(Stephanie Abramowicz/Natural History Museum)
LAURA GEGGEL, LIVE SCIENCE
24 DECEMBER 2021
A sea monster that lived during the early dinosaur age is so unexpectedly colossal, it reveals that its kind grew to gigantic sizes extremely quickly, evolutionarily speaking at least.
The discovery suggests that such ichthyosaurs – a group of fish-shaped marine reptiles that inhabited the dinosaur-era seas – grew to enormous sizes in a span of only 2.5 million years, the new study finds.
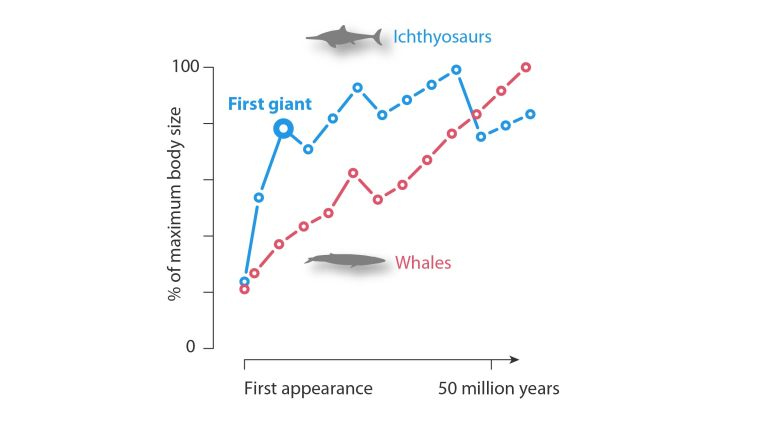
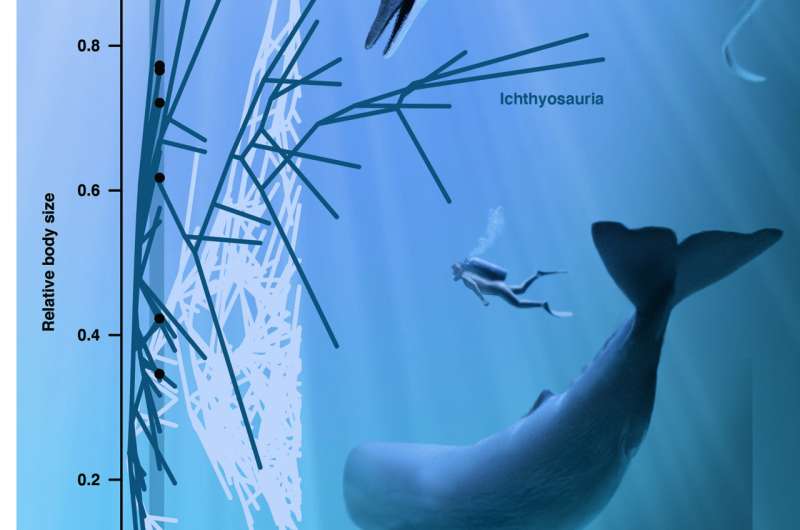
To put that in context, it took whales about 90 percent of their 55 million-year history to reach the huge sizes that ichthyosaurs evolved to in the first 1 percent of their 150 million-year history, the researchers said.
"We have discovered that ichthyosaurs evolved gigantism much faster than whales, in a time where the world was recovering from devastating extinction [at the end of the Permian period]," study senior researcher Lars Schmitz, an associate professor of biology at Scripps College in Claremont, California, told Live Science in an email.
"It is a nice glimmer of hope and a sign of the resilience of life – if environmental conditions are right, evolution can happen very fast, and life can bounce back."
 (Lars Schmitz)
(Lars Schmitz)Above: Ichthyosaurs evolved their large body sizes much quicker than whales. The curves depict the trajectory of the largest body size, expressed in percentage of the largest size ever reached, for ichthyosaurs and whales. The ichthyosaur curve is initially much steeper than the corresponding curve for whales.
