US prosecutors say plots to assassinate Sikh leaders were part of a campaign of planned killings
The attack plans were foiled, prosecutors said, because the hitman was actually an undercover U.S. agent.

NEW YORK (AP) — A foiled plot to assassinate a prominent Sikh separatist leader in New York, just days after another activist’s killing, was meant to precede a string of other politically motivated murders in the United States and Canada, according to U.S. prosecutors.
In electronic communications and audio and video calls secretly recorded or obtained by U.S. law enforcement, organizers of the plot talked last spring about plans to kill someone in California and at least three other people in Canada, in addition to the victim in New York, according to an indictment unsealed Wednesday.
The goal was to kill at least four people in the two countries by June 29, and then more after that, prosecutors contend.
After Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a Sikh activist who had been exiled from India, was shot and killed outside a cultural center in Surrey, British Columbia, on June 18, one of the men charged with orchestrating the planned assassinations told a person he had hired as a hitman that he should act urgently to kill another activist, Gurpatwant Singh Pannun.
“We have so many targets,” Nikhil Gupta said in a recorded audio call, according to the indictment. “We have so many targets. But the good news is this, the good news is this: Now no need to wait.”
He urged the hitman to act quickly because Pannun, a U.S. citizen living in New York, would likely be more cautious after Nijjar’s slaying.
“We got the go-ahead to go anytime, even today, tomorrow — as early as possible,” he told a go-between as he instructed the hitman to kill Pannun even if there were other people with him. “Put everyone down,” he said, according to the indictment.
The attack plans were foiled, prosecutors said, because the hitman was actually an undercover U.S. agent.
The U.S. attorney in Manhattan announced charges Wednesday against Gupta, and said in court papers that the plot to kill Pannun was directed by an official in the Indian government. That government official was not charged in the indictment or identified by name, but the court filing described him as a “senior field officer” with responsibilities in security management and intelligence.
Indian officials have denied any complicity in Nijjar’s slaying. External Affairs Ministry spokesperson Arindam Bagchi said Wednesday that the Indian government had set up a high-level inquiry after U.S. authorities raised concerns about the plot to kill Pannun.
Court filings revealed that even before Nijjar’s killing in Canada, U.S. law enforcement officials had become aware of a plot against activists who were advocating for the secession from India of the northern Punjab state, where Sikhs are a majority.
U.S. officials said they began investigating when Gupta, in his search for a hitman, contacted a narcotics trafficker who turned out to be a Drug Enforcement Administration informant.
Over the ensuing weeks, the pair communicated by phone, video and text messages, eventually looping in their hired assassin — the undercover agent.
The Indian government official told Gupta that he had a target in New York and a target in California, the indictment said. They ultimately settled on a $100,000 price and by June 3, Gupta was urging his criminal contact in America to “finish him brother, finish him, don’t take too much time …. push these guys, push these guys … finish the job.”
During a June 9 call, Gupta told the narcotics trafficker that the murder of Pannun would change the hitman’s life because “we will give more bigger job more, more job every month, every month 2-3 job,” according to the indictment.
It was unclear from the indictment whether U.S. authorities had learned anything about the specific plan to kill Nijjar before his ambush on June 18.
The indictment portrayed Gupta as boasting that he and his associates in India were behind both the Canadian and New York assassination plots. He allegedly told the Drug Enforcement Administration informant on June 12 that there was a “big target” in Canada and on June 16 told him: “We are doing their job, brother. We are doing their New York (and) Canada (job),” referring to individuals directing the plots from India.
After Nijjar was killed, Gupta told the informant that Nijjar was the target he had mentioned as the potential Canadian “job” and added: “We didn’t give to (the undercover agent) this job, so some other guy did this job … in Canada.”
On June 30, Gupta was arrested in the Czech Republic at the request of the United States after arriving there on a trip from India. Federal authorities have not said when he might be brought to the United States to face murder-for-hire and conspiracy charges. It was unclear who would provide legal representation if he arrives in the U.S.
