New program takes us one step closer to autonomous robots
We've watched the remarkable evolution of robotics over the past decade with models that can walk, talk and make gestures like humans, undertake tasks from moving heavy machinery to delicately manipulating tiny objects, and maintain balance on two or four legs over rough and hostile terrain.
As impressive as the latest robots are, their accomplishments are largely the result of task-specific programming or remote instruction from humans.
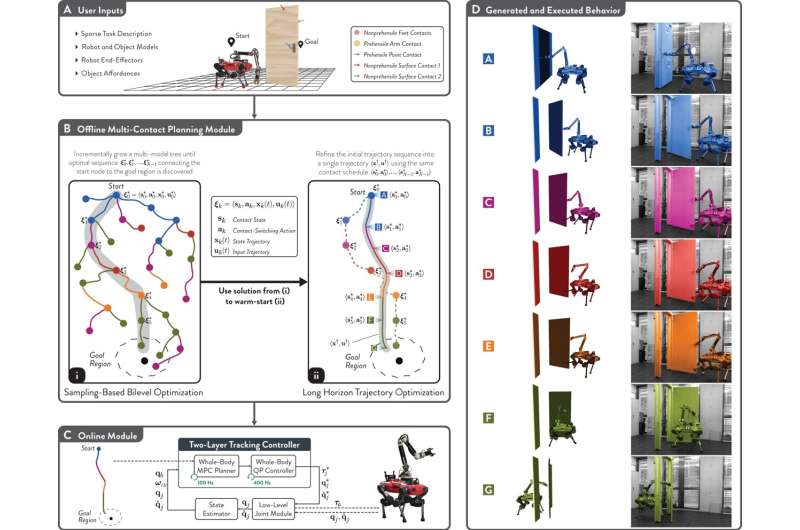
Researchers at ETH Zurich have developed a program that helps robots tackle activities that do not rely on "prerecorded expert demonstrations," as the developers put it, or "densely engineered rewards."
Instead, they designed an approach in which the robot can "rapidly discover a feasible and near optimal multi-modal sequence that solves the task." In other words, they provide an environment in which robots can achieve objectives with minimal guidance from human operators.
The research was reported in the Aug. 16 edition of Science Robotics. The paper, "Versatile multicontact planning and control for legged loco-manipulation," was prepared by Jean-Pierre Sleiman, Farbod Farshidian and Marco Hunter of the Robotic Systems Lab at the public research university ETH Zurich.
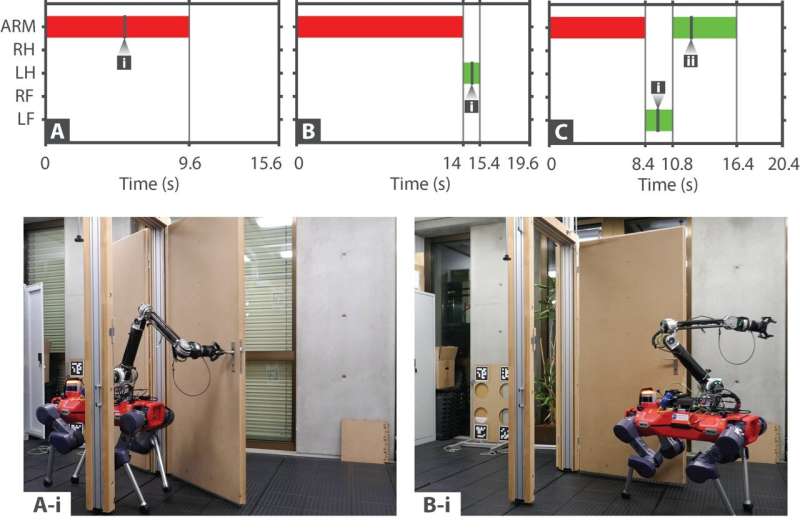
"Given high-level descriptions of the robot and object, along with a task specification encoded through a sparse objective," Sleiman said, "our planner holistically discovers how the robot should move, what forces it should exert, what limbs it should use, as well as when and where it should establish or break contact with the object."
Demonstration videos show ANYbotics' quadrupedal ANYmal mastering the opening of a dishwasher door and deftly opening a weighted door and keeping it open with a leg while maneuvering through.
"The framework can be readily adapted to different kinds of mobile manipulators," Sleiman said.
The last several years have seen great strides in robotic development. Boston Dynamics, a leading player in the field of robotics, created Atlas in 2013. With stereo vision and fine motor abilities, it could maintain balance in a hostile environment. It eventually was improved to get in and out of vehicles, open doors and handle power equipment. Agility Robotics' Cassie in 2016 exhibited superior walking and running capacity.
In 2017, a lifelike Sophia that smoothly mimicked human gestures and behavior was dispatched to assist the elderly in nursing facilities and play with children. And highly advanced tactile manipulation was demonstrated in 2019 with OpenAI's Dactyl: After training sessions that its developers estimated would take humans 13,000 years to complete, the single-handed Dactyl could easily manipulate a Rubik's cube and solve the 3D combination puzzle, which has stymied millions of users since its release in 1974, in just four minutes.
More recently, the last few years have seen Boston Dynamics' four-legged Spot, which can walk three miles, climb hills, conquer obstacles and perform specialized tasks. And Ameca, considered one of the most—if not the most—lifelike robot, engages in smooth conversation and generates facial expressions and hand gestures that are remarkably humanlike.
ETH Zurich, which would take the grand accomplishments of its predecessors and eliminate—or at least greatly reduce—the need for humans to control robots behind the scenes, has taken a key step in the next stage of robot development.