Related: Image gallery: Ancient monsters of the sea
Researchers first noticed the ancient ichthyosaur's fossils in 1998, embedded in the rocks of the Augusta Mountains of northwestern Nevada.
"Only a few vertebrae were sticking out of the rock, but it was clear the animal was large," Schmitz said.
But it wasn't until 2015, with the help of a helicopter, that they were able to fully excavate the individual – whose surviving fossils include a skull, shoulder, and flipper-like appendage – and airlift it to the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, where it was prepared and analyzed.
The team named the new species Cymbospondylus youngorum, they reported online Thursday (Dec. 23) in the journal Science. This big-jawed marine reptile lived 247 million years ago during the Triassic period. Like other creatures from that time, it was weird.
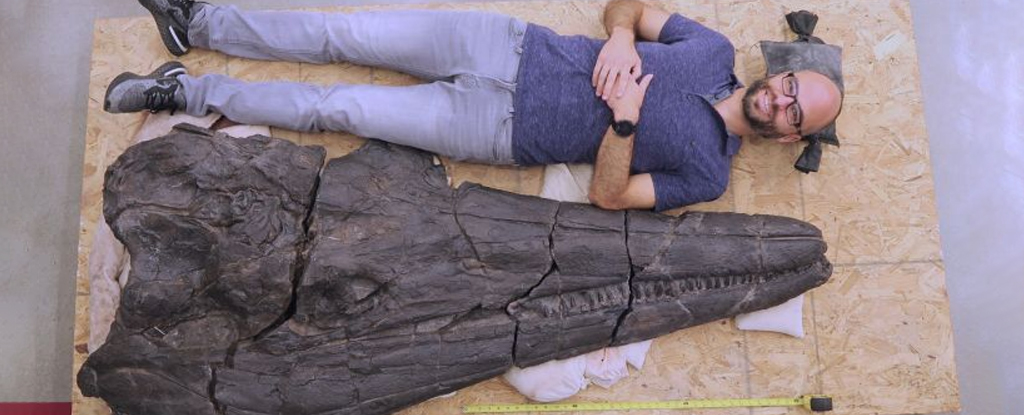 The new ichthyosaurs skull with a human for scale. (Martin Sander)
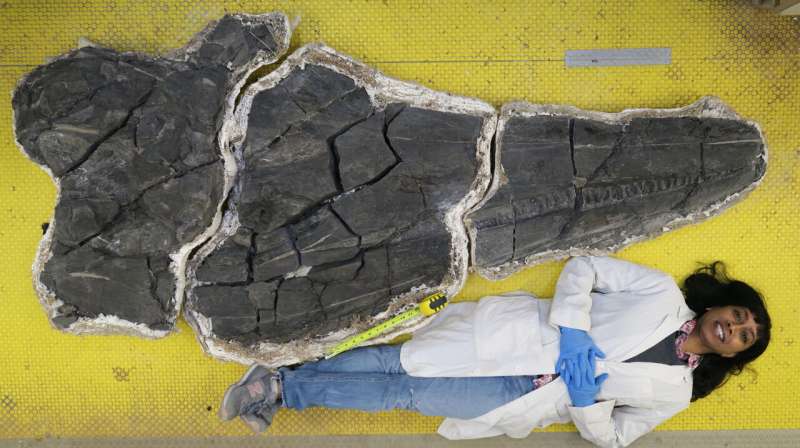
The new ichthyosaurs skull with a human for scale. (Martin Sander)"Imagine a sea-dragon-like animal: streamlined body, quite long, with limbs modified to fins, and a long tail," Schmitz said. With a nearly 6.5-foot-long (2 meters) skull, this full-grown C. youngorum would have measured over 55 feet (17 m), or longer than a semitrailer, the researchers found.
When the 45-ton (41 metric tons) C. youngorum was alive, C. youngorum would have lived in the Panthalassic Ocean, a so-called superocean, off the west coast of North America, Schmitz said.
