Fukushima’s Contaminated Wastewater Could Be Too Risky to Dump in the Ocean
Dharna Noor
Yesterday 5:10PM
•
Filed to:FUKUSHIMA
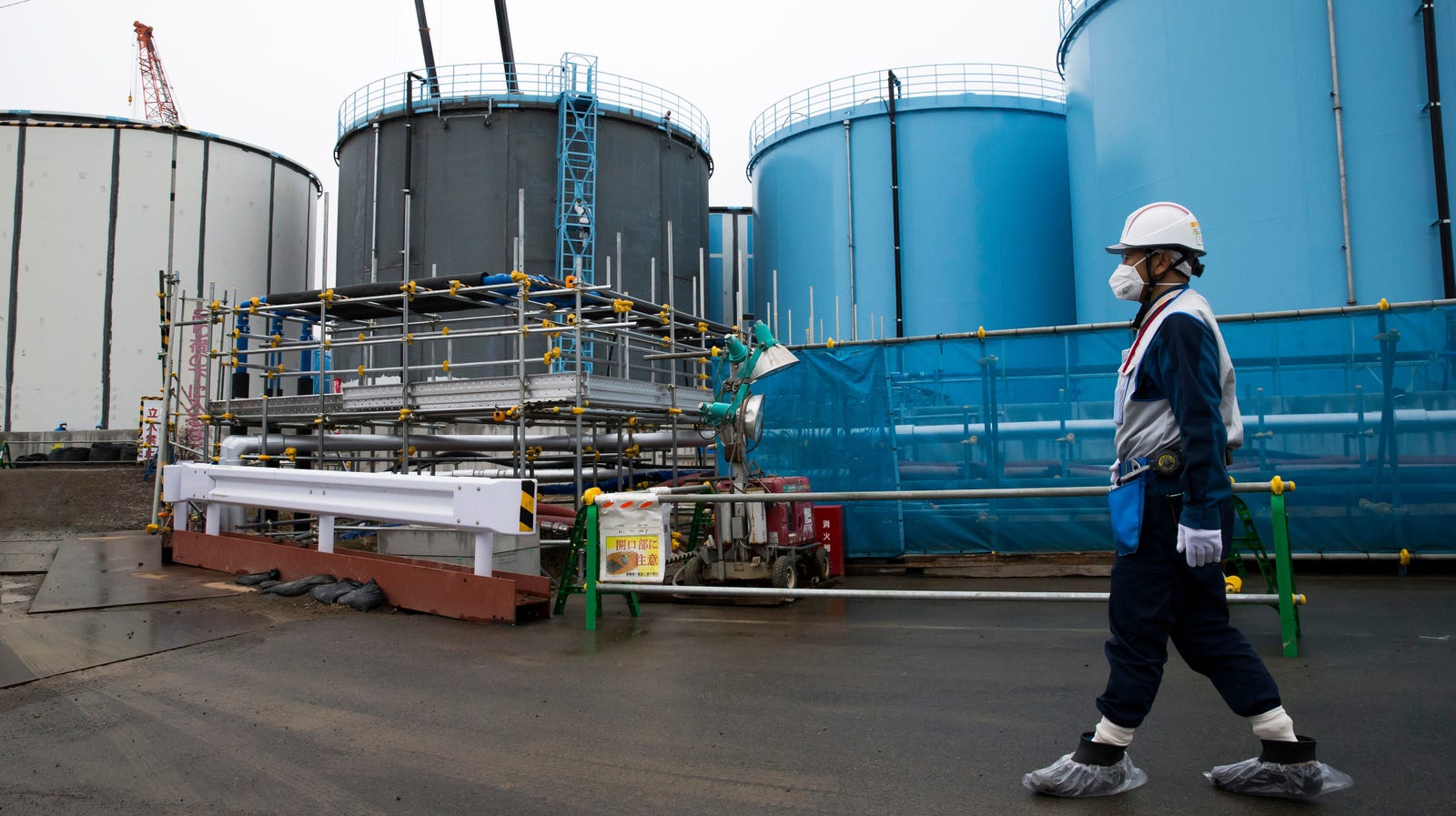

Almost a decade ago, the Tohoku-oki earthquake and tsunami triggered an explosion at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, causing the most severe nuclear accident since Chernobyl and releasing an unprecedented amount of radioactive contamination in the ocean. In the years since, there’s been a drawn out cleanup process, and water radiation levels around the plant have fallen to safe levels everywhere except for in the areas closest to the now-closed plant. But as a study from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution published in Science on Thursday shows, there’s another growing hazard: contaminated wastewater.