More information: Jean-Pierre Sleiman et al, Versatile multicontact planning and control for legged loco-manipulation, Science Robotics (2023). DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.adg5014
Journal information: Science Robotics
© 2023 Science X NetworkResearchers expand ability of robots to learn from videos
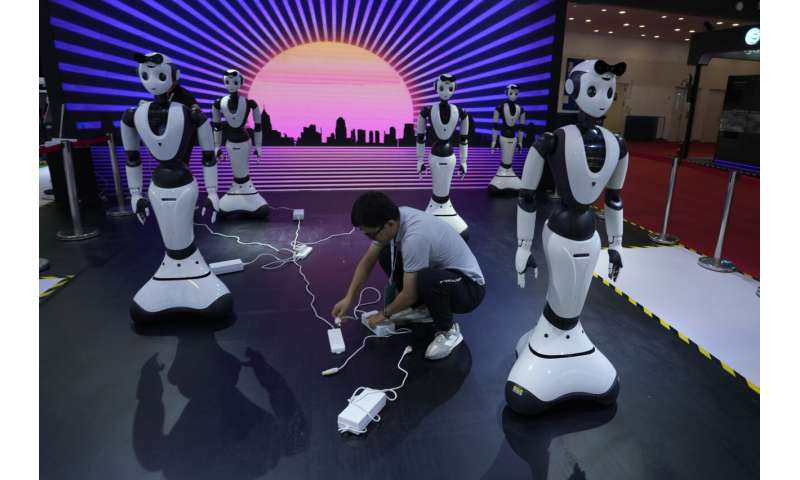
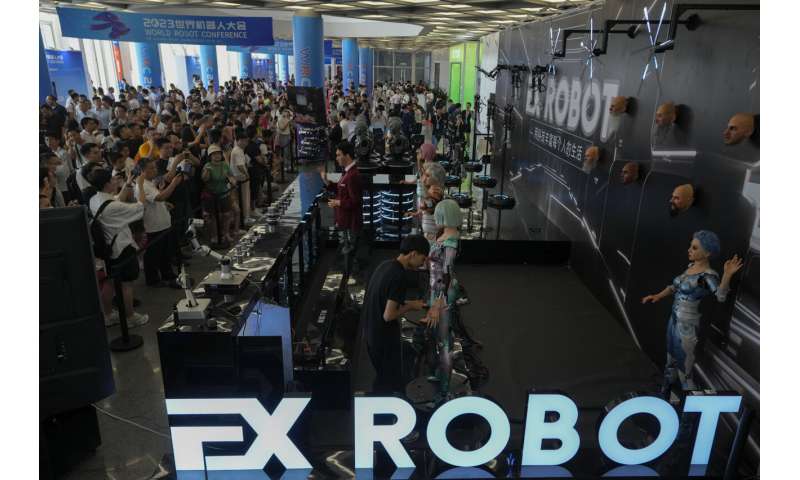
