POLITICAL PERSECUTION
Rahul Gandhi: India's Congress leader sentenced to jail for Modi 'thieves' remark
 REUTERS
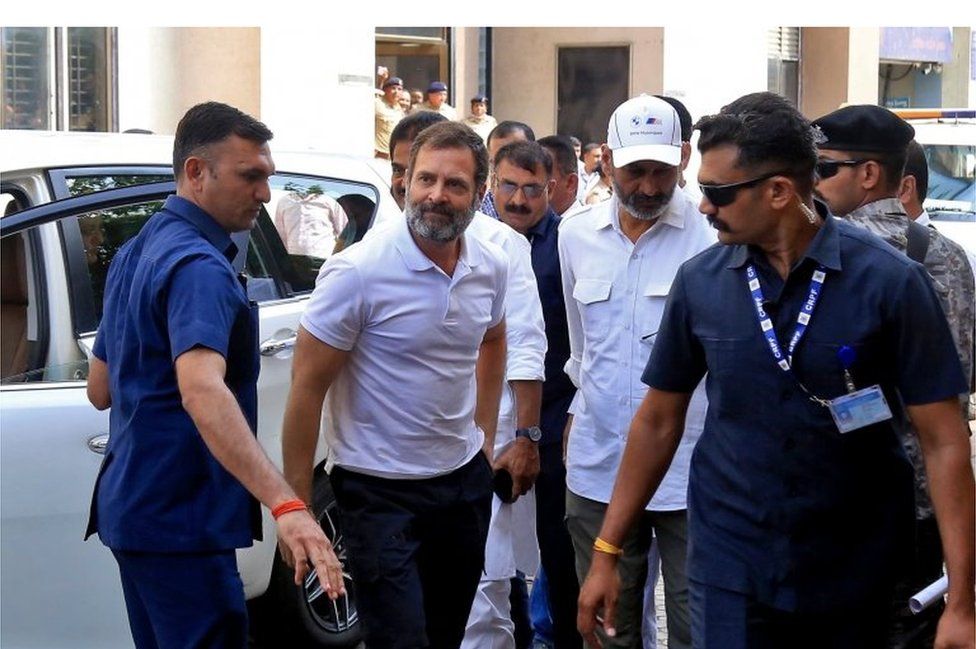
REUTERSIndian opposition leader Rahul Gandhi has been sentenced to two years in prison in a criminal defamation case.
The Congress MP was convicted by the court in Gujarat state for 2019 comments about Prime Minister Narendra Modi's surname at an election rally.
Mr Gandhi, who was present in court for sentencing, remains out of jail on bail for 30 days and will appeal.
His party said he was being targeted for exposing the government's "dark deeds". Elections are due next year.
A Congress spokesman said the ruling was full of "legally unsustainable conclusions" - and vowed its politicians would not be silenced.
"Make no mistake. All your attempts to create a chilling effect, a throttling effect, a strangulating effect on open fearless speech relating to public influence will not stop either Rahul Gandhi or the Congress Party," Abhishek Manu Singhvi told a news conference.
The ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) says due judicial process has been followed in the case, which dates back to the campaign ahead of the last election.
Speaking at a rally in Karnataka state in April 2019, Mr Gandhi had said: "Why do all these thieves have Modi as their surname? Nirav Modi, Lalit Modi, Narendra Modi."
Nirav Modi is a fugitive Indian diamond tycoon while Lalit Modi is a former chief of the Indian Premier League who has been banned for life by the country's cricket board. Mr Gandhi argues that he made the comment to highlight corruption and it was not directed against any community.
 REUTERS
REUTERSOther opposition politicians and organisations deemed critical of India's government have also faced legal action.
The Aam Admi Party (AAP), which rules Delhi, has two senior members currently in jail on charges it says are politically motivated. Its leader voiced support for Mr Gandhi.
"We have differences with the Congress, but it is not right to implicate Rahul Gandhi in a defamation case like this," Arvind Kejriwal tweeted. "It is the job of the public and the opposition to ask questions."
The case against Rahul Gandhi was filed on the basis of a complaint by Purnesh Modi, a BJP lawmaker who said his comments had defamed the entire Modi community.
But some experts were puzzled by the order handed down by the court in Surat. Legal scholar Gautam Bhatia tweeted that "references to a generic class of persons" - surnames in this case - are not "actionable unless an individual can show a direct reference to themselves".
"If a man says 'all lawyers are thieves', then I, as a lawyer, cannot file a case against him for defamation unless I can show its imputation aimed at me," Mr Bhatia said.
