Sizewell C Nuclear Project Secures £38 Billion Backing
- The Sizewell C nuclear power station project has been approved with a £38 billion investment, including a 44.9% initial stake from the UK government.
- Key investors in Sizewell C include Canadian investment fund La Caisse, British Gas owner Centrica, French state companies like EDF, and UK-based Amber Infrastructure and INPP.
- The project is anticipated to create 10,000 jobs, generate £2 billion in annual savings for the low-carbon electricity system, and benefit approximately 3,500 businesses.
The UK government signed on Tuesday the final investment decision to build the $51-billion Sizewell C nuclear power plant, which will help Britain generate more low-carbon electricity.
The final investment decision was made possible after new investors joined the government and French energy giant EDF. The UK will have an initial 44.9% stake to become the single biggest equity shareholder in the project. The other shareholders include La Caisse with 20%, UK energy group Centrica with 15%, and Amber Infrastructure with an initial 7.6%. EDF is taking a 12.5% stake in the project, as well as a proposed $6.7 billion (£5 billion) debt guarantee from France’s export credit agency, Bpifrance Assurance Export, to back the company’s commercial bank loans.
The funding model spreads the around $51 billion (£38 billion) cost of constructing Sizewell C between consumers, taxpayers, and private investors, the government said, adding the model has been decided after the lessons learned from the Hinkley Point C project, which has racked up huge cost overruns.
“We’re delighted to welcome new investors alongside Government and EDF who, like our suppliers, have strong incentives to keep costs under control and ensure we deliver Sizewell C successfully for consumers and taxpayers,” Julia Pyke and Nigel Cann, Joint Managing Directors of Sizewell C, said today.
Sizewell C was initially proposed years ago by France’s EDF and China General Nuclear Power Group. However, the UK government bought out the Chinese group’s stake in 2022 amid concerns about China’s influence.
Sizewell C is the first British-owned nuclear power station to be announced in over three decades.
The UK government has already committed billions of UK pounds of investment in Sizewell C on the Suffolk Coast in east England, including $19.5 billion (£14.2 billion) announced in June to support the project.
The UK has been betting big on nuclear power in recent years to boost its energy security and help reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
Apart from major conventional nuclear power projects, the UK government is supporting Small Modular Reactors (SMR) technology development with competitions to unlock private finance, with a long-term ambition to bring forward one of the first SMR fleets in Europe.
By Tsvetana Paraskova for Oilprice.com
Sizewell C gets final go-ahead decision
_94956_15662.jpg)
The government confirmed it will take an initial 44.9% stake to become the single biggest equity shareholder in the project. Canadian investment fund La Caisse will have a 20% stake, British multinational energy and services company Centrica 15%, and international infrastructure asset manager Amber Infrastructure will have an initial 7.6% (with an option to acquire a further 2.4% from the government exercisable within 24 months of Revenue Commencement). France's EDF announced earlier this month that it will be taking a 12.5% take in the project.
France's export credit agency, Bpifrance Assurance Export earlier proposed a GBP5 billion debt guarantee to back EDF's commercial bank loans. Alongside this investment, the UK's National Wealth Fund - the government's principal investor and policy bank - is making its first investment in nuclear energy. It will provide the majority of the project's debt finance, working alongside Bpifrance Assurance Export, to help support the building of the power plant. The government said it is providing the National Wealth Fund with additional capital to facilitate this lending to Sizewell C.
A set of procedural steps will now begin which include finalising Sizewell C's economic licence. A final statutory decision by the Secretary of State will follow, after which Revenue Commencement will be declared and the transaction completed. Centrica said it expects Revenue Commencement to take place in the fourth quarter of 2025.
Centrica noted that its investment in the project includes an agreement in principle for an initial 20-year offtake agreement for its share of Sizewell C's electricity production, and for Centrica "to provide Sizewell C with a route to market services for additional volumes".