Radioactive cooling water is leaking out of the the melted-down nuclear reactors and mixing with the groundwater there. In order to prevent the groundwater from leaking into the ocean, the water is pumped into more than 1,000 tanks. Using sophisticated cleaning processes, workers have been able to remove some of this contamination and divert groundwater flows, reducing the amount of water that must be collected each day. But those tanks are filling up, and some Japanese officials have suggested that the water should dumped into the ocean to free up space.
The water in the tanks goes through an advanced treatment system to remove many radioactive isotopes. The Japanese utility company TEPCO, which is handling the cleanup processes, claims that these processes remove all radioactive particles from the water except tritium, an isotope of hydrogen which is nearly impossible remove but is considered to be relatively harmless. It decays in about 12 years, which is faster than other isotopes, is not easily absorbed by marine life, and is not as damaging to living tissue as other forms of radiation.
But according to the new study, that’s not the only radioactive contaminant left in the tanks. By examining TEPCO’s own 2018 data, WHOI researcher Ken Buesseler found that other isotopes remain in the treated wastewater, including carbon-14, cobalt-60, and strontium-90. He found these particles all take much longer to decay than tritium, and that fish and marine organisms absorb them comparatively easily.
Nuclear Fusion Will Not Save Us
Last week, construction kicked off on the world’s largest experimental nuclear fusion reactor. It…Read more
 Top ArticlesApple's App Store Policies Are Reportedly Keeping Microsoft'sProject xCloud off iOS
Top ArticlesApple's App Store Policies Are Reportedly Keeping Microsoft'sProject xCloud off iOS



 READ MORE
READ MORESKIP AD
“[This] means they could be potentially hazardous to humans and the environment for much longer and in more complex ways than tritium,” the study says.
Though TEPCO’s data shows there is far less of these contaminants in the wastewater tanks than tritium, Buesseler notes that their levels vary widely from tank to tank, and that “more than 70% of the tanks would need secondary treatment to reduce concentrations below that required by law for their release.”
The study says we don’t currently have a good idea of how those more dangerous isotopes would behave in the water. We can’t assume they will behave the same way tritium does in the ocean because they have such different properties. And since there are different levels of each isotope in each different tank, each tank will need its own assessment.
“To assess the consequences of the tank releases, a full accounting after any secondary treatments of what isotopes are left in each tank is needed,” the study said.
Buesseler also calls for an analysis of what other contaminants could be in the tanks, such as plutonium. Even though it wasn’t reported in high amounts in the atmosphere in 2011, recent research shows it may have been dispersed when the explosion occurred. Buesseler fears it may also be present in the cooling waters being used at the plant. That points to the need to take a fuller account of the wastewater tanks before anything is done to dump them in the ocean.
“The first step is to clean up those additional radioactive contaminants that remain in the tanks, and then make plans based on what remains,” he said in a statement. “Any option that involves ocean releases would need independent groups keeping track of all of the potential contaminants in seawater, the seafloor, and marine life.”
Many Japanese municipalities have been pushing the government to reconsider its ocean dumping plans and opt to find a long-term storage solution instead, which makes sense, considering exposure to radioactive isotopes can cause myriad health problems to people. It could also hurt marine life, which could have a devastating impact on fishing economies and on ecosystems.
“The health of the ocean—and the livelihoods of countless people—rely on this being done right,” said Buesseler.
