Retrofit for First Hydrogen-Powered Inland Containership Completed

The first hydrogen-powered inland containership developed in a multi-year demonstration project was officially commissioned today in Rotterdam. The vessel renamed H2 Barge 1 joins a small but growing number of hydrogen-fueled vessels being introduced to demonstrate the path to zero emissions.
The vessel owned by Future Proof Shipping of the Netherlands will be carrying containers between Rotterdam and Antwerp. It will be under charter to BCTN Network of Inland Terminals on behalf of Nike EMEA. Making the trip several times a week, the vessel is expected to eliminate 2,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions annually.
The retrofit project took five years from the initial plans to final approval and delivery notes Holland Shipyards Group which carried out the work for the project. The project was supported by grant funding from the Interreg North Sea Region Programme (Zero Emission Ports North Sea – ZEM Ports NS), Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO), Port of Rotterdam and Expertis-en InnovatieCentrum Binnenvaart, to demonstrate the retrofit potential for shipping. Lloyd’s Register provided the classification with the shipyard explaining because there is no comprehensive framework of rules, the retrofit was performed on a risk-based approach.
The project worked with Future Proof’s FPS Maas, a 360-foot barge. After the conversion the vessel has a capacity of 200 TEU and there are provisions for an additional push barge according to the shipyard.
The contract for the conversion was awarded in March 2021 calling for replacing the internal combustion technology with hydrogen. This included removing both the main engine and gearbox and installing a new modular propulsion system. The new system consists of electric motors, hydrogen tanks, a PEM fuel cell for converting the hydrogen into electricity, and a battery storage system. The compressed hydrogen tanks, the fuel cells, and the battery system are separate units housed in containers and can be removed for maintenance.

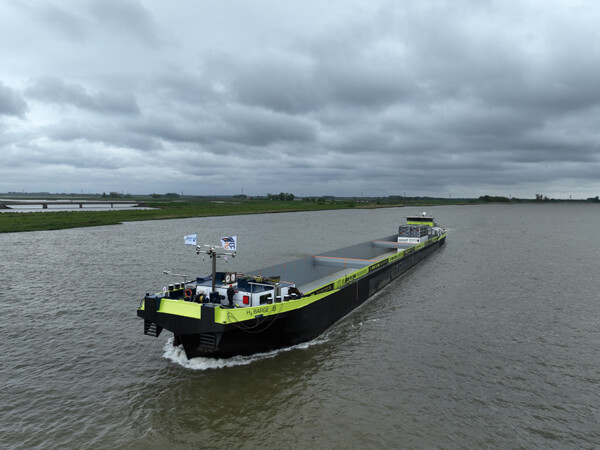
Hydrogen system was installed in three containers at the rear of the cargo area (FPS)
The hydrogen and fuel cell system were installed in the cargo space of the vessel. The hydrogen is placed above the fuel cell system in two 40-foot containers. They provide a capacity for 900 kg of sustainably generated hydrogen under a pressure of 300 bar. H2 Barge 1 is now equipped with an 800 kW electric motor, powered by a 750 VDC-bus. The DC-bus is fed by three fuel cells, each with a maximum power of 300 kW, and 1037 kWh Lithium-Ion batteries.
The vessel arrived at the shipyard approximately 10 months ago, and Holland Shipyards reports that after removing the existing drivetrain, all the vessel’s systems were updated to suit the new drivetrain and H2 installation. The engine room and bow thruster were modified to accommodate electrical switchboards and battery rooms, while the three fuel cell areas were constructed in the cargo area. Other work included adjustments to the cooling system for the new layout and all ventilation systems were modified.

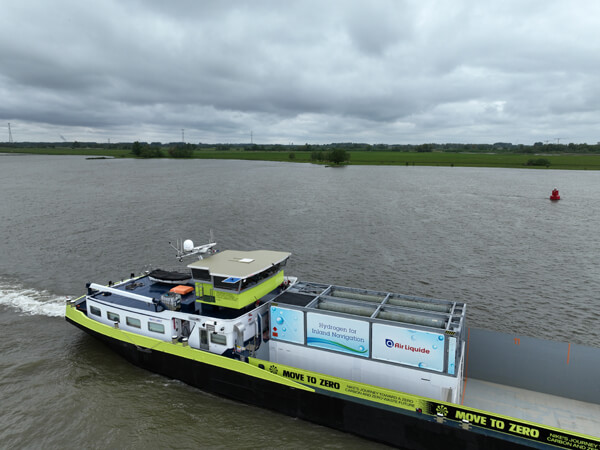
H2 Barge 1 will be supplying inland transport for Nike between the ports of Rotterdam and Antwerp (FPS)
“We have been working for a couple of years now to ensure we tread more lightly on the planet,” said Richard Klatten, CEO of Future Proof Shipping during today’s ceremonies in Rotterdam. “This shipping project proves that moving cargo with zero emissions and zero impact is possible, and we hope it accelerates the industry to follow in Nike’s footsteps and move to zero.”
The process for the conversion of Future Proof Shipping’s second barge is also underway at the Holland Shipyards Group. The FPS Waal is expected to arrive at the shipyard later this year for a conversion lasting approximately five months. The shipyard reports that long lead components such as the six Ballard FC WAVE fuel cells, the AYK batteries, electric propulsion motor, have been ordered as they prepared to begin cutting steel for the new technical space. The second ship will have a fuel cell with a capacity of 1.2 MW and an innovative cooling and ventilation system will be installed.
Future Proof Shipping aims to build and operate a fleet of 10 zero-emission inland and short-sea vessels over the next five years






