Can We Abolish War, Or Will War Abolish Us?

Image by Humphrey Muleba.
The organized murder of one group of humans by another group of humans is called war. We live in a world where the vilest of crimes, which are punished with severe consequences within most societies, are somehow acceptable when committed as part of war. War has been an integral part of human history and, in the nuclear age, is the most imminent threat to our continued existence. As modern, civilized people, most of us find war abhorrent, but few of us call for the abolition of war.
War exists because human society has been organized around the concept of the in-group and the out-group. The in-group could be a tribe, city, nation, or group of nations. The out-group may be tolerated, but in many instances, it is considered the enemy. The question of our time is, can we create a new story where humanity is the in-group? Can we civilize a lawless world by creating a basic system of enforceable global law?
Wars between countries continue because countries exist in relative anarchy at the international level. We have international law based on treaties that help maintain order, but this system is not an actual law, as it is voluntary. Valid law has consequences and enforcement mechanisms if one breaks the law. At the international level, we still live and die by the law of the jungle, which is “might makes right.”
The countries of the European Union have found peace after thousands of years of warfare and two world wars by trading away a piece of sovereignty to form a collective. They now resolve disputes in the European Union’s parliament and courts. The world’s countries can find peace by building an international union of nations and creating a similar system of courts and a global parliament.
The true challenge of our time is to bring rules, law, and democracy to the chaos of international relations. If we want to overcome the existential threats of nuclear weapons and abolish war, we will need a world governing body that is more democratic and empowered to act than the current United Nations.
The United Nations has a membership of almost all the countries on earth, and this in itself is an impressive accomplishment in that it creates an inclusive forum for discussion of international problems. Unfortunately, the UN lacks democratic standards and is flawed by its outdated design, and thus ineffective in addressing the major global security issues of our day.
International security issues are dealt with in the UN by the Security Council and, in particular, the five permanent members who were the victors of World War II: the United States, the United Kingdom, France, the Russian Federation, and the People’s Republic of China. They each have a veto, allowing a single country to block the action called for by the majority.
The General Assembly can pass resolutions, but they constitute no more than recommendations.
We are at a critical moment in human history. International laws exist, but they are often not enforceable. Force and military might still rule the world in terms of global affairs.
Fortunately, a US organization called Citizens for Global Solutions—like the World Federalist Movement, which brings together organizations with a similar orientation around the globe—works to create a world ruled by law rather than force, to build the legal institutions necessary for peace, and to abolish war. Citizens for Global Solutions is working to enhance the jurisdiction and use of the International Court of Justice to resolve disputes without violence in a campaign called Legal Alternatives to War(LAW, not War).
The challenge of our time is to abolish war and create the global intuitions of law necessary to resolve disputes through legal rather than lethal means.
Can the Internet Wage Peace?
With the Tiktok ban just days away, American youth have started flooding the Chinese social media app RedNote, pushing it into #1 position on the app store. Labeled “Tiktok refugees” by Chinese netizens, the newcomers have been welcomed by app users with open arms, curiosity, and a fair bit of humor.
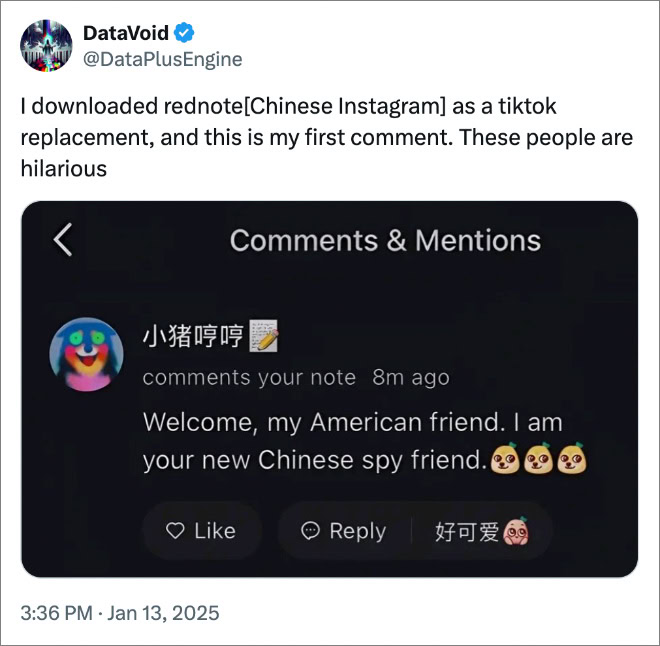
Though initially confused at the sudden influx of English speakers, long-dwelling app users quickly connected the dots and were quick to poke fun at the US government’s accusations of China spying on your typical American citizen.
The app “Xiaohongshu” directly translates to ‘Little Red Book,” but it has been dubbed RedNote in the United States. Many are quick to think of Chinese communist leader Mao Zedong’s famous Little Red Book, though app officials say it isn’t a direct reference. Still, the comedic composition is something to celebrate.
The Tiktok ban is quite evidently backfiring on the US government. As users snub the ban and move to a real Chinese social media app, spontaneous interactions between US and Chinese citizens are naturally sorting through years and years of anti-China propaganda.
WAIT! The social credit thing isn’t real??? One user commented, after locals revealed that there is no such thing as a social credit score in China — just one of the many stories the media has falsely fed us.
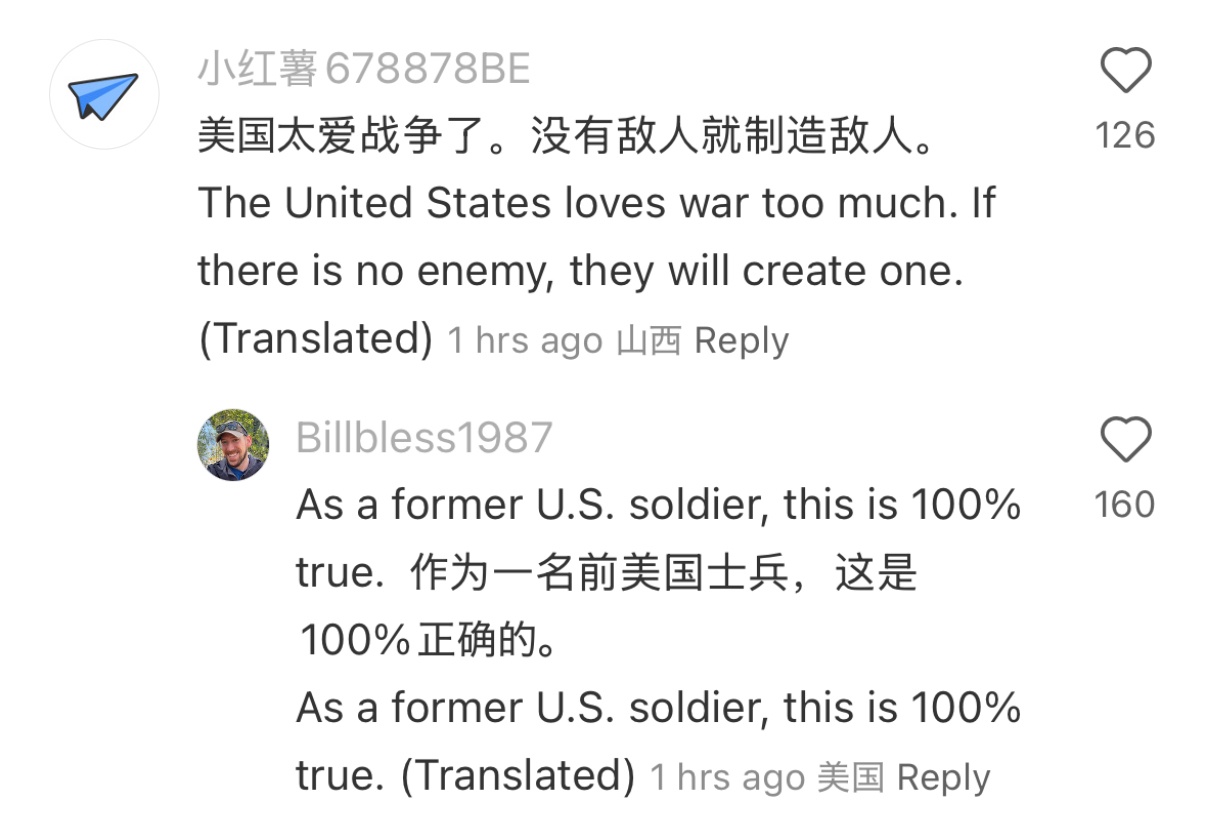
The app has ushered in a new wave of cross-cultural learning. Americans have been posting questions like, “How does China feel about Palestine?” and “What does the US government tell us about China that isn’t true?” There’s been comparisons between the US and China health systems (of which China’s is undoubtedly superior) and tours of China’s incredible EVs. The vast number of Americans agree: the US has fallen way behind.
Not only that, but American citizens cite a new appreciation for China, and the number of people learning Mandarin has grown. Duolingo has already seen a 216% spike. While Chinese citizens have taken it upon themselves to start teaching newcomers common Chinese phrases, Americans simultaneously help local users with their English homework.

