Learn from past to protect oceans

History holds valuable lessons—and stark warnings—about how to manage fisheries and other ocean resources, a new study says.
Researchers examined 20 historical examples of fisheries and aquaculture (fish farming), dating from 40 to 800 years ago.The study, led by the universities of Exeter, Hull and Boston, found consistent patterns that resulted in so-called "blue growth"—the development of sustainable ocean economies that benefitted whole communities.
It also noted common "recipes for failure"—and the authors say these offer grave warnings for today.
"Our aim was to see if we could learn from past successes and failures," said Dr. Ruth Thurstan, of the Centre for Ecology and Conservation at the University of Exeter's Penryn Campus in Cornwall.
"We often assume our problems are new, but a look at the past shows societies have faced similar issues before—though many of our challenges today are on a bigger scale.
"Some past societies ultimately failed at blue growth, while others succeeded in balancing economic growth, social equity and sustainability for varying lengths of time."
Dr. Thurstan added: "In basic terms, success came when societies managed to achieve fair—rather than unlimited or open—access to resources, and when they were responsive to change.
"Basing decisions on evidence, getting all parties involved and planning for the long-term were also key.
"Failure occurred when short-term gains were prioritised over long-term sustainability."
Dr. Bryony Caswell, of the School of Geography, Geology and the Environment at the University of Hull said: "Worryingly, the recipes for success that we discovered are rarely included in even the most advanced blue growth agendas today.
"The seas are destined to play an ever-more vital role in food security. If we don't take this chance to learn from history, we may be condemning ourselves to repeating past mistakes."
The study, by an international team of 28 historians, environmental scientists and marine ecologists, looked at examples from around the world.
These included:
- Galway Bay in Ireland where, before the 1850s, community-based management led to equitable access and sustainable management of fish stocks. In the 1850s, trawlers from England arrived. Locally agreed rules were ignored and fish stocks were over-exploited.
- In the Lagoon of Venice, Italy, local regulations achieved a "balance" between the economic freedom of citizens and the protection of shared resources, lasting from the 12th to the 18th Century. After that, political instability and growing demand for food led to regulations being scrapped, resulting in over-exploitation.
- In Japan, access to seaweed resources that benefitted the majority rather than a minority of people, use of traditional knowledge systems and enhanced seaweed cultivation techniques, helped achieve a balance between market demand and ecological sustainability from the 1600s onwards.
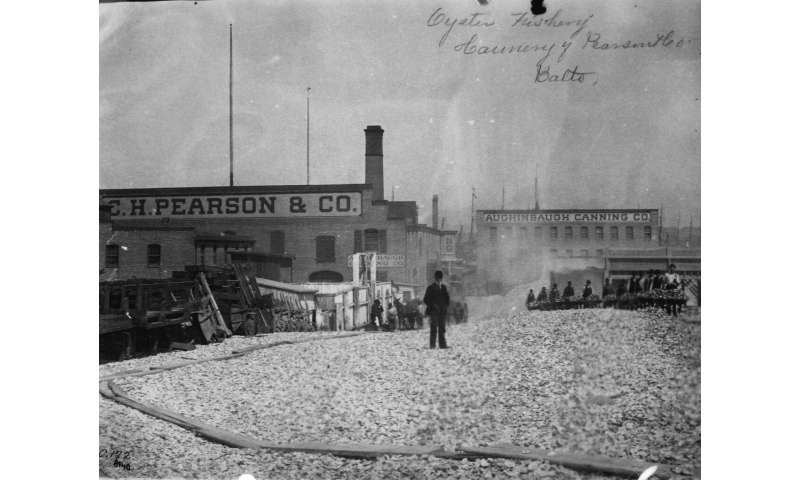
- In the east USA, two centuries of over-exploitation and worsening water quality led to a 20th Century collapse of once-widespread oyster reefs. While oyster production today is still far lower than historical levels, a growing appreciation of their benefits to coastal ecosystems has led to large-scale efforts by local communities to restore oyster reefs.
"The question is, can our modern societies achieve blue growth rather than exploiting and depleting our oceans?" said Dr. Emily Klein, of the Frederick S. Pardee Center for the Study of the Longer-Range Future, Boston University.
"History shows us that there are ways to balance sustainability, social equity and economic growth.
"It is difficult, but we believe there are opportunities to make it happen—especially if we can learn from the past."
The paper, published in the journal Fish and Fisheries, is entitled: "Something old, something new: Historical perspectives provide lessons for blue growth agendas."
More information: Bryony A. Caswell et al, Something old, something new: Historical perspectives provide lessons for blue growth agendas, Fish and Fisheries (2020). DOI: 10.1111/faf.12460
Journal information: Fish and Fisheries