The final investment decision also unlocks financing for British nuclear energy by adopting the Regulated Asset Base funding model, which will see consumers contributing towards the cost of new nuclear power plants during the construction phase. Under the previous Contracts for Difference system developers finance the construction of a nuclear project and only begin receiving revenue when the power plant starts generating electricity.
The plan is for Sizewell C to feature two EPR reactors producing 3.2 GW of electricity, enough to power the equivalent of around six million homes for at least 60 years. It would be a similar design to the two-unit plant being built at Hinkley Point C in Somerset, with the aim of building it more quickly and at lower cost as a result of the experience gained from what is the first new nuclear construction project in the UK for about three decades.
"Sizewell C will cost consumers around GBP1 per month as an average over the duration of construction," Julia Pyke, Joint Managing Director of Sizewell C, said. "Once operational, the project could lead to savings of GBP2 billion a year across the electricity system.
"Our plan is to deliver Sizewell C at a capital cost of around GBP38 billion [in 2024 prices]. Our estimate is the result of very detailed scrutiny of costs at Hinkley Point C and long negotiations with our suppliers. It has been subject to third-party peer review and has been scrutinised by investors and lenders and has been subject to extensive due diligence as part of the financing process. A capital cost of GBP38 billion represents around 20% saving compared with Hinkley Point C and demonstrates the value of the UK's fleet approach."
Nigel Cann, Joint Managing Director of Sizewell C, added: "Any infrastructure project of this scale will face risks and potentially disruptive events outside of its control, as well as opportunities to reduce costs. Our supply chain is strongly incentivised to keep costs down and our investors will lose potential revenue if there are overruns."
Energy Secretary Ed Miliband said. "This government is making the investment needed to deliver a new golden age of nuclear, so we can end delays and free us from the ravages of the global fossil fuel markets to bring bills down for good."
The final investment decision for Sizewell C was welcomed by the UK's Nuclear Industry Association, with its CEO Tom Greatrex, saying: "Sizewell C will be the greatest and greenest single project in the UK's history, driving investment into our industrial heartlands and providing energy security for the rest of this century. This is money well spent, creating thousands upon thousands of good jobs for communities that need them most, cutting gas imports, and providing a more competitive foundation for our economy.
“The project crucially marks the first time the UK has approved a true replica nuclear power station. That is the best way to build faster and cheaper, and we must apply those lessons to a full programme. This moment has been a decade in the making, and we cannot wait that long for the next project."
Kansai considers Mihama site for new reactor
_49483.jpg)
Kansai noted that it announced in November 2010 its intention to begin a voluntary survey at the Mihama site for the construction of a new reactor to replace unit 1 there. However, the survey has been suspended since the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi plant in March 2011.
"However, we will now resume the voluntary on-site survey to evaluate the possibility to construct the successor plant of Mihama Nuclear Power Station, and as a preparation to move forward conducting such a survey, we will provide explanations to the local community," the company said.
Kansai said that the construction of new installations and the expansion and replacement of existing facilities is one of its goals under its Zero Carbon Vision 2050 initiative. "To achieve such goal, we consider it necessary to resume voluntary on-site surveys as part of the evaluation to decide whether the business to construct successor plants is feasible."
It said the survey at the Mihama site is aimed at evaluating whether it is possible to construct a new plant there "by understanding the geomorphic and geological characteristics of the site to ensure that it conforms with the new regulatory requirements".
It added: "Whether the construction of the successor plant is feasible is required to be judged comprehensively, considering various factors, such as the status of development of advanced light water reactors, regulation policy and business environment conditions to make investment decisions, in addition to the results of this survey. Therefore, decisions to construct the successor plant will not be based solely on the results of this survey."
Kansai said it will hold briefings for the local community on this voluntary on-site survey, "and with their cooperation, plan to conduct geomorphic and geological surveys, etc".
According to a Reuters report, Kansai is considering deploying the SRZ-1200 advanced light water reactor being developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI).
In September 2022, MHI launched the SRZ-1200 design, which is being developed in collaboration with four Japanese utilities. The 1200 MWe reactor is designed to meet the country's enhanced regulatory safety standards.