Pannun told The Associated Press in an interview Wednesday that he will continue his work.
“They will kill me. But I don’t fear the death,” he said.
He mocked India’s claim that it is conducting its own investigation into the assassination plots.
“The only thing, I think, (the) Indian government is going to investigate (is) why their hitman could not kill one person. That’s what they will be investigating,” he said.
Pannun said he rejects the Indian government’s decision to label him a terrorist.
“We are the one who are fighting India’s violence with the words. We are the one who are fighting India’s bullets with the ballot,” he said. “They are giving money, hundreds of thousands, to kill me. Let the world decide who is terrorist and who is not a terrorist.”
Some international affairs experts told the AP that it was unlikely the incidents would seriously damage the relationship between the U.S. and India.
”In most cases, if Washington accuses a foreign government of staging an assassination on its soil, U.S. relations with that government would plunge into deep crisis,” said Michael Kugelman, director of the Wilson Centre’s South Asia institute. “But the relationship with India is a special case. Trust and goodwill are baked into the relationship, thanks to rapidly expanding cooperation and increasingly convergent interests.”
Derek Grossman, Indo-Pacific analyst at the Rand Corp., said the Biden administration has demonstrated that it is prioritizing the need to leverage India as part of its strategy to counter Chinese power.
“I think publicizing the details of the thwarted plot will have very little, if any, impact on the deepening U.S.-India strategic partnership,” he said.
___
Associated Press writers Krutika Pathi in New Delhi and Ted Shaffrey in New York contributed to this report.
The makers of the unconventional superhero film ‘American Sikh’
Sikh Captain America — a turbaned version of the Marvel comic book hero — hits the big screen.
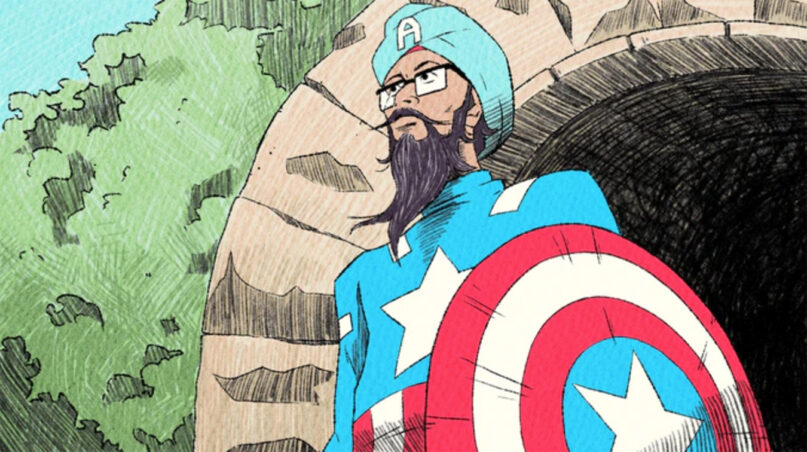

(RNS) — Once the idea for Sikh Captain America — a turbaned, bearded version of the Marvel comic hero — was born, it took more than a year for him to appear on the streets of his native New York City.
The creation of Vishavjit Singh, a writer and illustrator in Harlem, and the photographer Fiona Aboud, who was working on a photo project, “Sikhs: An American Portrait,” the character is a social experiment about what it means to be American, and to be Sikh in America. Now, it is also a short animated film by Singh and Ryan Westra that recently premiered at the Tribeca Film Festival.
The film tells the true story of Singh, 52, who, besides inventing Sikhtoons.com in the face of anti-Sikh bigotry after 9/11, is a performance artist and diversity speaker. After a lifetime of facing prejudice, self-doubt and violence, his animated self, as in life, finally finds acceptance in a superhero costume. He first drew Captain America in a turban and beard in 2011, but it took almost a year after Aboud discovered the character to convince Singh to step out as Sikh Captain America on the streets, where his mission is to tackle bias and intolerance, powered by his humor, turban, beard and storytelling prowess.
