Researchers successfully build
four-legged swarm robots
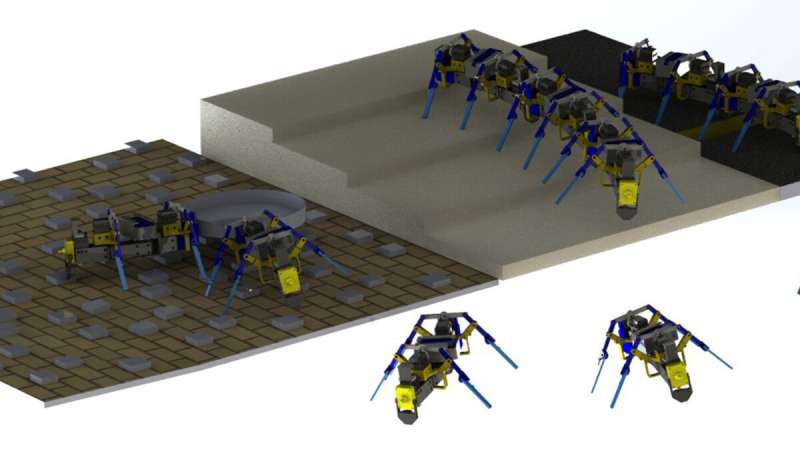
As a robotics engineer, Yasemin Ozkan-Aydin, assistant professor of electrical engineering at the University of Notre Dame, gets her inspiration from biological systems. The collective behaviors of ants, honeybees and birds to solve problems and overcome obstacles is something researchers have developed in aerial and underwater robotics. Developing small-scale swarm robots with the capability to traverse complex terrain, however, comes with a unique set of challenges.
In research published in Science Robotics, Ozkan-Aydin presents how she was able to build multi-legged robots capable of maneuvering in challenging environments and accomplishing difficult tasks collectively, mimicking their natural-world counterparts.
"Legged robots can navigate challenging environments such as rough terrain and tight spaces, and the use of limbs offers effective body support, enables rapid maneuverability and facilitates obstacle crossing," Ozkan-Aydin said. "However, legged robots face unique mobility challenges in terrestrial environments, which results in reduced locomotor performance."
For the study, Ozkan-Aydin said, she hypothesized that a physical connection between individual robots could enhance the mobility of a terrestrial legged collective system. Individual robots performed simple or small tasks such as moving over a smooth surface or carrying a light object, but if the task was beyond the capability of the single unit, the robots physically connected to each other to form a larger multi-legged system and collectively overcome issues.
"When ants collect or transport objects, if one comes upon an obstacle, the group works collectively to overcome that obstacle. If there's a gap in the path, for example, they will form a bridge so the other ants can travel across—and that is the inspiration for this study," she said. "Through robotics we're able to gain a better understanding of the dynamics and collective behaviors of these biological systems and explore how we might be able to use this kind of technology in the future."
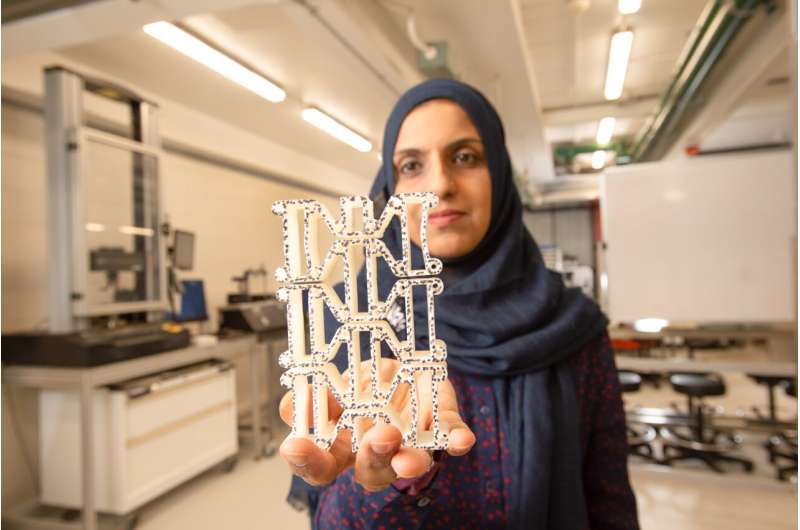
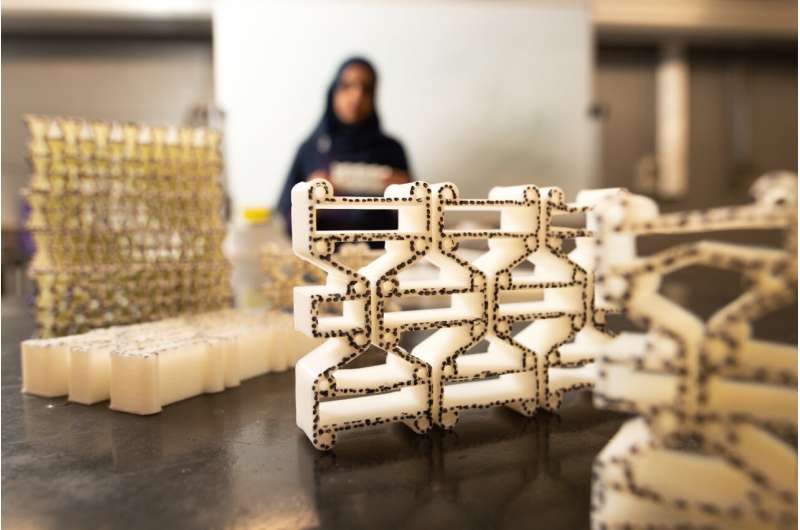
Using a 3D printer, Ozkan-Aydin built four-legged robots measuring 15 to 20 centimeters, or roughly 6 to 8 inches, in length. Each was equipped with a lithium polymer battery, microcontroller and three sensors—a light sensor at the front and two magnetic touch sensors at the front and back, allowing the robots to connect to one another. Four flexible legs reduced the need for additional sensors and parts and gave the robots a level of mechanical intelligence, which helped when interacting with rough or uneven terrain.