Design work progresses for Russian molten salt reactor
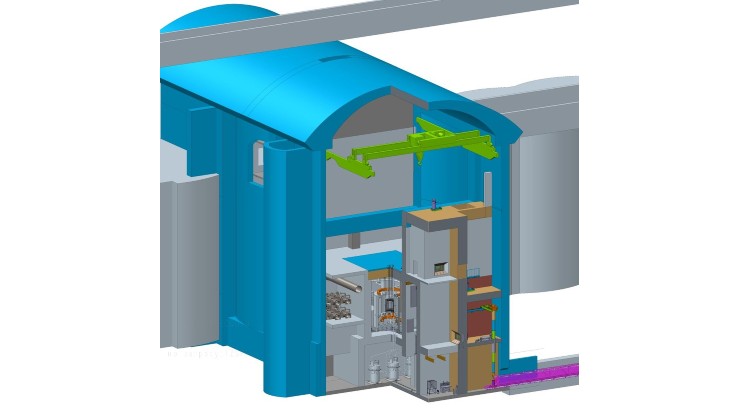
A preliminary design was unveiled in February 2024. The subsequent phase of design work included the development of materials for the design documentation, under the scientific supervision of the Kurchatov Institute.
Rosatom added: "A brief description of the design of the elements of the nuclear installation and the initial fuel preparation complex was also developed, and the main characteristics of the nuclear fuel and elements of the installation were given. This information will form the basis for the assessment of the impact ... on the environment and a preliminary report on the justification of its safety."
The design stage is due to last until 2027 - the next phase will see the creation of technical designs for the reactor installation and the initial fuel preparation complex.
Dmitry Kolupaev, director general of the Mining and Chemical Combine, said: "Successful implementation of this technology will, among other things, reduce the amount of waste subject to final isolation and the duration of its storage. And in the future, it will create the basis for the development of more powerful molten salt reactors, which will be sufficient for processing the entire volume of the most dangerous components of used nuclear fuel produced by thermal reactors."
Vasily Tinin, director of state policy in the field of radioactive waste, used nuclear fuel and decommissioning of nuclear and radiation hazardous facilities, said: "The implementation of the project will allow us to take the environmental safety of nuclear power to a new level - to take a big step towards waste-free nuclear technologies. The main objective of the technology that we are preparing to develop and which relates to fourth-generation nuclear energy technologies will be the creation of a new system for the disposal (afterburning) of hazardous radioactive substances - minor actinides - which are products of the processing of spent nuclear fuel from VVER and RBMK thermal reactors."
The project plans to use circulating molten salt fuel. And the intention is to continue research and developent work to justify the technological solutions in the design documentation with scaling of the technology expected to continue following the launch of the prototype reactor, which is targeted for 2031.
It is part of the wider Russian federal project to develop "new materials and technologies for advanced energy systems" and part of the country's goal of closing the fuel cycle. Rosatom says that the period of potential danger from minor actinides can be reduced from 10,000 years to 300 as a result of the process.
While both units 1 and 2 at the Mihama plant have been shutdown, unit 3 of the plant is among the Japanese reactors that have resumed operation, having been restarted in June 2021.
The last nuclear power reactor to be constructed in Japan was unit 3 of Hokkaido Electric Power Company's Tomari plant, which began operation in 2009.
Viewpoint: The vital role of medical isotopes in theranostics
This innovative field leverages the unique properties of medical isotopes to both diagnose and treat cancer, offering a targeted and effective approach to patient care. I have witnessed first-hand the transformative potential of medical isotopes in unlocking the capabilities of theranostics and the potential benefits they offer to patients, their families and the healthcare providers.
At the forefront of this revolution is Urenco, whose pioneering work in developing new production routes for copper isotopes - specifically copper-64 (Cu-64) and copper-67 (Cu-67) - is setting new standards in medical isotope production and delivery.