Based on its size and tooth shape, C. youngorum likely ate smaller ichthyosaurs, fish, and possibly squid, he added.
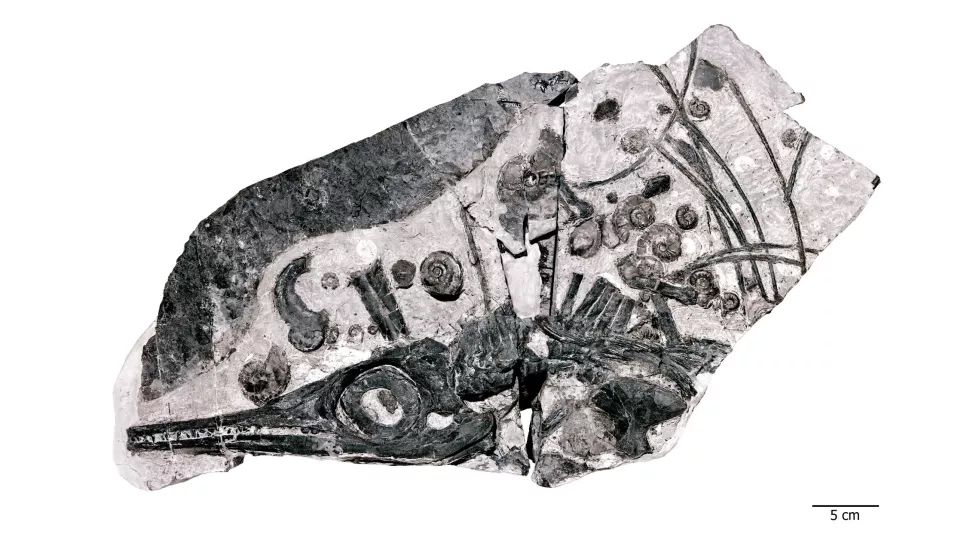
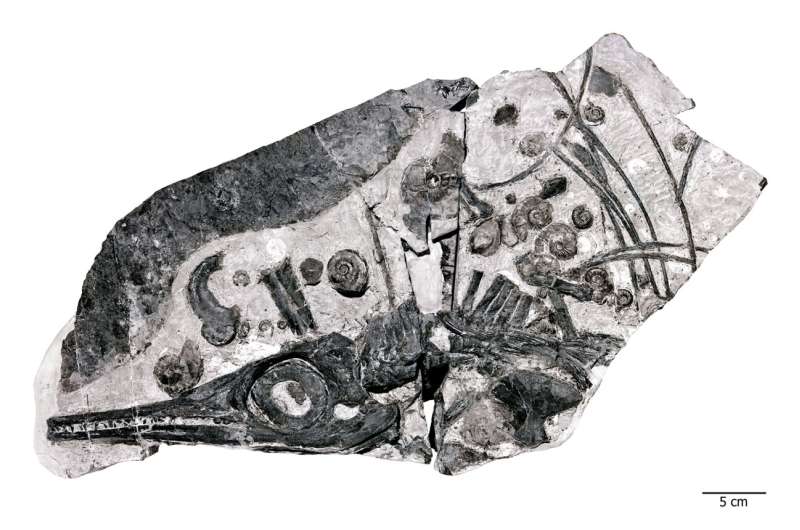
Above: The Fossil Hill fauna of Nevada not only includes the new giant species but also a number of other ichthyosaurs, such as this small (=30 cm skull length) Phalarodon. This specimen also includes examples of the very abundant ammonite fossils that are associated with the ichthyosaurs.
There are many huge beasts that lived during the dinosaur era, but C. youngorum stands out for several reasons. For instance, C. youngorum lived just 5 million years after "the Great Dying," a mass extinction event that occurred 252 million years ago at the end of the Permian period, which killed about 90 percent of the world's species.
