Two-Thirds of the World’s Most Polluted Cities Are in India
Iain Marlow and Hannah Dormido, Bloomberg•February 25, 2020
RESULTING FROM THE PRIMITIVE ACCUMULATION OF CAPITAL
Two-Thirds of the World’s Most Polluted Cities Are in India
(Bloomberg) -- Several Chinese cities, including Beijing, have dramatically improved their air quality in recent years, while Indian metropolises remain some of the world’s worst polluted, according to a new report.
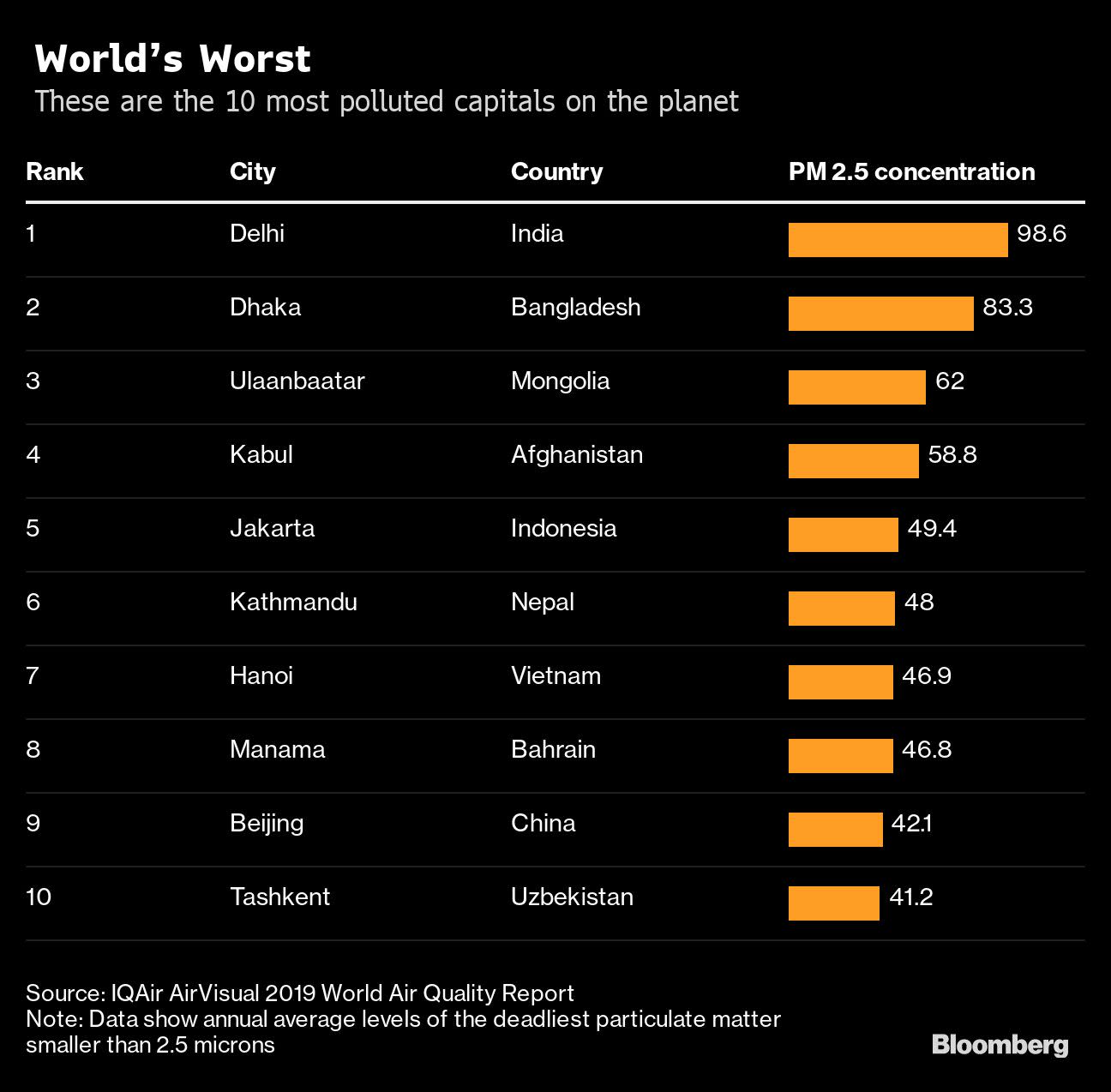
Beijing -- once infamous for its toxic haze -- has reduced smog levels and dropped down a list of the world’s most polluted cities, falling to 199 from 84 three years before, according to the 2019 World Air Quality Report published Tuesday by IQAir AirVisual. In contrast, India still dominated its list of the smoggiest urban areas, accounting for 14 of the top 20.
