US to award $3 billion to 25 projects for battery manufacturing sector

LMA material is expected to enable improved energy density, safety, and faster charging for advanced batteries. (Source: Albemarle)
The US Energy Department said Friday it plans to award $3 billion to 25 battery manufacturing sector projects in 14 states as the Biden administration works to shift the supply chain away from China.

The projects will increase domestic production of advanced batteries and battery materials and follows the adoption of US EV tax credit rules to shift battery production and critical minerals away from China.
The awards fund battery-grade processed critical minerals, components, battery manufacturing, and recycling, and will generate $16 billion in total investment for the projects and support 12,000 production and construction jobs, the department said.
“Mineral security is essential for climate security,” said White House climate adviser Ali Zaidi. “This sets us up to lead on the next generation of battery technologies – from solid state to other new chemistries.”
Albemarle is set to receive $67 million for a project in North Carolina to produce commercial quantities of anode material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries, while Honeywell is set to receive $126.6 million to build a commercial-scale facility in Louisiana to produce a key electrolyte salt needed for lithium batteries.
DOE plans to award Dow $100 million to produce battery-grade carbonate solvents for lithium-ion battery electrolytes, while Clarios Circular Solutions, which is partnering with SK ON and Cosmo Chemical, is set to receive $150 million for a project in South Carolina to recycle lithium-ion battery production scrap materials from SK ON, the battery unit of SK Innovation.
Currently most US production scrap is exported by material traders to be processed, mostly in China, DOE said.
DOE plans a $225 million award for production of lithium carbonate by SWA Lithium, jointly owned by Standard Lithium and Equinor, using direct lithium extraction (DLE) technology. DOE also plans to award $225 million to TerraVolta Resources to produce lithium from brine using DLE.
Revex Technologies, a partnership co-founded by Lundin Mining, is set to receive $145 million for three Michigan facilities to turn waste from the only operating US primary nickel mine to yield domestic nickel production for at least 462,000 EV batteries yearly.
DOE plans to award $166 million to South32 Hermosa in Patagonia, Arizona for the mining of high purity manganese sulfate monohydrate (HPMSM) for electric vehicle battery chemistries. Currently over 96% of HPMSM is made in China.
DOE also plans to award $166.1 million for another HPMSM project in Louisiana for Element 25 from manganese ore sourced from an Element 25 mine in Western Australia.
Group14 Technologies is to receive $200 million to develop a US-based silane manufacturing plant in Moses Lake, Washington. The largest source of silane today is China, a material needed for silicon batteries.
Birla Carbon is set to receive $150 million for next-generation synthetic graphite that will not use material from China.
DOE previously awarded $1.82 billion to 14 projects. DOE said the projects selected must complete negotiations and an environmental review before they are awarded.
(By David Shepardson; Editing by Stephen Coates)
Staff Writer | September 20, 2024 |
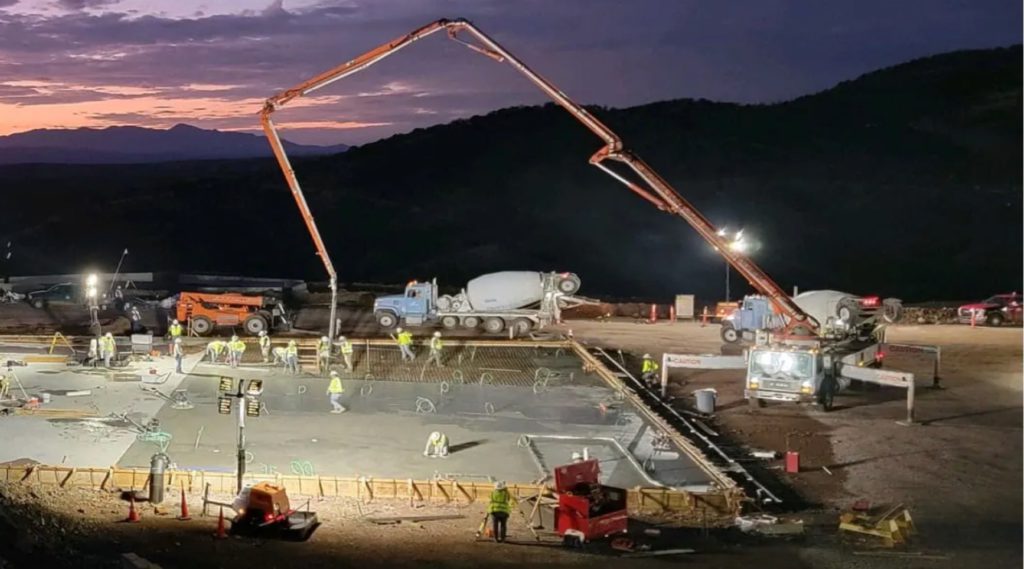