That makes the ichthyosaur's huge size all the more impressive, as it took about 9 million years for life on Earth to recover from that extinction, a 2012 study in the journal Nature Geoscience found.
However, there was a diversification boom of marine mollusks known as ammonoids within 1 million to 3 million years of the mass extinction, the 2012 study found.
It appears that ichthyosaurs' venture into gigantism was, in part, due to chowing down on the early Triassic boom of ammonites, as well as jawless eel-like conodonts that filled the ecological void following the mass extinction, the researchers of the new study said.
In contrast, whales got big by eating highly productive primary producers, such as plankton; but these were absent in dinosaur-age food webs, study co-author Eva Maria Griebeler, an evolutionary ecologist at the Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz in Germany, said in a statement.
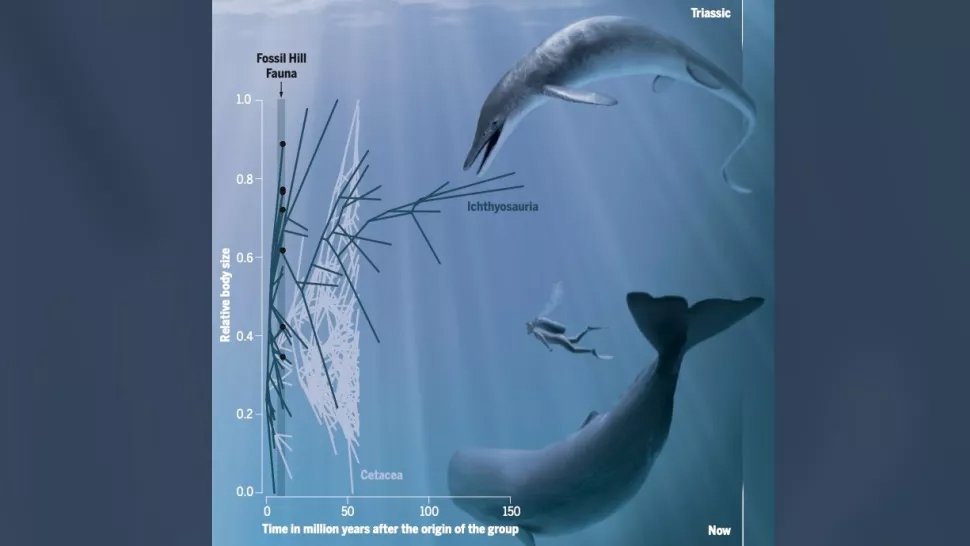
Above: Direct comparison of two ocean giants from different epochs side by side: The Triassic C. youngorum (the new species described in the paper) versus. today's sperm whale, with a human for scale.
Despite the whales' and ichthyosaurs' different paths and timetables toward achieving gigantism, the groups have a few similarities. For instance, there is a connection between large size and raptorial hunting, just like sperm whales dive to hunt giant squid, as well as a connection between large size and tooth loss, just like the giant filter-feeding whales that are toothless, the researchers said.
"This new fossil impressively documents the fast-track evolution of gigantism in ichthyosaurs," Schmitz said. In contrast, whales "took a different route to gigantism, much more prolonged and not nearly as fast.
"Ichthyosaur history tells us ocean giants are not guaranteed features of marine ecosystems, which is a valuable lesson for all of us in the Anthropocene," paleontologists Lene Delsett and Nicholas Pyenson, who weren't involved with the research wrote in a related Perspective published in the same issue of Science.
Related content:
Image gallery: Photos reveal prehistoric sea monster
In images: Graveyard of ichthyosaur fossils in Chile
Photos: Uncovering One of the largest plesiosaurs on record
This article was originally published by Live Science. Read the original article here.
Earth's first-known giant was as big as a sperm whale

The two-meter skull of a newly discovered species of giant ichthyosaur, the earliest known, is shedding new light on the marine reptiles' rapid growth into behemoths of the Dinosaurian oceans, and helping us better understand the journey of modern cetaceans (whales and dolphins) to becoming the largest animals to ever inhabit the Earth.
