Taylor Swift’s vintage ring shines new light on diamond industry

Some in the battered diamond industry believe an unlikely figure, pop star Taylor Swift, may have done more to revive interest in natural diamonds than years of marketing campaigns.
Diamond industry analyst Edahn Golan says the so-called ‘Swift effect’ follows a familiar pattern. “Celebrity style has long played a role in driving attention toward particular jewelry designs and diamond trends, with high-profile examples including Jennifer Lopez and Kobe Bryant,” he notes.
The global diamond business is deep in a downturn, squeezed by weak demand, geopolitical uncertainty and the rapid rise of lab-grown alternatives that are chemically and visually identical to mined stones but far cheaper.
Lab-grown diamonds now account for more than half of engagement rings sold in the US, according to The Knot wedding website, up sharply from 2019, as prices have collapsed amid oversupply from China and India. A one-carat lab-grown solitaire can retail for as little as $150 at Walmart, while the gap with natural stones can reach 90%.
They have significantly less resale value than natural diamonds, however, often dropping up to 40% of the original price due to their mass-producible nature, unlike rare natural stones.
The impact on miners has been severe. Botswana, the world’s leading exporter of natural diamonds, has been forced into production cuts and job losses as revenues fall. Debswana, its joint venture with De Beers, is estimated to have cut output by as much as 40% in 2025.
De Beers itself has stockpiled roughly $2 billion worth of unsold stones, cut prices by more than 10% in 2023 and announced plans to shed more than 1,000 jobs. Parent Anglo American (LON: AAL) has moved to sell the business as it pursues a merger with Canada’s Teck Resources (TSX: TECK.A, TECK.B; NYSE: TECK). Russia’s Alrosa saw profits plunge nearly 80% and suspended activity at key sites, which helped it end the year in a better shape than expected. Smaller miners entered administration or shut mines entirely.
Governments and producers are now scrambling to defend the sector’s relevance. Under the Luanda Accord, countries including Botswana and Angola agreed to spend 1% of annual diamond revenues on a global campaign to revive demand for natural stones.
Celebrity effect
Against this bleak backdrop, Swift’s engagement ring has landed like a cultural shockwave. Designed by New York jeweller Kindred Lubeck, it features a large old-mine-cut natural diamond set in hand-engraved yellow gold. This contrasts sharply to the sleek, minimalist solitaire styles popularized in recent years. Industry experts estimate the stone weighs between seven and ten carats.
Independent sector analyst Paul Zimnisky told MINING.COM that celebrity engagement rings have always driven positive attention toward the diamond industry.
Old-mine cuts date back to the 18th and 19th centuries, when diamonds were shaped by hand under candlelight, producing chunky facets, open culets and warmer light than modern round brilliants.
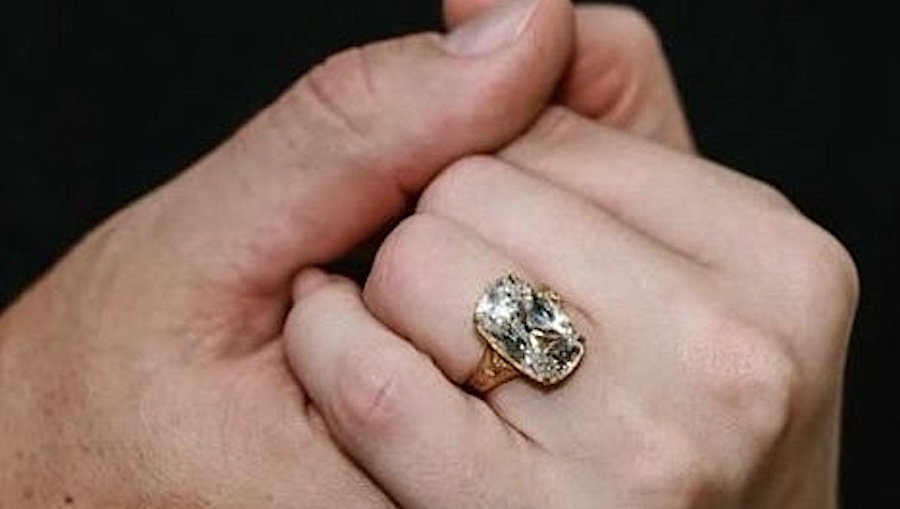
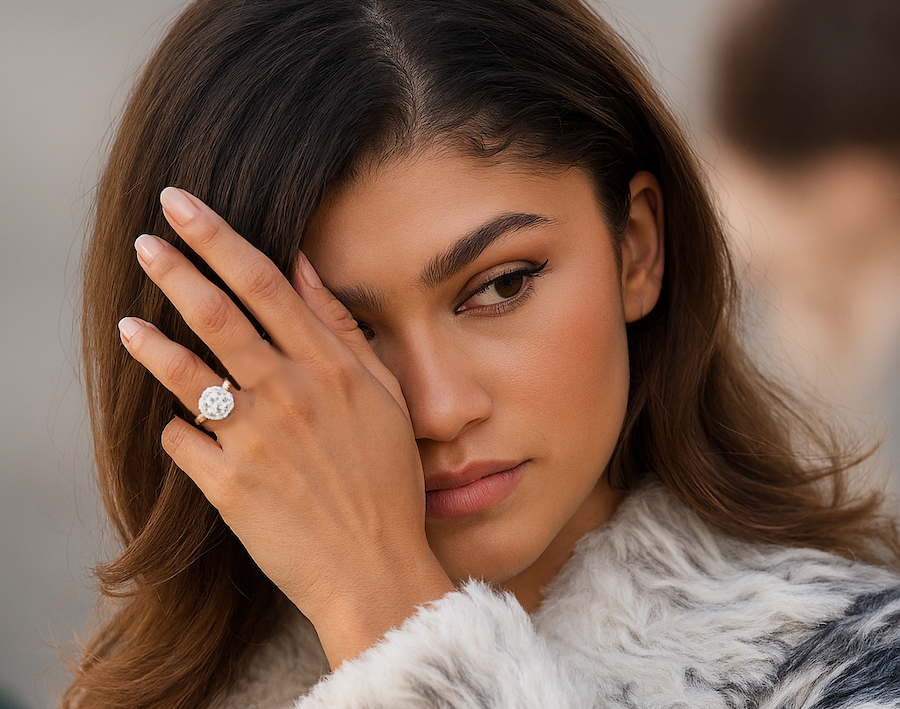
“Not just Taylor Swift, but also Zendaya and Miley Cyrus, have garnered significant publicity over the last year with diamond rings fit for a fantasy,” Zimnisky said. “All three feature large stones, but all are unique in style: Swift’s antique-cut diamond, Zendaya’s east-west setting and Cyrus’s bezel.”

