The South American country of Guyana has recently emerged as a world-recognized oil-producing nation. This occurred due to ExxonMobil’s string of world-class discoveries in offshore Guyana, starting with the 2015 Liza-1 wildcat well, drilled 118 miles northeast of the capital, Georgetown, in the 6.6 million-acre Stabroek Block. Big Oil is pouring billions of dollars into Guyana, an impoverished country of less than one million, now among the world’s top offshore drilling locations. Ongoing exploration and development will further boost production, enabling the former British colony to pump over two million barrels per day by 2030. This will make Guyana South America’s second-largest oil producer and a leading petroleum exporter.
U.S. energy supermajor Exxon is ideally placed to benefit from Guyana’s mega oil boom, having secured extremely favorable terms for its holding in the prolific Stabroek Block. The supermajor was an early mover in Guyana, which saw i,t along with partners Hess and CNOOC acquire extremely favorable terms for the exploration and development of the Stabroek Block. Exxon, which controls 45% of the Stabroek Block, is the operator while Hess and CNOOC hold working interests of 30% and 25% respectively. Since July 2025, another U.S. supermajor, Chevron, has entered the Stabroek Block, acquiring Hess’s 30% working interest in a controversial $53 billion all-stock deal. This acquisition followed two years of arbitration initiated by Exxon.
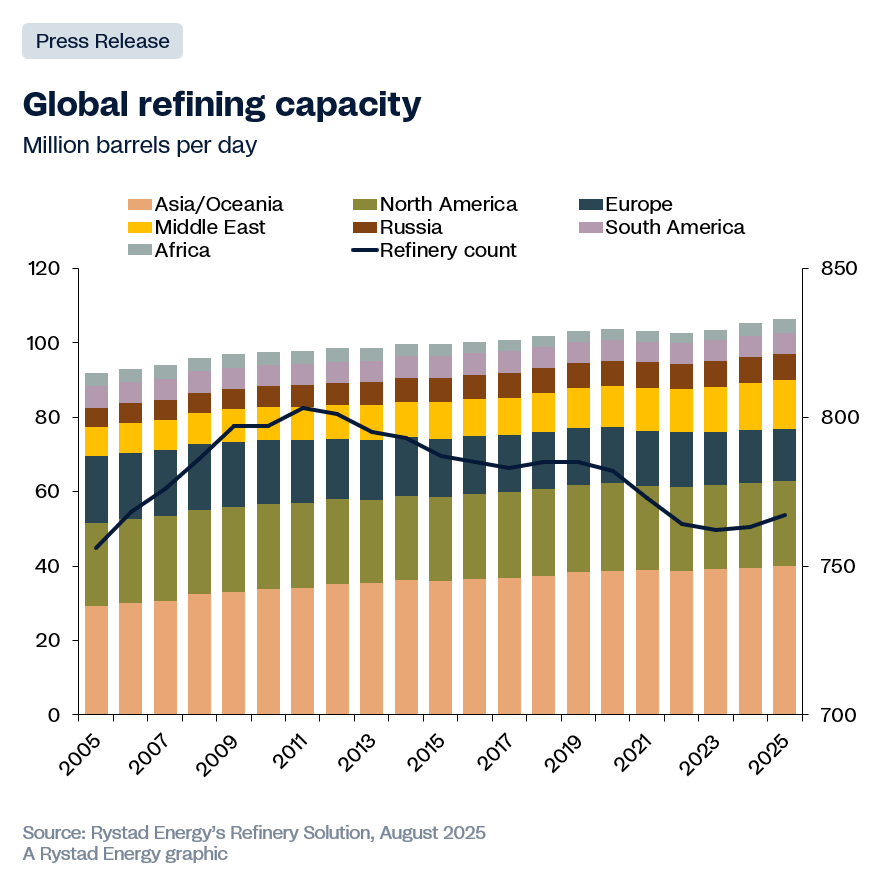
Chevron’s desire to acquire a substantial stake in the 6.6 million-acre Stabroek Block is easily understandable. Since 2015, Exxon has made over thirty major oil discoveries, leading to estimates that the petroleum acreage is believed to contain nearly 12 billion barrels of crude oil, placing the Stabroek Block among South America's most prolific and promising offshore acreage. Not only are recoverable oil resources growing at a solid rate, but production is also soaring to record highs. Since the first floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) vessel, Liza Destiny, commenced operations, petroleum output has roared ever-higher to a notable 677,000 barrels per day, according to official government data. This makes Guyana South America’s fifth-largest oil producer.