"You don't need additional sensors to detect obstacles because the flexibility in the legs helps the robot to move right past them," said Ozkan-Aydin. "They can test for gaps in a path, building a bridge with their bodies; move objects individually; or connect to move objects collectively in different types of environments, not dissimilar to ants."
Ozkan-Aydin began her research for the study in early 2020, when much of the country was shut down due to the COVID-19 pandemic. After printing each robot, she built each one and conducted her experiments at home, in her yard or at the playground with her son. The robots were tested over grass, mulch, leaves and acorns. Flat-ground experiments were conducted over particle board, and she built stairs using insulation foam. The robots were also tested over shag carpeting, and rectangular wooden blocks were glued to particle board to serve as rough terrain.
When an individual unit became stuck, a signal was sent to additional robots, which linked together to provide support to successfully traverse obstacles while working collectively.
Ozkan-Aydin says there are still improvements to be made on her design. But she expects the study's findings will inform the design of low-cost legged swarms that can adapt to unforeseen situations and perform real-world cooperative tasks such as search-and-rescue operations, collective object transport, space exploration and environmental monitoring. Her research will focus on improving the control, sensing and power capabilities of the system, which are essential for real-world locomotion and problem-solving—and she plans to use this system to explore the collective dynamics of insects such as ants and termites.
"For functional swarm systems, the battery technology needs to be improved," she said. "We need small batteries that can provide more power, ideally lasting more than 10 hours. Otherwise, using this type of system in the real world isn't sustainable." Additional limitations include the need for more sensors and more powerful motors—while keeping the size of the robots small.
"You need to think about how the robots would function in the real world, so you need to think about how much power is required, the size of the battery you use. Everything is limited so you need to make decisions with every part of the machine."
Daniel I. Goldman at the Georgia Institute of Technology co-authored the study.Collective worm and robot 'blobs' protect individuals, swarm together
More information: Yasemin Ozkan-Aydin et al, Self-reconfigurable multilegged robot swarms collectively accomplish challenging terradynamic tasks, Science Robotics (2021). DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.abf1628
Journal information: Science Robotics
Provided by University of Notre Dame
An online method to allocate tasks to robots on a team during natural disaster scenarios
Teams of robots could help users to complete numerous tasks more rapidly and efficiently, as well as keeping human agents out of harm's way during hazardous operations. In recent years, some studies have particularly explored the potential of robot swarms in assisting human agents during search-and-rescue missions; for instance, while seeking out survivors of natural disasters or delivering food and survival kits to them.
Researchers at University of Buffalo have recently developed a technique that could enhance the performance of robot teams during disaster response missions. This technique, introduced in a paper published in Elsevier's journal Robotics and Autonomous Systems, is designed to allocate tasks to different robots in a team, so that they can complete missions most effectively.
"Over the past three to four years, we have been exploring unique ways to coordinate large teams of ground robots and drones for assisting in hazard mapping and search-and-rescue operations that are critical to emergency and disaster response applications," Dr. Souma Chowdhury, one of the researchers who led the study, told Tech Xplore. "During these research explorations, we converged upon the need for an algorithm that can quickly (on the go) allocate tasks among robots in the team."
When they reviewed previous research studies, the researchers found that very few of the existing methods for multi-robot task allocation were able to handle simultaneous tasks with strict time deadlines and adapt to new unexpected tasks that may arise during a mission, while also considering the flight range, payload capacity and onboard computing constraints of real-world robots. They thus set out to develop an approach that would successfully do all these things.