Dharna Noor
PostsTwitter
Staff writer, Earther
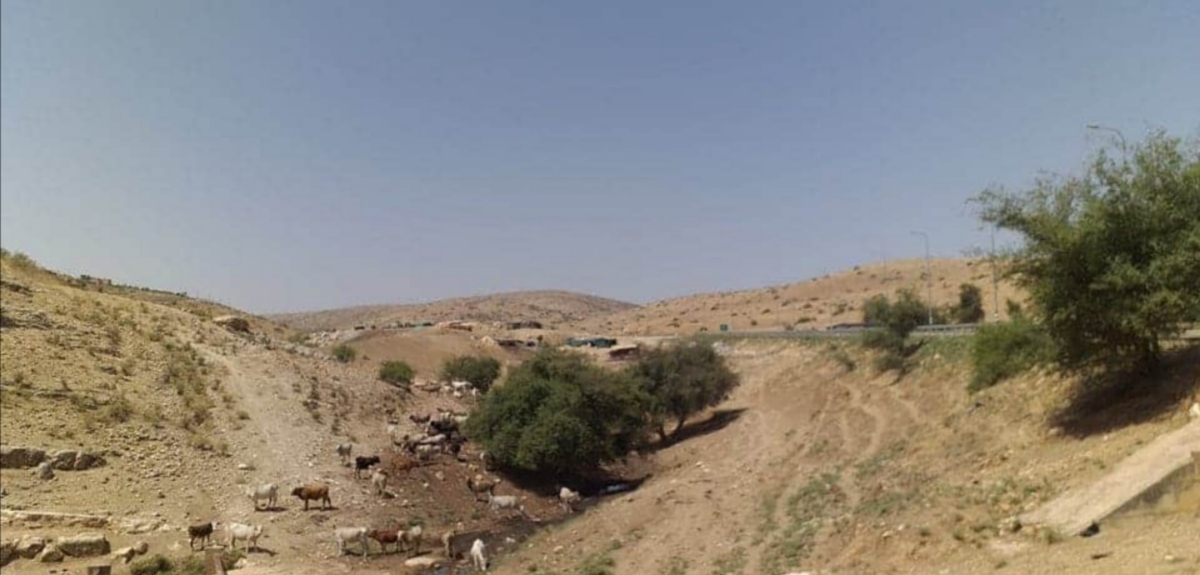








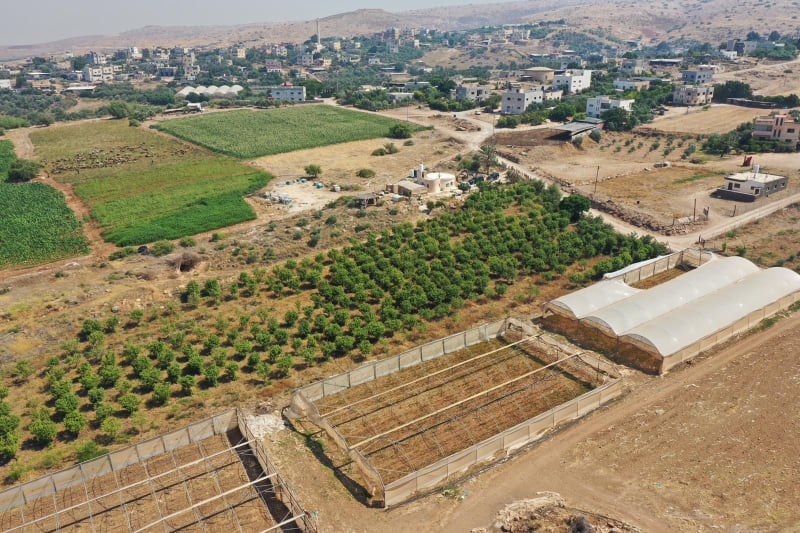
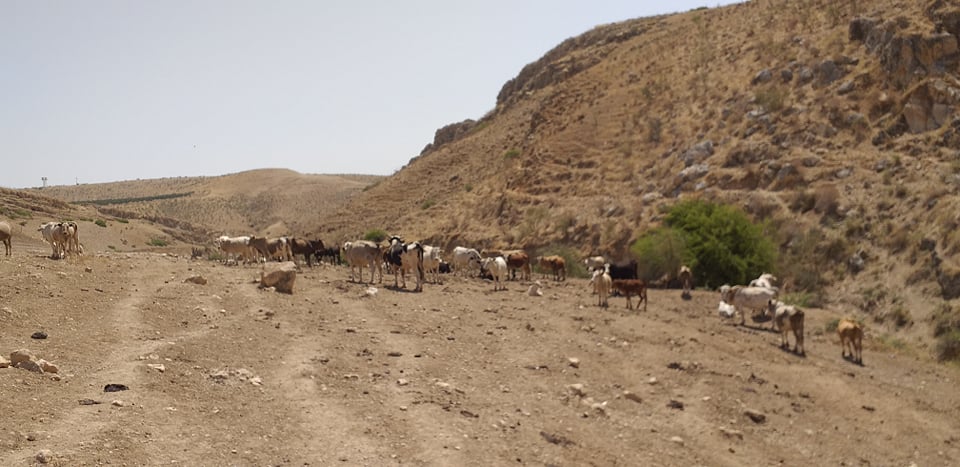
 Ein al-Hilweh, north of the Jordan Valley, is an empty area. There is a water spring there where Palestinians come to provide water for their flock. The Israeli military stated the area must be used for military training purposes. It is forbidden for sheep and people to enter the area now.SIREEN KHUDAIRI
Ein al-Hilweh, north of the Jordan Valley, is an empty area. There is a water spring there where Palestinians come to provide water for their flock. The Israeli military stated the area must be used for military training purposes. It is forbidden for sheep and people to enter the area now.SIREEN KHUDAIRI