Lifelike robots and android dogs wow visitors at Beijing robotics fair
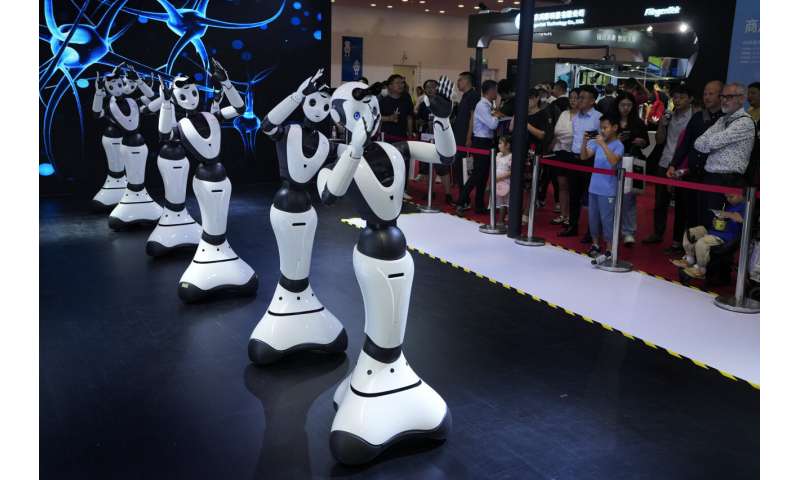
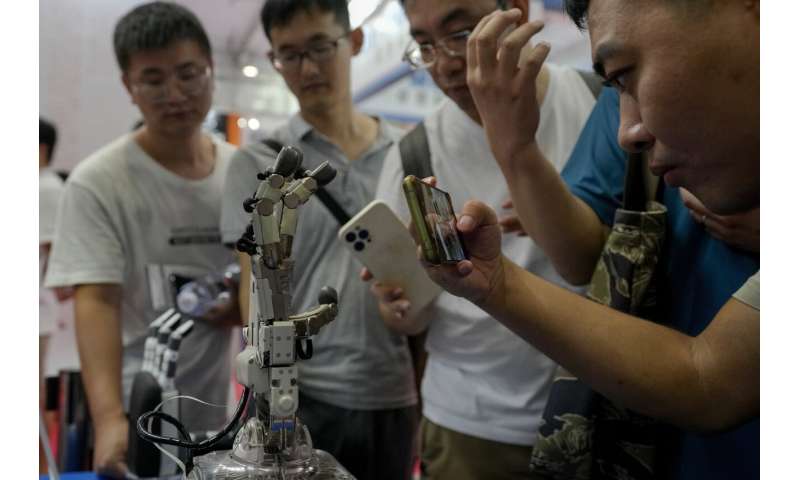
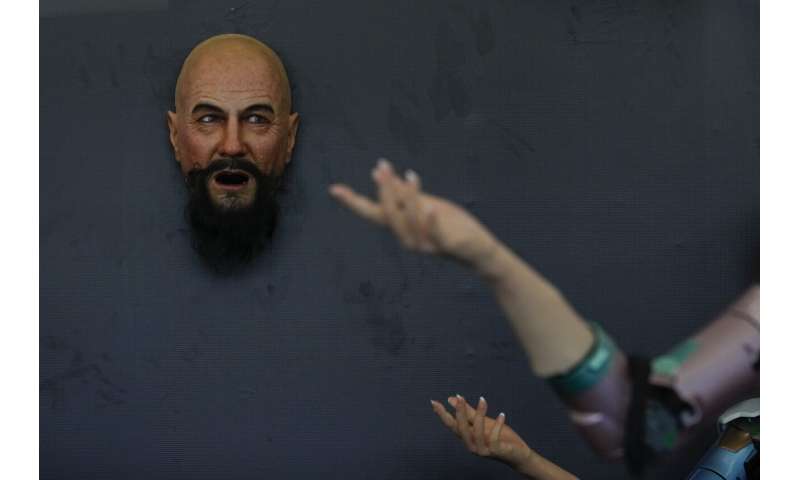
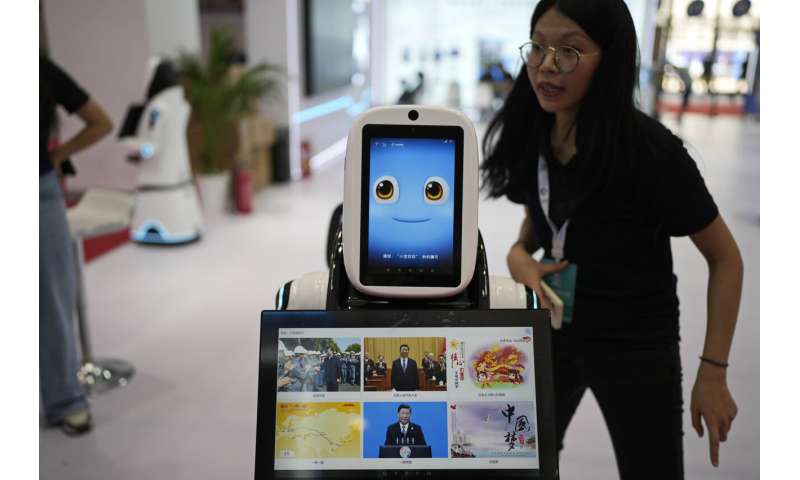
Winking, grimacing or nodding their heads, robots mimicked the expressions of visitors at a robot expo in Beijing.
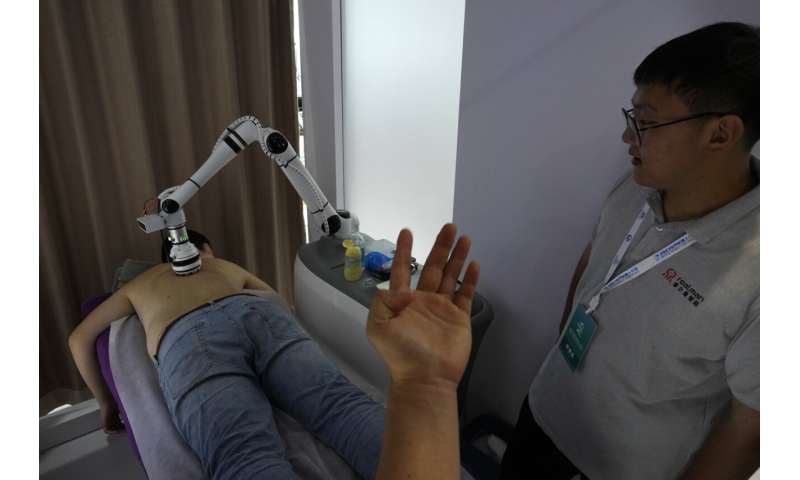