Once a niche obsession among collectors, the style exploded across social media after Swift’s engagement became public.
“What a diamond!” De Beers CEO Al Cook wrote on LinkedIn, calling it a reminder that every natural diamond is “a unique and ancient treasure from the Earth.”
Dealers say the attention has triggered renewed interest in antique and heritage stones, which offer something lab-grown diamonds cannot easily replicate: scarcity and story. At Sim Gems USA in New York’s diamond district, president Chirag Mehta said clients are increasingly looking for stones that feel different from mass-produced brilliance. “People know what a round brilliant is,” he told The New Yorker earlier this month. “After what happened, they’re looking for something else.”
A new narrative
For an industry built on marketing, that shift matters. “Diamonds are all about emotion, romance and selling a dream, and the industry thrives on PR like this,” Zimnisky noted.
Lab-grown diamonds excel at purity and price, undermining a century-old message that equated value with flawless, colourless stones. Now, natural-diamond producers are reframing rarity around character, age and provenance, even embracing once-shunned brown or “textured” stones.
Zimnisky said the renewed attention has coincided with a clear shift in buying preferences. There has been an uptick in larger natural diamond sizes in fancy-cut shapes such as long cushions, marquis and ovals, with 2–4-carat elongated fancy shapes emerging as the hottest category over the past year.

Antique diamonds also offer a perceived ethical middle ground for buyers wary of mining but unconvinced by lab-grown gems, though their supply remains limited and their histories complex.
Whether Swift can truly “save” the industry is doubtful, but her ring has given natural diamonds something they desperately need: cultural relevance. In a market where consumers can buy size and sparkle for a fraction of the cost, miners are betting that romance, individuality and celebrity influence still have the power to sell a story.