Robot to recover treasure worth billions from legendary shipwreck
CBS News
Gold coins found in centuries-old shipwrecks off Colombia
Duration 0:53 View on Watch
Culture Minister Juan David Correa told AFP that more than eight years after the discovery of the wreck off Colombia's coast, an underwater robot would be sent to recover some of its bounty.
Between April and May, the robot would extract some items from "the surface of the galleon" to see "how they materialize when they come out (of the water) and to understand what we can do" to recover the rest of the treasures, said Correa.
The operation will cost more than $4.5 million and the robot will work at a depth of 600 meters to remove items such as ceramics, pieces of wood and shells "without modifying or damaging the wreck," Correa told AFP aboard a large naval ship.
The location of the expedition is being kept secret to protect what is considered one of the greatest archaeological finds in history from malicious treasure hunters.
The San Jose galleon was owned by the Spanish crown when it was sunk by the British navy near Cartagena in 1708. Only a handful of its 600-strong crew survived.
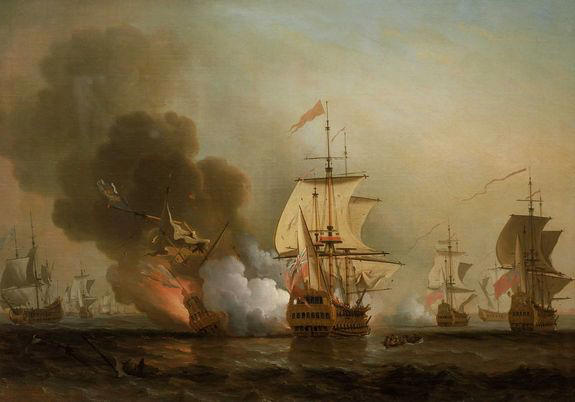
The Spanish San Jose Galleon sunk in the Caribbean in 1708 after a battle with the British. New data suggests such shipwrecks could reveal the history of hurricanes in the region. / Credit: Samuel Scott© Provided by CBS News
"It makes it very touchy because one is not supposed to intervene in war graves," Justin Leidwanger, an archaeologist at Stanford University who studies ancient shipwrecks, told Live Science.
The ship had been heading back from the New World to the court of King Philip V of Spain, laden with treasures such as chests of emeralds and some 200 tons of gold coins.
Before Colombia announced the discovery in 2015, it was long sought after by treasure hunters.
"As if we were in colonial times"
The discovery of the galleon sparked a tug-of-war over who gets custody of its bounty.
Spain insists that the bounty is theirs since it was aboard a Spanish ship, while Bolivia's Qhara Qhara nation says it should get the treasures as the Spanish forced the community's people to mine the precious metals.

Colombian Rear-admiral Herman Ricardo Leon (L) and Colombian Director of Anthropologic and History Institute Alhena Caicido deliver a press conference at the Navy Museum in Cartagena, Colombia, on February 23, 2024. / Credit: LUIS ACOSTA/AFP via Getty Images© Provided by CBS News
Since Thursday, Spain's ambassador to Colombia Joaquin de Aristegui, and representatives of Bolivia's Indigenous people have been taking part in a symposium with experts to discuss the best way to access the treasure.
The government of leftist president Gustavo Petro, in power since 2022, wants to use the country's own resources to recover the wreck and ensure it remains in Colombia.
De Aristegui said he has instructions to offer Colombia a "bilateral agreement" on the protection of the wreck.
Correa said Bolivia's Indigenous people have expressed their willingness to work with Petro's government.
The idea is "to stop considering that we are dealing with a treasure that we have to fight for as if we were in colonial times, with the pirates who disputed these territories," he added.
The expedition to start recovering the shipwreck's trove comes as a case is underway at the UN's Permanent Court of Arbitration between Colombia and the U.S.-based salvage company Sea Search Armada -- which claims it found the wreck first over 40 years ago.
The company is demanding $10 billion dollars, half the wreck's estimated value today.
In June 2022, Colombia said that a remotely operated vehicle reached 900 meters below the surface of the ocean, showing new images of the wreckage.
The video showed the best-yet view of the treasure that was aboard the San Jose — including gold ingots and coins, cannons made in Seville in 1655 and an intact Chinese dinner service.
At the time, Reuters reported the remotely operated vehicle also discovered two other shipwrecks in the area, including a schooner thought to be from about two centuries ago.
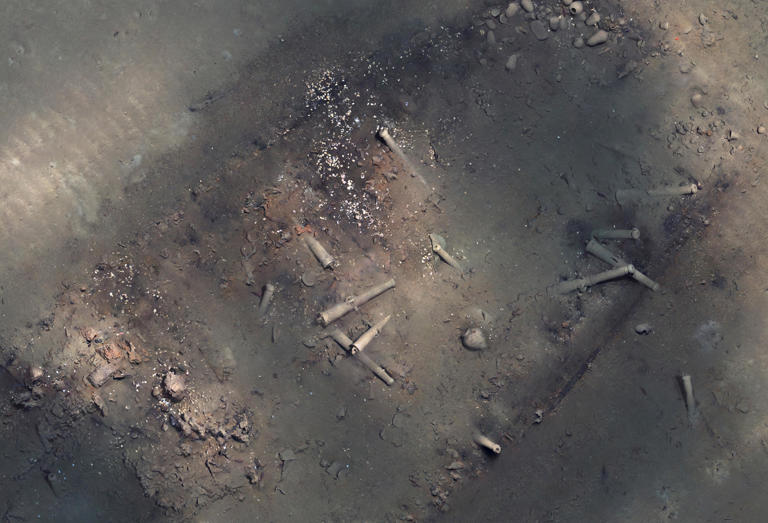

This undated image made from a mosaic of photos taken by an autonomous underwater vehicle, released by the Colombian Institute of Anthropology and History, shows the remains of the Spanish galleon San Jose, that went down off the Colombian Caribbean coast more than 300 years ago. / Credit: / AP© Provided by CBS News
No comments:
Post a Comment