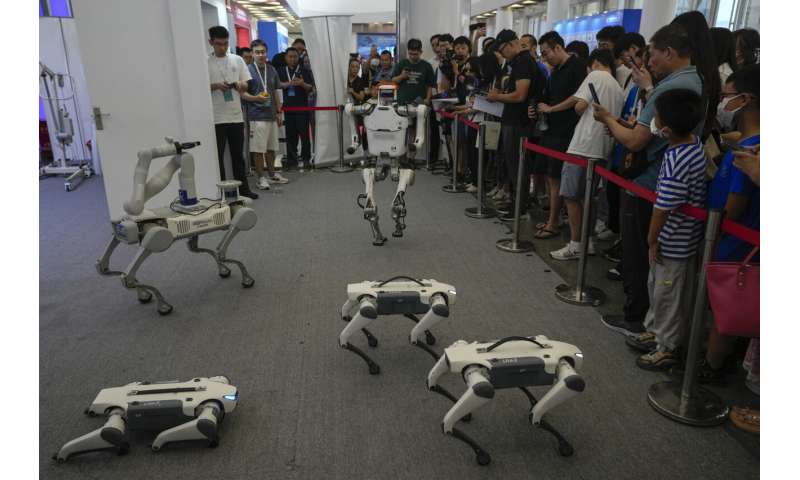
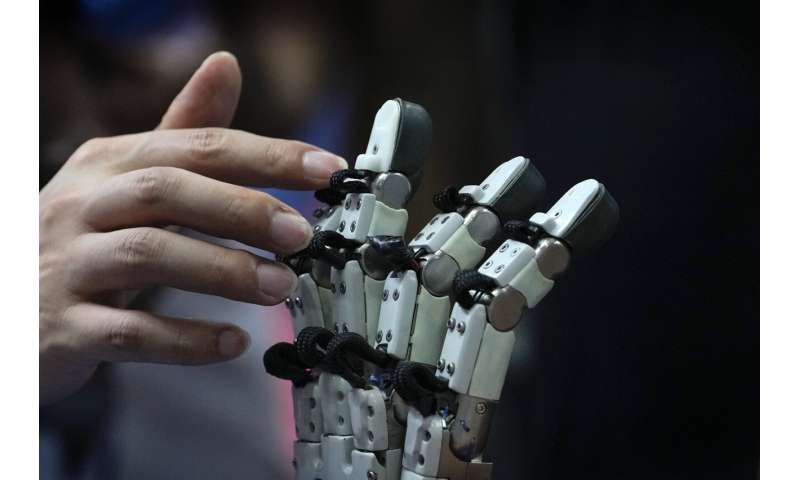
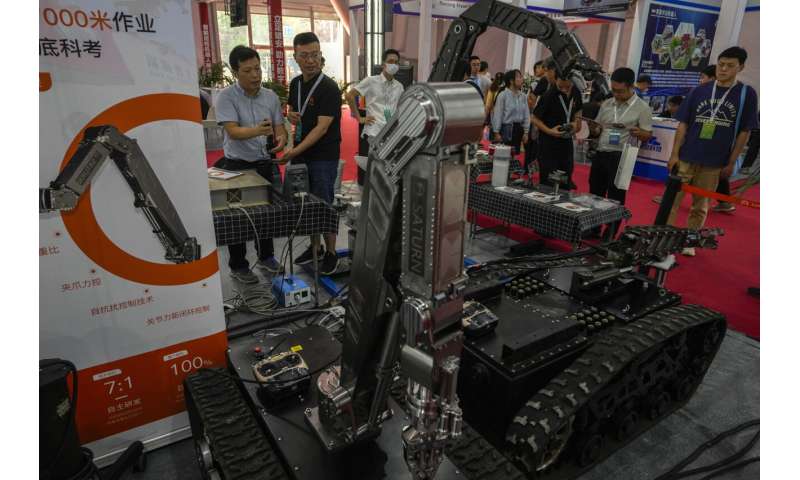
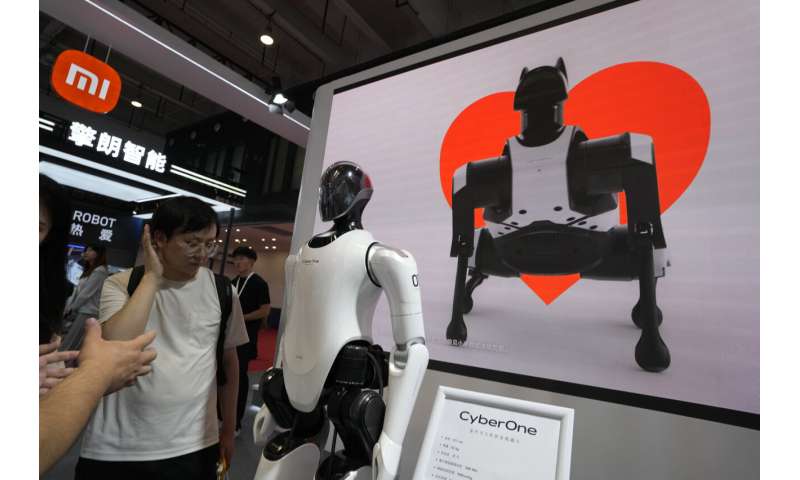
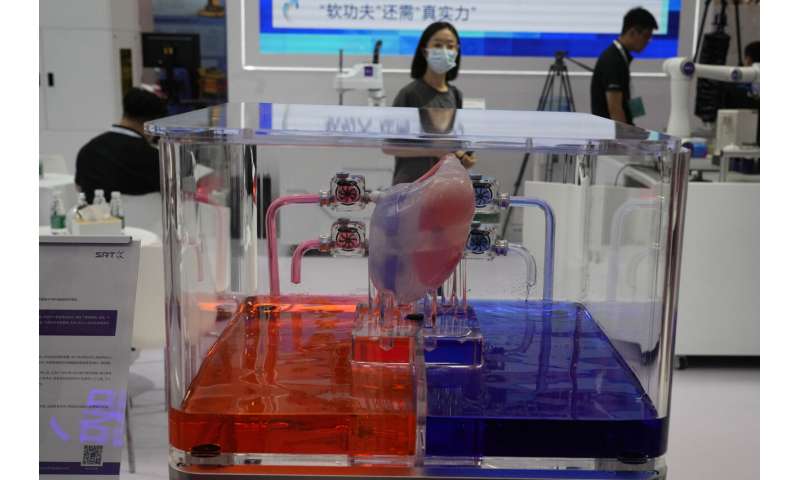
They were among the creations dazzling people attending the annual World Robot Conference, where companies showed off robots designed for a wide range of uses, including manufacturing, surgery and companionship.
