Christy Somos
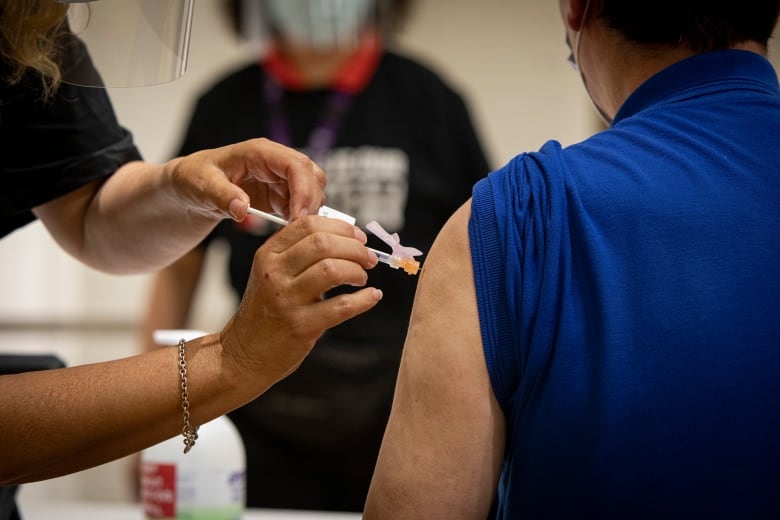
TORONTO -- The Canadian Medical Association (CMA) and the Canadian Nurses Association (CNA) are calling for COVID-19 vaccines to be mandatory for health-care workers.
In a news release, the CMA and CNA stated jointly that in the face of the highly contagious COVID-19 variants and the plateauing of Canada’s vaccination rate, the mandatory vaccination of health-care workers is “an additional measure to protect patients, the health workforce and health-care system capacity.”
“What we're seeing is that these variants of the COVID virus are much more contagious and that makes the cry for vaccination even stronger,” said CMA president Dr. Ann Collins in a telephone interview with CTVNews.ca Tuesday. “And at the same time, we're seeing a plateauing in vaccine uptake and we know that vaccines are what are going to get us through and out of this pandemic. So we felt it was important, along with our nursing partners, to bring this forward.”
Collins said that so far, reaction to the announcement has been positive because the public recognizes that the organizations are “putting patients at the centre of their call-to-action.”
The organizations are also calling on all levels of government and employers to implement strategies to lower barriers to vaccine access, the statement says.
“While vaccines are readily available across Canada, we recognize that the history of inequity within the health-care system impacts trust,” the statement continues. “Therefore, governments and employers must continue to support and address vaccine hesitancy and system barriers to achieving the highest rate of vaccination among the public and health workforce.”
Health-care workers were among the first to receive COVID-19 vaccines to protect them and their patients from infection and to prevent outbreaks, but specific data on how many chose to get inoculated is not readily available.
As of Tuesday, 67 per cent of Canada’s eligible population has been fully vaccinated against COVID-19.
Requiring vaccinations as a condition of employment in health-care settings like hospitals and long-term care homes is not a new phenomenon, as many workplaces require doctors, nurses and support staff to be fully immunized against diseases like tetanus and hepatitis B.
In Europe, France has ordered all health-care workers to get vaccinated by mid- September, with Greece and Italy following suit with their own mandates in the face of the Delta variant driving COVID-19 cases up.
Ontario Premier Doug Ford told reporters in July that health-care workers have a “constitutional right” to opt out of vaccination, saying he doesn’t “believe in forcing anyone to get a vaccination that doesn’t want it.”
Alberta Premier Jason Kenney also flatly dismissed the idea of mandatory vaccines, going so far as to amend Alberta’s Public Health Act and removing a century-old order that allows the government to force people to be vaccinated.
“We have an incredibly powerful tool at our disposal to combat this virus and its variants,” Collins said. “We should be using everything that we can to get people vaccinated.”

A woman wears a face mask as she walks by a COVID-19 vaccination sign in Montreal, Sunday, August 1, 2021, as the COVID-19 pandemic continues in Canada and around the world. (THE CANADIAN PRESS/Graham Hughes)