The oil being lifted from the Stabroek Block is particularly attractive to foreign energy investors because it is light and sweet with a low carbon footprint. Exxon’s petroleum assay shows Liza crude oil is light with an API gravity of 32 degrees and sulfur content of 0.58%. This makes it lighter than the Brent international benchmark, which has an API gravity of 38 degrees, although Liza crude is slightly more sour. High-quality light sweet crude oil is easier, cheaper and more profitable to refine into the premium low-emission fuels demanded in a world where greenhouse gas emissions are top of mind and governments are focused on reducing the carbon footprint.
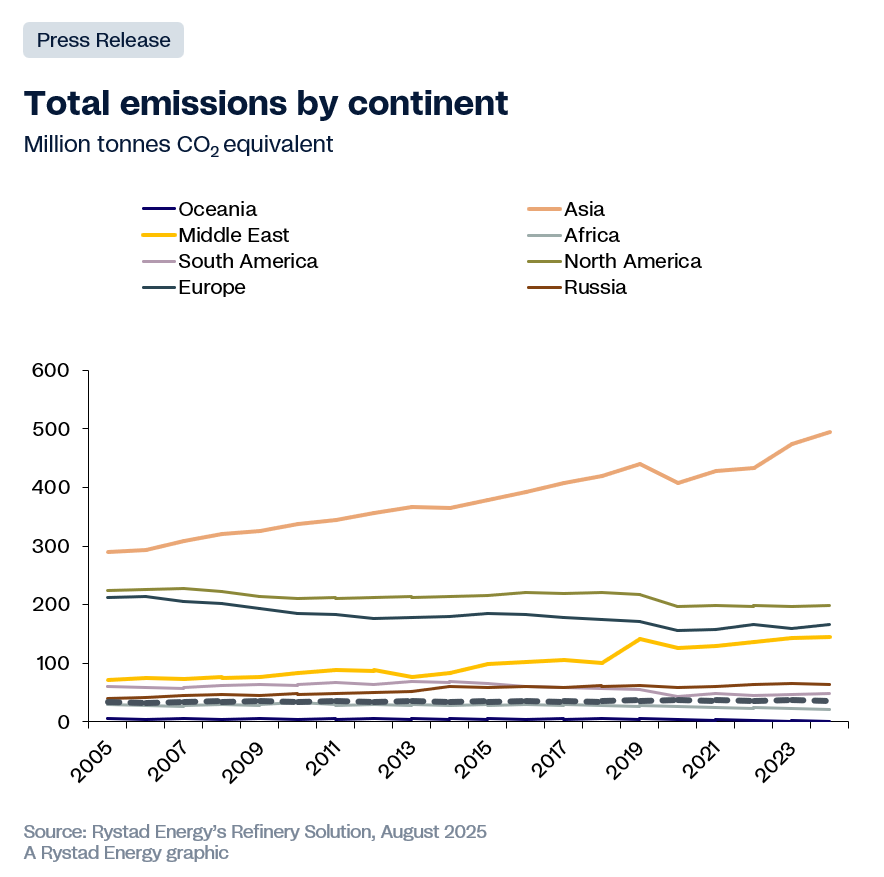
The greenhouse gas emissions associated with oil extraction in Guyana are lower than the global average and among the lowest in South America, which is a particularly appealing attribute in the current operating environment. Indeed, there is considerable pressure on Big Oil to make its operations carbon-neutral. In 2022, Exxon introduced a plan to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions for operated assets by 2050. At the same time, Chevron is focused on reducing its operational carbon footprint by securing assets with low greenhouse gas emissions. This is another reason for Chevron’s decision to acquire Hess, which enabled the supermajor to secure a 30% stake in the Stabroek Block, one of the world's most promising offshore petroleum assets
Oil production in offshore Guyana remains lucrative, even as the world moves away from consuming fossil fuels. The former British colony is estimated to have an average break-even cost of $36 per barrel, making it one of the lower-cost jurisdictions in South America and globally. Indeed, even in the current low-price environment, with Brent trading at around $66.80 per barrel, the oil being lifted in Guyana is highly profitable to extract. This is particularly true in the Exxon-controlled Stabroek Block, where the breakeven cost is estimated to be as low as $30 per barrel or even lower.