While dinosaurs ruled the land, ichthyosaurs and other aquatic reptiles (that were emphatically not dinosaurs) ruled the waves, reaching similarly gargantuan sizes and species diversity. Evolving fins and hydrodynamic body-shapes seen in both fish and whales, ichthyosaurs swam the ancient oceans for nearly the entirety of the Age of Dinosaurs.
"Ichthyosaurs derive from an as yet unknown group of land-living reptiles and were air-breathing themselves," says lead author Dr. Martin Sander, paleontologist at the University of Bonn and Research Associate with the Dinosaur Institute at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County (NHM). "From the first skeleton discoveries in southern England and Germany over 250 years ago, these 'fish-saurians' were among the first large fossil reptiles known to science, long before the dinosaurs, and they have captured the popular imagination ever since."
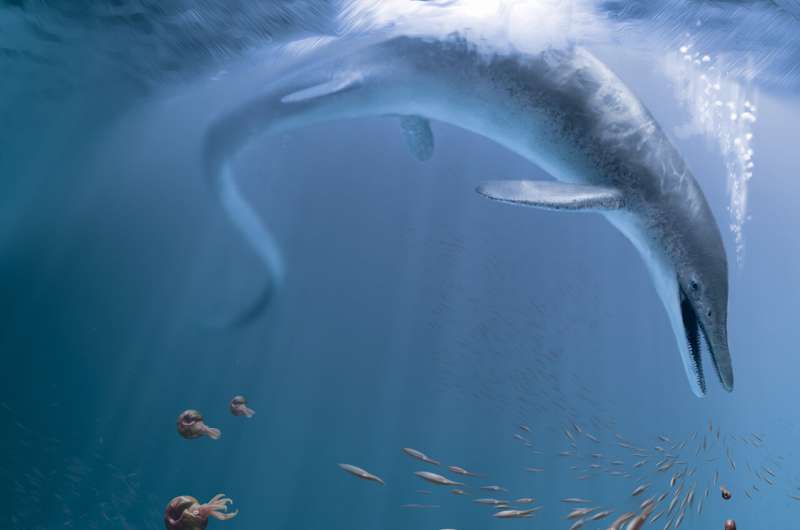

Excavated from a rock unit called the Fossil Hill Member in the Augusta Mountains of Nevada, the well-preserved skull, along with part of the backbone, shoulder, and forefin, date back to the Middle Triassic (247.2-237 million years ago), representing the earliest case of an ichthyosaur reaching epic proportions. As big as a large sperm whale at more than 17 meters (55.78 feet) long, the newly named Cymbospondylus youngorum is the largest animal yet discovered from that time period, on land or in the sea. In fact, it was the first giant creature to ever inhabit the Earth that we know of.
"The importance of the find was not immediately apparent," notes Dr. Sander, "because only a few vertebrae were exposed on the side of the canyon. However, the anatomy of the vertebrae suggested that the front end of the animal might still be hidden in the rocks. Then, one cold September day in 2011, the crew needed a warm-up and tested this suggestion by excavation, finding the skull, forelimbs, and chest region."
The new name for the species, C. youngorum, honors a happy coincidence, the sponsoring of the fieldwork by Great Basin Brewery of Reno, owned and operated by Tom and Bonda Young, the inventors of the locally famous Icky beer which features an ichthyosaur on its label.
In other mountain ranges of Nevada, paleontologists have been recovering fossils from the Fossil Hill Member's limestone, shale, and siltstone since 1902, opening a window into the Triassic. The mountains connect our present to ancient oceans and have produced many species of ammonites, shelled ancestors of modern cephalopods like cuttlefish and octopuses, as well as marine reptiles. All these animal specimens are collectively known as the Fossil Hill Fauna, representing many of C. youngorum's prey and competitors.