Theranostics is a combination of "therapy" and "diagnostics", reflecting its dual role in healthcare, particularly that associated with cancer care. This approach utilises radioisotopes to first image the tumour for diagnostic purposes and then treat the tumour therapeutically in a targeted fashion designed to offer the patient the best form of cancer care and treatment.
The process begins with the administration of a diagnostic radiotracer, which travels through the bloodstream and binds to cancer cells. This allows clinicians to visualise the tumour using imaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET). This technique is maturing significantly and high-resolution total body PET is revolutionising the way that tumours are found and screened. Once the tumour is accurately located and characterised, a therapeutic radiotracer is administered to deliver targeted radiation to the cancer cells, minimising damage to surrounding healthy tissue and reducing the overall body burden to the already compromised system.
The precision of theranostics lies in its ability to provide tailored, customised treatment to the individual accounting for the type of tumour, the stage of cancer and physiological factors of the patient. By combining diagnostic imaging with targeted therapy, theranostics not only improves the accuracy of cancer treatment but also enhances patient outcomes by reducing side effects and improving quality of life.
Medical isotopes are the cornerstone of theranostics, providing the radioactive properties necessary for both imaging and treatment. At Urenco, our focus has traditionally been on the production of stable isotopes, which serve as precursors for the creation of radioisotopes used in theranostics. At the heart of this offering is the copper 64/67 isotope pair; Cu-64 acts as an imaging agent to detect cancerous cells while predicting treatment efficacy using Cu-67. This dual functionality holds promise for patient treatment but also helps to reduce side effects by sparing healthy tissues. The production of these isotopes involves sophisticated enrichment processes and extensive R&D efforts.
We are exploring new ways to expand our offering of enriched isotopes to meet the growing demand from the medical community. Our work with zinc isotopes, for example, has positioned us at the forefront of developing precursors for theranostic applications, particularly in the emerging field of theranostics.
The impact of theranostics on patient care shows promise. By enabling more precise targeting of cancer cells, theranostics reduces the risk of secondary damage to healthy tissues, a common side-effect of traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy and external beam radiation. Moreover, theranostics allows for real-time monitoring of treatment efficacy. By using diagnostic imaging to track the distribution and impact of therapeutic agents, clinicians can adjust treatment plans dynamically, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
Despite its promise, the field of theranostics faces several challenges. One of the primary hurdles is the limited production capacity for medical isotopes. Currently, the production landscape for Cu isotopes faces challenges due to reliance on nickel-based processes concentrated within limited supply chains. The demand for these isotopes has surged, particularly in the wake of geopolitical events that have disrupted traditional supply chains. At Urenco, we are actively working to expand our production capabilities to meet this demand, but it remains a significant challenge for the industry as a whole.
Another challenge is the need for continued research and development to explore new isotopes and refine existing processes. The field of theranostics is gaining momentum but still requires further understanding and optimisation. There is much to learn about the use of different isotopes in a variety of therapeutic contexts. Collaborative efforts between all parties in the supply chain including industry and academia are crucial to advancing our knowledge and strengthening our resilience and capabilities in this area.
Looking ahead, the future of theranostics is one which has so many benefits to offer. As we continue to refine our techniques and expand our understanding of the underlying science, the potential applications of theranostics will grow and mature offering the much-needed ray of hope for those affected by life-limiting conditions such as cancer. The integration of advanced imaging technologies with novel therapeutic agents holds the promise of advancing healthcare treatments and providing new options for patients.
At Urenco, we are committed to playing a leading role in this transformation. By investing in R&D and expanding our production capabilities, we aim to ensure a reliable supply of the medical isotopes that are critical to the success of theranostics. Our partnerships with academic institutions and other industry leaders will be key to driving innovation and overcoming the challenges that lie ahead.
In conclusion, theranostics have the potential to drive a paradigm shift in life-limiting conditions such as cancer, and offer more targeted, effective, and personalised approach to patient care. The role of medical isotopes in this field is pivotal, providing the foundation for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
No comments:
Post a Comment