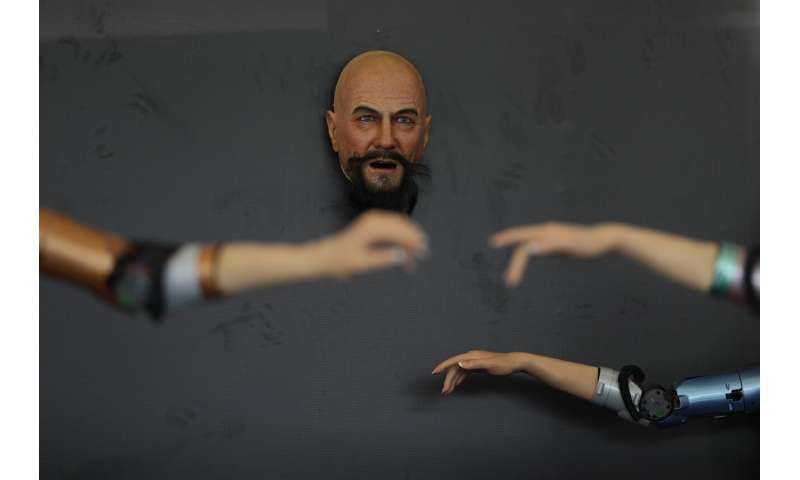
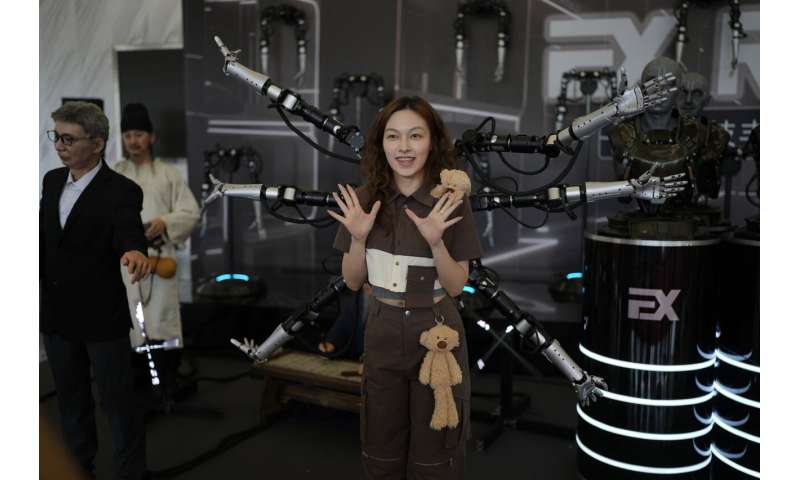
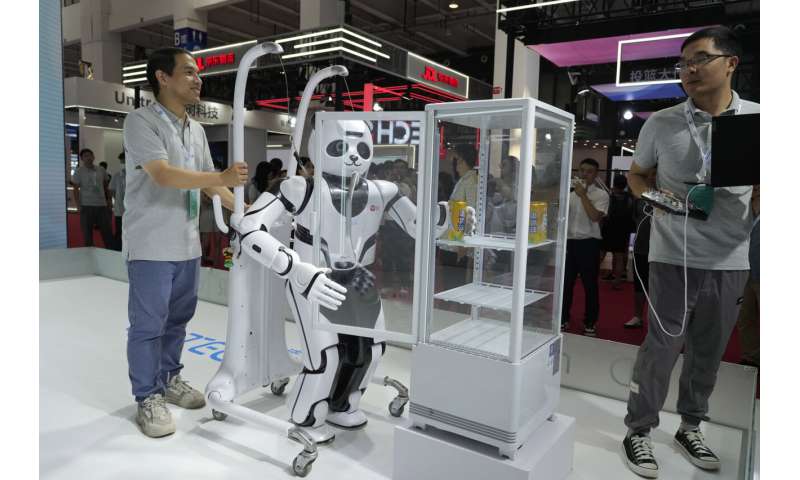
The animatronic heads and humanoid robots on display at the EX Robots booth this week personified the image of what robots are supposed to be in the popular imagination, with synthetic skin and lifelike facial expressions complimented by moving arms and hands.
CEO Li Boyang said they're ideal for roles that require interacting with the public, such as in museums, tourist attractions, school settings and "companion scenarios."