C. youngorum stalked the oceans some 246 million years ago, or only about three million years after the first ichthyosaurs got their fins wet, an amazingly short time to get this big. The elongated snout and conical teeth suggest that C. youngorum preyed on squid and fish, but its size meant that it could have hunted smaller and juvenile marine reptiles as well.
The giant predator probably had some hefty competition. Through sophisticated computational modeling, the authors examined the likely energy running through the Fossil Hill Fauna's food web, recreating the ancient environment through data, finding that marine food webs were able to support a few more colossal meat-eating ichthyosaurs. Ichthyosaurs of different sizes and survival strategies proliferated, comparable to modern cetaceans'— from relatively small dolphins to massive filter-feeding baleen whales, and giant squid-hunting sperm whales.
Co-author and ecological modeler Dr. Eva Maria Griebeler from the University of Mainz in Germany, notes, "Due to their large size and resulting energy demands, the densities of the largest ichthyosaurs from the Fossil Hill Fauna including C. youngourum must have been substantially lower than suggested by our field census. The ecological functioning of this food web from ecological modeling was very exciting as modern highly productive primary producers were absent in Mesozoic food webs and were an important driver in the size evolution of whales."

Whales and ichthyosaurs share more than a size range. They have similar body plans, and both initially arose after mass extinctions. These similarities make them scientifically valuable for comparative study. The authors combined computer modeling and traditional paleontology to study how these marine animals reached record-setting sizes independently.
"One rather unique aspect of this project is the integrative nature of our approach. We first had to describe the anatomy of the giant skull in detail and determine how this animal is related to other ichthyosaurs," says senior author Dr. Lars Schmitz, Associate Professor of Biology at Scripps College and Dinosaur Institute Research Associate. "We did not stop there, as we wanted to understand the significance of the new discovery in the context of the large-scale evolutionary pattern of ichthyosaur and whale body sizes, and how the fossil ecosystem of the Fossil Hill Fauna may have functioned. Both the evolutionary and ecological analyses required a substantial amount of computation, ultimately leading to a confluence of modeling with traditional paleontology."

They found that while both cetaceans and ichthyosaurs evolved very large body sizes, their respective evolutionary trajectories toward gigantism were different. Ichthyosaurs had an initial boom in size, becoming giants early on in their evolutionary history, while whales took much longer to reach the outer limits of huge. They found a connection between large size and raptorial hunting—think of a sperm whale diving down to hunt giant squid—and a connection between large size and a loss of teeth—think of the giant filter-feeding whales that are the largest animals ever to live on Earth.
Ichthyosaurs' initial foray into gigantism was likely thanks to the boom in ammonites and jawless eel-like conodonts filling the ecological void following the end-Permian mass extinction. While their evolutionary routes were different, both whales and ichthyosaurs relied on exploiting niches in the food chain to make it really big.

"As researchers, we often talk about similarities between ichthyosaurs and cetaceans, but rarely dive into the details. That's one way this study stands out, as it allowed us to explore and gain some additional insight into body size evolution within these groups of marine tetrapods," says NHM's Associate Curator of Mammalogy (Marine Mammals), Dr. Jorge Velez-Juarbe. "Another interesting aspect is that Cymbospondylus youngorum and the rest of the Fossil Hill Fauna are a testament to the resilience of life in the oceans after the worst mass extinction in Earth's history. You can say this is the first big splash for tetrapods in the oceans."
C. youngorum will be permanently housed at the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, where it is currently on view.Extinct swordfish-shaped marine reptile discovered
More information: P. Martin Sander et al, Early giant reveals faster evolution of large size in ichthyosaurs than in cetaceans, Science (2021). DOI: 10.1126/science.abf5787
Lene Liebe Delsett et al, Early and fast rise of Mesozoic ocean giants, Science (2021). DOI: 10.1126/science.abm3751 , www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abm3751
Journal information: Science
Provided by Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County