive and supercharge an outbreak.
Then the virus can infect "10, 20, 50, or even more people", said Benjamin Althouse, research scientist at the Institute for Disease Modeling.
This corresponds to the "80/20 rule" of epidemiology, where 80 percent of cases come from only 20 percent of those infected, but Althouse said this coronavirus may be even more extreme, with 90 percent of cases coming from potentially just 10 percent of carriers.
This transmission pattern is like "throwing matches on a pile of kindling", he told AFP.
"You throw one match, it doesn't ignite. You throw another match, it doesn't ignite. You throw yet another match, and this time you see flames blaze up," he said.
"For SARS-CoV-2, this means that while it is difficult to establish in new places, once established, it can spread rapidly and far."
Virus 'hallmark'
Superspreading events have grabbed headlines, looming large in the narrative of the unfolding pandemic.
In February, the Diamond Princess and its 4,000 passengers spent weeks in quarantine at port in Japan as the number of infections on board climbed, reaching 700.
The same month a 61-year-old woman, known as "Patient 31", attended several church services of the Shincheonji Church of Jesus in the South Korean city of Daegu.
The Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has since linked more than 5,000 infections to Shincheonji.
More recently the virus managed to infiltrate the White House despite a host of measures to keep it out.
Political gatherings, business conferences, and sports tournaments have all acted as infection incubators, but these high profile events could just be the tip of the iceberg.
A study by US researchers, based on one of the world's largest contact tracing operations and published in Science in September, found that "superspreading predominated" in transmission.
Analysing data from the first four months of the pandemic in the states of Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh in India, the authors found that just eight percent of infected individuals accounted for 60 percent of new cases, while 71 percent of people with the virus did not pass it on to any of their contacts.
Perhaps this should not be a surprise.
Maria Van Kerkhove, an infectious disease epidemiologist at the heart of the World Health Organization's pandemic response, tweeted in October that "superspreading is a hallmark" of coronaviruses.
Indeed, it has been observed in many infectious diseases.
One of the most famous superspreaders was Mary Mallon, a cook working in New York in the early 1900s who was the first documented healthy carrier of typhoid bacteria in the US.
Blamed for giving the illness to dozens of people, she was given the unsympathetic label "Typhoid Mary" and forcibly confined for years.
Measles, smallpox and Ebola also see clustering patterns, as did the other coronaviruses, SARS and MERS.
K factor
Early in the pandemic, much attention was focused on the basic reproduction number (R0) of SARS-CoV-2.
This helps calculate the speed a disease can spread by looking at the average number of others a person with the virus infects.
But looking at transmission through this metric alone often "fails to tell the whole story", said Althouse, who co-authored a paper on the limitations of R0 in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface this month.
For instance, he said Ebola, SARS-CoV-2, and influenza, all have an R0 value of around two to three.
But while people with the flu tend to infect two or three others "consistently", the transmission pattern for those with Ebola and SARS-CoV-2 is overdispersed, meaning most will hardly spread it and some will give rise to tens of other cases.
A different metric – "k" – is used to capture this clustering behaviour, although it usually requires "more detailed data and methodology", said Akira Endo, a research student at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
His modelling from the early international spread of the virus, published in Wellcome Open Research, suggested SARS-CoV-2 could be highly overdispersed.
A telltale clue, he said, was that some countries reported numerous imported cases but no signs of sustained transmission – like the match analogy – while others reported large local outbreaks with only a few imported cases.
But even k may not give the full picture, said Felix Wong, a postdoctoral fellow at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
His research analysing known COVID-19 superspreading events, published this month in the journal PNAS, found that they were happening even more frequently than predicted by traditional epidemiological models.
They are "extreme, yet probable occurrences", Wong told AFP.
Biology vs opportunity
So why does superspreading occur?
We don't know definitively whether biological factors, such as viral load, play much of a role.
But what we do know is people can spread SARS-CoV-2 without symptoms and given a poorly-ventilated, crowded space – particularly where people talk, shout, or sing – the virus can run rampant.
This could be why a study in Nature this month found that restaurants, gyms, and cafes account for most COVID-19 infections in the United States.
Using the mobile phone data of 98 million people, researchers found about 10 percent of venues accounted for over 80 percent of cases.
Given this, experts say the focus should be on these types of spaces – and reducing opportunities for the virus to access large numbers of people.
Wong said his modelling showed that if each individual was limited to ten transmissible contacts, "viral transmission would quickly die down".
Tracking back
Overdispersed spread also means that most people testing positive for the virus are likely to be part of a cluster.
This opens up another way to trace infections: backwards.
"The idea being that it could be more efficient to trace back, and isolate, superspreaders than it is to trace downstream and isolate individuals who, even if they were infected, might transmit the virus to very few people," said Wong.
Both Japan and South Korea have used backwards contact tracing, which has been credited with helping them curb their epidemics, along with other control measures.
Masks, social distancing and reducing contacts are all ways to limit transmission opportunities, Althouse said, adding that even characterising people as "superspreaders" is misleading.
"There are vast differences in biology between individuals – I may have a million times more virus in my nose than you – but if I am a recluse, I can infect no one," he said.
© Agence France-Presse