Despite new government policies meant to address the issue, New Delhi’s air quality has fallen from where it was five years ago, rising to the fifth-worst spot globally and making it by far the world’s most polluted major city, the report said. The worst-ranked city -- Ghaziabad -- is a Delhi suburb, as are a number of others ranked separately in the top 20.
India, China and other Asian countries remain disproportionately affected by toxic air as a result of factors ranging from crowded cities, vehicular exhaust, coal-fired power plants, agricultural burning and industrial emissions. The issue is hardly tangential. The World Health Organization estimates that dirty air kills around 7 million people each year, while the World Bank says it drains the global economy of $5 trillion annually.
Even before the coronavirus outbreak and trade war slowed China’s smog-producing industries, Chinese officials had mobilized the country’s top-down, authoritarian state to implement -- and enforce -- sweeping measures, as well as shifting production away from its biggest cities. A recent report from the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air separately found that Beijing and Shanghai had seen “major progress,” while levels of fine particular called PM 2.5 increased in other parts of the country.
India faces a starkly different situation. Across much of northern India, air quality remains catastrophic as politicians prioritize economic growth and spar over responsibility. Many citizens are still unaware of health concerns and resource-starved agencies struggle to carry out new -- or even existing -- measures designed to curb the smog.
Story continues
“In Beijing, it’s a priority -- in China, when they say something, they do it, they put the resources in,” said Yann Boquillod, AirVisual’s director of air quality monitoring. “In India, it’s just starting. People need to put more pressure on government.”
A spokesman for India’s environment ministry didn’t respond to a request for comment.
Why Winter Brings Deadly Smog to India’s Capital: QuickTake
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government has won praise for promoting solar power and improving emission standards. It has handed out millions of gas canisters to reduce the number of families using smoky household cooking fires. In January of last year, the government also launched the National Clean Air Programme.
But these measures haven’t had a serious impact on increased coal power plant usage, dust left by the thousands of under-regulated construction sites and exhaust from millions of new cars and motorcycles. Air quality experts have also criticized the national program for lacking strong enforcement and funding.
Indians Are Addicted to Cheap Coal Power and It’s Killing Them
Although many Indian cities saw progress between 2018 and 2019, “unfortunately these improvements are not representative of the very recent, but promising National Clean Air Programme” and cleaner fuel standards, according to the AirVisual report.
Instead, the authors said, they signal a lagging economy, which grew at about 5% -- the slowest expansion since 2009 -- compared with 8.3% in 2017. The deadly air also kills roughly 1.2 million Indians each year, according to a recent study in the Lancet.
India, however, was far from the only country that remained deeply challenged by smog. Although several Chinese cities -- including Shanghai -- saw improvement in air quality, Kashgar and Hotan in the restive, western Xinjiang region were among the world’s worst.
Cities across Asia -- including Chiang Mai, Hanoi, Jakarta and Seoul -- saw sharp increases in PM 2.5 levels. Since 2017, Jakarta saw pollution increase by 66%, making it the worst in Southeast Asia. In Thailand, Chiang Mai and Bangkok both saw a number of extremely smoggy days -- some of which led authorities in the capital to close schools -- resulting from construction, diesel fuel and crop fires in surrounding regions.
The problem is particularly challenging for South Asian countries. Using a weighted population average, Bangladesh was actually ranked the world’s most polluted country, while its capital Dhaka was the second worst after Delhi. Pakistan was the second-most-polluted country, while Afghanistan, India and Nepal were all in the top 10.
--With assistance from Bibhudatta Pradhan.
To contact the reporters on this story: Iain Marlow in Hong Kong at imarlow1@bloomberg.net;Hannah Dormido in Hong Kong at hdormido@bloomberg.net
©2020 Bloomberg L.P.
No comments:
Post a Comment