Mr Gandhi's lawyer, Kirit Panwala, told BBC Gujarati their defence was based on four points: "Firstly, Mr Gandhi is not a resident of Gujarat and so, before the complaint, an inquiry should be conducted. Secondly, there is no community named Modi. Thirdly, there is no association of people with Modi as their surname and lastly, there was no ill intention behind Mr Gandhi's speech."
India's criminal defamation law is British-era legislation under which there can be a maximum prison sentence of two years, a fine or both. Free speech advocates have often argued the law goes against the principles of freedom and that it is used by politicians to silence their critics.
In 2016, some top Indian politicians including Mr Gandhi filed legal pleas arguing for defamation to be decriminalised. But India's Supreme Court upheld the validity of the law, saying the "right to free speech cannot mean that a citizen can defame the other".
Some have raised questions over Mr Gandhi's status as a member of parliament after the conviction.
Defamation, by itself, cannot be a ground for disqualification in India. An MP can be disqualified from the office for offences ranging from promoting enmity, and election-related fraud. But they can also be disqualified if sentenced for two years or more for an offence.
A two-year jail term would mean Mr Gandhi would not be able to contest the 2024 general election.
"What they will do [is] they are likely to go to the top court, which will stay the judgement," says a political commentator, who insisted on anonymity. "But the question is: does this judgement mean that there's a sword of Damocles hanging over any leader? There are cases filed against leaders for all sorts of so-called crimes. Normally nothing happens."

Mr Gandhi is the scion of the Nehru-Gandhi political dynasty, which has given three prime ministers to India. His great-grandfather, Jawaharlal Nehru, was the first and longest-serving prime minister of India. His grandmother, Indira Gandhi, was the first female prime minister of the country, and his father, Rajiv Gandhi, was India's youngest prime minister.
Their party, the Congress, governed India almost continuously - except for a few years - from independence in 1947 to 2014, when Narendra Modi's BJP swept to power by a landslide. Since then, the Congress has become a shadow of its former self, and was routed again by the BJP in 2019.
Only once in India's history has the main opposition leader been jailed. In December 1978, Indira Gandhi, by then no longer PM, was expelled from the lower house and jailed for nine days for committing a breach of privilege and contempt of parliament.

Rahul Gandhi, a senior leader of India's main opposition Congress party, arrives to appear before a court in Surat in the western state of Gujarat, India, March 23, 2023. REUTERS/Stringer
India's opposition leader Rahul Gandhi faces the risk of being immediately disqualified as a lawmaker after being convicted in a defamation case and sentenced to two years in jail.
Here are some examples of how that might play out:
The Representation of the People Act, 1951, the law that governs elections in India, mandates disqualification of any lawmaker who is "convicted of any offence and sentenced to imprisonment for not less than two years".
Gandhi, 52, was on Thursday found guilty of defamation by a magistrate's court in the western state of Gujarat for an election speech he made in 2019 in which he referred to thieves having Modi as their surnames.
The disqualification comes into effect from the date of conviction.
A formal disqualification order will, however, have to be passed by the secretariat of the lower house of parliament of which Gandhi is a member.
CAN GANDHI CONTEST ELECTIONS?
Gandhi faces the risk of not being able to contest national elections due in 2024 if his conviction is not suspended or overturned by a higher court before the elections.
The law also mandates that a convicted lawmaker cannot contest elections for six years after the end of their jail sentence.
Gandhi represents the Wayanad constituency in the southern state of Kerala.
HOW CAN GANDHI AVOID DISQUALIFICATION?
To avoid disqualification, a convicted lawmaker has to secure an order from a higher court suspending the conviction, lawyers said.
The Representation of the People Act does not give any timeframe for securing such a suspension or acquittal before parliament passes the formal disqualification order.
The disqualification can also be overturned and the lawmaker reinstated to parliament if the conviction is stayed or overturned and a fresh election to the seat is yet to be conducted.
Gandhi was present in the Gujarat court which gave him bail immediately and suspended the sentence for a month, allowing him to appeal against it.
He can secure bail extensions during the appeal period but cannot contest elections until the conviction is stayed or he is acquitted in the case.
"So while it appears from reports that Mr. Gandhi's sentence has been suspended by the court that convicted him, he would have to soon obtain a stay on the conviction from an appellate court to save himself from disqualification," Supreme Court lawyer Vikram Hegde told Reuters.
Gandhi, a senior leader of the Congress party and the scion of the Nehru-Gandhi political dynasty, will appeal in a higher court, his party said.