 Abandoned projectiles found on the bottom (Royal Navy)
Abandoned projectiles found on the bottom (Royal Navy)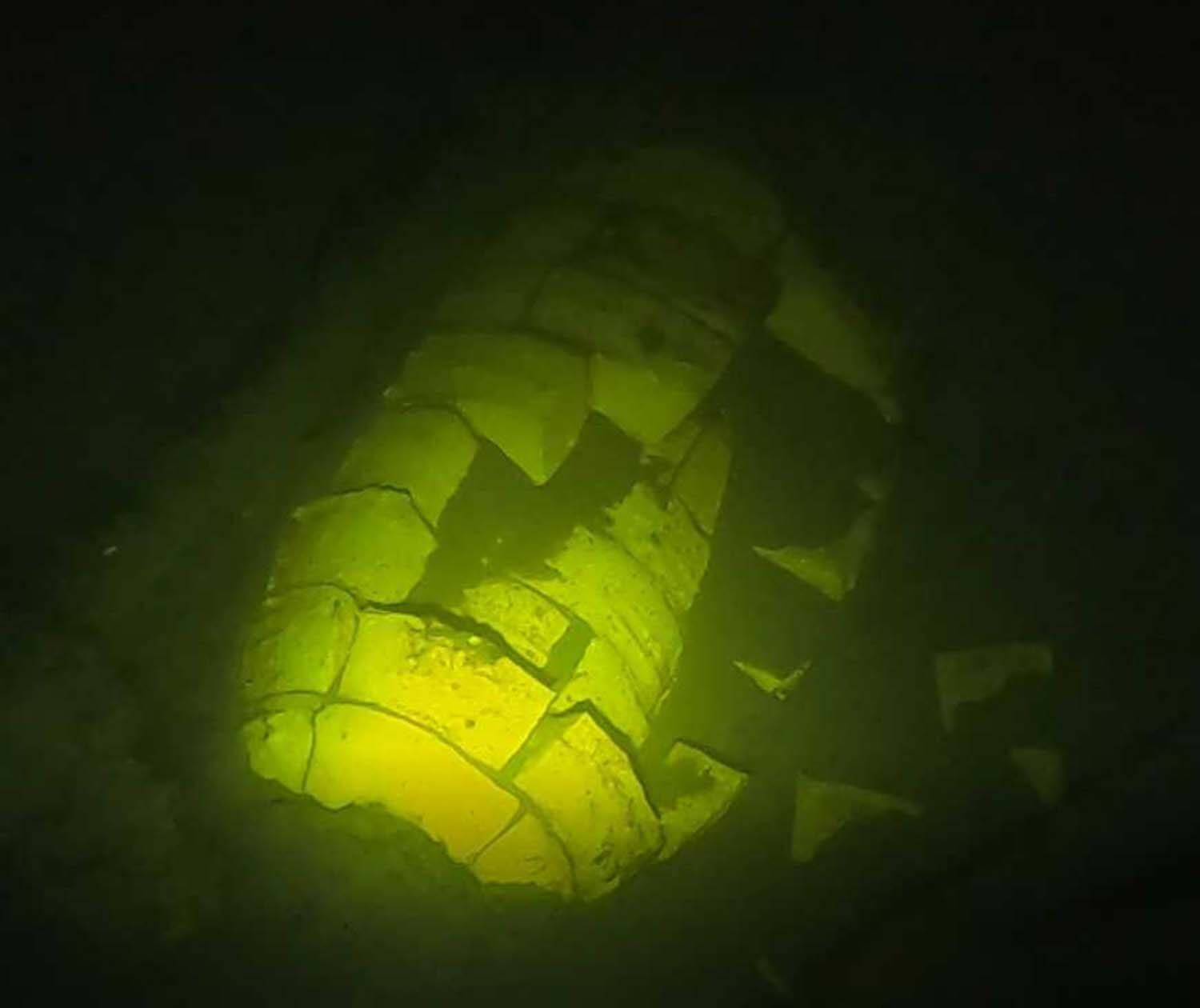 Exposed blocks of explosive in a damaged torpedo warhead (Royal Navy)
Exposed blocks of explosive in a damaged torpedo warhead (Royal Navy)