I had the opportunity to speak with Singh and Westra to discuss the what, why and how of “American Sikh.” This interview has been adapted for clarity and concision.
How did this film come together?
RW: In 2014, as my very last student project in film school, I happened to be assigned to do a live action documentary about Vishavjit’s work as Sikh Captain America. While shooting that project (“Red, White, and Beard”), I was so impressed by Vishavjit’s ability to inspire people to open up about their stereotypes and biases in a positive way. Yet as we wrapped the shoot, I watched a stranger on the street call Vishavjit “Osama bin Laden,” moments after changing out of his superhero costume.
It was a shocking juxtaposition to witness, and it made Vishavjit’s work even more impactful to me. Ever since then, I had been interested in working with Vishavjit again on a more in-depth and ambitious project. In 2019, I reached out with the idea of doing an animated short about his life and, more broadly, the struggles that the Sikh community has gone through.
What do you hope the film will accomplish?
RW: In a recent interview, our incredible executive producer, Vikas Khanna, had a beautiful answer to this question. He said, “I believe that the answer to hate cannot be hate.” With the difficult times we are facing right now around the world, I think now, more than ever, is a perfect time for us to gain greater understanding, empathy and compassion for those around us.
VS: I’ve spent years traveling around the nation visiting schools, companies and government agencies to share my story and create a space for conversations about identity, bias, vulnerability and transformative power of art. I hope in amplifying this message via an animated film, we can encourage others to do the same with their story.
I hope this film opens doors for the most underrepresented and misrepresented stories to be shared across American media, cultural and entertainment landscape.
RW: Unfortunately, especially since 9/11, turbans and beards have been villainized and portrayed as un-American in the media. Sikh Captain America challenges those stereotypes in a lighthearted, creative and familiar way. Our hope is that this image sticks with people, and they are able to walk away with a greater empathy for all Americans who, as Vishavjit says, “look a little different.”
What’s been most gratifying so far now that audiences have seen the movie?
VS: Hearing feedback from people from varying backgrounds about connections they find with my story.