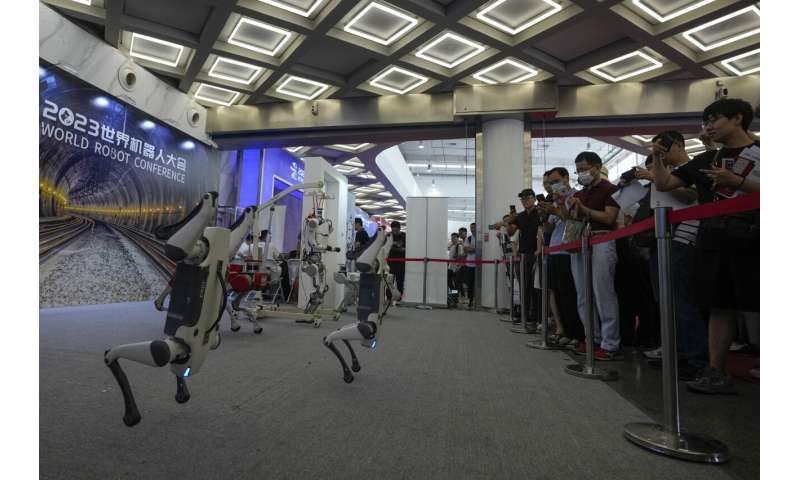
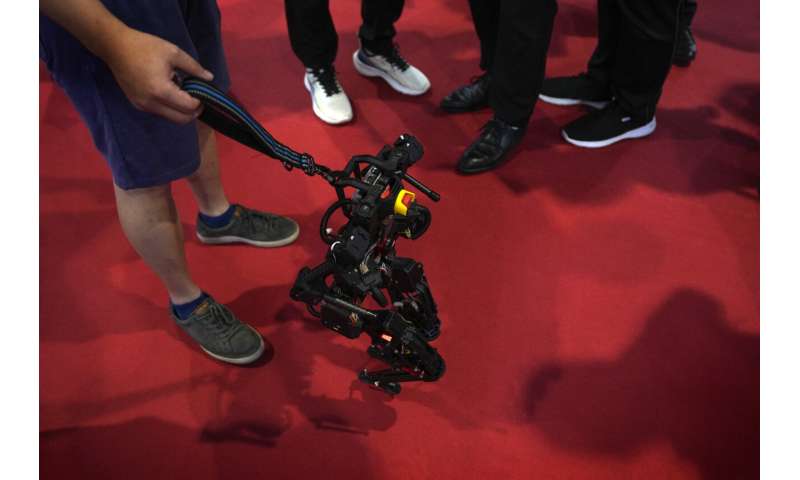
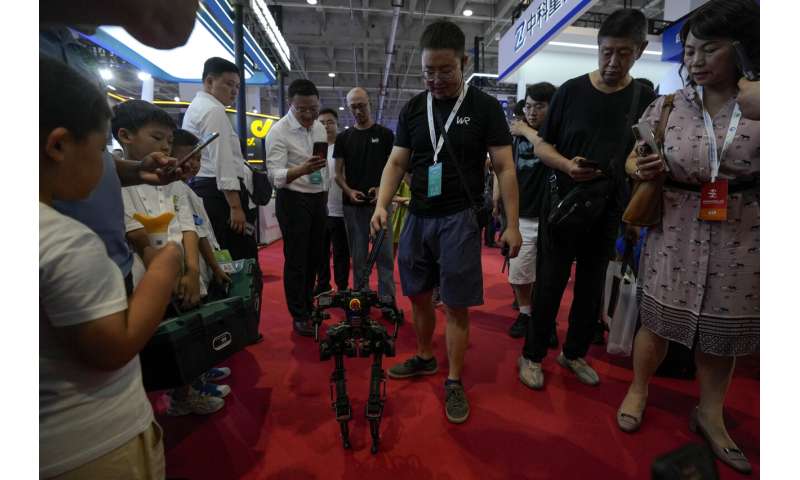
Doggie droids—a mainstay of high tech fairs—were out in force. Canine robots shook hands with fairgoers and performed handstands on their front paws.
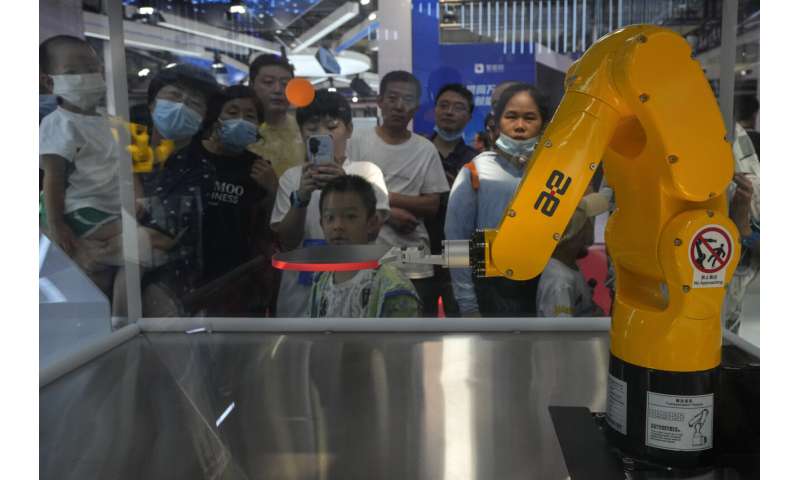
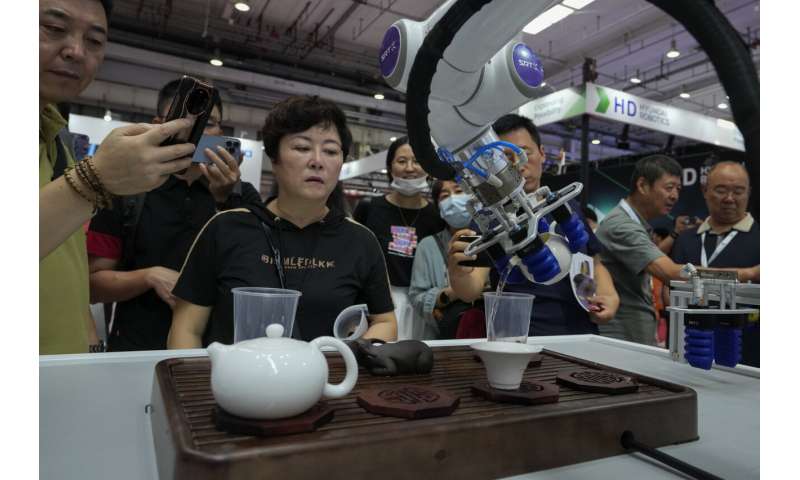
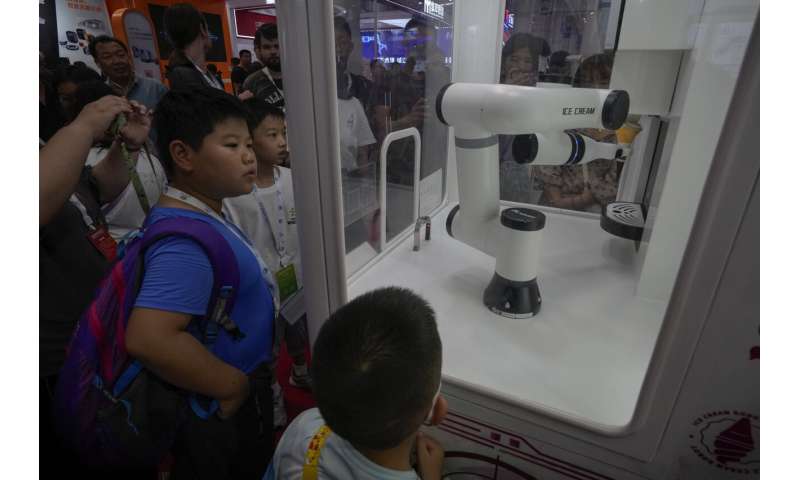
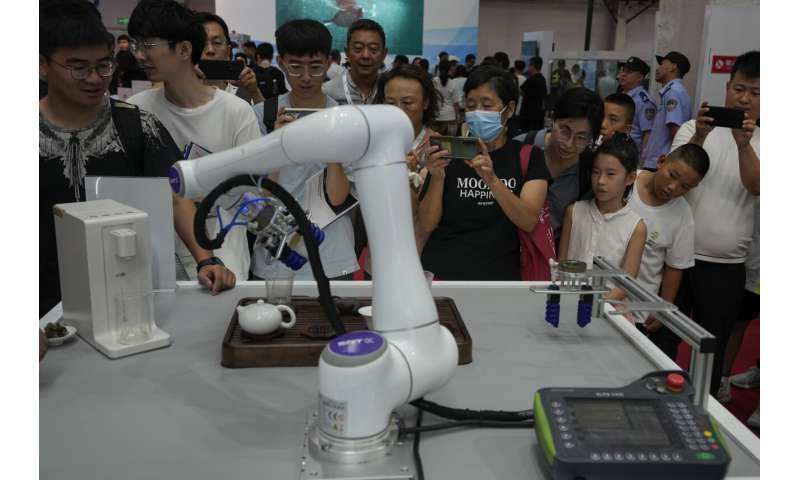
Elsewhere at the fair, robotic arms served Chinese tea, prepared ice cream cones, bounced ping pong balls and gave visitors back massages.