"A further objective of our study was to demonstrate the capabilities of this new method on an original flood response application, where a team of drones is employed to quickly deliver or drop survival kits at specified task locations during a simulated flood scenario over a 20x30 km2 area," Dr. Chowdhury said.
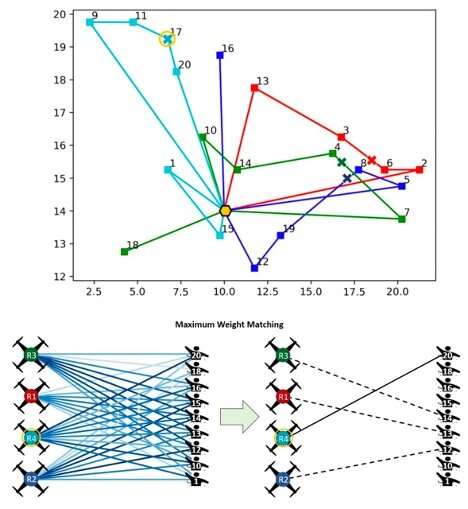
In their study, Dr. Chowdhury and his colleague Dr. Payam Ghassemi considered teams of robots and the tasks they are meant to complete as two distinct sets of data. This allowed them to reduce the task of allocating problems to them, so that it primarily entailed mapping or matching pairs of elements from these two sets (i.e., a robot in the team with the task it would complete). Essentially, at any point when the model is required to make a decision, it connects every idle robot in set 1 to one of the tasks remaining in set 2, via an "edge."
"Our technique then uses an incentive function to weight these edges, with a higher weight indicating a higher relative affinity of a robot to undertake the task connected by the concerned edge," Dr. Ghassemi, the other researcher involved in the study, said. "A weighted bigraph matching problem is then solved to produce a one-to-one mapping that yields the immediate next task to be assigned to each robot. By designing the incentive function to account for the robot's global state, the robot's state relative to a task and the remaining time to complete the task, our approach becomes uniquely cognizant of robot's constraints and task deadlines."
The technique has several advantages over alternative, existing optimization-based multi-robot task allocation methods. For instance, its execution times are significantly shorter, as it can make task allocation decisions within a few hundred milliseconds.
In addition to being faster than other existing methods, the researchers' technique alleviates the need for synchronous decision-making among robots. This means that its functioning has a lower dependence on the communication networks connecting robots in a team.
Drs. Chowdhury and Ghassemi evaluated their technique in a series of tests. Remarkably, they found that it could complete the same percentage of tasks as general optimization-based methods that provide provably optimal solutions, yet its computing times were almost 1,000 times lower.
"This observation, along with our technique's ability to make asynchronous decisions, implies that our method could be readily implemented on widely available and inexpensive ground robots and drones," Dr. Chowdhury said. "Such simple robots usually present frugal computing and communication capabilities."
Interestingly, the researchers showed that their method can also be scaled up to tackle highly complex problems that involve teams with up to 100 robots that are meant to complete 1,000 tasks, while retaining its sub-second computing time performance. So far, very few teams have tried to tackle these large-scale problems using existing task allocation tools.
"The outcome of our study represents an important step forward for the multi-robotics community in terms of providing tangible evidence for the vision that very large and scalable teams of robots could revolutionize disaster response and other time sensitive operations," Dr. Chowdhury said. "Lastly, by directly considering the realities of robot's range and payload constraints, task deadlines and appearance of new tasks on the go (the latter are ubiquitous to disaster response operations), our findings take us closer to transitioning multi-robot task allocation algorithms to practice in complex large-scale operations."
In the future, the online multi-robot task allocation technique developed by this team of researchers could facilitate the large-scale deployment of drone swarms or other robot teams during complex search and rescue missions. Meanwhile, Drs. Chowdhury and Ghassemi plan to conduct further experiments to evaluate their algorithm in more realistic simulations, created using contemporary gaming engines. This could finally allow them to deploy and test their technique on real teams of drones and four-wheeled ground robots.
"The University at Buffalo, School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, has recently unveiled a massive state-of-the-art outdoor drone testing facility, which would be a perfect setting for conducting these experiments in real-world conditions," Dr. Chowdhury added. "On a more fundamental level, we plan to alleviate the need for handcrafting the incentive function for different types of operations and robots, and further minimize inter-robot communication needs. To this end, under a new research grant from the National Science Foundation, we are exploring how machine learning approaches can be used to learn incentive functions that will allow our algorithm to generalize over a wide range of real-world scenarios with minimal human inputs."A framework for adaptive task allocation during multi-robot missions
More information: Payam Ghassemi and Souma Chowdhury, Multi-robot task allocation in disaster response: addressing dynamic tasks with deadlines and robots with range and payload constraints, Robotics and Autonomous Systems(2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.robot.2021.103905
© 2021 Science X Network
