RW: It’s extremely exciting to be working with Vishavjit on such a historic project. Never has an American Sikh story reached this level of prominence. With so little representation in the media, it’s exciting that we have the privilege of introducing Vishavjit’s beautiful religion and work to so many for the first time.
How does this film depict Sikh characters differently than other media?
VS: Much of the Sikh media I’ve seen has been created by Sikhs for Sikhs. This film is meant for people who maybe have had little to no experience with Sikhs. It’s created with a national audience in mind and tells a story that is relatable to many Americans, not just Sikhs.
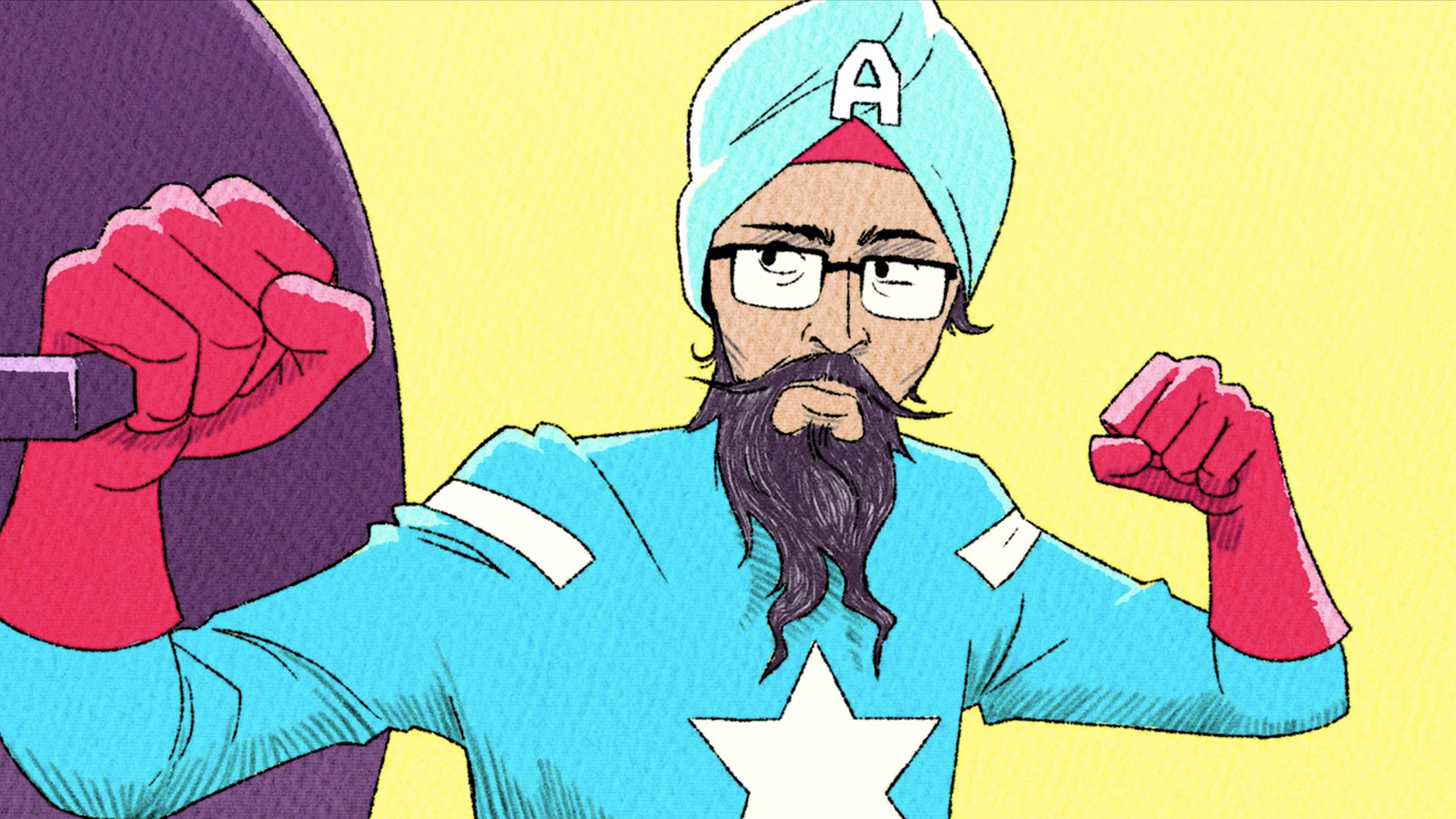
A still from “American Sikh” depicting Vishavjit Singh as his Captain America persona. Image via Kickstarter
What were some of the biggest challenges to pulling this story together?
VS: With animation being extremely expensive, we had a lot of back and forth narrowing down the few key chapters of my life to tell the most compelling and concise story. There were 30 different cuts of the film that we user-tested on Ryan’s friends and family who knew nothing about me or Sikhism at all. This helped us pick the most impactful moments. But there are a few poignant moments and experiences that did not make it into the final version of the film that I typically include in my life story.
Did you ever doubt that animation was the right medium?
VS: We knew there are two major tragedies that are part of this story — the 1984 genocidal massacre of Sikhs in India, which I survived, and the post-9/11 hate/bias crime wave, which targeted many Sikhs, including me. One of the main reasons we chose animation was it allowed us to showcase these tragedies without overwhelming the viewer.
RW: We didn’t want the tone to focus too much on tragedy, but rather leave the audience feeling inspired and encouraged at the end.
Where do you go from here?
VS: The “American Sikh” has had an amazing journey on the film festival circuit. We always wanted this film to be accessible to American and global audiences. Ryan and I are also writing pitches for full-length films and series. We would love to tell a more comprehensive American story with a Sikh lead character.
RW: We are interested in working together again on a longer and more ambitious project featuring a Sikh lead character. We want to make Sikh characters a part of the bigger cultural landscape we see in all media — not just exclusively Sikh stories.


No comments:
Post a Comment