The Hermosa project in Arizona. (Image courtesy of South32.)
South32’s (LSE: S32; ASX: S32) Hermosa project in Arizona has been tapped for a US government grant of up to $166 million. This potential funding is part of the US Energy Department’s plans to invest $3 billion into the domestic battery manufacturing sector announced Friday.

Located in the Patagonia Mountains, about 80 km southeast of Tucson, the Hermosa project is targeted to produce two federally designated critical minerals — zinc and manganese — from the Taylor sulphide and Clark oxide deposits, respectively.
The Taylor deposit represents the first phase of the project, targeting first production in fiscal 2027. It has the potential to become one of the world’s largest, lowest-cost zinc producers, with a nameplate capacity of 4.3 million tonnes annually and unit costs of $86/tonne of ore processed, as shown in its feasibility study. Its initial mine life is estimated at 28 years.
Following the delivery of the feasibility study, the board of South32 approved an investment of $2.16 billion to fund the construction of key infrastructure for the zinc mine, which had already begun last year.
Also last year, Hermosa became the first mining project added to the US FAST-41 permitting process designed to promote faster development of clean energy assets.
According to South32, the infrastructure at the zinc mine would support future potential development of other deposits at the site, including the battery-grade manganese deposit at Clark, which is subject to further study.
Manganese facility
The DOE funding, once negotiated and secured, would provide 30% of the cost of its proposed commercial-scale manganese production facility, the Australian miner said in a press release on Friday.
While the exact location of the facility is yet to be determined, it will be in southern Arizona, South32 said. Construction for the manganese decline to enable bulk sampling through a demonstration plant and further underground exploration are continuing on schedule, with access targeted for the end of 2025.
The funding follows a $20 million award to the Hermosa project earlier this year from the Department of Defense Production Act Investment (DPAI) program to help accelerate the domestic production of battery-grade manganese.
“This project has the potential to provide a reliable, lower carbon and cost-effective domestic option for manganese products within the electric vehicle battery supply chain that currently relies entirely on foreign imports,” Pat Risner, president of South32 Hermosa said in the statement.
South32 says Hermosa could be scaled up as the only fully integrated source of battery-grade manganese for EV battery chemistries sufficient to supply the emerging North American market. Based on a third-party life cycle assessment, production from its deposit at Hermosa is projected to be the lowest carbon impact project in manganese chemicals in North America.
The US has not mined any manganese since the 1970s, and more than 95% of the current production of battery-grade manganese is currently in China, according to company estimates.
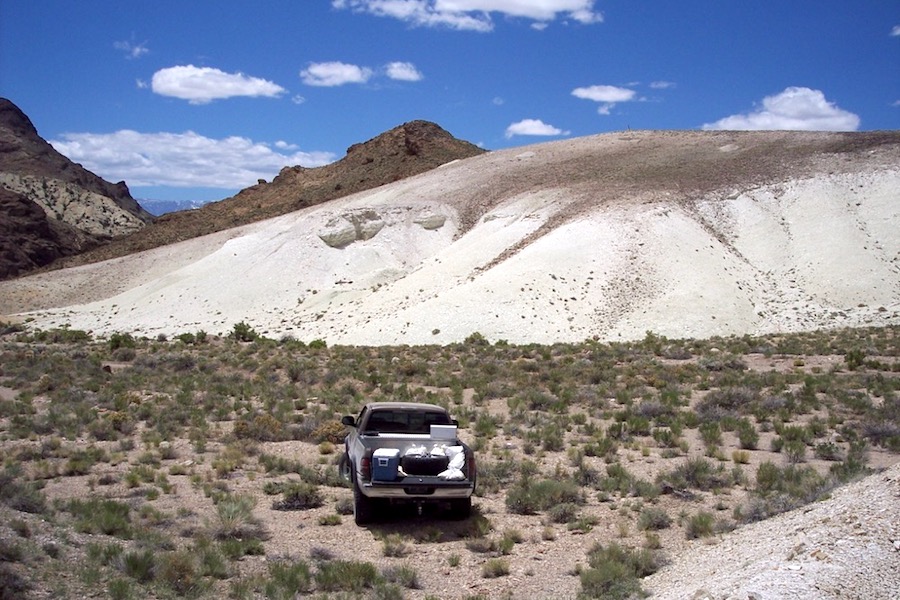