It is more than just cultural exchange, however. This is an unprecedented people-to-people moment, allowing two communities to come together and realize they are more alike than not. Such a realization is desperately needed, and undercuts a rapidly escalating war climate between the US and China.
Recently, the US approved a $2 billion arms sale to Taiwan, citing potential war with China. In response, China sanctioned numerous US weapons companies for violating the one-China principle and destabilizing the region. War talk isn’t new — the US government has been pushing and planning for it ever since China rose to power in the early 2000s. A natural threat to US global hegemony, our politicians have been plotting the fall of China for decades, spending billions and billions of dollars to militarize the region around China and pushing a narrative of hatred and fear in the media.
Just this week, China hawk Marco Rubio underwent his Secretary of State confirmation hearing. Due to his push for war against China, he has been travel-sanctioned by the Chinese government for years. Our nation’s top “diplomat” is going to have some trouble conducting diplomacy when he’s unable to even travel to the nation where we need it most. Not that anything Rubio does could ever be considered diplomacy.
But despite the constant anti-China rhetoric plaguing our politicians and media, new RedNote users appear to be taking a different path:

The internet is a modern tool not previously available to the people during the great power wars of previous decades. It provides a fresh avenue that can circumvent the weaponization of the media and allow people to easily connect from different sides of the globe.
Perhaps an app like RedNote is exactly what we need to continue diffusing all the anti-China propaganda attempting to manufacture consent for the next great war. It’s about time the people decide for themselves who they should and shouldn’t be calling “enemy” rather than adhering to the whims of a war-obsessed government.
No comments:
Post a Comment