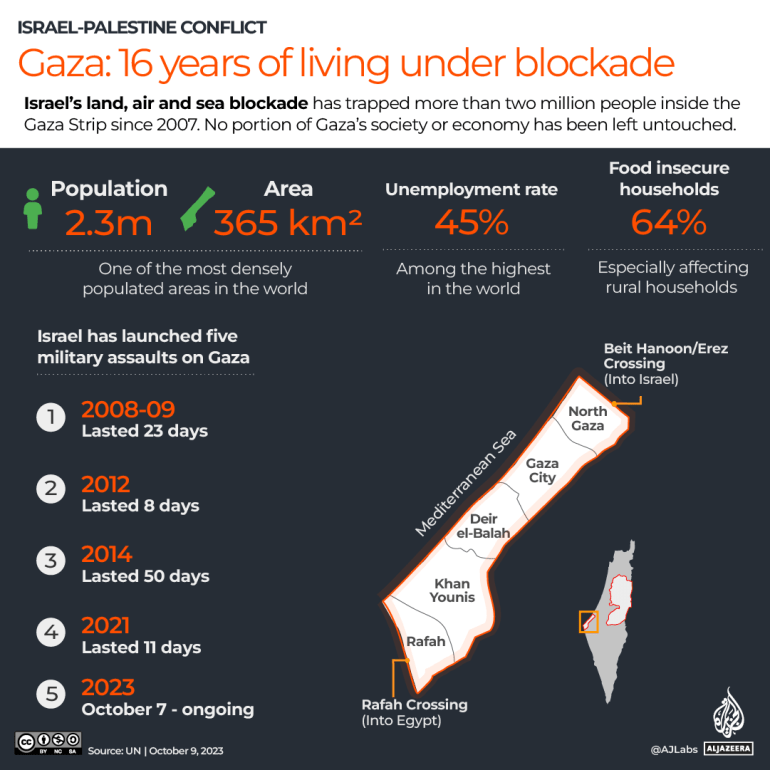
As Bloomberg News reported, Russian shipments of donated grain are due to begin landing in Africa within days.
NOVEMBER 26, 2023

As Bloomberg News reported, Russian shipments of donated grain are due to begin landing in Africa within days, giving fresh impetus to its bid to bolster its influence in the continent.
President Vladimir Putin promised to send free grain to six African countries that have strong ties with Moscow at a Russia-Africa summit in St. Petersburg in July. The move followed criticism that Russia’s war in Ukraine and its withdrawal from a deal that facilitated the export of Ukrainian grain through the Black Sea were pushing up global food and fertilizer prices.
The shipments will total 200,000 tons by year-end, the Russian Agriculture Ministry was cited by the Interfax news agency as saying Nov. 17, with Somalia and Burkina Faso set to be the first recipients. Zimbabwe, Mali, Eritrea and the Central African Republic are also due to get between 25,000 and 50,000 tons of grain each, Putin said in July. That’s a tiny fraction of what they consume.
Russia’s push to strengthen ties with African nations by increasing trade and deploying Wagner mercenaries to prop up unstable governments follows efforts by the US and its allies to isolate it in response to the invasion of Ukraine. It remains a minor player however — its two-way trade with the continent was only $18 billion in 2022, a fraction of China’s $282 billion.
Research presented at a conference in Cape Town on Sunday organized by a foundation set up by former South African President Thabo Mbeki sought to dispel the notion that Moscow bore primary responsibility for rising food costs. Direct or indirect sanctions imposed on Russia and its ally Belarus cut global fertilizer and ammonia supplies by 40.8 million tons through April 2023, according to the study, which was backed by a fund founded by Russian fertilizer billionaire Andrey Melnichenko.
Ukraine and Russia are two of the world’s leading exporters of grain and vegetable oil. The war has impacted on global supplies of both commodities, with Russia bombing Ukrainian stores and ports.
While Russian fertilizer hasn’t been subjected to international sanctions, penalties imposed on owners of companies that produce it and restrictions by the banking and logistics industries, saw exports fall last year. They have since recovered, spurring a decline in prices.
The study’s analysis of the impact of the Black Sea grain deal showed that it helped to feed about 95 million people but fell short in ensuring that fertilizer originating from Russia could flow freely to global markets. Had that happened, food could have been produced that fed about 199 million people, it said.
Billionaire Melnichenko, who holds dual citizenship from Russia and the United Arab Emirates, was sanctioned by the European Union and the US following the invasion of Ukraine. He traveled to South Africa late last year to lobby politicians to support his pleas for the EU to resolve fertilizer supply issues.
Pretoria has adopted a non-aligned stance toward the war in Ukraine that has drawn criticism from the US and some of its other largest trading partners. Thabo Mbeki spent time in exile in Russia during apartheid rule and served as South Africa’s president from 1999 until 2008. –With assistance from Paul Vecchiatto.





)