The Rhyolite Ridge lithium-boron project in Nevada. (Image courtesy of ioneer.)
The US Bureau of Land Management (BLM) cleared on Thursday one of the final regulatory hurdles for ioneer’s (ASX: INR) Rhyolite Ridge lithium mine in Nevada, a project that would be a key supplier of the electric vehicle battery metal to the local auto industry.

The proposed lithium mine, about 225 miles (362 km) north of Las Vegas, contains one of the largest sources of lithium in North America. It could produce enough of the metal to power nearly 370,000 electric vehicles per year.
The agency’s decision follows a review process spanning over more than six years, and is part of Washington’s ongoing efforts to strengthen domestic critical minerals production and counteract China’s dominance of battery mentals. If granted final approval, Rhyolite Ridge would be the first lithium project permitted by the Joe Biden administration.
Shares in ioneer soared on the news, closing more than 15% higher to A$0.19 each on the Australian Stock Exchange (ASX). This leaves the company with a market capitalization of A$432.42 million ($294m).
The Rhyolite Ridge asset is also home to a rare flower, which has given conservation groups arguments to oppose the project, highlighting the complexity of trying to balance the protection of biodiversity and the need for metals to reduce the globe’s emissions.
Rhyolite Ridge is the only known lithium-boron deposit in North America and one of only two known such deposits in the world.
BLM officials said they worked closely with local, state and tribal governments on the environmental review announced Thursday.
Once it is published in the Federal Register, the public will have 30 days to submit comments. After the review period, the BLM will publish a final environment impact analysis, with a final decision — essentially a mining permit — to be issued within 30 days after that.
The Rhyolite Ridge lithium project “represents another step by the Biden-Harris administration to support the responsible, domestic development of critical minerals to power the clean energy economy,” the BLM said in statement.
Laura Daniel-Davis, Acting Deputy Secretary of the Interior, noted the proposed mine exemplifies what can be achieved when industry, states, tribes, and stakeholders collaborate to ensure prompt consideration and adaptation of projects that meet the US energy needs while respecting cultural and environmentally sensitive areas.
Breaking away from imports
Lithium is one of 50 minerals identified as critical by the U.S. Geological Survey, which considers importance of the mineral to the country’s economy and national security and the vulnerability of its supply chains. Lithium batteries are used extensively in the growing market for portable electronic devices, vehicles, and grid storage applications.
The US government has already backed another lithium mine in Nevada. Lithium Americas’ (TSX: LAC) (NYSE: LAC) Thacker Pass project is targeting 80,000 tonnes per annum of battery-quality lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) production capacity in two phases of 40,000 tonnes. Phase 1 production is expected to commence in the second half of 2026. The project is expected to create 1,000 jobs during construction and 500 jobs during operations.
US mining policy is currently administered through multiple agencies, including the BLM, the Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Mine Safety and Health Administration.





.png)