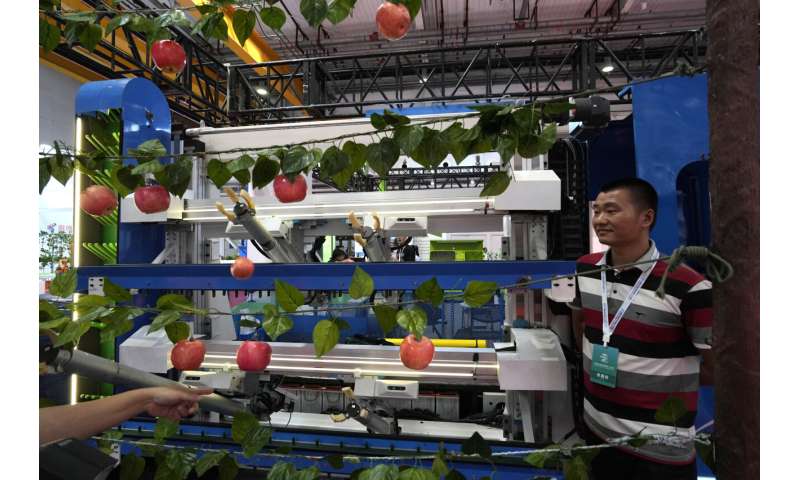
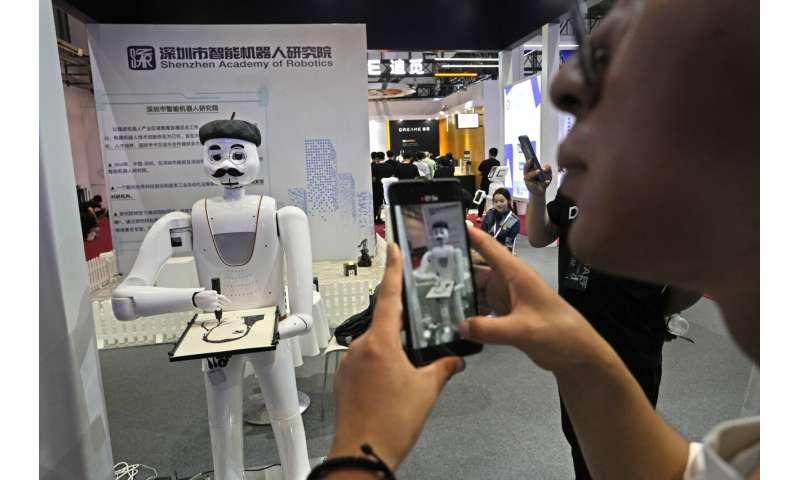
Harvesting robots demonstrated how they could pick apples off the branch, while an artist robot drew portraits of visitors.
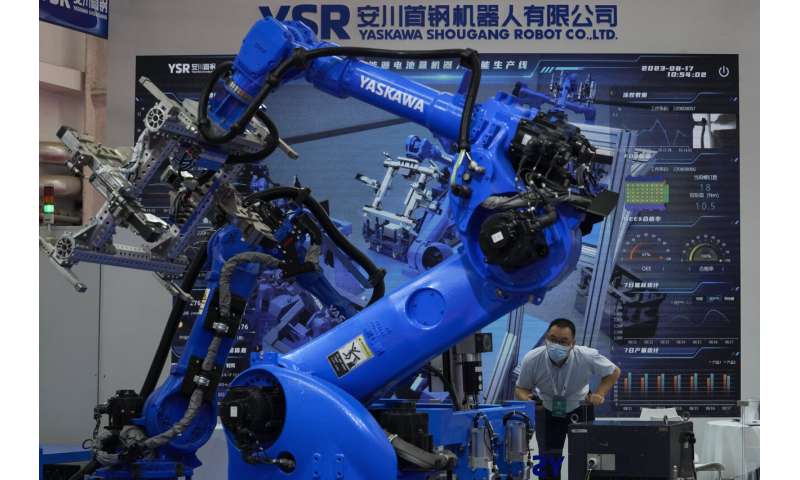
Industrial robot arms for factory production lines also grabbed focus. One of Chinese leader Xi Jinping's goals is to move the country's vast manufacturing sector away from low-cost creation of cheap goods into more high-tech production, and industrial robots will be an important element of that plan.