Finally, the Exxon-led consortium, as early movers in Guyana, was able to secure extraordinarily favorable terms for the production sharing agreement (PSA) established for the Stabroek Block. Key among those terms is an industry-low royalty rate of just 2%, compared to 8% or more in other South American jurisdictions, along with the ability to deduct 75% of oil produced for cost recovery purposes and no corporate taxes. It is those contractual advantages that endow the 6.6 million-acre Stabroek Block with such a low breakeven price, making the oil acreage one of the jewels in Exxon’s crown and a highly lucrative oil asset to own. Exxon, as the dominant partner in the consortium and the block’s operator, benefits most from these characteristics.
There is tremendous upside ahead for the Houston-based supermajor. Production is poised to significantly grow once again with the fourth project in the Stabroek Block, the Yellowtail facility, coming online earlier this month. The ONE GUYANA FPSO will initially pump 250,000 barrels of crude oil per day, lifting Guayana’s total production to around 900,000 barrels per day. This will see the tiny South American nation, with a population of less than one million, become the continent’s second-largest oil producer, after Brazil, and rank among the world’s top 20 petroleum-producing countries. Notably, Yellowtail came online four months ahead of schedule, underscoring the significant resources Exxon is investing in developing the Stabroek Block, which is now a key growth driver for the supermajor.
There are three additional projects under development in the Stabroek Block. These are expected to become operational before the end of the decade. The fifth facility under construction is the $12.7 billion, 250,000-barrel-per-day Uaru project, which is expected to begin production in 2026 from an oilfield believed to contain over 800 million barrels of crude oil. Then there is the Whiptail development, also costing $12.7 billion, which is expected to commence operations in 2027, adding a further 250,000 barrels daily to Guyana’s oil output. The seventh is the Hammerhead project, which is scheduled to start lifting crude oil in 2029. This project will be smaller than previous ones, with production expected to range from 120,000 to 180,000 barrels per day from 30 wells. Exxon estimates that Guyana’s petroleum output will reach 1.4 million barrels per day.
The completion of those projects will solidify Guyana’s position as the world's newest petrostate, making it the seventeenth-largest producer globally, ahead of OPEC member Algeria and behind Nigeria. It will also confirm the country’s position as South America’s second-largest oil producer while boosting Exxon’s petroleum output, revenue and profitability. Even after the completion of seven facilities, there is considerable upside ahead in the Stabroek Block. Data indicates that more significant oil discoveries will be made. The most recent being the Bluefin discovery announced in March 2024, where the well was drilled to a depth of 197 feet (60 meters) to the southeast of the Sailfin-1 discovery. Exxon’s 2025 drilling campaign involves drilling two exploration wells, Hamlet-1 and Lukanani-2, along with 30 development wells to support the Uaru and Whiptail projects.
Significant volumes of capital are flowing into offshore Guyana as Exxon and its partners develop the Stabroek Block. The impoverished South American country’s oil resources, production, and ultimately, oil revenues will continue to grow as Guyana’s oil boom remains in its early stages, illustrating the considerable opportunities that still exist for Exxon to build low-cost petroleum reserves and production. This delivers a significant financial benefit for Exxon. The supermajor’s non-U.S. upstream income for the first half of 2025 grew nearly 2% year over year because of rising production from Guyana, although softer oil prices weighed heavily on Exxon’s bottom line.
By Matthew Smith for Oilprice.com

_97940_33341.jpg)
_66735.jpg)


_36120.jpg)

_96509.jpg)