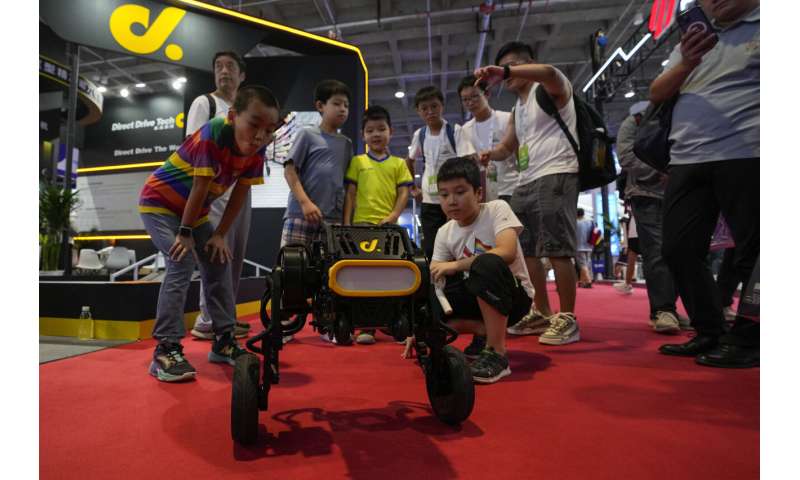
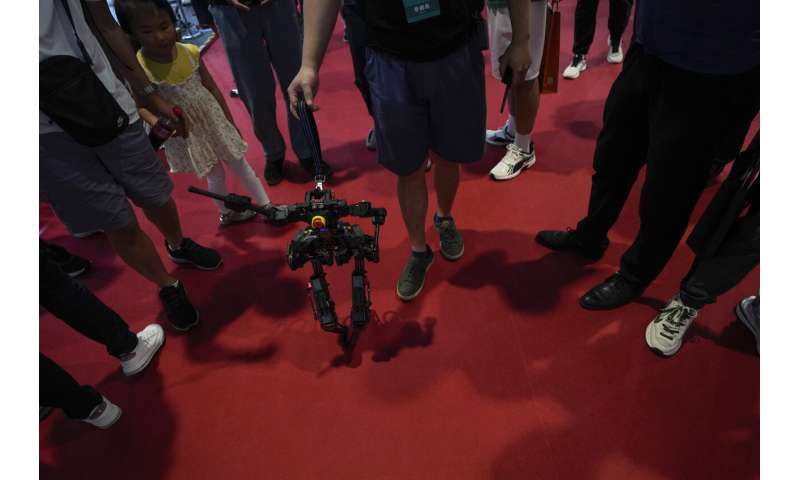
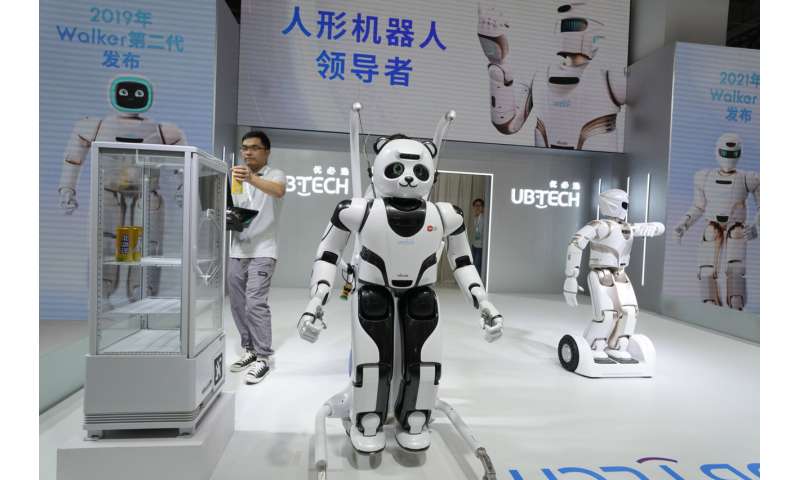
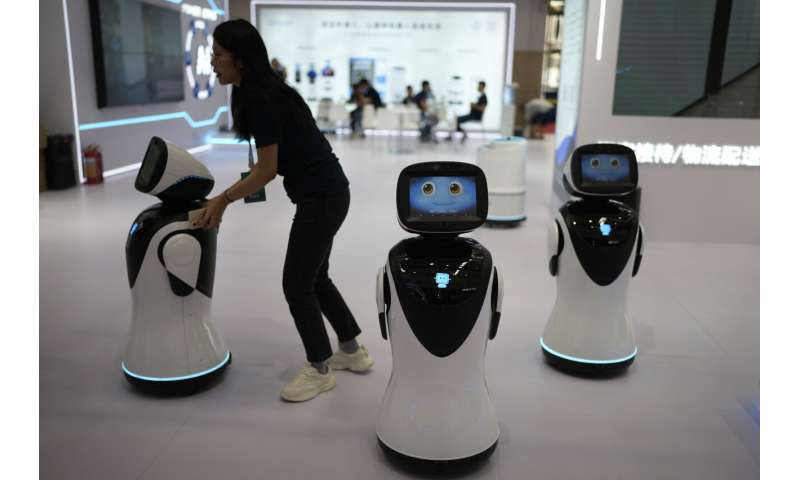



































© 2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.

